Method for genetically modifying intestinal primitive bacteria
A technology of genetic modification and protozoa, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, pharmaceutical formulations, etc., can solve the problems of not fully meeting research needs, high price of germ-free mice, long transplantation period, etc., and achieve efficient and convenient colonization. , the effect of improving biological compliance and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
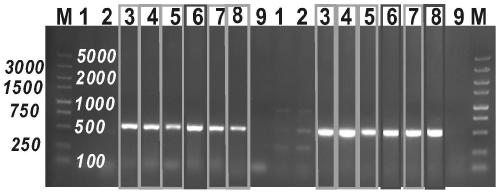
[0038] Using the method of synthetic biology, the screened intestinal native Escherichia coli is genetically modified and then microencapsulated:
[0039] 1) Screening of native Escherichia coli in the intestine of C57BL / 6 mice
[0040] ①Take fresh intestinal tissue from C57BL / 6 mice in a sterile EP tube;
[0041] ② Wash the intestinal contents with pre-cooled sterile PBS;
[0042] ③After cutting the intestinal wall, cut the intestinal wall with a sterile glass slide, mix the intestinal wall with sterile pre-cooled PBS at a mass volume ratio of m / v=1:10, and vortex for 15 minutes;
[0043] ④ Centrifuge the mixture at 4°C, 2000rpm for 5min, discard the precipitate, centrifuge the supernatant at 4°C, 12000rpm for 20min, discard the supernatant, and keep the precipitate;
[0044] ⑤ After resuspending the pellet with 100 μL PBS, take 10 μL and spread it on a solid LB plate for blue-white plate screening, and culture overnight at 37°C;
[0045] ⑥The next day, according to the gr...
Embodiment 2
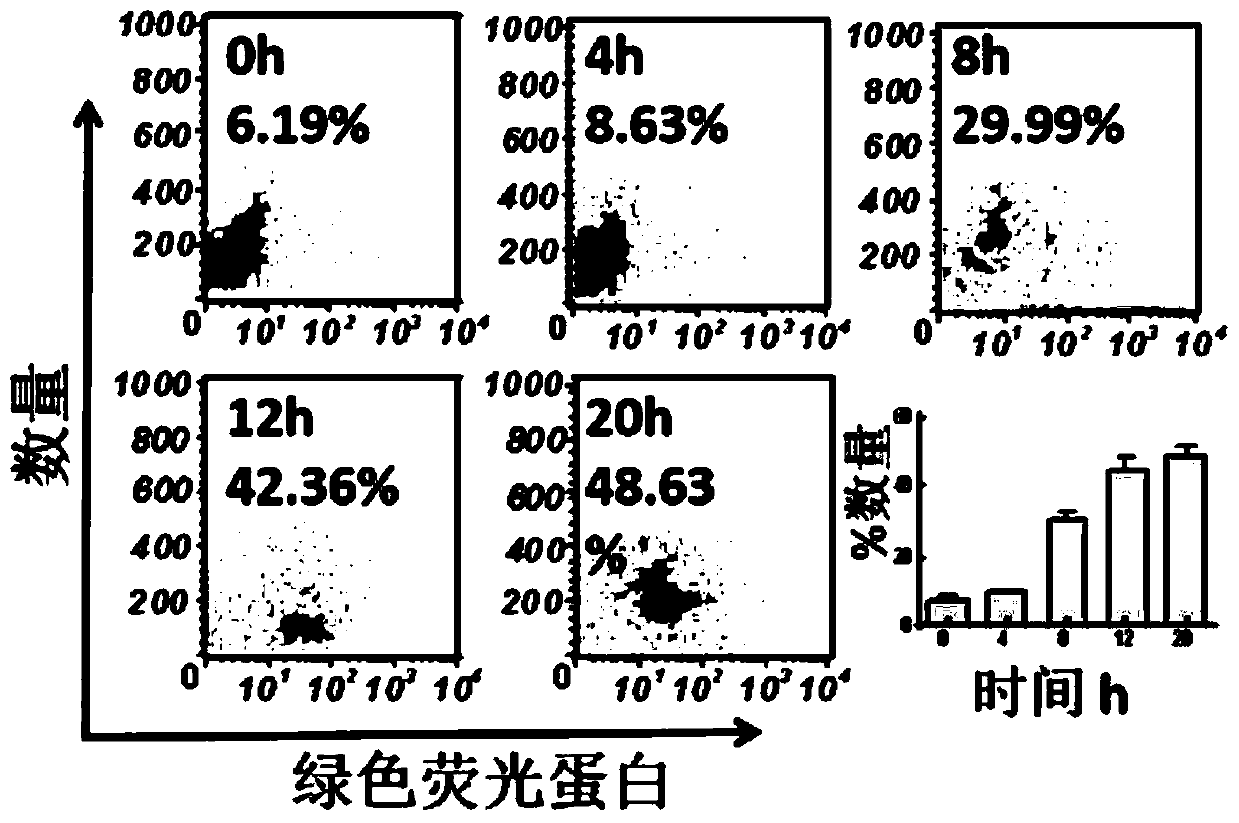
[0064] A method for treating intestinal diseases with microencapsulated intestinal native bacteria, the specific steps are as follows:
[0065] 1) Using the method of synthetic biology to genetically modify the screened intestinal native Escherichia coli and then carry out microencapsulation treatment:
[0066] (1) Screening of Escherichia coli native to the intestinal tract of C57BL / 6 mice
[0067] ①Take fresh intestinal tissue from C57BL / 6 mice in a sterile EP tube;
[0068] ② Wash the intestinal contents with pre-cooled sterile PBS;
[0069] ③After cutting the intestinal wall, cut the intestinal wall with a sterile glass slide, mix the intestinal wall with sterile pre-cooled PBS at a mass volume ratio of m / v=1:10, and vortex for 15 minutes;
[0070] ④ Centrifuge the mixture at 4°C, 2000rpm for 5min, discard the precipitate, centrifuge the supernatant at 4°C, 12000rpm for 20min, discard the supernatant, and keep the precipitate;
[0071] ⑤ After resuspending the pellet wi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com