Method for performing living tracing on exogenous cells by using magnetosome coding gene
A technology that encodes genes and magnetosomes is applied in the direction of introducing foreign genetic material by using carriers, cells modified by introducing foreign genetic material, animal cells, etc. Problems such as accurate judgment and inability to track exogenous cells in vivo
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Embodiment 1 A method for long-term in vivo tracing of neural stem cells using genes encoding magnetosomes, comprising the following steps:
[0041] 1) Magnetosome gene modification
[0042] The neural stem cells were trypsinized and blown away, and the confluence of the neural stem cells was about 50-60% using a 6-well plate.
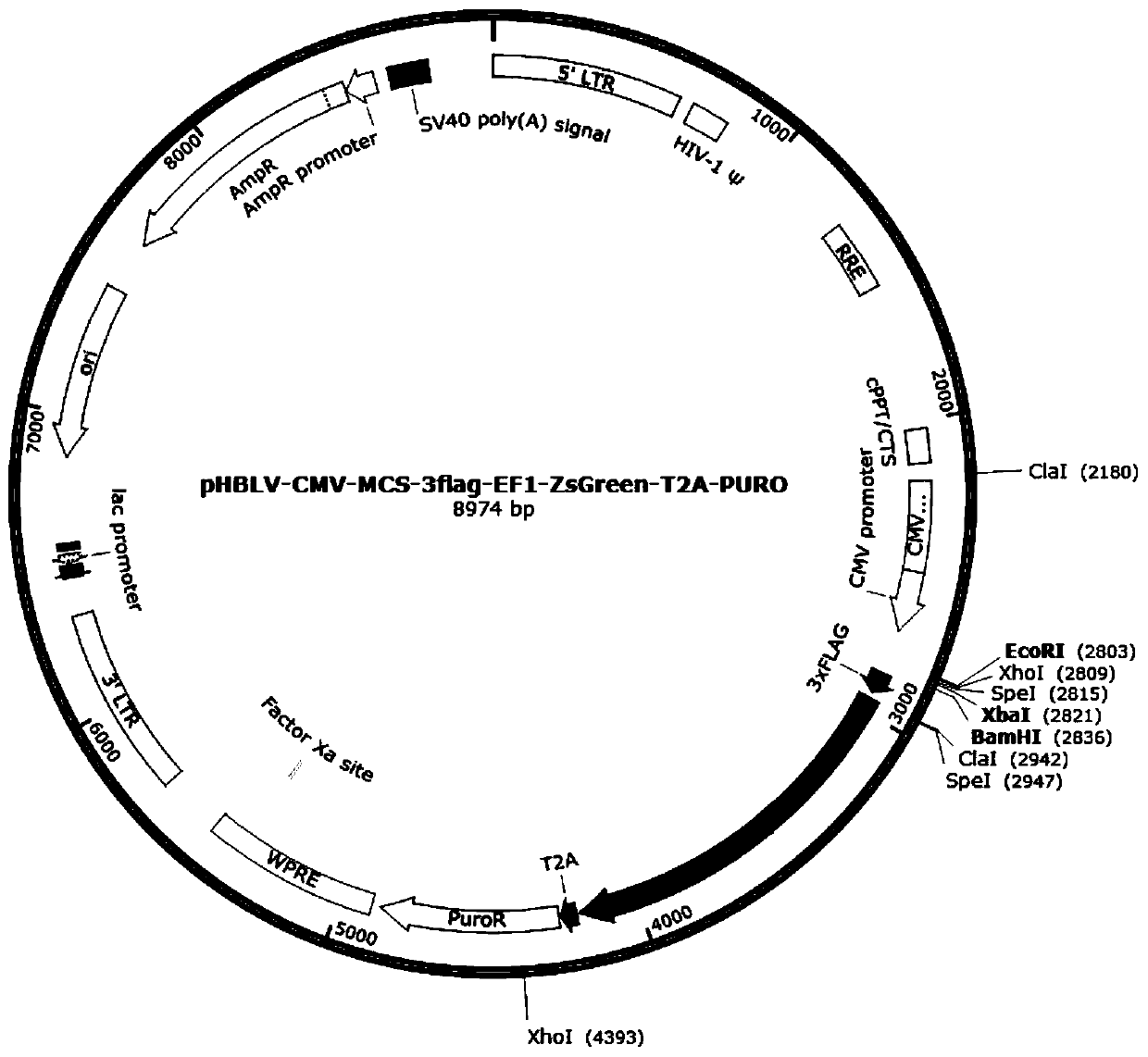
[0043] Add 2.0-2.5ml of stem cell medium, and use the magnetosome lentiviral plasmid mms6-GFP-Puro( figure 1 ) to neural stem cells at a ratio of 5-10:1, while using Envirus TM Lentivirus enhancement reagent 10-20μl / ml, mix well, put in 37℃, 5%CO 2 Incubator, transfection 24 hours.
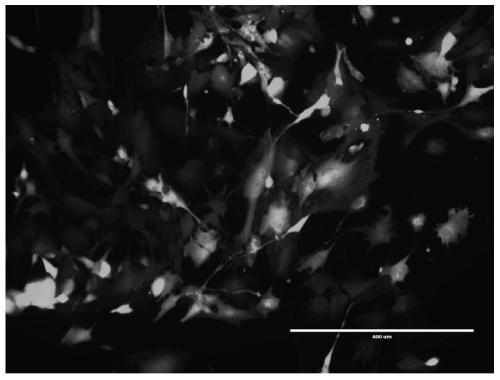
[0044] After 24 hours, the transfected cells were collected by centrifugation, and replaced with fresh stem cell medium. After 3 days of culture, puromycin was added to continue to culture for 5-7 days for screening, and the stem cells that could stably express the magnetosome gene were screened out. Among them, The concentration of puromycin is 2-5 μg / ml.
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com