Application of gene ESP for regulating and controlling development of rice spikes
A rice and gene technology, applied in the genetic improvement of rice panicle type, the application of gene ESP, the field of gene ESP to control rice panicle type, can solve the problems of limited understanding of molecular regulation mechanism, and improve the population structure and light receiving situation , reduce shading, broaden the effect of genetic basis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Embodiment 1 rice esp mutant phenotype and genetic effect analysis
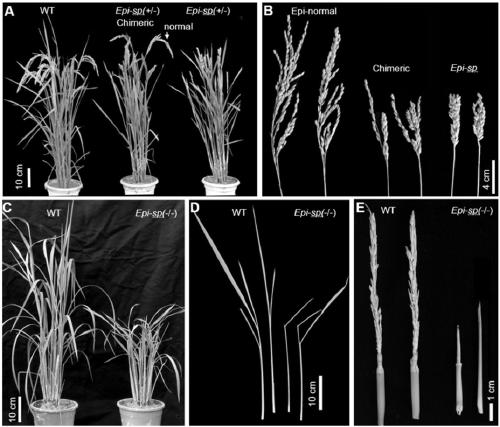
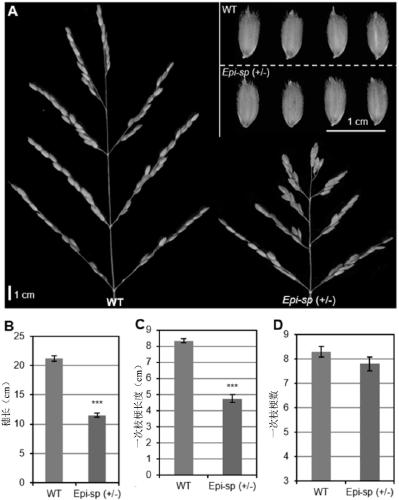
[0039] Among the progeny of wild-type japonica rice Zhonghua 11, a plant with slightly shorter panicle length, erect panicle type and increased grain density was screened out, which was named rice esp mutant.
[0040] At the grain filling stage and maturity stage, the plants and ear types of the wild-type and mutant heterozygotes were photographed, and the phenotypes were as follows: figure 1 As shown in A and 1B, the spikes of the esp heterozygous mutants were shorter than those of the wild type, and the grain density increased ( figure 1 A and 1B). Interestingly, this mutation has a low-frequency spontaneous back mutation phenomenon, so different tillers of a single plant or even different panicle branches of the same rice panicle can show the coexistence of wild type and mutant type. The seedling phenotypes of esp homozygous mutants and wild type are as follows figure 1 As shown in C, the esp hom...
Embodiment 2e
[0042] Embodiment 2Esp mutant panicle character analysis
[0043] The spikes of esp heterozygous mutants and wild-type rice from the completion of grouting to yellow maturity were photographed, and statistical analysis was performed on the panicle traits such as spike length, grain shape, number of primary branches, and primary branch length. The results are as follows figure 2 shown. The panicle length of esp heterozygous mutants was significantly shorter ( figure 2 A and 2B), the primary branch length was also significantly shortened ( figure 2 C), while the grain shape and the number of primary branches did not change significantly ( figure 2 A and 2D), indicating that ESP mainly affects the panicle shape and panicle length by affecting the primary branch development of rice panicle, and basically has no effect on the number of primary branches and grain shape.
Embodiment 3
[0044] Map-position cloning and candidate gene expression analysis of embodiment 3ESP gene
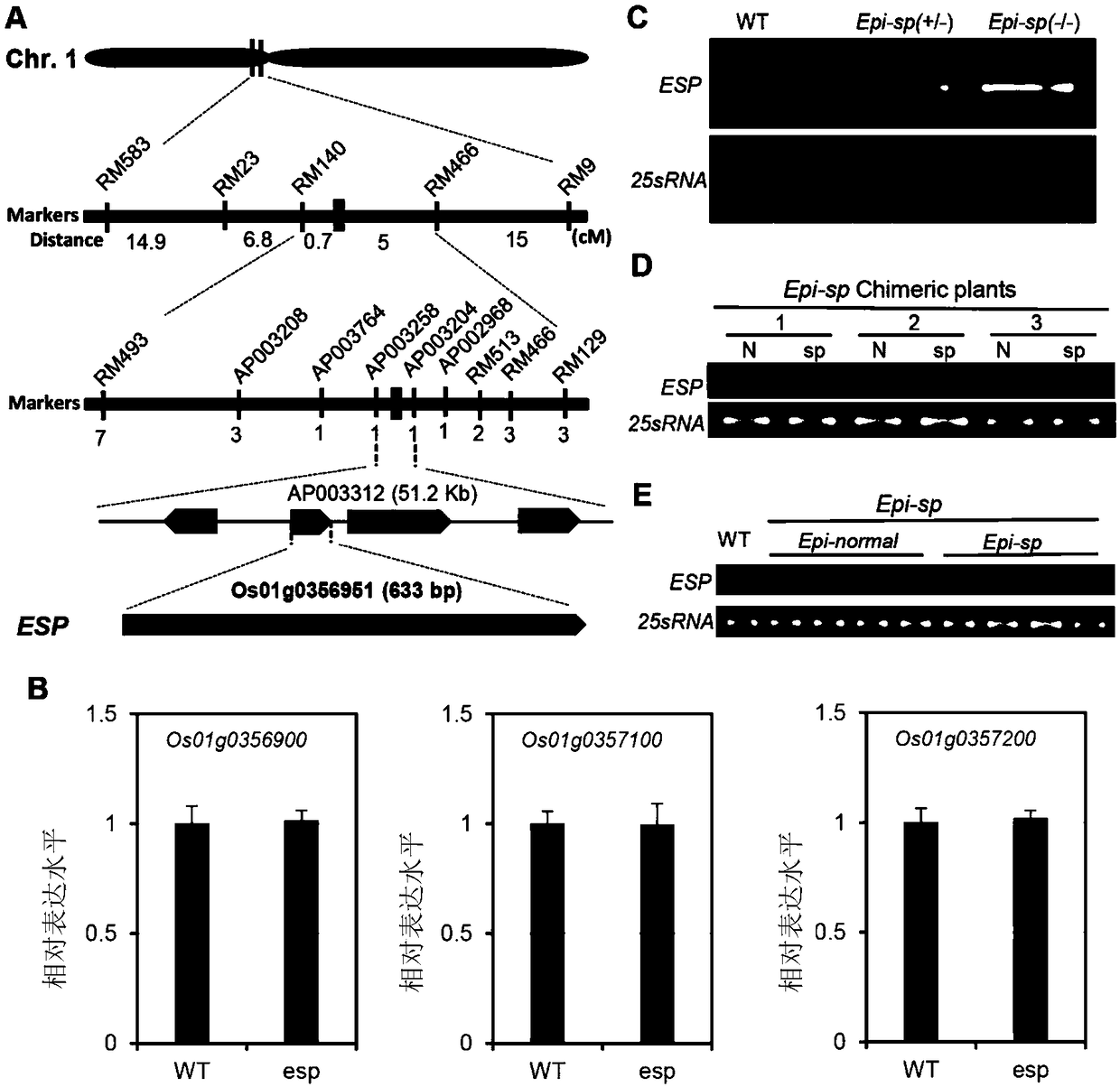
[0045] F constructed using the esp mutant and the indica rice variety Huajingxian 74 (a rice variety publicly available, commercially available) 2 population (esp crossed with Huajingxian 74 to obtain F 1 , F 1 F 2 Population), ESP gene mapping was carried out, and it was initially located between the SSR markers RM583 and RM9 on chromosome 1, with a genetic distance of 42.4cM. According to the Nipponbare and 9311 reference sequences, an Indel (insertion-deletion) marker was developed between these two markers, and the ESP gene was further positioned on the 51.2kb interval of the rice chromosome 1 ( image 3 A). There are 4 genes in this interval, namely Os01g0356900, Os01g0356951, Os01g0357100 and Os01g0357200.
[0046] In order to identify the candidate gene ESP, the expression levels of these four genes in the esp mutant and wild type were detected respectively, and the specifi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com