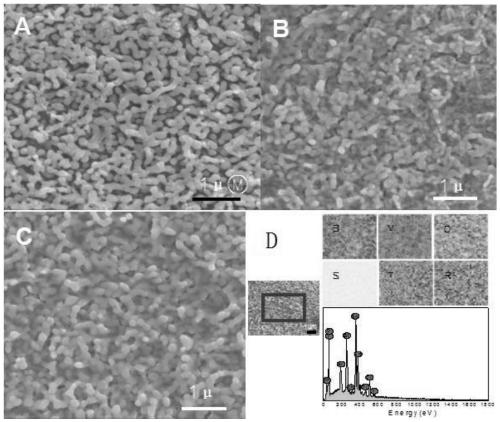
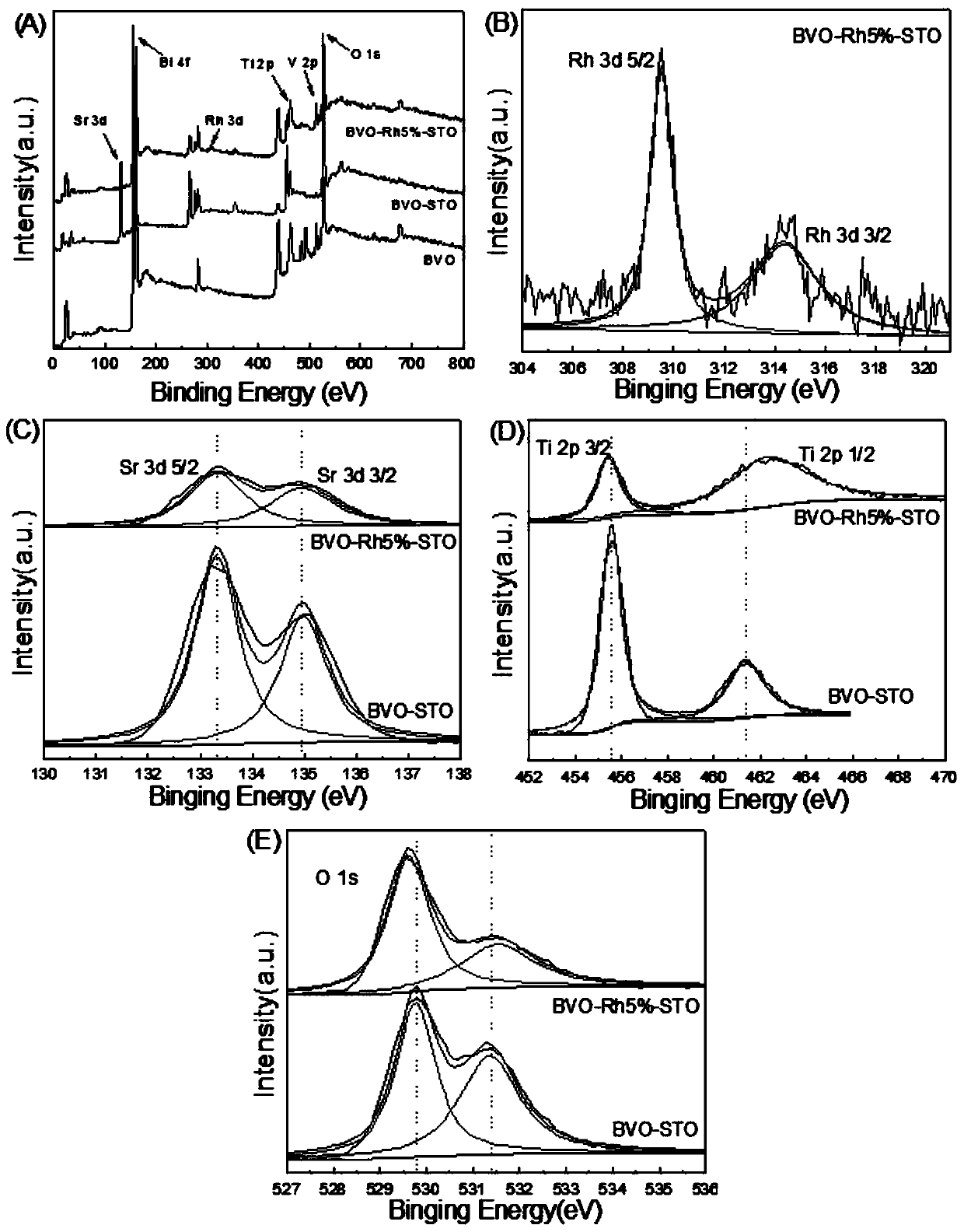
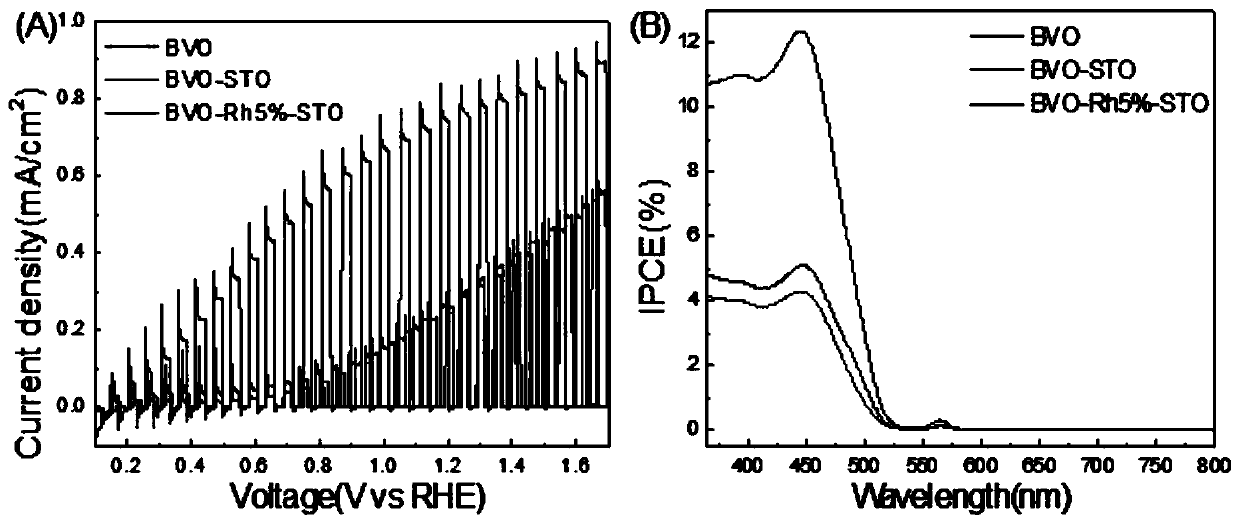
Rhodium-doped strontium titanate ultrathin nano-layer covered bismuth vanadate photoanode, and preparation method and application thereof
A bismuth vanadate and photoanode technology, which is applied in the direction of electrodes, electrolytic components, energy input, etc., to achieve the effects of improving photoelectrochemical performance, reducing reaction energy barriers, and increasing reactive sites
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Step 1. Deposit the BiOI precursor on the FTO surface by means of electrochemical deposition: the electrodeposition solution is composed of 100 milliliters of pH 1.2 containing Bi(NO 3 ) 3 Mix with NaI solution A and 45 ml of solution B containing p-benzoquinone. Electrodeposition adopts a three-electrode system, Pt is the counter electrode, Ag / AgCl is the reference electrode, blank FTO is used as the working electrode, and the deposition potential is deposited in steps of -0.3V and -0.1V to obtain a BiOI electrode;
[0026] Step 2, exchange with 0.2M vanadium acetylacetonate solution to obtain bismuth vanadate BiVO 4 electrode, hereafter denoted as BVO, the extra V 2 o 5 Remove with NaOH solution;
[0027] Step 3. BiVO 4 -Rh-SrTiO 3 Synthesis of photoanode:
[0028] Dissolve 0.5-1ml of tetrabutyl titanate in acetic acid, then add 2.5ml of deionized water, stir until the solution is transparent, then add 2.5ml of strontium nitrate and citric acid aqueous solution...
Embodiment 2
[0030] The difference from Example 1 is: Dissolve 0.5-1ml tetrabutyl titanate in acetic acid, add rhodium nitrate solution at a molar ratio of Ti:Rh=99:1, then add 2.5ml deionized water, and stir until the solution After it becomes transparent, add 2.5ml of strontium nitrate and citric acid aqueous solution respectively, then stir until the solution is transparent, and apply it on the prepared bismuth vanadate electrode by spin coating, and anneal at high temperature after drying to crystallize to obtain BiVO 4 -Rh1%-SrTiO 3 Photoanode, hereinafter referred to as BVO-Rh1%-STO.
Embodiment 3
[0032] The difference from Example 1 is: dissolve 0.5-1ml tetrabutyl titanate in acetic acid, add rhodium nitrate solution according to the ratio of Ti:Rh=97:3, then add 2.5ml deionized water, and stir until the solution is transparent , add 2.5ml of strontium nitrate and citric acid aqueous solution respectively, then stir until the solution is transparent, apply it on the bismuth vanadate electrode that has been prepared by spin coating, and anneal at high temperature after drying to crystallize BiVO 4 -Rh3%-SrTiO 3 The photoanode is hereinafter referred to as BVO-Rh3%-STO.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com