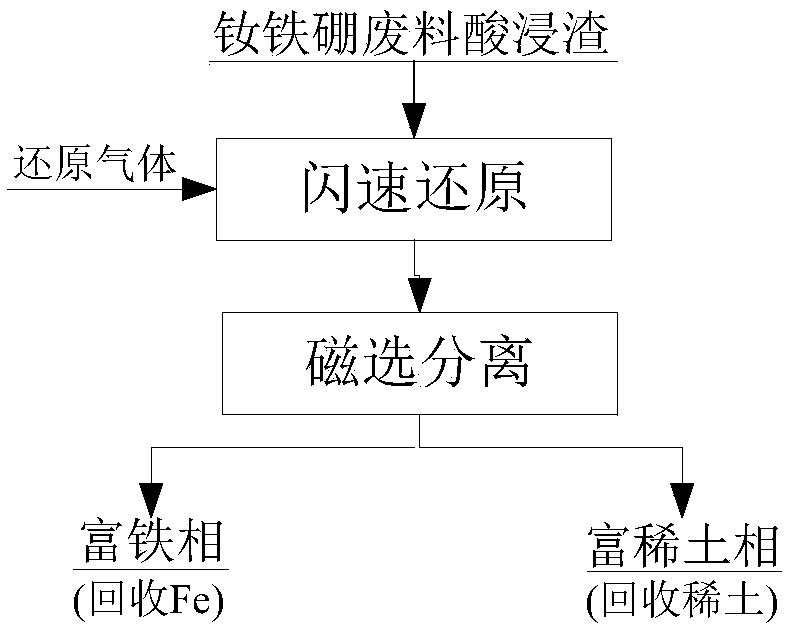
Flash reduction comprehensive recovery method of neodymium iron boron waste acid leaching residue
A waste acid and neodymium-iron-boron technology, which is applied in the direction of improving process efficiency and reducing gas emissions, can solve the problems of no suitable comprehensive utilization method for iron-boron waste acid leaching residue, high equipment requirements, environmental pollution, etc., and achieve good promotion Application value, accurate atmosphere control, environment-friendly effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
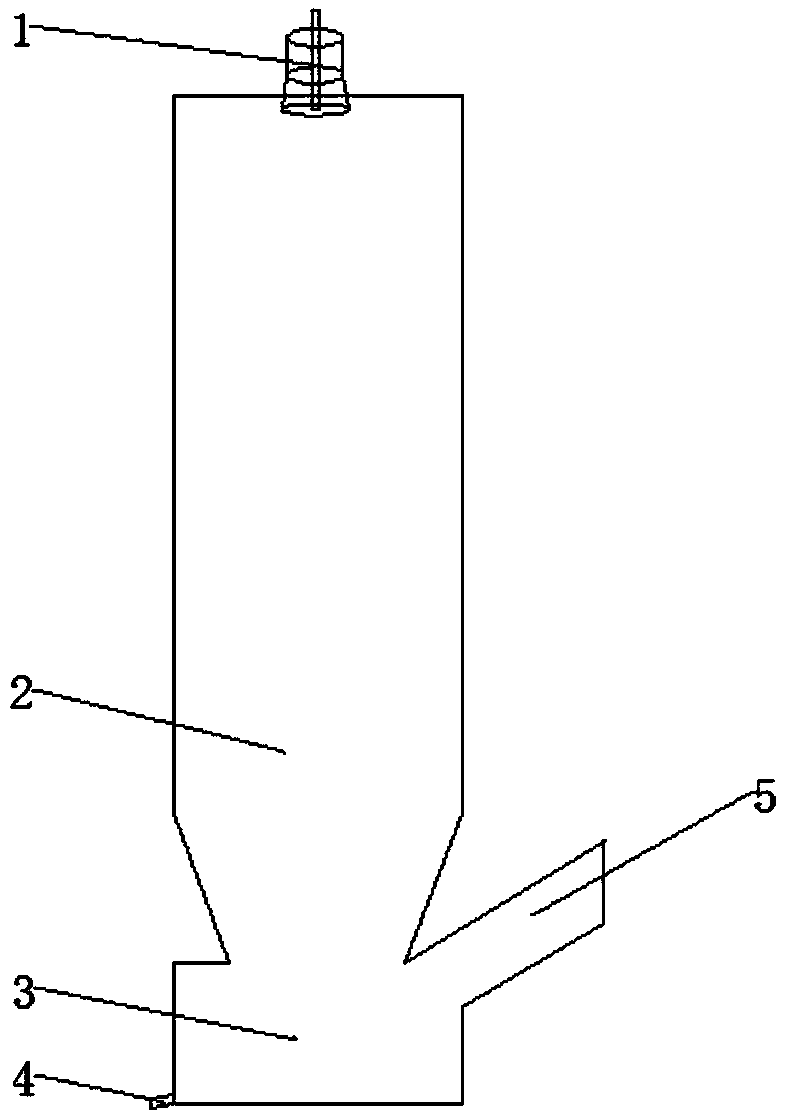
[0017] The powdery NdFeB waste acid leaching residue with a particle size of 100 mesh is sprayed into a reaction tower (2) with a height of 3.5 meters and a temperature of 1200 ° C through a nozzle (1) together with hydrogen, and the material is in a highly dispersed floating state. The upper end of the reaction tower falls to the lower end. During this process, the reaction atmosphere is controlled so that the oxygen partial pressure is 10 -16 Atm, 45.1% of the iron oxides in the material were reduced to metallic iron, 54.4% were reduced to ferric oxide, while the rare earth oxides in the material were not reduced. The reduction products fall into the collector (3) below the reaction tower, and after being discharged from the outlet (4), iron-rich phase and rare earth-rich phase are obtained by magnetic separation. The reduced flue gas is discharged through the flue (5) at the upper end of the collector (3), and is emptied after secondary combustion, waste heat recovery and d...
Embodiment 2
[0019] The powdery NdFeB waste acid leaching residue with a particle size of 200 mesh is sprayed together with hydrogen into a reaction tower (2) with a height of 5.5 meters and a temperature of 1300 °C through a nozzle (1). The material is in a highly dispersed floating state from The upper end of the reaction tower falls to the lower end. During this process, the reaction atmosphere is controlled so that the oxygen partial pressure is 10 -18 Atm, 60.5% of the iron oxides in the material were reduced to metallic iron, 39.1% were reduced to ferric oxide, while the rare earth oxides in the material were not reduced. The reduction products fall into the collector (3) below the reaction tower, and after being discharged from the outlet (4), iron-rich phase and rare earth-rich phase are obtained by magnetic separation. The reduced flue gas is discharged through the flue (5) at the upper end of the collector (3), and is emptied after secondary combustion, waste heat recovery and du...
Embodiment 3
[0021] The powdery NdFeB waste acid leaching residue with a particle size of 300 mesh is sprayed together with hydrogen into a reaction tower (2) with a height of 8.5 meters and a temperature of 1450 °C through a nozzle (1). The material is in a highly dispersed floating state from The upper end of the reaction tower falls to the lower end. During this process, the reaction atmosphere is controlled so that the oxygen partial pressure is 10 -20 Atm, 80.5% of the iron oxides in the material were reduced to metallic iron, 19.3% were reduced to ferric oxide, while the rare earth oxides in the material were not reduced. The reduction products fall into the collector (3) below the reaction tower, and after being discharged from the outlet (4), iron-rich phase and rare earth-rich phase are obtained by magnetic separation. The reduced flue gas is discharged through the flue (5) at the upper end of the collector (3), and is emptied after secondary combustion, waste heat recovery and du...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com