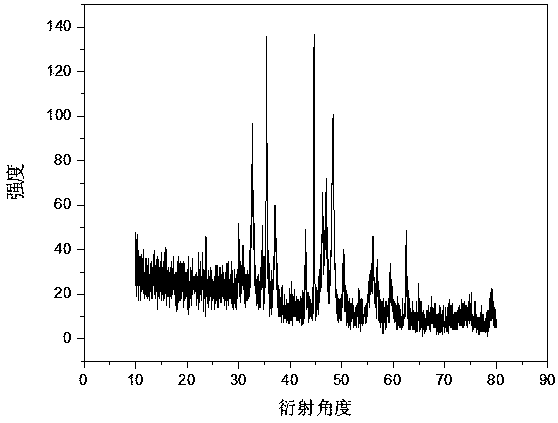
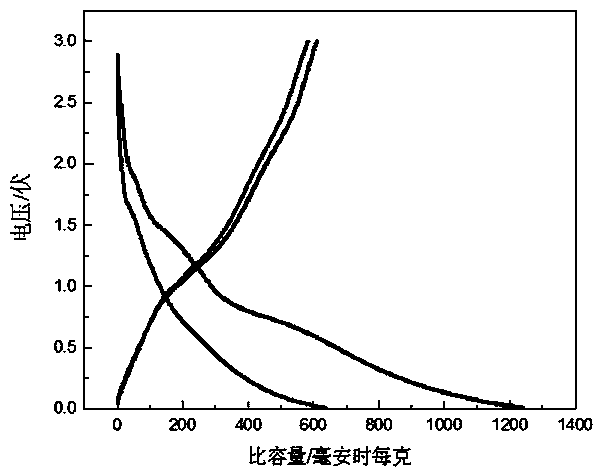
Transition metal phosphide iron phosphide negative electrode material
A technology of transition metal and negative electrode material, applied in the field of negative electrode material, can solve problems such as low reversible capacity, and achieve the effects of shortening the transmission path, simple preparation process and low reaction temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] (1) Mix 10mL deionized water and 70mL N,N-dimethylformamide evenly to obtain 80mL homogeneous solution;
[0042](2) Add 10 mmol ferric chloride hexahydrate and 10 mmol terephthalic acid to the 80 mL homogeneous solution obtained in step (1), stir and dissolve evenly to obtain a mixed solution;
[0043] (3) Put the mixed solution obtained in step (2) in a polytetrafluoroethylene high-pressure reaction kettle, seal it, put it in a high-temperature drying oven, heat it at 120°C for 12 hours, cool it naturally to room temperature, filter it, and use Water, ethanol and deionized water were used to cross-wash the filtrate 4 times respectively, and dry in an oven at 60°C for 24 hours to obtain a yellow powder;
[0044] (4) Roast the yellow powder obtained in step (3) in a high-purity argon atmosphere at 450°C for 5 hours, and cool naturally to room temperature to obtain black ferric oxide powder; the purity of high-purity argon gas is ≥99.99% (“ %" is volume percentage);
[...
Embodiment 2
[0052] (1) Mix 20mL deionized water and 60mL N,N-dimethylformamide evenly to obtain 80mL homogeneous solution;
[0053] (2) Add 8 mmol of ferric nitrate nonahydrate and 2 mmol of terephthalic acid to the 80 mL homogeneous solution obtained in step (1), stir and dissolve evenly to obtain a mixed solution;
[0054] (3) Put the mixed solution obtained in step (2) in a polytetrafluoroethylene high-pressure reaction kettle, seal it, put it in a high-temperature drying oven, heat it at 120°C for 10 hours, cool it naturally to room temperature, filter it, and use it without Water, ethanol and deionized water were respectively cross-washed and filtered 4 times, and dried in an oven at 100°C for 12 hours to obtain a yellow powder;
[0055] (4) Roast the yellow powder obtained in step (3) in a high-purity argon atmosphere at 450°C for 4 hours, and cool naturally to room temperature to obtain black ferric oxide powder; the purity of high-purity argon gas is ≥99.99% (“ %" is volume perce...
Embodiment 3
[0063] (1) Mix 30mL deionized water and 60mL N,N-dimethylformamide evenly to obtain 90mL homogeneous solution;
[0064] (2) Add 0.4mmol ferric nitrate nonahydrate and 0.8mmol 3,5-diaminobenzoic acid to the 90mL homogeneous solution obtained in step (1), stir and dissolve evenly to obtain a mixed solution;
[0065] (3) Put the mixed solution obtained in step (2) in a polytetrafluoroethylene high-pressure reaction kettle, seal it, put it in a high-temperature drying oven, heat it at 100°C for 24 hours, cool it to room temperature naturally, filter it, and use it without Water, ethanol and deionized water were respectively cross-washed and filtered 4 times, and dried in an oven at 60°C for 24 hours to obtain a yellow powder;
[0066] (4) Roast the yellow powder obtained in step (3) in a high-purity nitrogen atmosphere at 450°C for 6 hours, and cool naturally to room temperature to obtain black ferric oxide powder; the purity of high-purity argon gas is ≥99.99% (“% " is the volum...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com