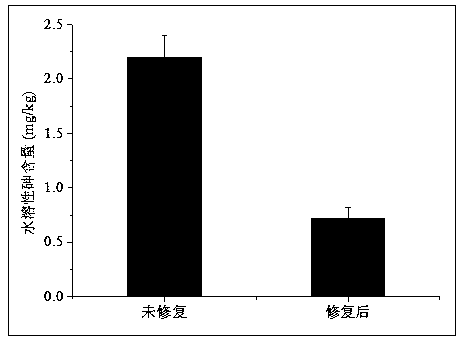
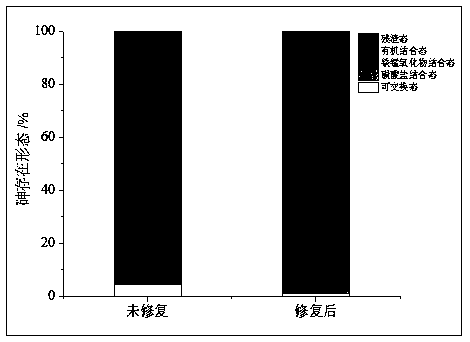
Method for repairing arsenic-polluted soil by inducing active iron and manganese oxides through bacteria under aerobiotic/microaerobic conditions
An iron-manganese oxide, inducing activity technology, applied in the restoration of polluted soil and other directions, can solve the problems of easy migration of arsenic and limited arsenic repair ability, and achieve the effects of low treatment cost, convenient operation and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment example 1
[0027] 1) Enrichment culture of bacteria
[0028] Pseudomonas putida P. putida Strain MnB1 was inoculated in Pseudomonas putida enrichment medium A at a volume ratio of 5%, and then aerobic enrichment culture was carried out at 25 degrees Celsius (150 rpm) for 2 days;
[0029] The components of the medium A are 0.5 g of yeast extract powder, 0.5 g of hydrolyzed casein, 0.5 g of glucose, 0.29 g of calcium chloride, 0.5 g of magnesium sulfate, 1 mL of trace elements, and 1 liter of deionized water;
[0030] The selected bacterial strains come from ATCC, the American Type Bacteria Collection Center, with the preservation number ATCC 23483;
[0031] 2) Preparation of active metabolites:
[0032] Add the Pseudomonas putida bacteria solution enriched in step 1) to the Pseudomonas putida culture medium B with an initial concentration of manganese carbonate of 1 g / L and a pH of 6.8 at an inoculum of 6% by volume, and then in 25 Celsius, cultivated under aerobic conditions for 4 day...
Embodiment example 2
[0038] 1) Enrichment culture of bacterial strains:
[0039] Pseudomonas putida P. putida Strain MnB1 was inoculated in Pseudomonas putida enrichment medium A at a volume ratio of 10%, and then aerobic enrichment culture was carried out at 25 degrees Celsius for 5 days under horizontal shaking (150 rpm);
[0040] The components of medium A are 0.5g of yeast extract powder, 0.5g of hydrolyzed casein, 0.5g of glucose, 0.2g of calcium chloride, 0.3g of magnesium sulfate, 4mL of trace elements, and 1 liter of deionized water;
[0041] The selected bacterial strains come from the American Type Bacteria Collection Center, with the preservation number ATCC 23483;
[0042] 2) Preparation of active iron manganese oxide:
[0043] Add the Pseudomonas putida bacteria solution enriched in step 1) to the Pseudomonas putida culture medium B containing manganese carbonate with an initial concentration of 1.0g / L and a pH of 6.8 at an inoculation volume of 10% by volume, and then in 30 degree...
Embodiment example 3
[0048] 1) Enrichment culture of bacterial strains:
[0049] Pseudomonas putida P. putida Strain MnB1 was inoculated in Pseudomonas putida enrichment medium A at a volume ratio of 8%, and then aerobic enrichment culture was carried out at 20 degrees Celsius (120 rpm) for 5 days;
[0050] The composition of medium B is 0.35g of yeast extract powder, 0.35g of hydrolyzed casein, 0.35g of glucose, 0.2g of calcium chloride, 0.5g of magnesium sulfate, 2mL of trace elements, and 1 liter of deionized water;
[0051] The selected bacterial strains come from the American Type Bacteria Collection Center, with the preservation number ATCC 23483;
[0052] 2) Preparation of active iron manganese oxide:
[0053] Add Pseudomonas putida culture medium B containing manganese carbonate with an initial concentration of 1.0g / L and a pH of 7.0 to the inoculum of Pseudomonas putida obtained in step 1) at a volume ratio of 7%. The ingredients are 0.25g of ferrous ammonium sulfate, 0.25g of sodium c...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Repair efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Repair efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Repair efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com