Azo-quaternary pyridinium salts with acid-enhanced antibacterial efficacy, methods of use, methods of syntheses, and uses thereof
A technology of quaternary pyridinium salts and azo compounds, applied in the direction of active ingredients of heterocyclic compounds, medical preparations of non-active ingredients, medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
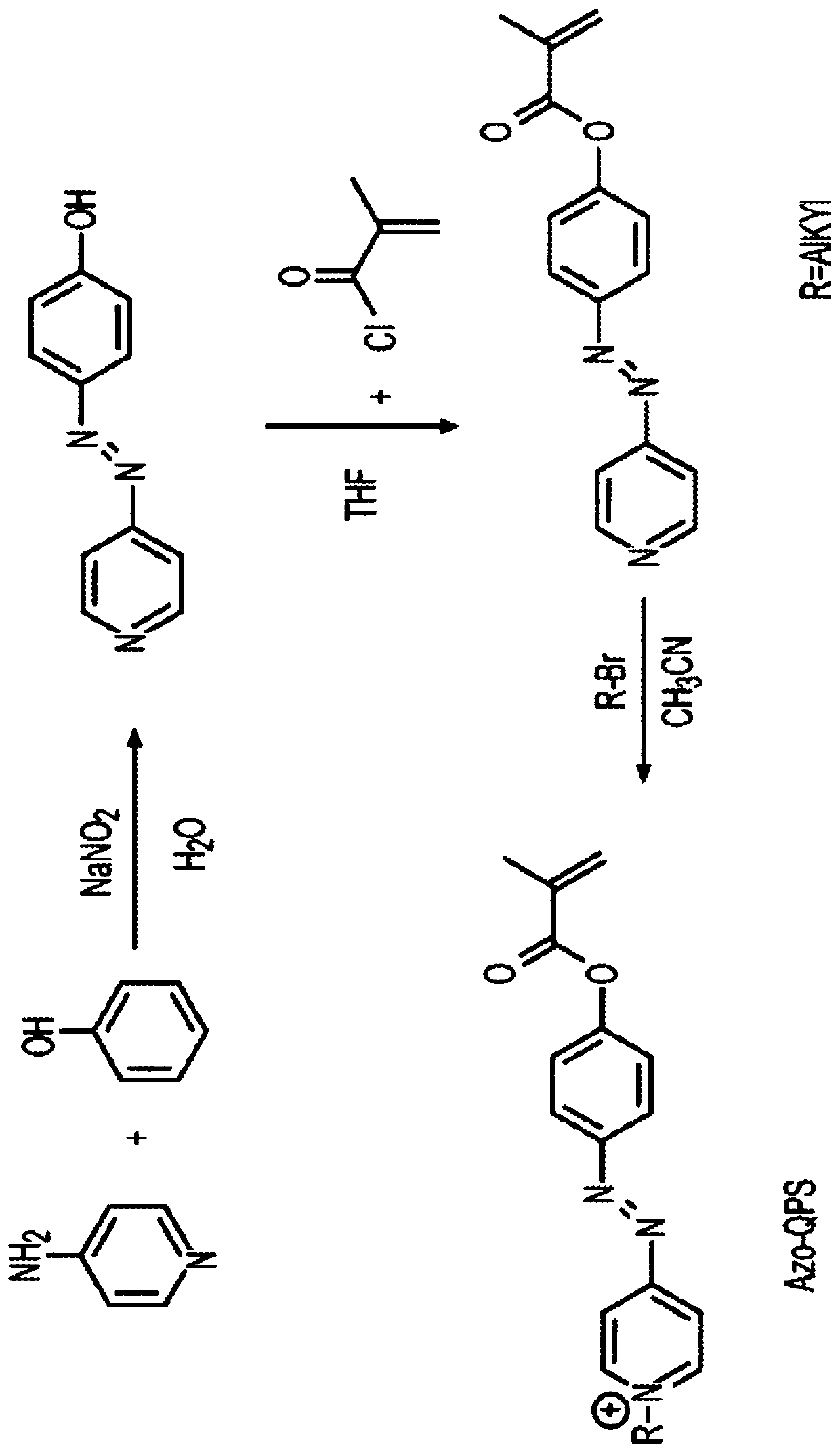
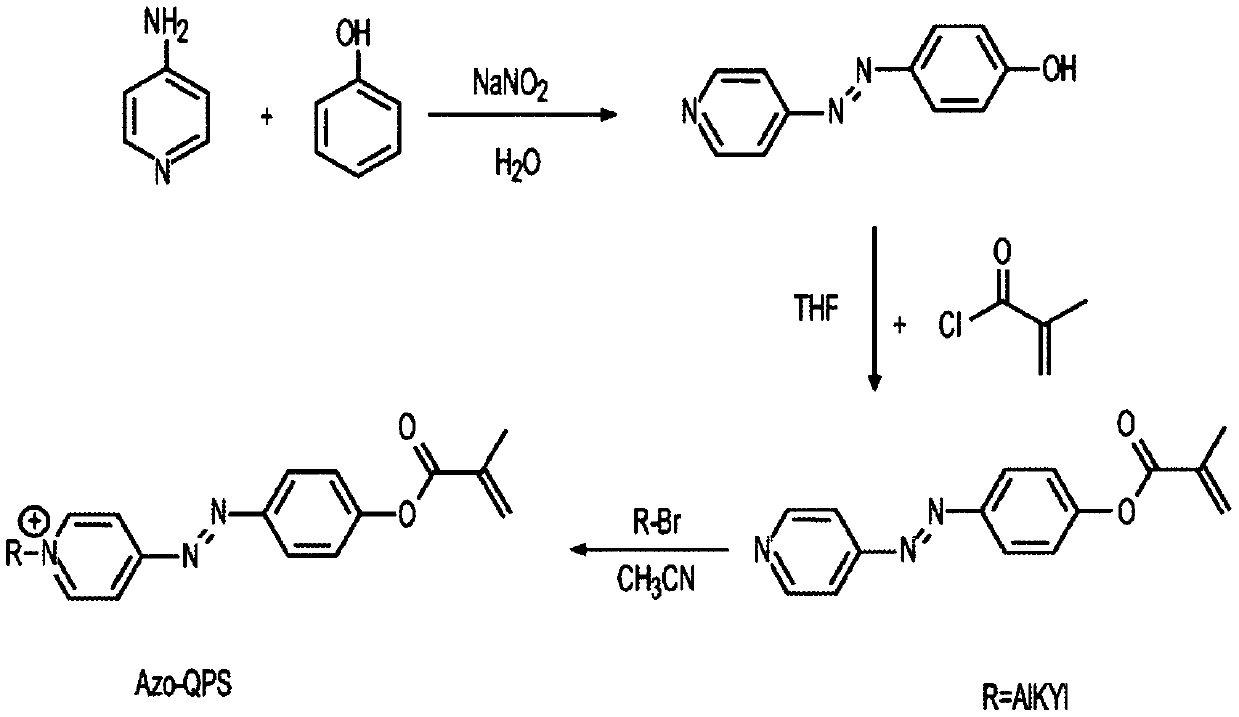
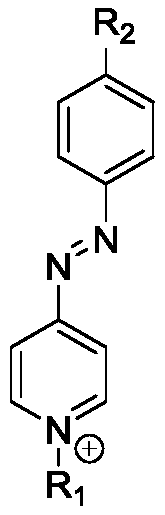
[0022] Example 1. (E)-1-hexadecyl-4-((4-(methacryloyloxy)phenyl)diazenyl)-pyridinium bromide (named Azo-QPS-C16 )Synthesis.
[0023] General information on synthesis and characterization. Commercially available materials from Alfa Aesar (Tewksbury, MA, USA), Sigma-Aldrich (Saint Louis, MO, USA) and TCI America (Portland, OR, USA) were used as received. Proton and carbon nuclear magnetic resonance (1H and13CNMR) spectra were recorded on a Bruker instrument (600MHz, Billerica, MA, USA) using 5mm tubes. Chemical shifts are reported in parts per million (ppm, δ) relative to tetramethylsilane (δ = 0.00), dimethylsulfoxide (δ = 2.50) or chloroform (δ = 7.26). 1H NMR splitting patterns are assigned as singlet (s), doublet (d), triplet (t), quartet (q), dd (double doublet) and m (multiplet). High resolution mass spectra (MS) were recorded on a JEOL AccuTOF (Peabody, MA, USA) for ESI-TOF-MS analysis.
[0024] Azo-QPS-C16 is a smaller organic molecule. An exemplary synthesis proced...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Example 2. Acid Enhanced Antimicrobial Efficacy.
[0029] Azo-QPS-C16 is effective against both Gram-positive bacteria (Escherichia coli) and Gram-negative bacteria (Streptococcus mutans). The ability of bacteria to proliferate after exposure to Azo-QPS-C16 was characterized by adding growth medium and measuring optical density (OD) at 600 nm every 15 minutes in pH 4.1, 5.8 and 7.9 buffers. Exposure to 2.5 μg / mL of Azo-QPS-C16 at pH 4.1 completely inhibited E. coli growth for 19 hours. However, exposure at pH 7.9 required much higher concentrations (40 μg / mL) to inhibit cell growth. Significant growth of E. coli was observed for control assays containing all buffers at different pH values with and without dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO). The pH dependence of the bactericidal activity of Azo-QPS-C16 in terms of minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) was evaluated by plating the culture onto Lysogeny Broth (LB) agar plates after treating cells with two-fold serial dilution...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Example 3. Physicochemical properties of pH sensitivity.
[0036] Azo-QPS-C16 exhibited pH-sensitive physicochemical properties associated with its acid-enhanced antibacterial activity. Aqueous solutions of Azo-QPS-C16 (0.01 mmol / L, 5.7 μg / mL) were light orange and purple under acidic and basic conditions, respectively, which was consistent with the red shift observed in the UV–Vis spectrum. After baseline correction, UV-vis spectra were recorded on a Thermo Spectronic Genesys 5 UV-Vis spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA USA) using a quartz cuvette with a 1 cm path length at 298K. The intensification of the peak centered at 554 nm and the simultaneous decrease of the peak at 347 nm are proportional to the pH change from 4.1 to 7.9. A similar absorption peak was detected in DMSO (0.05 mmol / L, 28.6 μg / mL) with the addition of a molar equivalent of a base such as triethylamine (TEA); the decrease in peak intensity at 347 nm was proportional to the molar rati...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com