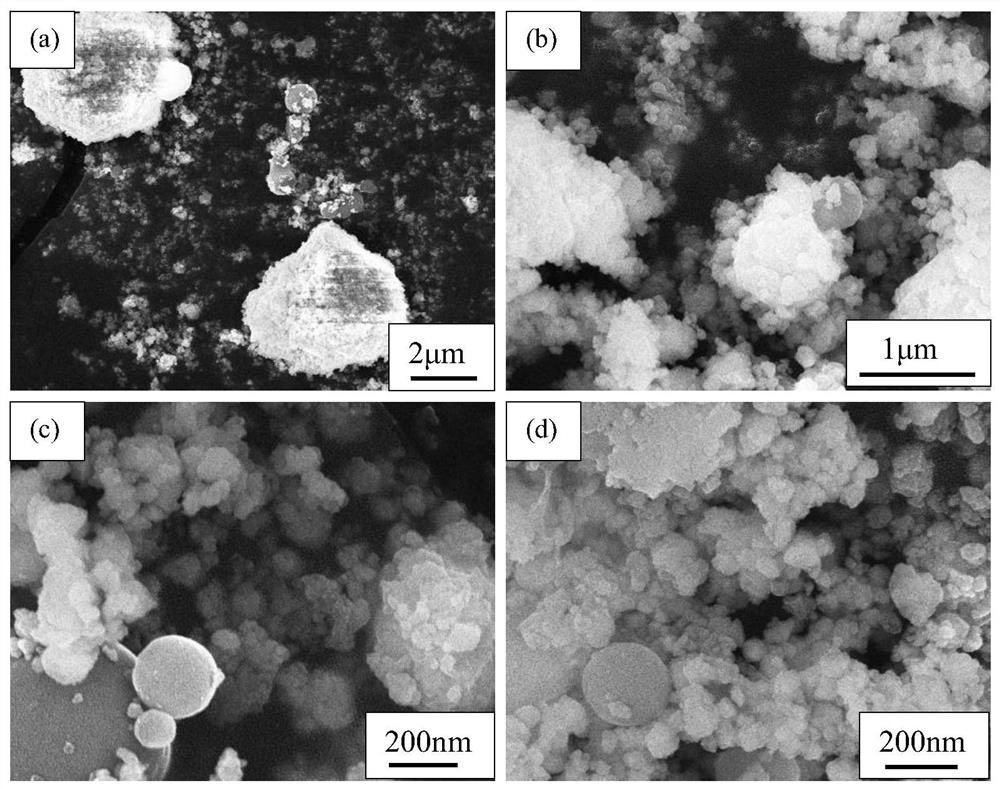
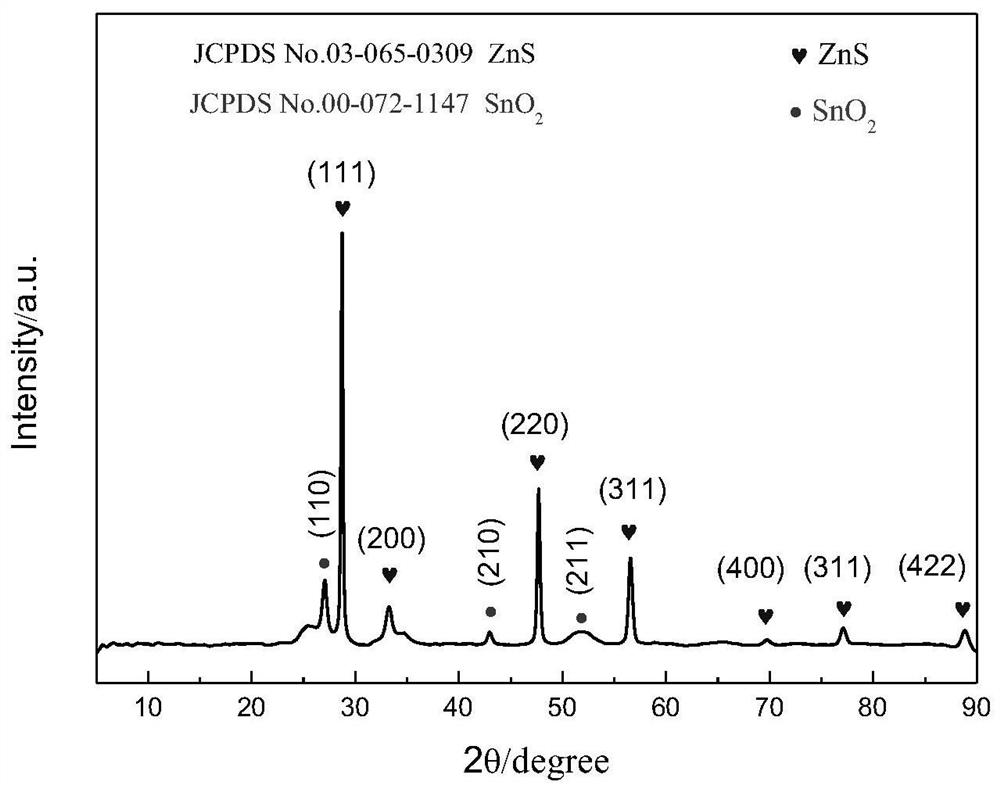
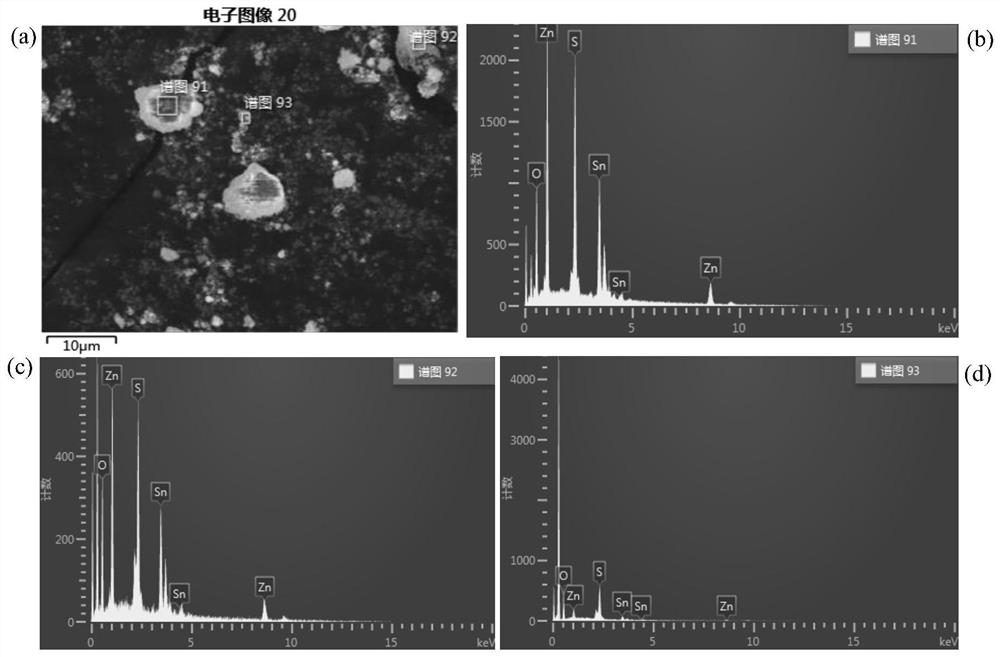
A negative electrode material zns/c-sno for sodium ion battery prepared by using tin mud 2 Methods
A sodium ion battery and negative electrode material technology, applied in battery electrodes, secondary batteries, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of expensive SnO2, increased tin anode consumption, and aggravated environmental pollution, so as to improve battery cycle stability and initial The effect of capacity, simple operation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] Example 1: Preparation of ZnS / C-SnO using tin mud 2 composite material
[0054] ①Using zinc acetate, sodium sulfide and anhydrous glucose as raw materials, weigh 2.153g of C 4 h 6 o 4 Zn·2H 2 O, 4.712g of Na 2 S·9H 2 O and 5.454g of anhydrous glucose were simultaneously dissolved in 150mL of distilled water to form a clear and transparent solution, then transferred to a reaction kettle for hydrothermal reaction at 180°C for 12 hours, centrifuged-washed-ultrasonic dispersion, washed with distilled water and absolute ethanol three times, respectively, 60 ℃ drying for 12h to obtain a light gray precursor, and then in N 2 Calcined at 750°C for 2 hours in the atmosphere to obtain ZnS / C material.
[0055] ②The viscous tin sludge obtained directly from the production workshop, in order to remove the influence of impurity ions, was cleaned with distilled water / absolute ethanol, and then the solution was centrifuged, washed 3 times repeatedly, and placed in a drying box f...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Example 2: Preparation of ZnS / C-SnO using tin mud 2 composite material
[0061] ①Using zinc acetate, sodium sulfide and anhydrous glucose as raw materials, weigh 2.153g of C 4 h 6 o 4 Zn·2H 2 O, 4.712g of Na 2 S·9H 2 O and 5.454g of anhydrous glucose were simultaneously dissolved in 150mL of distilled water to form a clear and transparent solution, then transferred to a reaction kettle for hydrothermal reaction at 180°C for 12 hours, centrifuged-washed-ultrasonic dispersion, washed with distilled water and absolute ethanol three times, respectively, 60 ℃ drying for 12h to obtain a light gray precursor, and then in N 2 Calcined at 750°C for 2 hours in the atmosphere to obtain ZnS / C material.
[0062] ②The viscous tin sludge obtained directly from the production workshop, in order to remove the influence of impurity ions, was cleaned with distilled water / absolute ethanol, and then the solution was centrifuged, washed 3 times repeatedly, and placed in a drying box f...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Embodiment 3: Utilize tin mud to prepare ZnS / C-SnO 2 composite material
[0067] ①Using zinc acetate, sodium sulfide and anhydrous glucose as raw materials, weigh 2.153g of C 4 h 6 o 4 Zn·2H 2 O, 4.712g of Na 2 S·9H 2 O and 5.454g of anhydrous glucose were simultaneously dissolved in 150mL of distilled water to form a clear and transparent solution, then transferred to a reaction kettle for hydrothermal reaction at 180°C for 12 hours, centrifuged-washed-ultrasonic dispersion, washed with distilled water and absolute ethanol three times, respectively, 60 ℃ drying for 12h to obtain a light gray precursor, and then in N 2 Calcined at 750°C for 2 hours in the atmosphere to obtain ZnS / C material.
[0068] ②The viscous tin sludge obtained directly from the production workshop, in order to remove the influence of impurity ions, was cleaned with distilled water / absolute ethanol, and then the solution was centrifuged, washed 3 times repeatedly, and placed in a drying box ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| current efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| current efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com