Gray leaf spot resistance-related protein ZmWAK-RLK and encoding gene and applications thereof
A kind of gray spot disease and coding technology, applied in the fields of application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve the economic loss of corn production and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] Embodiment 1, the discovery of ZmWAK-RLK protein and its coding gene
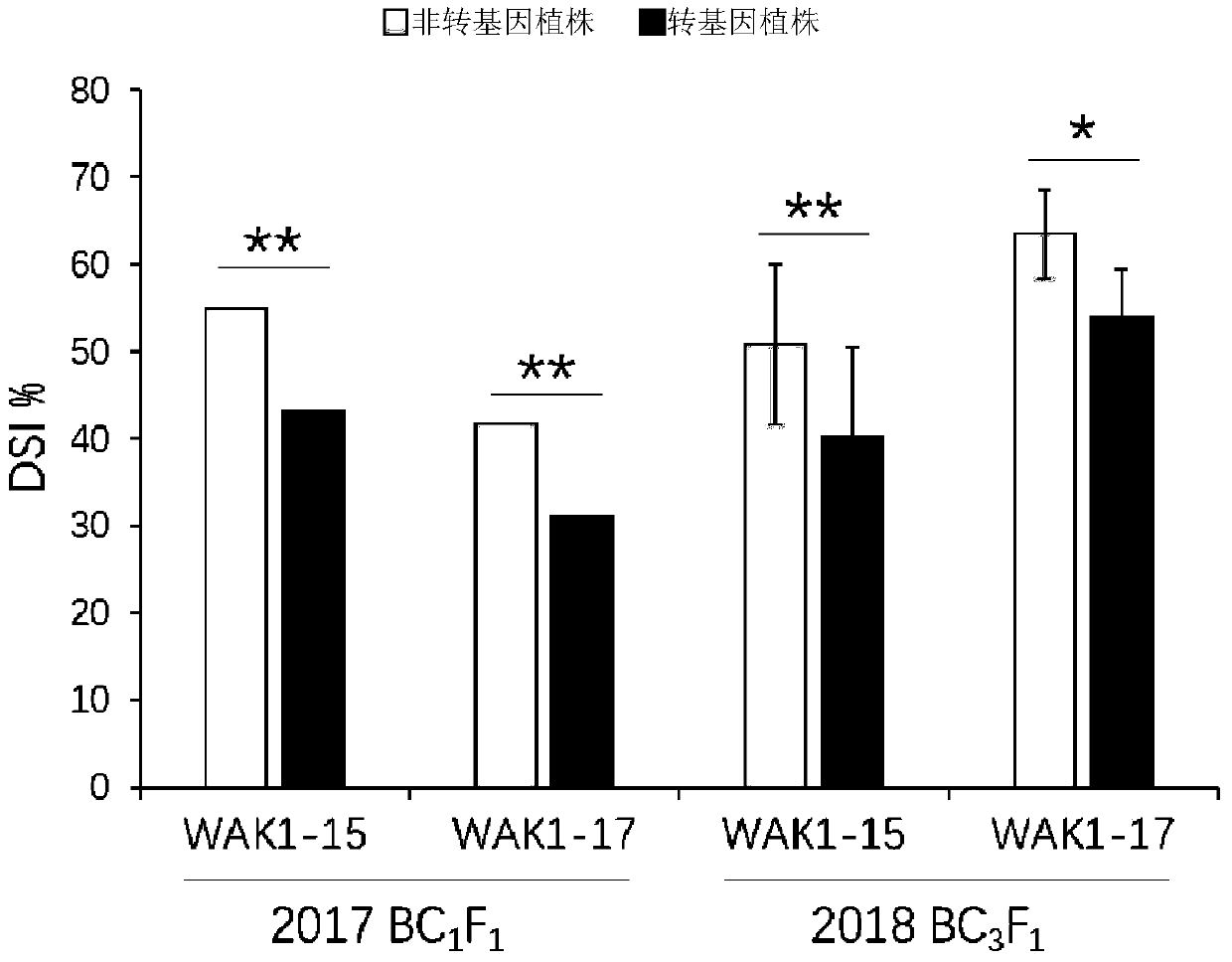
[0060] Maize inbred line Y32 (as the donor parent) and maize inbred line Q11 (as the recurrent parent) were used to construct primary mapping populations and fine mapping populations. Mapping qRgls1 to maize chromosome 8 between IDP2 and M2, the physical location is about 120kb.
[0061] The Y32BAC library of the disease-resistant parent was screened by PCR using molecular markers located in the finely mapped QTL-qRgls1 region. Perform BAC clone fingerprint analysis to construct BAC contigs covering the entire gene segment. The clone that covers the least amount of gene region is selected for sequencing. Through sequence alignment and expression analysis, a new gene was found, encoding the protein shown in Sequence 1 of the Sequence Listing.
[0062] The protein shown in Sequence 1 of the sequence listing is named ZmWAK-RLK protein. The gene encoding ZmWAK-RLK protein was named ZmWAK-RLK gene. T...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Embodiment 2, verify the function of the fragment of 7.2kb
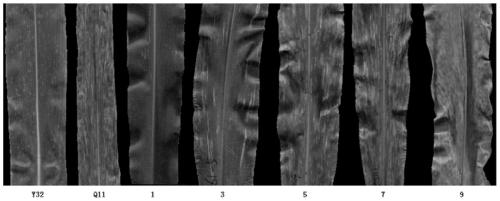
[0064] 1. Obtaining of transgenic plants
[0065] 1. A fragment of about 7.2kb in maize inbred line Y32 (this fragment is shown in sequence 4 of the sequence table; in sequence 4, the 1st-2103rd nucleotide is a promoter, and the 2104-4316th nucleotide (identical to sequence 3 in the sequence listing) was inserted into the BamH I restriction site of the pCAMBIA3301 vector to obtain a recombinant plasmid.
[0066] 2. Introduce the recombinant plasmid obtained in step 1 into Agrobacterium EHA105 to obtain recombinant Agrobacterium.
[0067] 3. Take the recombinant Agrobacterium obtained in step 2, and use the Agrobacterium-mediated method to genetically transform the immature embryos of the maize inbred line B73-329 to obtain T0 generation plants.
[0068] 4. The T0 generation plants are self-crossed, the grains are harvested, and the grains are cultivated into plants, which are T1 generation plants.
[0069] ...
Embodiment 3
[0104] Embodiment 3, verify the function of open reading frame
[0105] 1. Obtaining of transgenic plants
[0106] 1. Insert the double-stranded DNA molecule shown in nucleotides 87-2084 of Sequence 2 in the sequence listing into the XcmI restriction site of pBCXUN vector to obtain a recombinant plasmid.
[0107] 2. Introduce the recombinant plasmid obtained in step 1 into Agrobacterium EHA105 to obtain recombinant Agrobacterium.
[0108] 3. Take the recombinant Agrobacterium obtained in step 2, and use the Agrobacterium-mediated method to genetically transform the immature embryos of the maize inbred line B73-329 to obtain T0 generation plants.
[0109] 4. The T0 generation plants are self-crossed, the grains are harvested, and the grains are cultivated into plants, which are T1 generation plants.
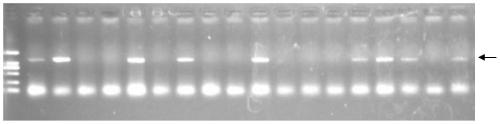
[0110] 5. The T1 generation plants were identified by PCR, and the transgenic plants were screened. The transgenic plants selected from the T1 generation plants are T1 transgen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com