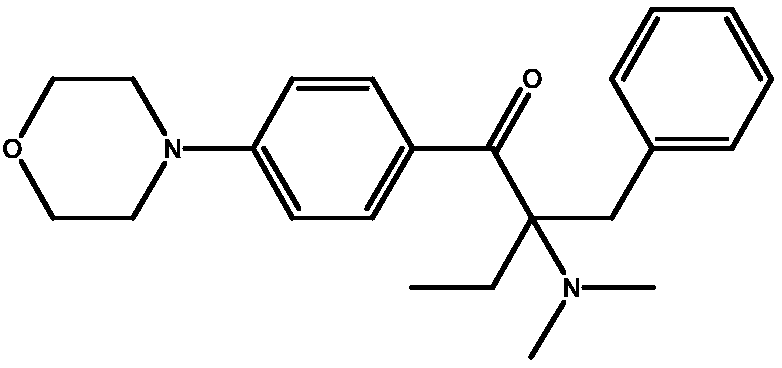
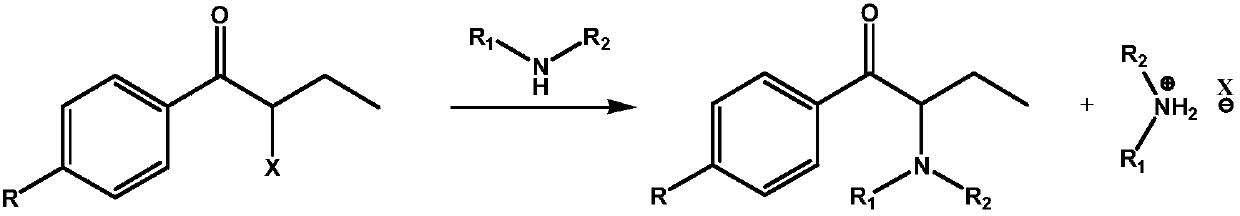
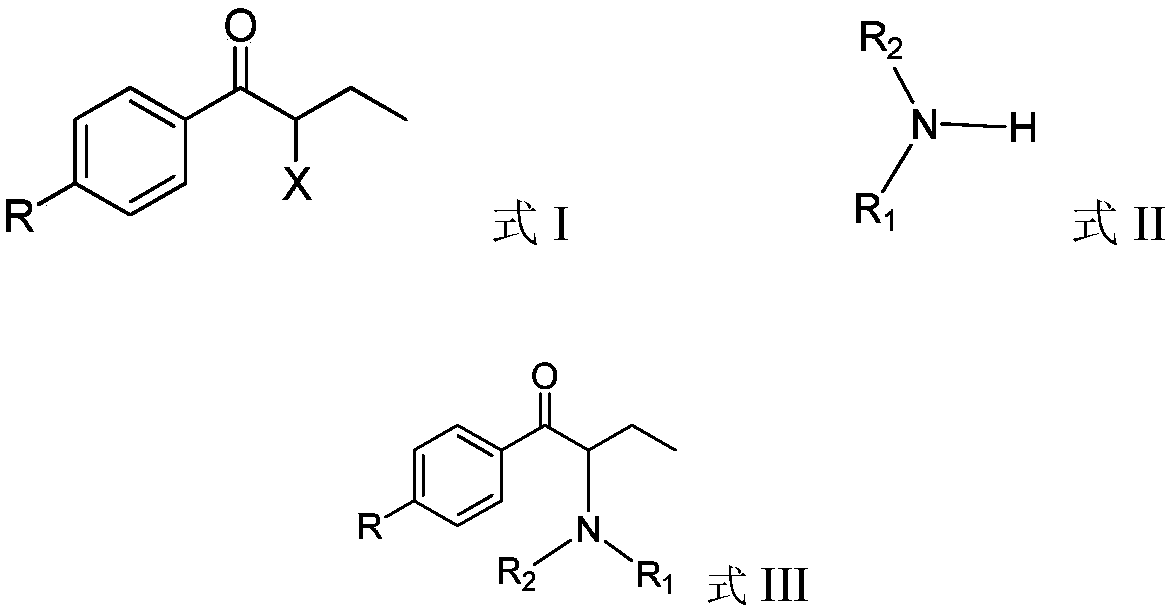
In-situ recycling technology of alkylamine
An alkylamine, in-situ technology, applied in the field of in-situ recycling of amines, can solve the problems of increased difficulty in disposal of process wastewater, waste of amine compounds, disadvantage, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Example 1: Substitution reaction of dimethylamine gas, using a solid basic compound as an acid-binding agent.
[0042] Experimental steps: Take a 2000mL reaction bottle and add 1000mL organic solvent;
[0043] Put in α-haloketone and start stirring;
[0044] Put in the basic compound solid;
[0045] Dimethylamine gas is introduced, and the temperature is kept at 40-45°C for 2 hours, and the organic phase is taken into liquid chromatography to detect the remaining α-haloketone of the raw material and the content of the product α-(N,N-dimethyl)aminoketone;
[0046] The response data is as follows:
[0047]
[0048] From the above experimental data, it can be seen that since basic compounds such as potassium carbonate, sodium carbonate, sodium hydroxide, and potassium hydroxide are basically insoluble in organic solvents, solid-liquid two-phase contact basically cannot play the role of binding halogen anions. Dimethylamine gas is under the condition of 40-45°C, a lar...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2: Substitution reaction of dimethylamine gas, using a basic compound solution as an acid-binding agent.
[0050] Experimental steps: Take a 3000mL reaction bottle and add 1000mL organic solvent;
[0051] Put in α-haloketone and start stirring;
[0052] Put into the prepared alkaline compound solution;
[0053] Dimethylamine gas is introduced, and the temperature is kept at 40-45°C for 2 hours, and the organic phase is taken into liquid chromatography to detect the remaining α-haloketone of the raw material and the content of the product α-(N,N-dimethyl)aminoketone;
[0054] The response data is as follows:
[0055]
[0056] From the above experimental data, it can be seen that after adding the aqueous solution of the alkali compound, the alkali compound is completely dissolved, and the liquid-liquid two-phase contact can promote the combination of the alkali compound and the halogen anion. At the same time, the introduction of water can also bind dimethyl...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Example 3: A 40% aqueous solution of dimethylamine is used for substitution reaction, and a basic compound solution is used as an acid-binding agent.
[0058] Experimental steps: Take a 3000mL reaction bottle and add 1000mL organic solvent;
[0059] Put in α-haloketone and start stirring;
[0060] Put into the prepared alkaline compound solution;
[0061] Add 40% dimethylamine aqueous solution, keep it warm at 40-45°C for 2 hours, take the organic phase and enter it into liquid chromatography to detect the remaining α-haloketone of the raw material and the content of the product α-(N,N-dimethyl)aminoketone;
[0062] The response data is as follows:
[0063]
[0064]
[0065]It can be seen from the above experimental data that when 40% dimethylamine aqueous solution is used for the reaction, due to the reduction of gas dissolution and escape process, dimethylamine can react rapidly when it contacts with materials, and the utilization rate of dimethylamine is obvi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com