Application of carbon microspheres serving as blocking agent for high-temperature water-based drilling fluid and high-temperature water-based drilling fluid
A technology of water-based drilling fluid and carbon microspheres, which is applied in the direction of drilling compositions, nano-carbon, chemical instruments and methods, etc., and can solve the problems of poor high temperature resistance and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0017] According to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the biomass contains cellulose, and the reaction temperature for the hydrothermal reaction is 215-320°C, preferably 230-300°C.
[0018] According to another preferred embodiment of the present invention, the biomass is selected from at least one of glucose, fructose, chitosan, sucrose, β-cyclodextrin and starch, and the reaction temperature for hydrothermal reaction is 160- 240°C.
[0019] According to the present invention, after the completion of the hydrothermal reaction, a dark brown suspension is obtained, which can be centrifuged, washed and dried to obtain carbon microspheres. The methods for centrifuging, washing and drying can be common methods in the art, and the present invention is not limited here.
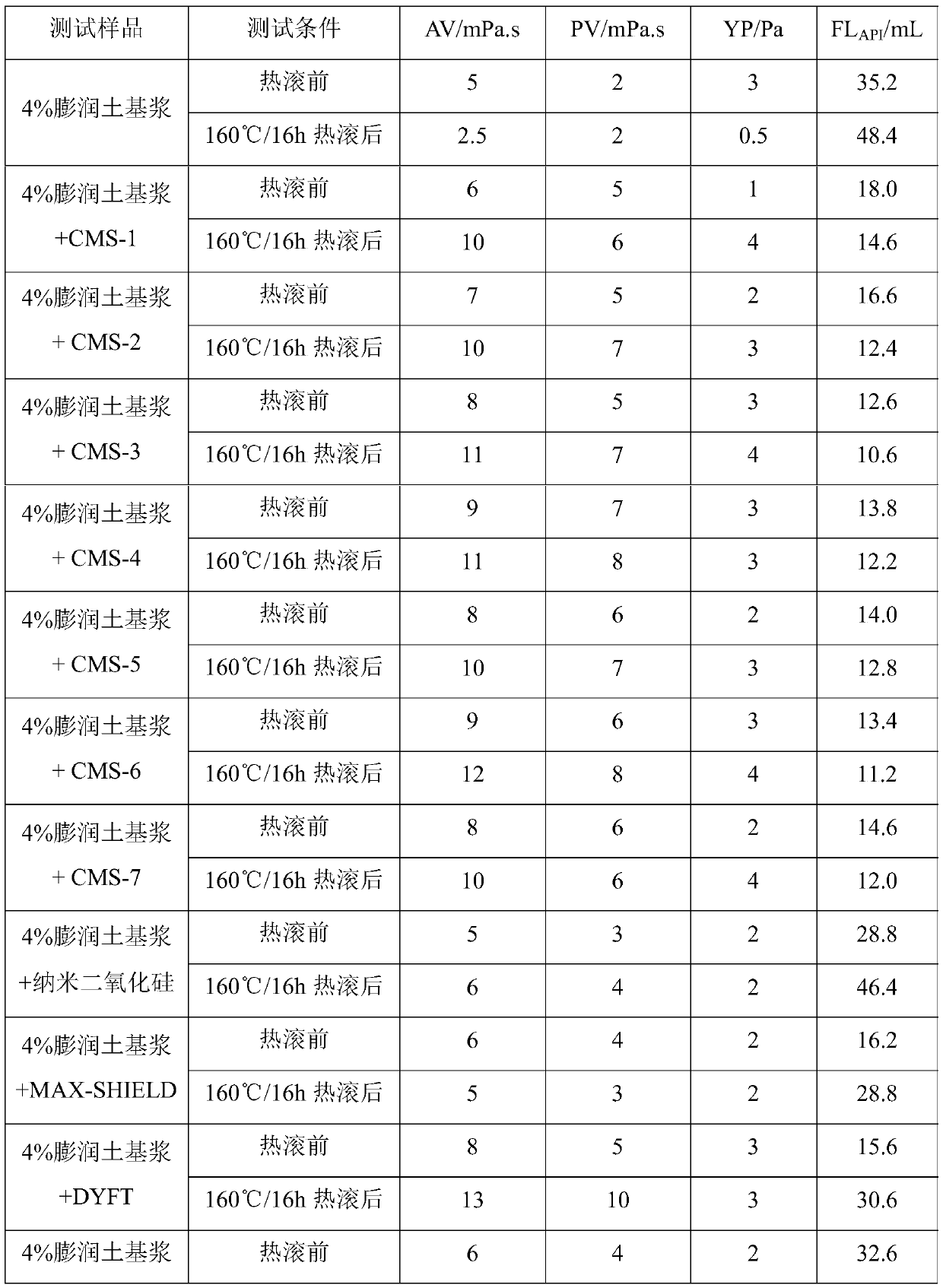
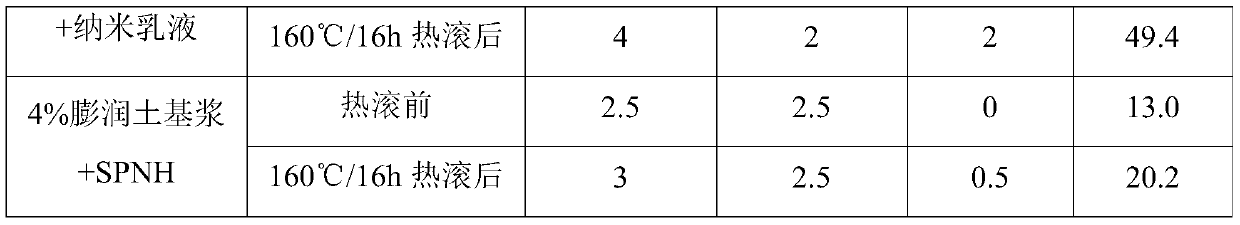
[0020] The second aspect of the present invention provides a high-temperature water-based drilling fluid, which contains water, bentonite, carbon microspheres, high-temperature shale inhibitors, hig...
preparation example 1
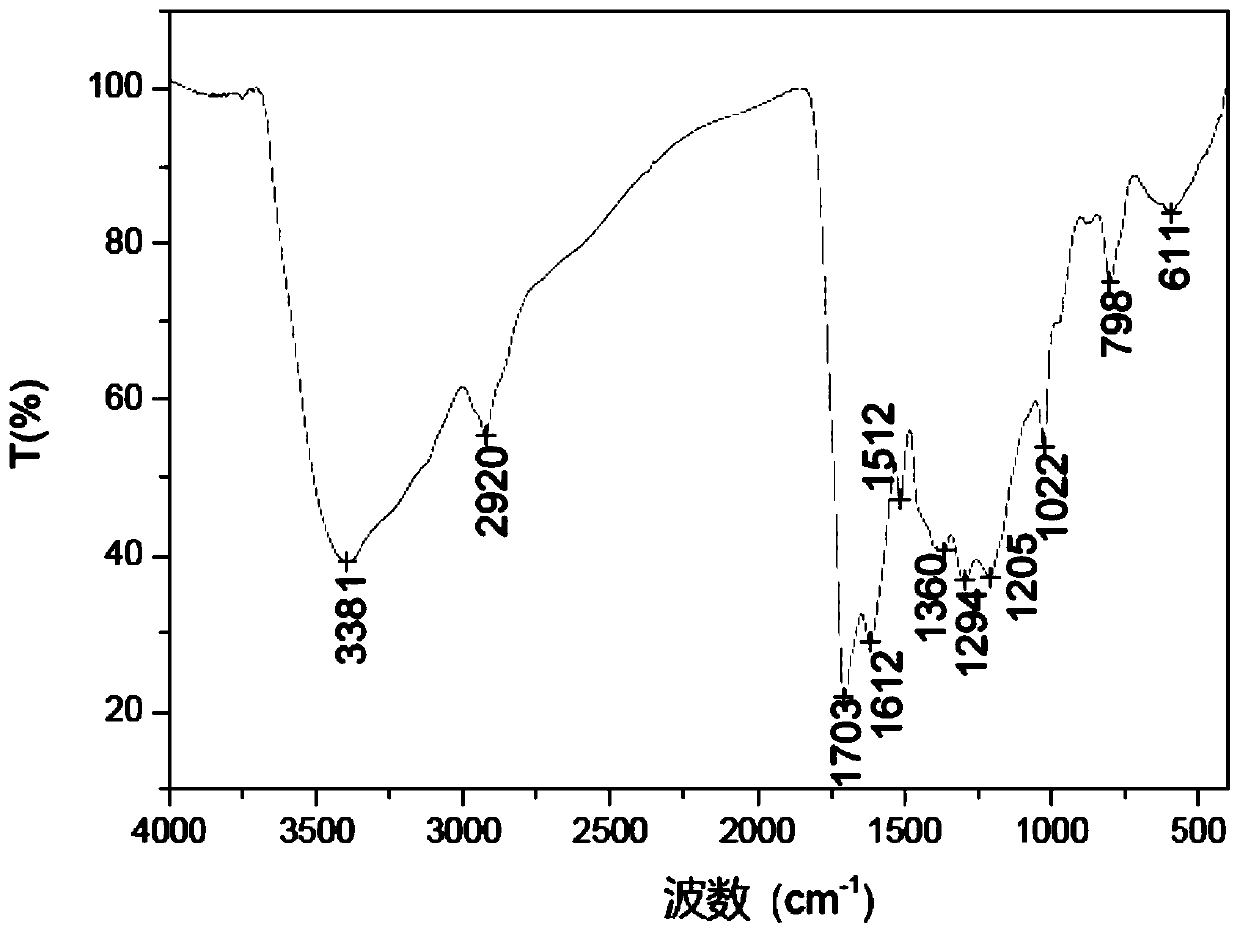
[0032] Weigh 25g of β-cyclodextrin, stir it at high speed and disperse it into 500mL of deionized water, transfer the mixture to a hydrothermal reaction kettle, put it in an oil bath, and react at 160°C for 30h. After it was lowered to room temperature, the dark brown suspension solution generated after the reaction was centrifuged at 15000rpm for 20min, and the precipitate obtained by centrifugation was ultrasonicated with absolute ethanol and deionized water respectively, centrifuged and washed three times, and the dark brown precipitate obtained was placed on Dry in an oven at 60°C to obtain a fluffy black powdery substance, i.e. carbon microspheres, denoted as CMS-1, with an average particle size of 246nm and a total amount of oxygen-containing functional groups of 0.214mmol / g.
preparation example 2
[0034] Disperse 5 g of fiber cotton pulp (cellulose) in 100 mL of deionized water, stir at a rate of 500 rpm at room temperature for 2 h to obtain a milky white paste system, and then use a cell pulverizer to sonicate for 10 min and transfer it to a hydrothermal reaction kettle with a volume of 250 mL. In a high-temperature roller heating furnace, control the temperature in the furnace to 300°C for 8 hours, then cool naturally to room temperature, and centrifuge the dark brown suspension solution at 15,000 rpm for 20 minutes. Water ultrasonication, centrifugation, and washing three times, the obtained dark brown precipitate was placed in an oven and dried at 50°C to obtain a fluffy black powdery substance, that is, carbon microspheres, which were recorded as CMS-2, and the average particle size was measured It is 409nm, and the total amount of oxygen-containing functional groups is 0.254mmol / g.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com