Quinonemethide triterpenoids and pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment of refractory rheumatoid arthritis
A quinone methyl triterpenoid, rheumatoid technology, applied in the field of treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
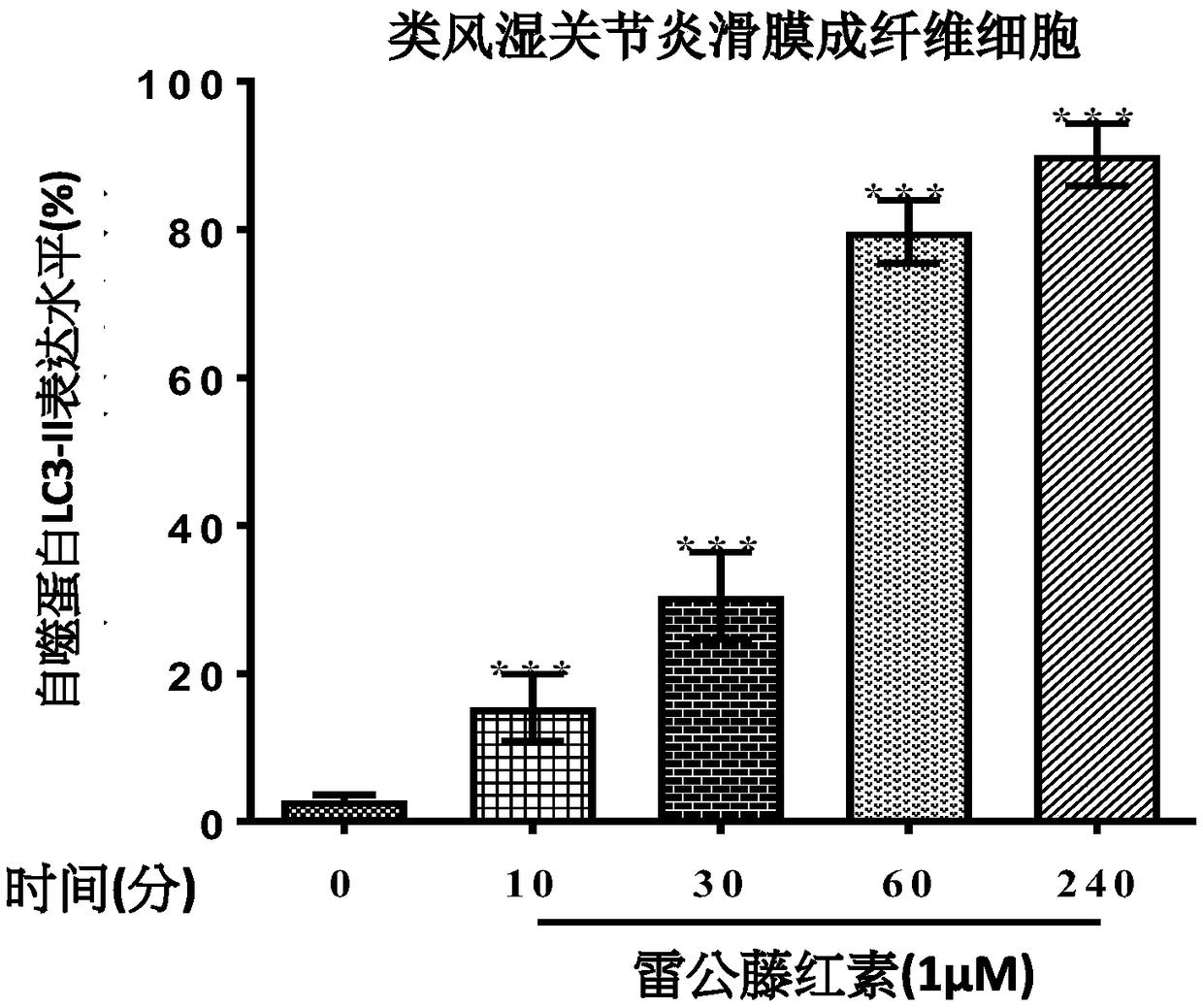
[0147] Example 1: Induction of autophagy
[0148] In these examples, all rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts (RASFs) were isolated from rheumatoid patients, while immortal rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts (RAFLS) were isolated from primary rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts (RAFLS). Derived from membranous fibroblasts (RASFs).
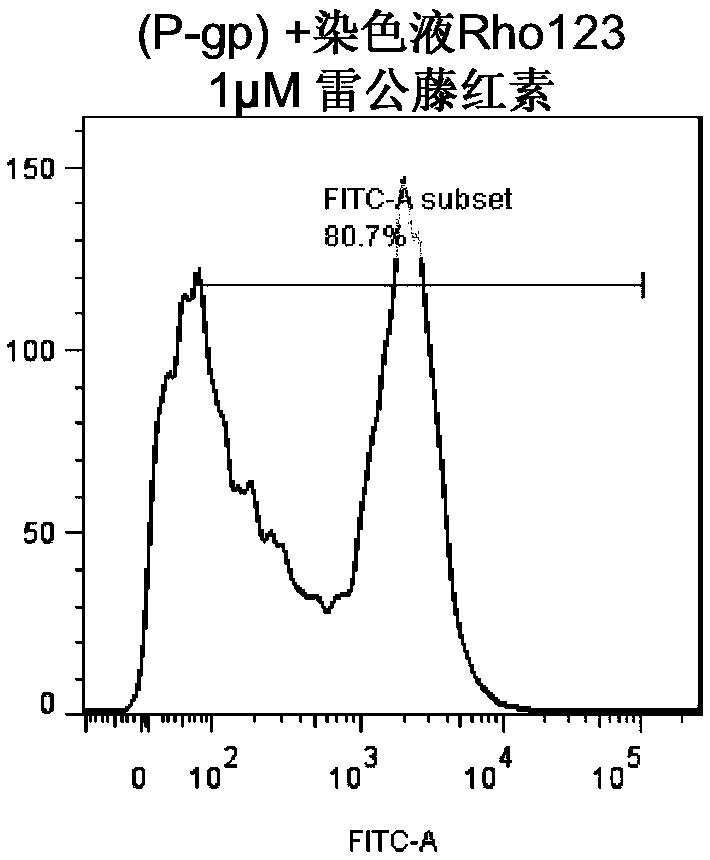
[0149] In order to detect the endogenous expression of autophagy-related protein LC3-II, RASFs or RAFLS cell lines were treated and fixed with specified concentrations of tripterine (CEL) at specific times, and then LC3-II was used to fluorescently stain the binding protein against Mouse antibody, photographed under a fluorescent microscope using red fluorescence.
[0150] Analysis by flow cytometry. Cell death and viability were measured using Annexin V staining kit (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA).
[0151] Briefly, RAFLS were treated with 0-2 μM tripterine for 24 hours. Then the cells were harvested and stained with FITC...
example 2
[0153] Example 2: Mobilization of cytosolic calcium to induce autophagy
[0154] The calcium ion concentration in the cytoplasm was dynamically measured using the FLIPR calcium 6 kit (Molecular Devices) according to the kit instructions. Briefly, RASFs were seeded at a density of 10,000 cells per well in a black-walled / white-bottomed 96-well plate (Tewksbury, MA, USA) for 24 hours, after which calcium 6 reagent was directly added to the cells, at 37 °C and 5% carbon dioxide for 2 hours. Immediately after adding tripterine or thapsigargin at different concentrations into the 96-well plate, data was collected using a Spectramax Paradigm multimode microplate reader (Molecular Devices), and the values were read at room temperature with a reading interval of 1 second.
[0155] Cytosolic calcium levels were measured using flow cytometry. Intracellular free calcium is measured by a Fluo-3 fluorescent dye. Briefly, RAFLS were treated with Celastrol (1 μM) for 4 hours, washed twic...
example 3
[0161] Example 3: Inhibitory effect of tripterine on apoptosis-deficient RAFLS
[0162] RAFLS transfected with mutant p53 were lysed with RIPA lysis buffer. Protein concentrations were determined using the Bio-Rad protein assay (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Hercules, CA, USA). Cell lysate samples were electrophoresed on SDS polyacrylamide gels and transferred to enhanced chemiluminescent nitrocellulose membranes (Amersham Biosciences, Piscataway, NJ) and blocked with 5% nonfat dry milk protein for 1 hour. The membrane was then incubated overnight at 4°C with an apoptotic marker antibody. Antibody binding was visualized by ECL Western Blot Detection Reagent (Invitrogen, Paisley, Scotland, UK) with a peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody. Band intensities were quantified by using the software ImageJ (NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA).
[0163] Perform cytotoxicity test. All test compounds were dissolved in DMSO at a final concentration of 50 mmol / L and stored at -20°C until use. Cy...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com