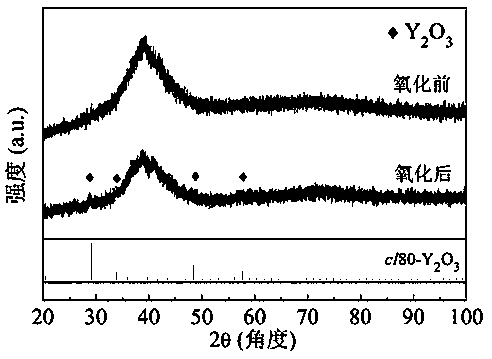
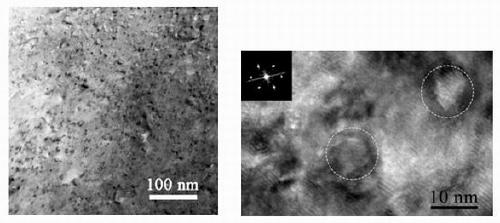
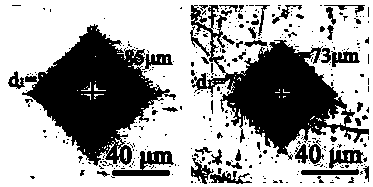
Preparation method of yttria dispersion strengthened copper alloy
A technology of dispersion strengthening copper and yttrium trioxide, applied in the field of metal matrix composite materials and preparation, which can solve problems such as complex process, low diffusion efficiency, and component deviation, and achieve simple process, high diffusion efficiency, and uniform components Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Example 1 ODS-Cu alloy with nominal composition Cu -0.3 wt. % Y
[0019] Step 1: Prepare the composition as Cu 75 Y 25 Alloy ingots with amorphous strips:
[0020] Using Cu (99.99%), Y (99.9%) metal raw materials, by weight percentage Cu 75 Y 25 To prepare Cu-Y alloy, mix the weighed metal raw materials and place them in the water-cooled copper crucible of the non-consumable arc melting furnace, and then evacuate to 5×10 -3 ~1×10 -2 Pa, and then filled with 0.01-0.08 MPa of pure argon protective gas for melting, the working current of the arc melting is 50-200 A; then the alloy ingot is turned upside down, and the melting is repeated 3 times to obtain an alloy ingot with uniform composition;
[0021] The alloy ingot was crushed and put into a quartz tube, and Cu-Y amorphous was prepared by vacuum copper roller single-roller spin quenching technology. The size of the quartz tube nozzle is about 1-1.5 mm in diameter. Place the charged quartz tube in the induction...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Example 2 ODS-Cu alloy with nominal composition Cu -0.6 wt. % Y
[0029] Step 1: Prepare the composition as Cu 65 Y 35 Alloy ingots with amorphous strips:
[0030] Same as Step 1 in Embodiment 1. Cu is measured here 65 Y 35 The crystallization temperature Tx of the amorphous is 290°C.
[0031] Step 2: Cu 65 Y 35 Oxidation of amorphous strips:
[0032] Same as Step 2 in Embodiment 1. Cu here 65 Y 35 The oxidation treatment temperature of the amorphous is 250°C, and the temperature is kept for 3 h.
[0033] Step 3: Melting and preparing ODS-Cu alloy
[0034] Same as Step 3 in Embodiment 1. The microstructure is similar to that of the alloy in Example 1, and the particles of the oxide strengthening phase are slightly smaller, but the distribution density is nearly 30% higher than that of the former. The performance test results show that the ODS-Cu alloy with Cu-0.6 wt. % Y has a hardness of 62 HV0.2 / 20 and a room temperature tensile strength of 675 MPa, but ...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Example 3 ODS-Cu alloy with nominal composition Cu -1.0 wt. % Y
[0036] Step 1: Prepare the composition as Cu 50 Y 50 Alloy ingots with amorphous strips:
[0037] Same as Step 1 in Embodiment 1. Cu is measured here 50 Y 50 The crystallization temperature Tx of the amorphous is 230°C.
[0038] Step 2: Cu 50 Y 50 Oxidation of amorphous strips:
[0039] Same as Step 2 in Embodiment 1. Cu here 50 Y 50 The oxidation treatment temperature of the amorphous is 200°C, and the temperature is kept for 5 h.
[0040] Step 3: Melting and preparing ODS-Cu alloy
[0041] Same as Step 3 in Embodiment 1. The microstructure is similar to that of the alloy in Example 1, the oxide particles are more dispersed, and the phase distribution density is also larger, which is 50% higher than the former. The performance test results show that the ODS-Cu alloy with Cu -1.0 wt. % Y has a hardness of 63.5HV0.2 / 20 and a tensile strength of over 700MPa at room temperature, reaching 705MPa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com