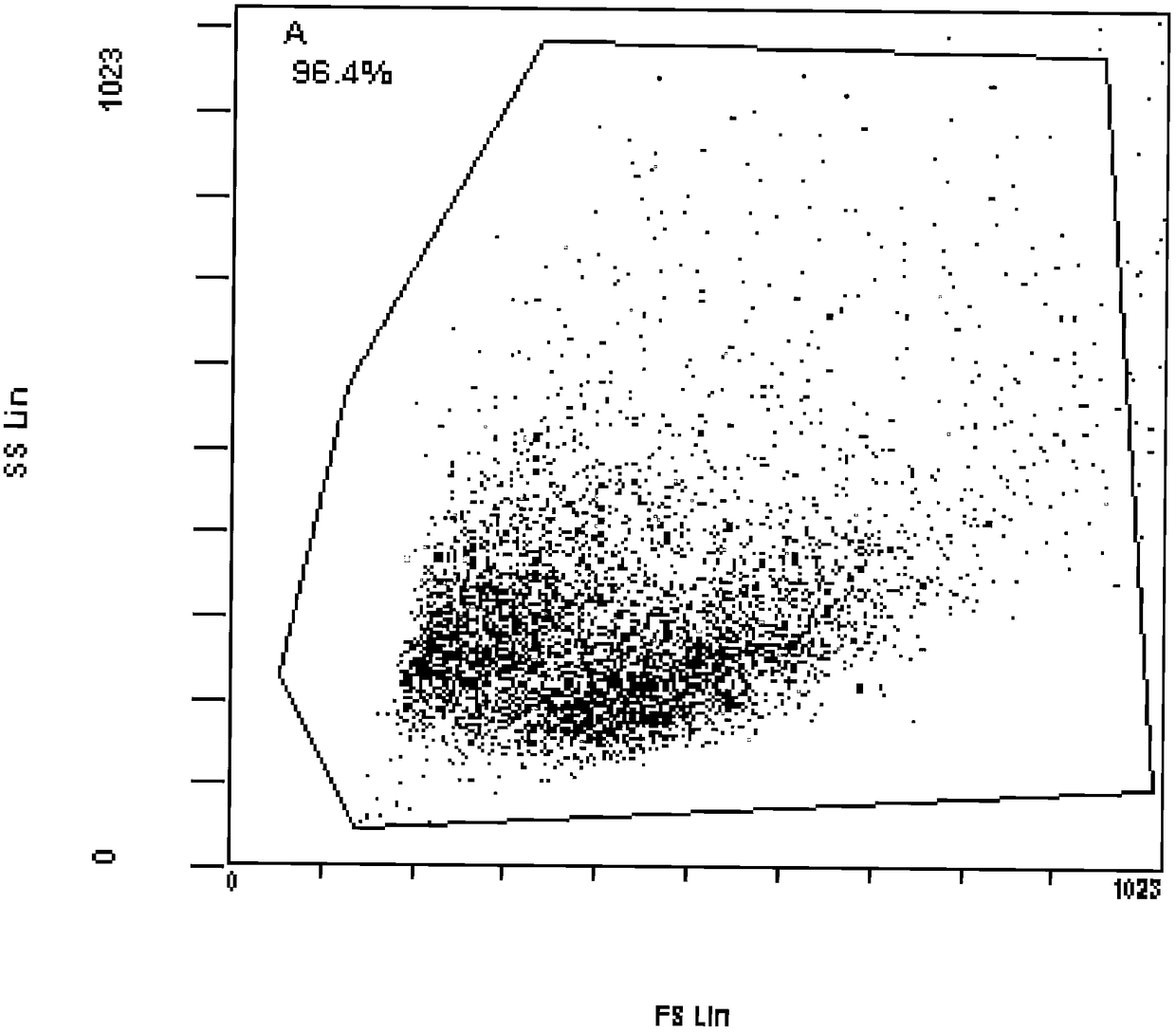
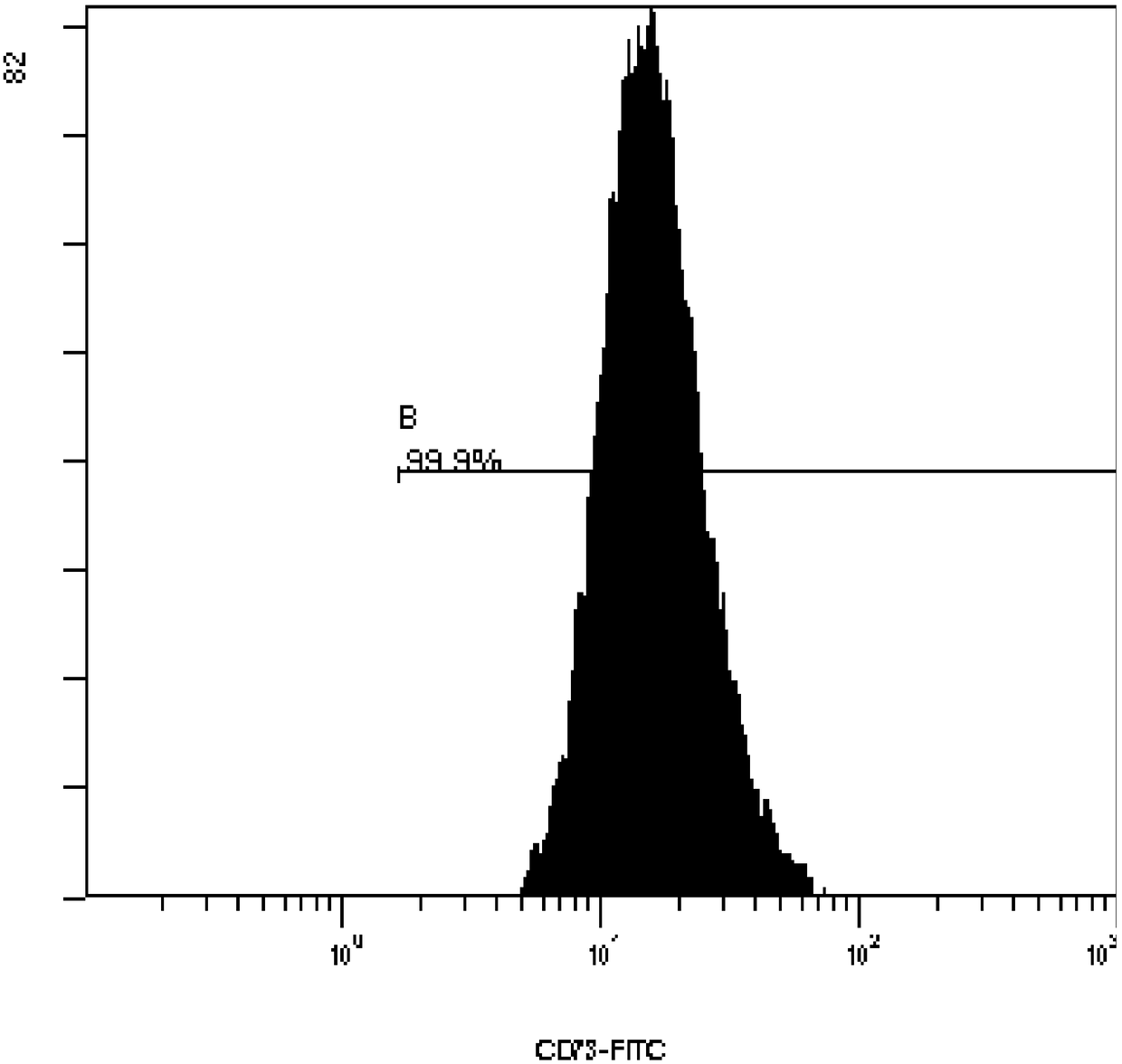
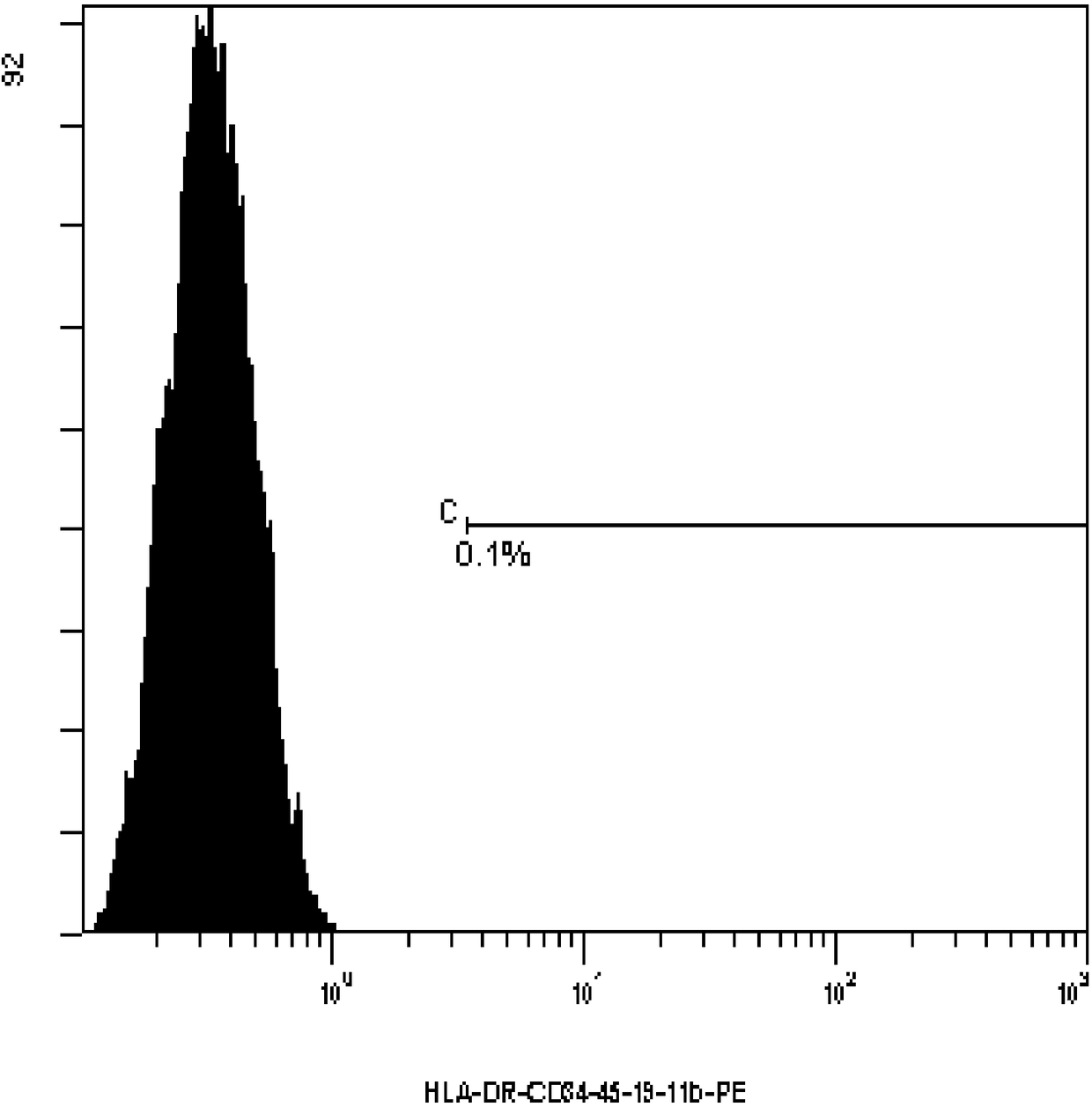
Method for isolating mesenchymal stem cells from placental vessel and used digestive enzyme composition
A technology of mesenchymal stem cells and digestive enzymes, applied in the field of isolating stem cells, can solve problems such as isolating mesenchymal stem cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0086] Embodiment 1. Isolation, subculture, and cryopreservation of placental MSCs
[0087] (1) Within four hours after delivery, soak the placenta in 75% alcohol for 30 seconds under aseptic conditions, and then wash it twice with PBS;
[0088] (2) Strip the placental blood vessels from the umbilical cord root of the placenta, and squeeze the blood vessels with surgical forceps to remove blood stains;
[0089] (3) Cut the blood vessels into pieces of about 1.5 mm^3, wash them with PBS, and then filter through a 300-mesh filter to remove residual blood stains to obtain placental vascular tissue (5.8 g of placental vascular tissue was obtained from one placenta in this embodiment);
[0090] (4) Add mixed enzyme solution (including: 0.2% collagenase II, 0.15% collagenase IV, 0.1% deoxyribonuclease I in PBS buffer) to digest for 1 hour;
[0091] (5) Add serum to stop the digestion, then filter through a 300-mesh filter, collect the tissue fluid, wash with PBS, and combine the ...
Embodiment 2
[0096] Embodiment 2, the isolation of placental MSC, subculture, cryopreservation
[0097] (1) Within four hours after delivery, soak the placenta in 75% alcohol for 30 seconds under aseptic conditions, and then wash it twice with PBS;
[0098] (2) Strip the placental blood vessels from the umbilical cord root of the placenta, and squeeze the blood vessels with surgical forceps to remove blood stains;
[0099] (3) Cut the blood vessels into 1mm^3 fragments, wash them with PBS, and then filter through a 300-mesh filter to remove residual blood stains to obtain placental vascular tissue (5.5 g of placental vascular tissue was obtained from one placenta in this embodiment);
[0100] (4) Add mixed enzyme solution (including: 0.3% collagenase II, 0.1% collagenase IV, 0.15% deoxyribonuclease I in PBS buffer) to digest for 0.5h;
[0101] (5) Add serum to stop the digestion, then filter through a 300-mesh filter, collect the tissue fluid, wash with PBS, and combine the cleaning sol...
Embodiment 3
[0106] Embodiment 3, the isolation of placental MSC, subculture, cryopreservation
[0107] (1) Within four hours after delivery, soak the placenta in 75% alcohol for 30 seconds under aseptic conditions, and then wash it twice with PBS;
[0108] (2) Strip the placental blood vessels from the umbilical cord root of the placenta, and squeeze the blood vessels with surgical forceps to remove blood stains;
[0109] (3) Cut the blood vessels into 2 mm^3 pieces, wash them with PBS, and then filter through a 300-mesh filter to remove residual blood stains to obtain placental vascular tissue (4.7 g of placental vascular tissue was obtained from one placenta in this embodiment);
[0110] (4) Add mixed enzyme solution (including: 0.1% collagenase II, 0.2% collagenase IV, 0.05% deoxyribonuclease I in PBS buffer) for digestion for 2 hours;
[0111] (5) Add serum to stop the digestion, then filter through a 300-mesh filter, collect the tissue fluid, wash with PBS, and combine the cleanin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com