A chemical exchange saturation transfer contrast agent and its preparation method and application
A technology of chemical exchange and contrast agent, which is used in pharmaceutical formulations, preparations for in vivo testing, and emulsion delivery to achieve high safety, high sensitivity, and improve the effect of EPR.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
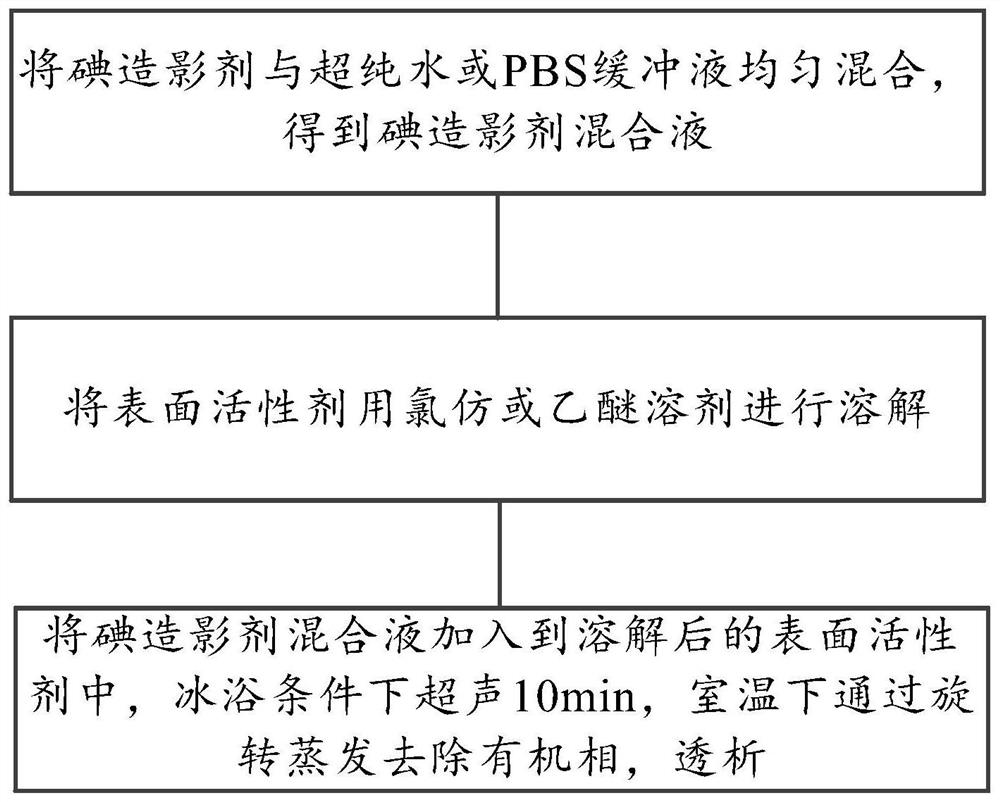
[0057] Such as figure 1 As shown, another embodiment of the present invention provides a preparation method of a chemical exchange saturation transfer contrast agent. The method specifically may include the following steps:
[0058] Uniformly mix the iodine contrast agent with ultrapure water or PBS buffer to obtain the iodine contrast agent mixture. Wherein, the molar ratio of iodine contrast agent to ultrapure water is 8:1.
[0059] Dissolve the surfactant with chloroform or ether solvent.
[0060] Add the iodine contrast agent mixture to the dissolved surfactant, ultrasonicate for 10 minutes in an ice bath, remove the organic phase at room temperature, and dialyze to obtain a chemical exchange saturation transfer contrast agent made of surfactant-coated iodine contrast agent .
[0061] Further, the definitions of surfactant and iodine contrast agent are as above. For example, the surfactant is one or a mixture of phosphatidylcholine liposomes, phosphatidylethanolamine ...
Embodiment 1
[0070] Preparation of lipoCEST contrast agent
[0071] 1) uniformly mixing iohexol and ultrapure water to obtain iohexol mixed solution;
[0072] 2) dissolving lecithin and cholesterol with chloroform to obtain the dissolved surfactant, wherein lecithin:cholesterol=8:1 (molar ratio);
[0073] 3) Add the iohexol mixture to the dissolved surfactant (iohexol:surfactant = 1:1 (molar ratio)), use a probe-type ultrasonic ice bath to sonicate for 10 minutes, and use a rotary evaporator The organic phase was removed at room temperature, followed by dialysis to obtain lipoCEST nanoparticles, namely lipoCEST contrast agent.
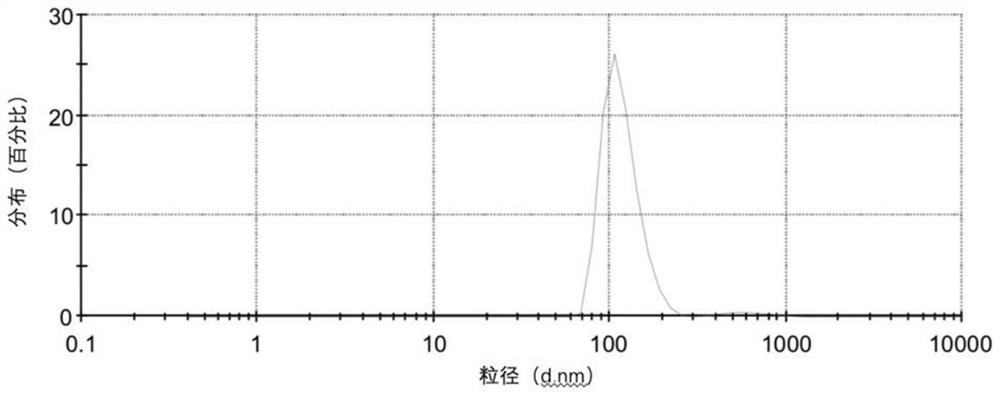
[0074] figure 2 The DLS plot of the resulting lipoCEST nanoparticles is shown, as figure 1As shown, its particle size (hydrated particle size) is basically distributed in the range of 70-240nm (the particle size of 116nm accounts for about 97.4%), mainly concentrated around 100nm, which is in line with the size supported by the EPR effect.
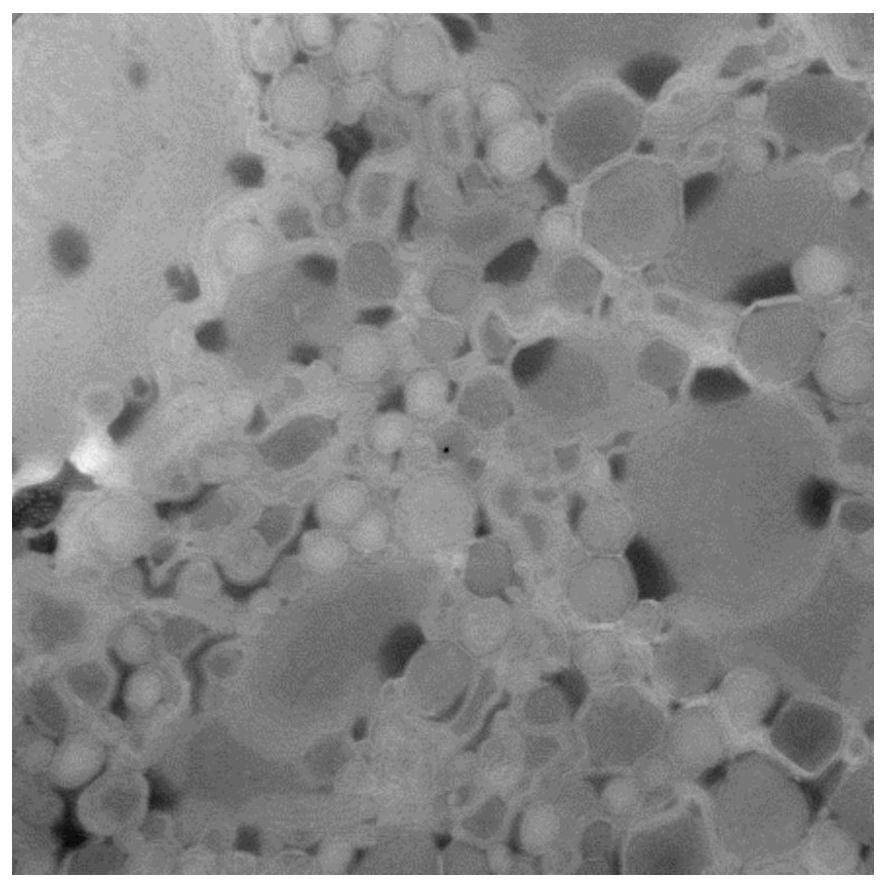
[0075] image 3 A...
Embodiment 2
[0086] Preparation of lipoCEST contrast agent
[0087] 1) uniformly mixing iopamidol and ultrapure water to obtain iopamidol mixed solution;
[0088] 2) dissolving lecithin and cholesterol with chloroform to obtain the dissolved surfactant, wherein lecithin:cholesterol=8:1 (molar ratio);
[0089] 3) Add the iopamidol mixture to the dissolved surfactant (iopadol:surfactant = 1:0.8 (molar ratio)), ultrasonicate for 10 minutes with a probe-type ultrasonic ice bath, and use a rotary evaporator The organic phase was removed at room temperature, followed by dialysis to obtain lipoCEST nanoparticles, namely lipoCEST contrast agent.
[0090] The signal strength of CEST is shown in Table 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com