Transparent conducting layer for heterojunction solar cell and heterojunction solar cell
A transparent conductive layer, solar cell technology, applied in circuits, photovoltaic power generation, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of expensive reactive sputtering deposition equipment, expensive indium elements, and high production costs, and achieve transmission and collection. Chemical effect, good mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
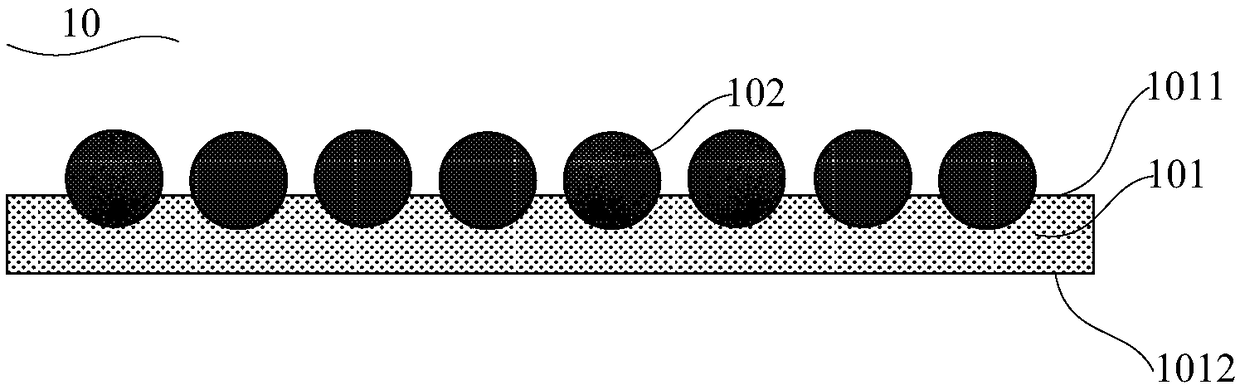
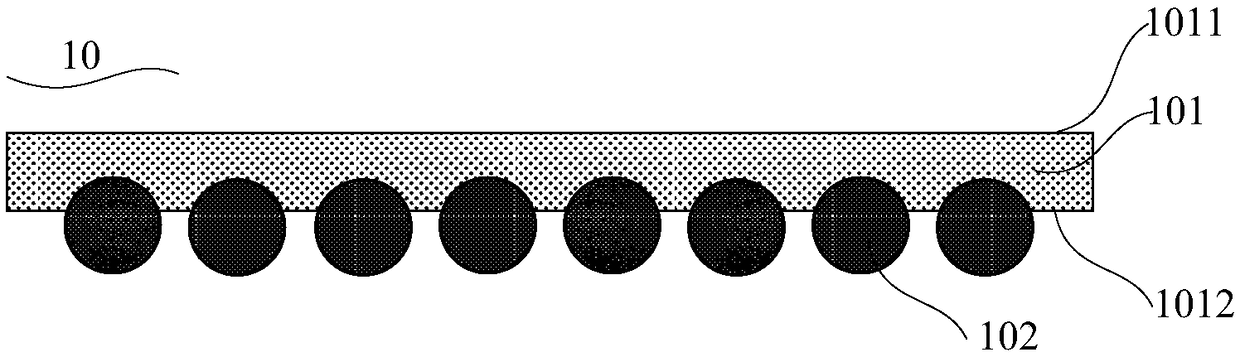
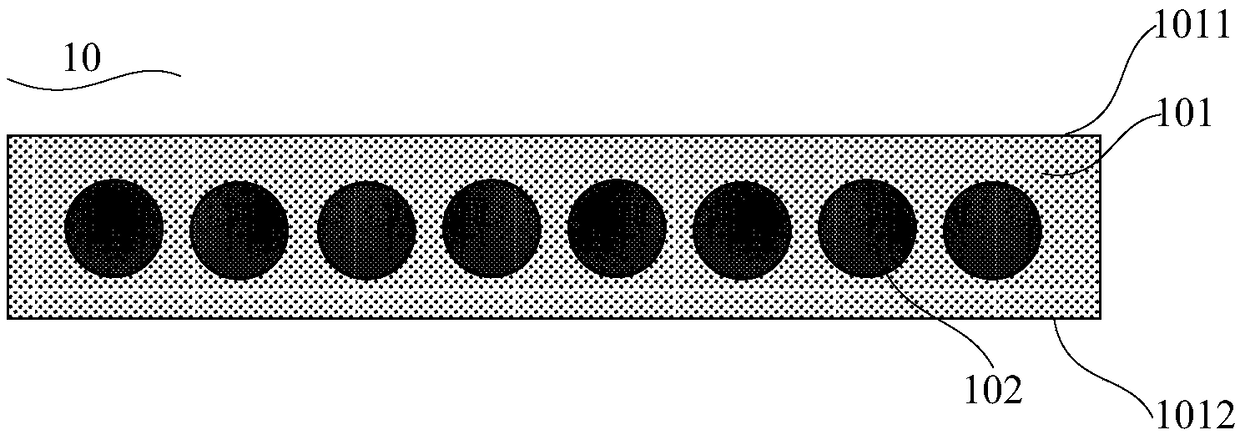
[0067] see Figure 1 to Figure 3 , this embodiment provides a transparent conductive layer 10 for a heterojunction solar cell, the transparent conductive layer 10 comprising:
[0068] Conductive polymer layer 101, described conductive polymer layer 101 comprises opposite first surface 1011 and second surface 1012;
[0069] A one-dimensional conductive material 102 , the one-dimensional conductive material 102 is located on at least one of two opposite surfaces of the conductive polymer layer 101 , or is covered inside the conductive polymer layer 101 .
[0070] In one example, the conductive polymer layer 101 can be at least any one of dipping, spin coating, blade coating, spray coating, wet coating, screen printing, roller coating and plate coating at room temperature. After coating, it is formed by drying and curing at 120-180°C. The one-dimensional conductive material 102 is formed by dipping and pulling, spin coating, blade coating, spray coating, wet coating, screen prin...
Embodiment 2
[0087] Please combine Figure 4 , the present invention also provides a heterojunction solar cell, the heterojunction solar cell comprising:
[0088] A silicon-based substrate 11, said silicon-based substrate 11 comprising a first surface and a second surface opposite to each other;
[0089] A first intrinsic silicon-based thin film layer 12, the first intrinsic silicon-based thin film layer 12 is located on the first surface of the silicon-based substrate 11;
[0090] A second intrinsic silicon-based thin film layer 13, the second intrinsic silicon-based thin film layer 13 is located on the second surface of the silicon-based substrate 11;
[0091] A first doped silicon-based thin film layer 14, the first doped silicon-based thin film layer 14 is located on the surface of the first intrinsic silicon-based thin film layer 12 away from the silicon-based substrate 11;
[0092] The second doped silicon-based thin film layer 15, the second doped silicon-based thin film layer 15 ...
Embodiment 3
[0100] see Figure 5 , the present invention also provides a heterojunction solar cell. The specific structure of the heterojunction solar cell described in this embodiment is roughly the same as the specific structure of the heterojunction solar cell described in Embodiment 2. The difference is: the second transparent conductive layer in the heterojunction solar cell described in Embodiment 2 is the transparent conductive layer 10 described in any one of Embodiment 1, while the heterojunction solar cell described in this embodiment The second transparent conductive layer in the solar cell is an indium oxide-based transparent oxide conductive thin film layer 16 (indium oxide-based TCO thin film).
[0101] Other structures of the heterojunction solar cell described in this embodiment are the same as those corresponding to the heterojunction solar cell described in Embodiment 2, please refer to Embodiment 2 for details, and will not be repeated here.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com