Application of BRAF inhibitor to preparation of novel drugs for treating programmed necrotic diseases and screening method of BRAF inhibitor
A technique of programmed necrosis and screening methods, which is applied in the field of cytology and pharmacology, can solve the problems of difficult compound families, long screening cycle and verification experiments, and long research and development time, so as to achieve targeting and safety , reduce cost and failure risk, and avoid the effect of long investment time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
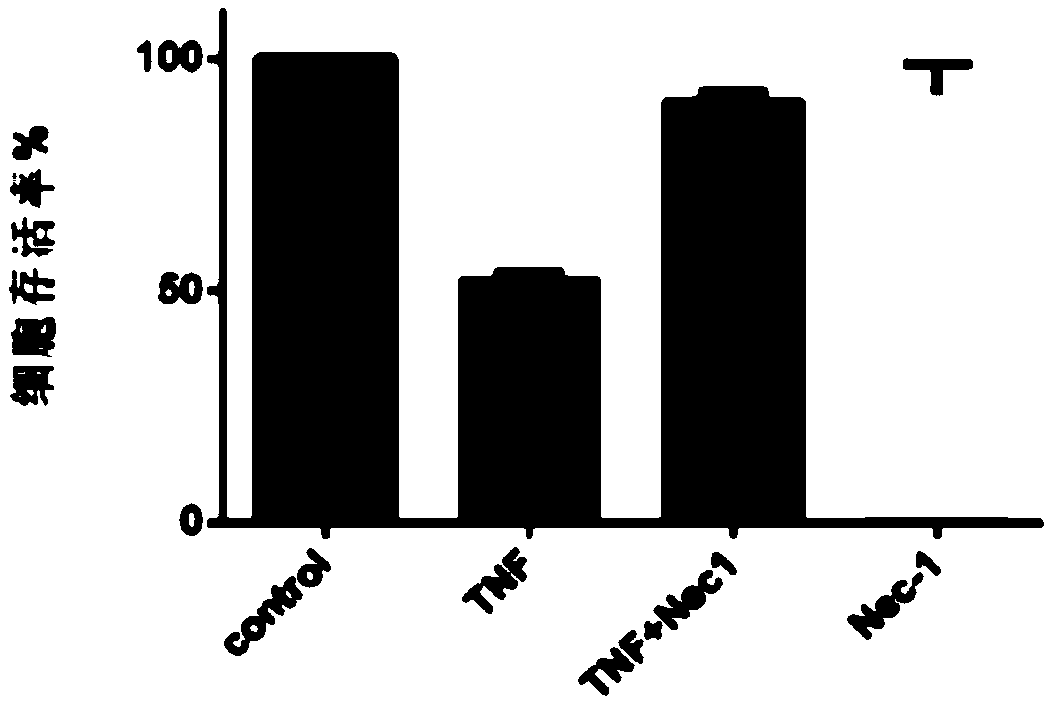
[0057] Use the positive control TNF (TNFα group) and the antagonistic group (Nec-1 group) of Nec-1 anti-necrosis inhibitors to detect and determine the sensitivity of the cell line to different functional drugs in the FADD-KO cell line, each group of drugs After the L929-FADD-KO cells were treated for 24 hours, the cell survival rate was detected by the ATP level, the Control group was used as the standard, and the data analysis of the chemiluminescence instrument was shown in Table 1 and figure 1 As shown, the lethality of TNFα group (10ng / mL) to cells almost reached 50%, and Nec-1 group (30μM) could restore the cells to 90%.
[0058] Table 1 Cell survival rate of L929 FADD-KO cells treated with TNF, Nec-1, TNF+Nec-1
[0059]
Embodiment 2
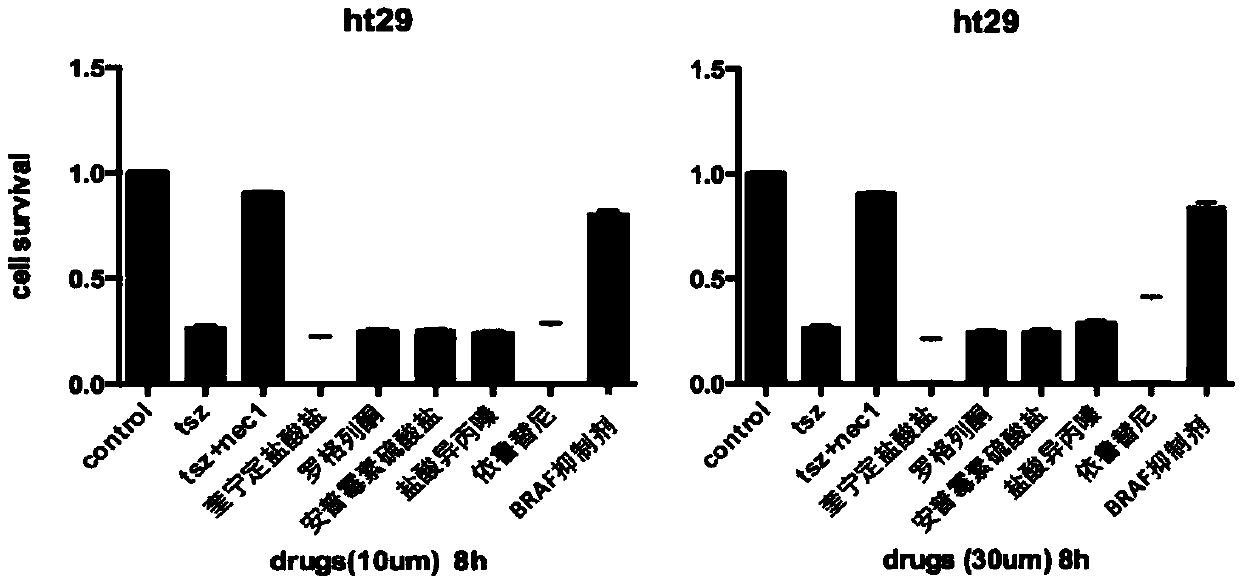
[0061] The L929 cell proliferation model was used to screen the FDA drug library for necrosis. After more than a thousand FDA drugs (10 μM) were treated for 24 hours, if the cell survival rate of the three replicate wells treated with the same drug was higher than 50% ( value above 0.5), it is considered that the drug has a strong necrosis-inhibiting effect on L929-FADD-KO cells and can be used as a candidate drug.
[0062] The necrosis inhibitory function of the above candidate drugs was tested at different concentrations and different treatment times. Using the human cell line HT29 as a cell model, it was found that there was no difference in treatment at different times for 8 hours and 24 hours, and drug concentrations of 10uM and 30uM could be obtained. Very good results, with BRAF inhibitors working best, such as figure 2 shown.
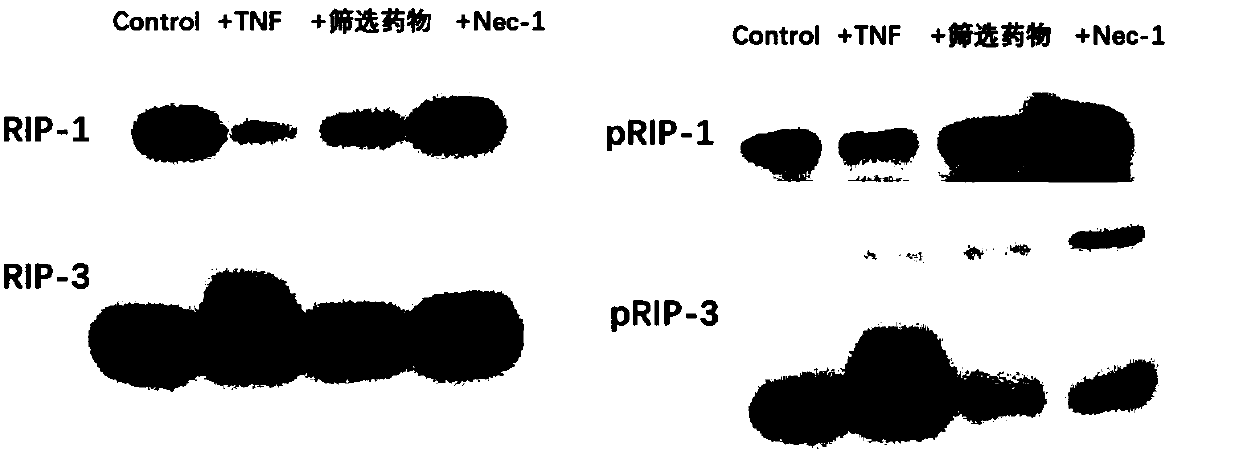
[0063] The cells were used as control group, TNF necrosis group, TNF+BRAF inhibitor group, TNF+Nec-1 group for target verification, Nec-1 was...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com