A method and detection kit for label-free fluorescent detection of Staphylococcus aureus meca gene
A detection kit and fluorescence detection technology, applied in the field of analysis and detection, can solve the problems of unfavorable rapid on-site detection, limited wide application, cumbersome operation, etc., and achieve the effects of convenient and rapid popularization, cost reduction, and high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
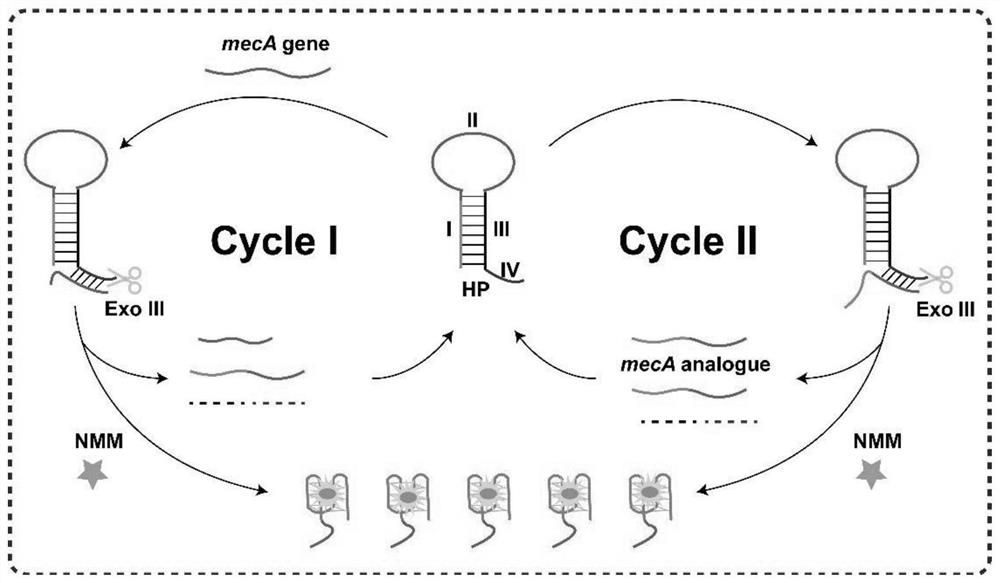
[0036] A detection kit for label-free fluorescent detection of Staphylococcus aureus, comprising the following components:
[0037] (1) Hairpin probe HP, the sequence is as follows:
[0038] HP: 5'-GGGTAGGGCGGGTTGGGATTGGGATCA (region I)-TAGCGTCAT (region II)-TGATCCCAATCCCAACCCGCCCTACCC (region III)-CTATGATCCCAAT (region IV)-3' (SEQ ID NO: 5);
[0039] (2) Exo III and 1×NEBuffer buffer;
[0040](3) 20mM Tris-HCl buffer solution containing 100mM NaCl, 10mM MgCl 2 , 15 mM KCl, pH=7.4.
[0041] A method for label-free fluorescent detection of Staphylococcus aureus is carried out according to the following steps:
[0042] (1) Formation of hairpin probe HP. Heat the hairpin probe HP at a concentration of 10 μM in a water bath at 90°C for 10 minutes, then slowly cool to room temperature;
[0043] (2) Detection of the mecA gene of Staphylococcus aureus. First, 2 μL of the solution to be tested was added to 38 μL Tris-HCl buffer solution containing 300 nM hairpin probe HP and 37....
Embodiment 2
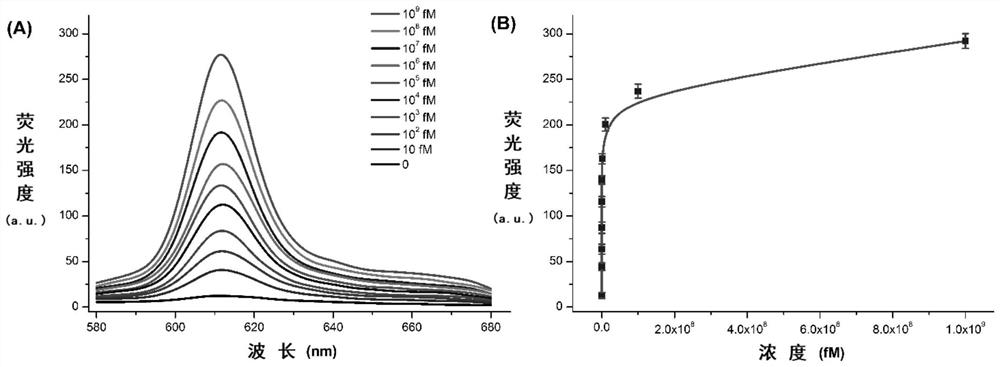
[0045] Detection of different concentrations of Staphylococcus aureus mecA gene:
[0046] Prepare Staphylococcus aureus mecA gene standard solution, the concentration is 0, 10fM, 10 2 fM, 10 3 fM, 10 4 fM, 10 5 fM, 10 6 fM, 10 7 fM, 10 8 fM and 10 9 fM, stored at 4°C.
[0047] The mecA gene solutions of different concentrations were added to the reaction system described in Example 1, and the fluorescence intensity of the system was observed after sufficient reaction. The results were as follows: figure 2 ( figure 2 A: at λ ex = Under the condition of 399nm, the emission spectrum corresponding to different mecA gene concentrations; figure 2 B: at lambda ex =399nm condition, λ em =610nm fluorescence standard curve; ), 10fM of the mecA gene can produce obvious changes in fluorescence, indicating that its detection limit <10fM. As the concentration of mecA gene increased, the fluorescence intensity also increased, and gradually tended to saturation.
Embodiment 3
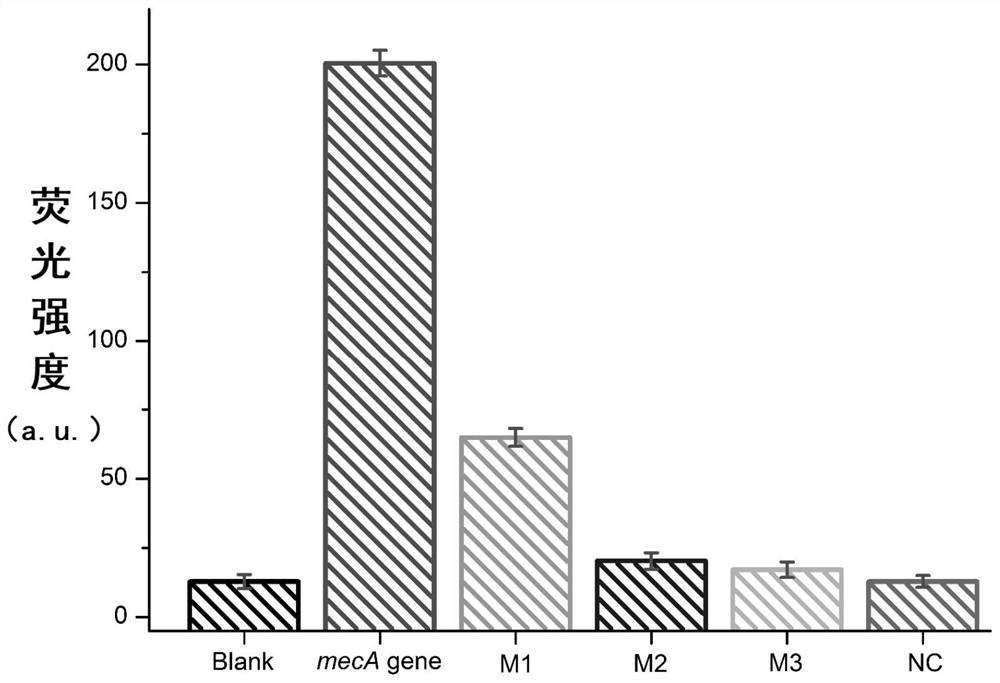
[0049] Specificity experiment:
[0050] Prepare 10 nM standard solutions of different nucleic acids, which are M1, M2, M3 and NC.
[0051] M1:5'-ATTGGGAT G ATAGCGTCATT-3' (SEQ ID NO: 6),
[0052] M2:5'-ATTGGGAT G ATA C CGTCATT-3' (SEQ ID NO: 7);
[0053] M3:5'-ATTG C GAT G ATA C CGTCATT-3' (SEQ ID NO: 8);
[0054] NC:5'- TGCCGCTCATCCGCCACATA -3' (SEQ ID NO: 9).
[0055] The underlined letters represent mismatched bases.
[0056] 10nM different interfering substance standard solutions and 10nM mecA gene solution were added to the reaction system described in Example 1, and the fluorescence changes of the system were observed after sufficient reaction. The results were as follows: image 3 As shown, the fluorescence intensities of M1, M2, M3 and NC at 10 nM are far lower than those of the mecA gene at 10 nM, and the fluorescence intensities of the M1 system and M2 are 32% and 1% of the mecA gene, respectively. The fluorescence intensity of the M3 system and NC is th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com