Discrimination method of marine and terrestrial sedimentary environment based on selectively extracted exchangeable strontium-barium ratio in terrigenous clastic sediments
A discrimination method and sediment technology, applied in the direction of sampling, improvement of process efficiency, preparation of test samples, etc., can solve problems affecting the correct judgment of marine and continental depositional environment of sediments, and affect the correct judgment of marine and continental depositional environment, to achieve Improve effectiveness and accuracy, avoid distracting effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
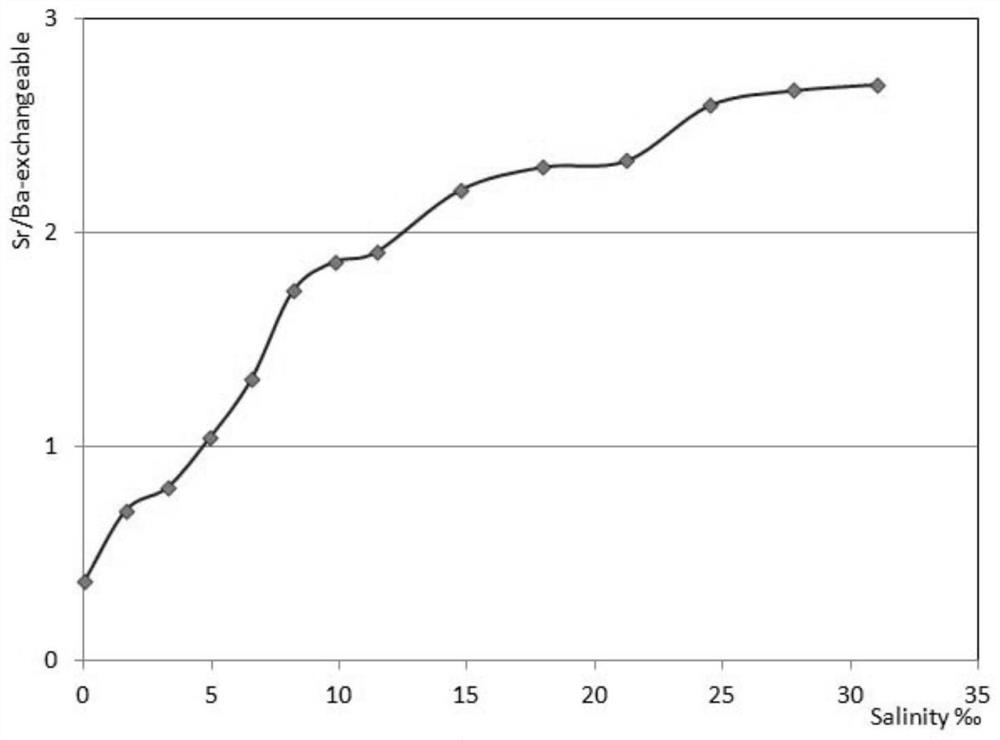
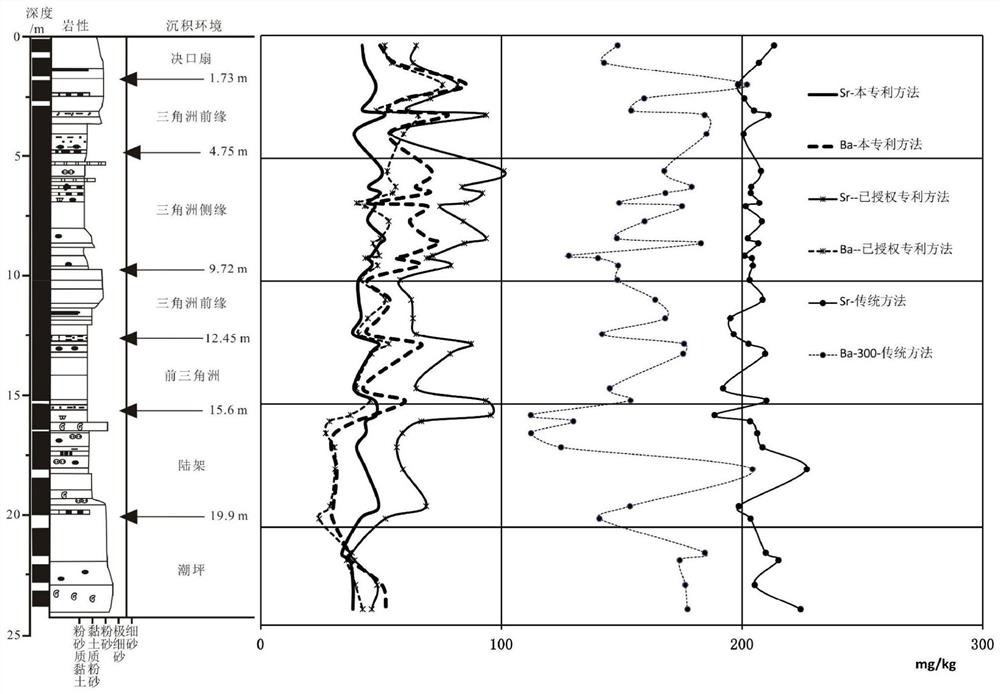
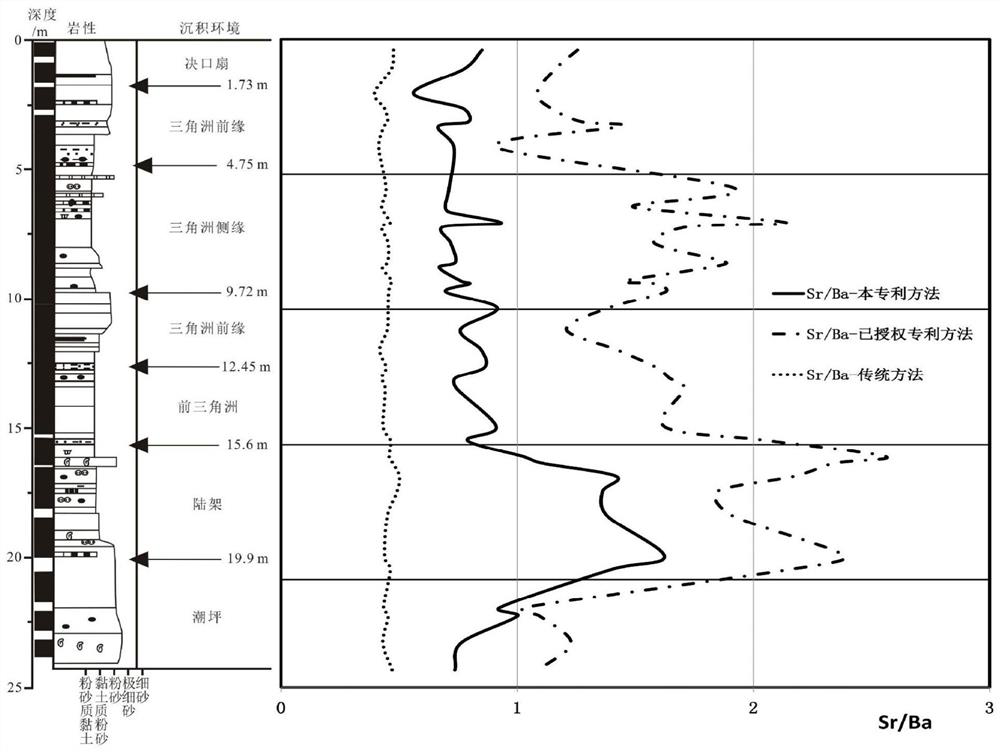
[0023] The selective extraction method of strontium and barium, which is the cause of sedimentation in terrigenous clastic sediments, includes the following steps: collect a representative amount of loose sediment samples, remove visible biological debris (shells, etc.), dry them, and crush them to No more than 100 mesh for use; accurately weigh an appropriate amount of sample, add ammonium acetate or sodium acetate with a mass concentration of 50% at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:50 as an extractant, and stir or shake at normal temperature (20-30°C) and normal pressure ( Ultrasonic vibration can also be used) for more than 120 minutes, but the solid-liquid separation is carried out and the supernatant is reserved; the supernatant is diluted to an appropriate concentration for instrumental analysis (ICP-OES or ICP-MS, etc.) to determine strontium and barium, and the obtained ions can be exchanged The ratio of strontium to barium can better reflect the marine and continental depo...
Embodiment 2
[0025] The selective extraction method of strontium and barium, which is the cause of sedimentation in terrigenous clastic sediments, includes the following steps: collect a representative amount of loose sediment samples, remove visible biological debris (shells, etc.), dry them, and crush them to Not larger than 100 mesh for later use; accurately weigh an appropriate amount of sample, add 5% ammonium acetate or sodium acetate as the extractant at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:500, stir or shake at normal temperature (20-30°C) and normal pressure ( Ultrasonic vibration can also be used) for more than 120 minutes, but the solid-liquid separation is carried out and the supernatant is reserved; the supernatant is diluted to an appropriate concentration for instrumental analysis (ICP-OES or ICP-MS, etc.) to determine strontium and barium, and the obtained ions can be exchanged The ratio of strontium to barium can better reflect the marine and continental depositional environment wh...
Embodiment 3
[0027]The selective extraction method of strontium and barium, which is the cause of sedimentation in terrigenous clastic sediments, includes the following steps: collect a representative amount of loose sediment samples, remove visible biological debris (shells, etc.), dry them, and crush them to Not larger than 100 mesh for later use; accurately weigh an appropriate amount of sample, add ammonium acetate or sodium acetate with a mass concentration of 40% at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:100 as an extractant, and stir or shake at normal temperature (20-30°C) and normal pressure ( Ultrasonic vibration can also be used for more than 120 minutes, but the solid-liquid separation is carried out and the supernatant is reserved; the supernatant is diluted to an appropriate concentration for instrumental analysis (ICP-OES or ICP-MS, etc.) to determine strontium and barium, and the obtained ions can be exchanged The ratio of strontium to barium can better reflect the marine and continen...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com