Method of preparing zirconium carbide nanomaterial with waste plastics
A technology of waste plastics and nanomaterials, applied in the direction of nanotechnology, chemical instruments and methods, carbon compounds, etc. for materials and surface science, can solve environmental pollution and other problems, achieve wide sources of raw materials, simple production equipment, and solve environmental problems problem effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
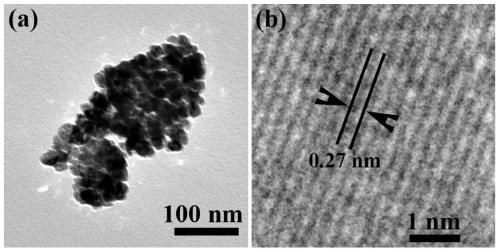
[0028] Add 0.60g of zirconium dioxide, 0.13g of waste polyethylene and 1.20g of metal lithium into a 20ml stainless steel autoclave, seal it and put it into an electric furnace capable of temperature-programming, and the furnace temperature rises from room temperature to 700°C, then maintained at 700°C for 10 hours and then cooled to room temperature naturally. The final product in the autoclave consisted of black deposits and residual gas. Collect the black deposits stuck on the inner surface of the kettle wall, wash with distilled water, dilute hydrochloric acid and absolute ethanol several times, obtain samples after filtration, and dry the samples in a vacuum drying oven at 50°C for 4 hours, and finally collect them for use in representation.
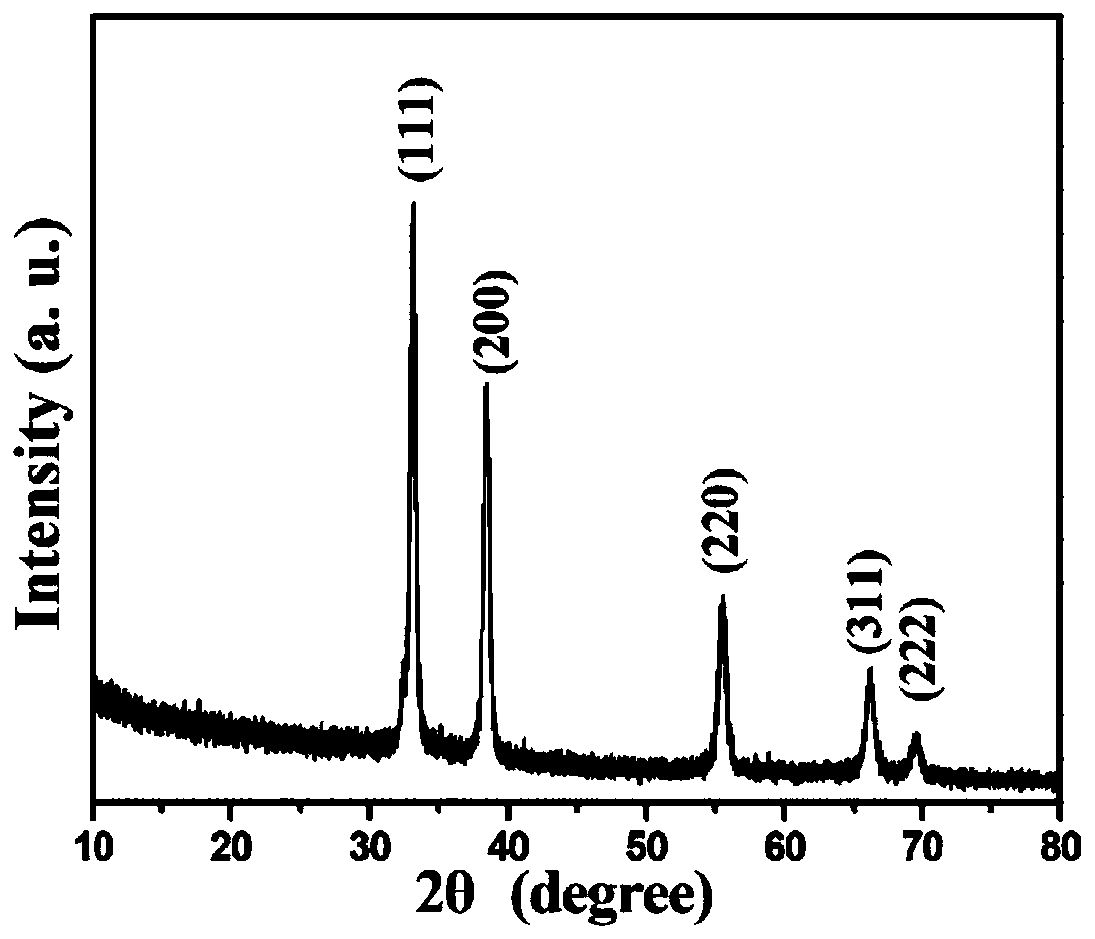
[0029] The phase analysis of the powder was carried out by a Japanese Rigaku D / max-γA X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) instrument, Cu Graphite monochromator, the tube voltage and current are 40kV and 40mA, respectively, and the sca...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Add 0.60g of zirconium dioxide, 0.35g of waste polyvinyl chloride and 1.20g of metal lithium into a 20ml stainless steel autoclave, seal it and put it into an electric furnace capable of temperature programming, and the furnace temperature will rise from room temperature within 68 minutes. to 700°C, then maintained at 700°C for 10 hours and then cooled to room temperature naturally. The final product in the autoclave consisted of black deposits and residual gas. Collect the black deposits stuck on the inner surface of the kettle wall, wash with distilled water, dilute hydrochloric acid and absolute ethanol several times, obtain samples after filtration, and dry the samples in a vacuum drying oven at 50°C for 4 hours, and finally collect them for use in representation.
[0033] image 3 It is the X-ray diffraction spectrum of the prepared zirconium carbide sample. All the diffraction peaks in the spectrogram correspond to the five diffraction peaks of zirconium carbid...
Embodiment 3
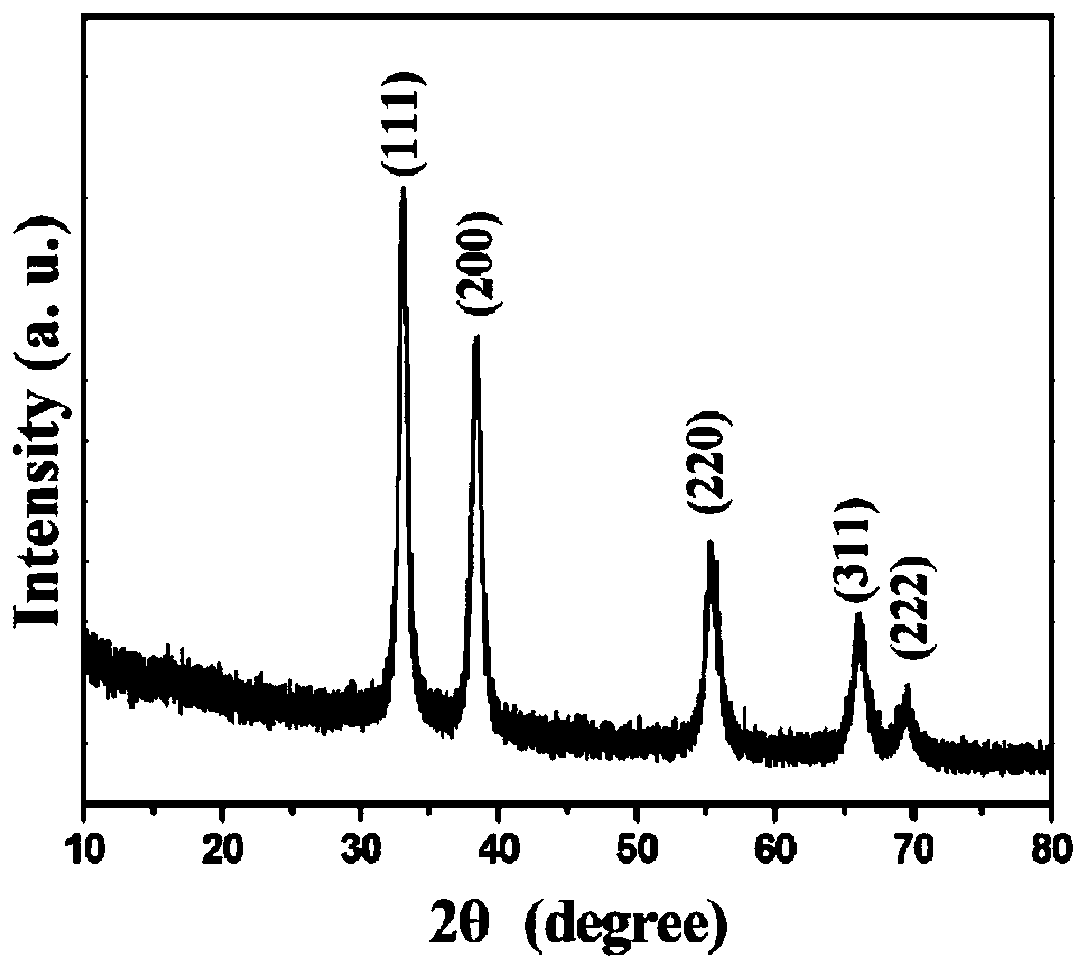
[0035] Add 0.60g of zirconium dioxide, 0.30g of waste polytetrafluoroethylene and 1.20g of metal lithium into a 20ml stainless steel autoclave. Raised to 700°C, then maintained at 700°C for 40 hours and then cooled to room temperature naturally. The final product in the autoclave consisted of a black deposit. Collect the black deposits stuck on the inner surface of the kettle wall, wash with distilled water, dilute hydrochloric acid and absolute ethanol several times, obtain samples after filtration, and dry the samples in a vacuum drying oven at 50°C for 4 hours, and finally collect them for use in representation.
[0036] Figure 5 is a typical X-ray powder diffraction pattern of prepared zirconium carbide samples, from Figure 5 The XRD pattern shown, in which all five diffraction peaks can be indexed as five diffraction peaks of cubic zirconium carbide, proves that zirconium carbide can also be prepared by using polytetrafluoroethylene as a carbon source through the abo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Average size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com