Efficient and general two-dimensional nanometer sheet-zero-dimensional nanocrystalline co-assembly method
A two-dimensional nano, zero-dimensional nano technology, applied in the direction of nanotechnology, chemical instruments and methods, oxides of ferrous iron, etc., can solve problems such as the limitation of nanoparticle types, and achieve wide applicability and broad application prospects of components , Wide applicability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] (1) 12 nm Fe 3 o 4 Preparation of nanoparticles: 36 g of iron oleate and 8.6 g of oleic acid were dissolved in 200 g of octadecene, and reacted at 320 ° C for 30 min under the protection of nitrogen to obtain Fe with a particle size of about 13 nm. 3 o 4 Nanoparticles, add ethanol to precipitate the nanoparticles, after centrifugation, dissolve the obtained nanoparticles in n-hexane to form a concentration of 5 mg mL -1 stable colloidal solution.
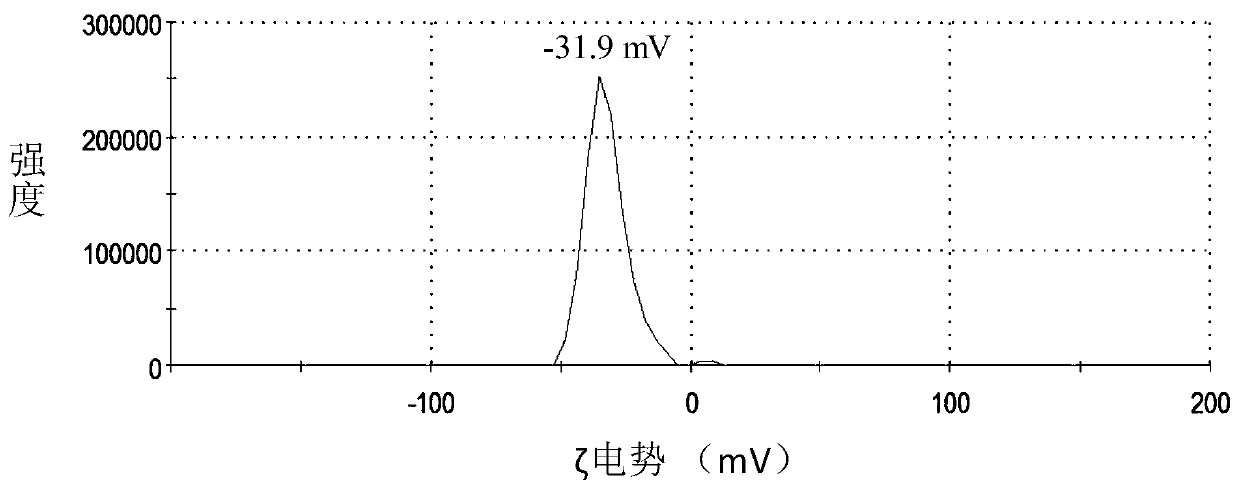
[0036] (2) Fe 3 o 4 Phase transfer of nanoparticle colloidal solutions: taking Fe 3 o 410 mL of nanoparticle colloidal solution was placed in a centrifuge tube, and 10 mL of DMF was added thereto. Add HBF dropwise 4 , while adding and shaking until the nanoparticles are exchanged into the DMF phase. Add 15 mL of toluene, centrifuge, and dissolve the obtained nanoparticles in 1 mL of DMF to obtain a concentration of about 50 mg mL -1 stable colloidal solution.
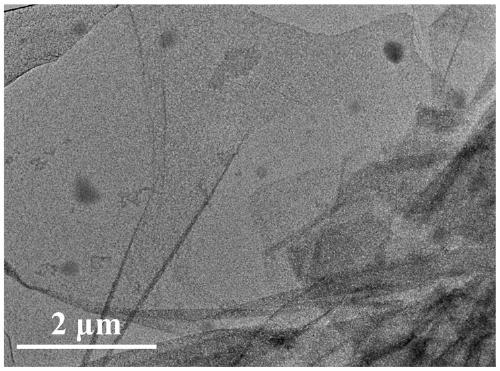
[0037] (3) GO-Fe 3 o 4 Preparation of the composite:...
Embodiment 2
[0046] (1) 6nm NiFe 2 o 4 Preparation of nanoparticles: same as Example 1
[0047] (2) NiFe 2 o 4 Phase transfer of nanoparticle colloidal solution: same as Example 1.
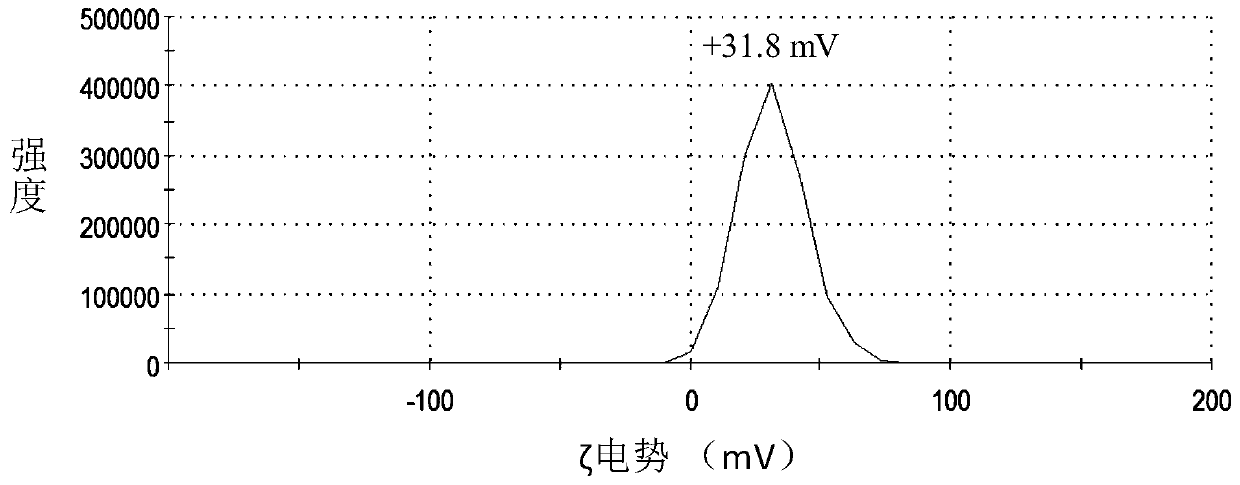
[0048] (3) few layers of Ti 3 C 2 T x Preparation of Mxene: take 1 g Ti 3 AlC 2 Added to 20 mL of 1.6 g LiF in 9 M HCl solution at 35 o C under stirring for 24 h. After the reaction was completed, the solution was centrifuged and washed with deionized water until the upper layer solution turned black and green, and then the solution was sonicated for 30 min under nitrogen protection. Centrifuge at 1500 rpm for 30 min, and the upper layer solution is the few-layer Ti 3 C 2 T x colloidal solution.
[0049] (4) Ti 3 C 2 T x -NiFe 2 o 4 Preparation of the composite: Take NiFe in DMF phase 2 o 4 Nanoparticle colloidal solution (30 mgmL -1 ) 10 mL, to which was added Ti 3 C 2 T x Aqueous solution (3 mg mL -1 ) 10 mL, sonicate for 30s. Centrifuge, discard the supernatant, and precipitate a...
Embodiment 3
[0055] (1) Preparation of 18 nm MnO nanoparticles: 24 g manganese oleate and 8.6 g oleic acid were dissolved in 200 g octadecene, and reacted at 320 °C for 30 min under nitrogen protection to obtain MnO nanoparticles with a particle size of about 18 nm. Add ethanol to precipitate the nanoparticles, and after centrifugation, dissolve the obtained nanoparticles in n-hexane to form a concentration of 5 mg mL -1 stable colloidal solution.
[0056] (2) Phase transfer and hollowing of the MnO nanoparticle colloidal solution: 10 mL of the MnO nanoparticle colloidal solution was placed in a centrifuge tube, and 10 mL of DMF was added to it. Add NOBF slowly 4 , while adding and shaking until the nanoparticles are exchanged into the DMF phase. Add 15 mL of toluene, centrifuge, and dissolve the obtained nanoparticles in 1 mL of DMF to obtain a concentration of about 50 mg mL -1 stable colloidal solution.
[0057] (3) few layers of Ti 3 C 2 T x The preparation of Mxene: with embod...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com