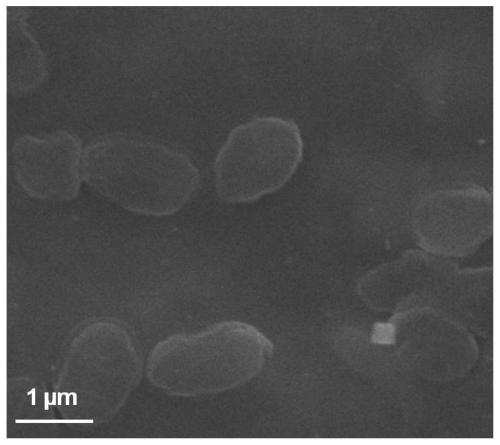
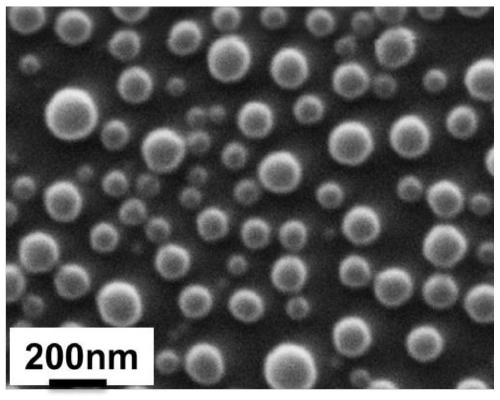
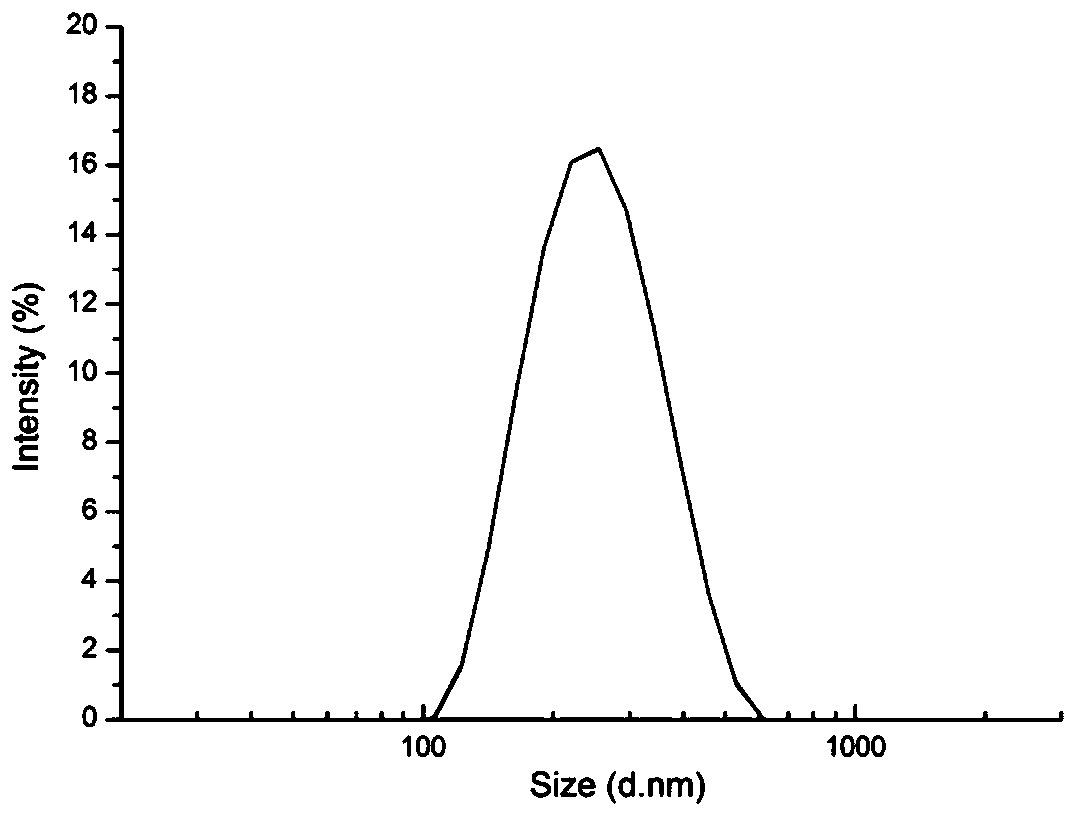
Enzymatic degradation type polypeptide-based polyester ammonia and preparation method and application thereof
A technology based on polyester and enzyme degradation, applied in the field of biomedical materials, can solve the problems of slow degradation rate, long cycle, low drug loading rate of complexes, etc., achieve excellent biocompatibility, safe production process, and broaden the application Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] 1. Preparation of Polypeptide-Based Diamines
[0050] (1) Preparation of tripeptide:
[0051] Using standard FMOC solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) technology, the substances involved in the reaction are as follows: 2-chlorotrityl chloride resin is 2g, 1.6mmol FMOC-Lys(Boc)-OH is 3.78g, 6.4mmol FMOC-Phe-OH was 2.48 g, 6.4 mmol FMOC-Leu-OH was 2.26 g, 6.4 mmol HBTU was 2.42 g, 6.4 mmol HOBt was 0.87 g, 6.4 mmol DIEA was 3 ml, and piperidine was 5 ml. Proceed as follows:
[0052] Add the resin into the peptide synthesis device, add dry DMF and soak it for half an hour to make it fully swollen, and finally discharge the solvent DMF.
[0053] The amino acid was dissolved in DMF, and then the solution was transferred to the peptide synthesis device containing the treated resin in the previous step, and then the catalyst DIEA was added, and the reaction was carried out at room temperature for 1.5 h to fully fix it on the resin, and the resin was washed with DMF. .
[0...
Embodiment 2
[0067] 1. Preparation of Polypeptide-Based Diamines
[0068] (1) Preparation of tetrapeptide:
[0069] Using standard FMOC solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) technology, the substances involved in the reaction are as follows: 2-chlorotrityl chloride resin is 2g, 1.6mmol FMOC-Lys(Boc)-OH is 3.78g, 6.4mmol FMOC-Phe-OH was 2.48 g, 6.4 mmol FMOC-Leu-OH was 2.26 g, 6.4 mmol HBTU was 2.42 g, 6.4 mmol HOBt was 0.87 g, 6.4 mmol DIEA was 3 ml, and piperidine was 5 ml. Proceed as follows:
[0070] Add the resin into the peptide synthesis device, add dry DMF and soak it for half an hour to make it fully swollen, and finally discharge the solvent DMF.
[0071] The amino acid was dissolved in DMF, and then the solution was transferred to the peptide synthesis device containing the treated resin in the previous step, and then the catalyst DIEA was added, and the reaction was carried out at room temperature for 1.5 h to fully fix it on the resin, and the resin was washed with DMF. .
...
Embodiment 3
[0086] 1. Preparation of Polypeptide-Based Diamines
[0087] (1) Preparation of tetrapeptide: The preparation method of tetrapeptide in Example 2 was used to prepare tetrapeptide.
[0088] (2) Preparation of di-tert-butyl dicarbonate anhydride-protected ethanolamine: To ethanolamine (10.0 ml, 165 mmol) in anhydrous CH at -10°C 2 Cl 2 To the solution in (500 mL) was added triethylamine (24.5 mL, 250 mmol) followed by di-tert-butyl dicarbonate anhydride (36 g, 165 mmol). The solution was stirred at 25 °C for 20 h, then washed with saturated NHCl 4 The solution (100ml) was quenched. The aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate (3 x 200 ml). The combined organic layers were then washed with brine, MgSO 4 Drying and concentration under reduced pressure gave the di-tert-butyl dicarbonate anhydride protected ethanolamine as a colorless oil.
[0089] (3) reaction of tetrapeptide with phthalic anhydride, di-tert-butyl dicarbonate acid anhydride protected ethanolamine: in th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com