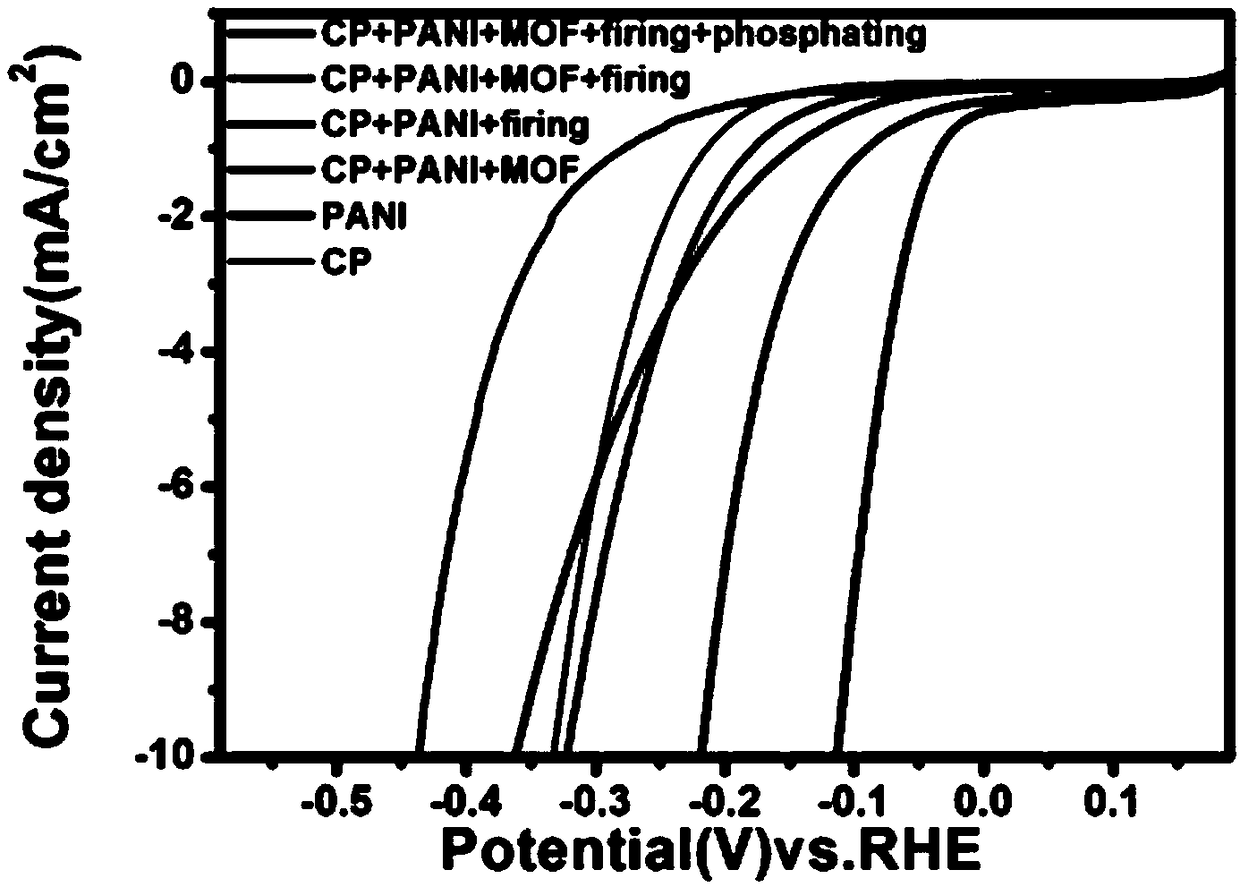
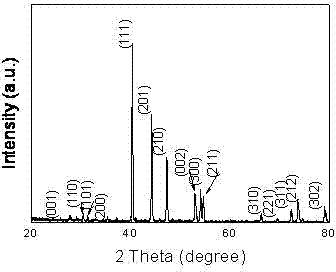
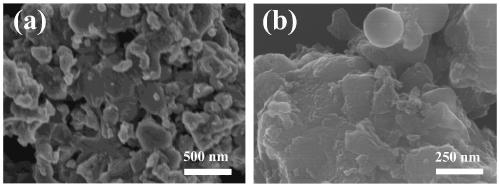
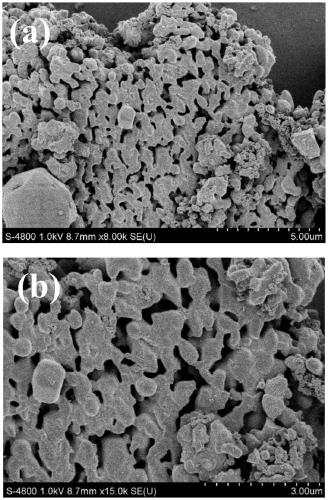
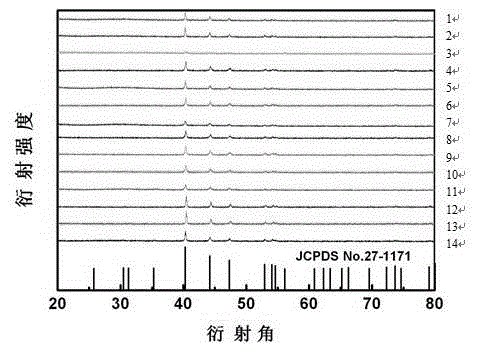
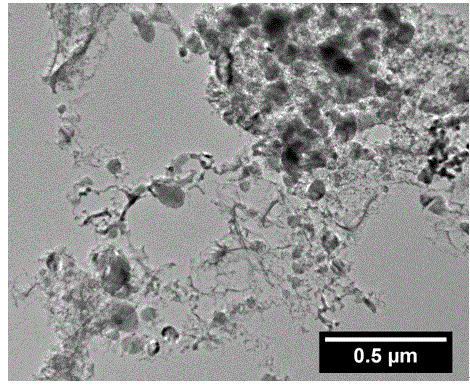
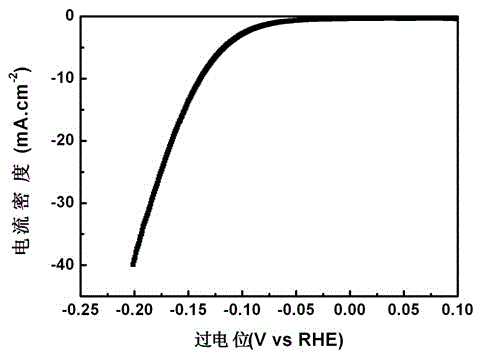
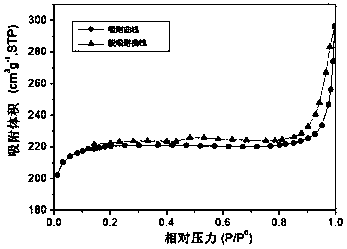
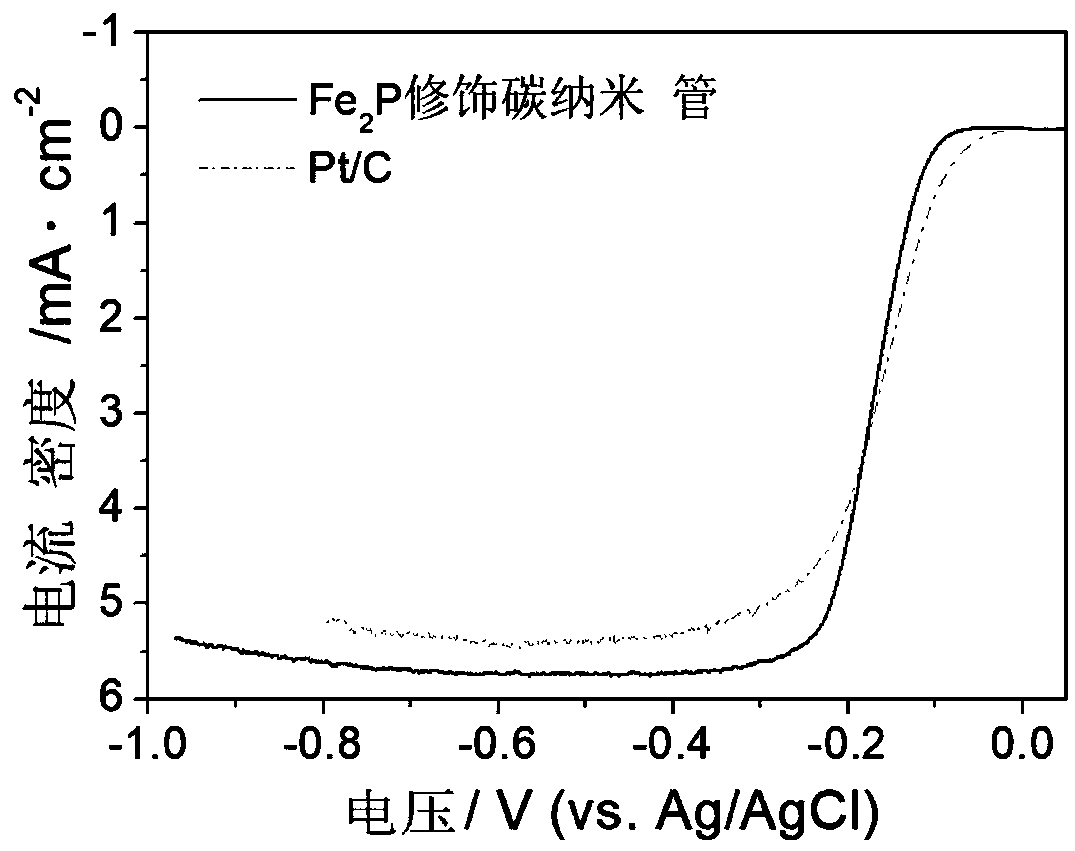
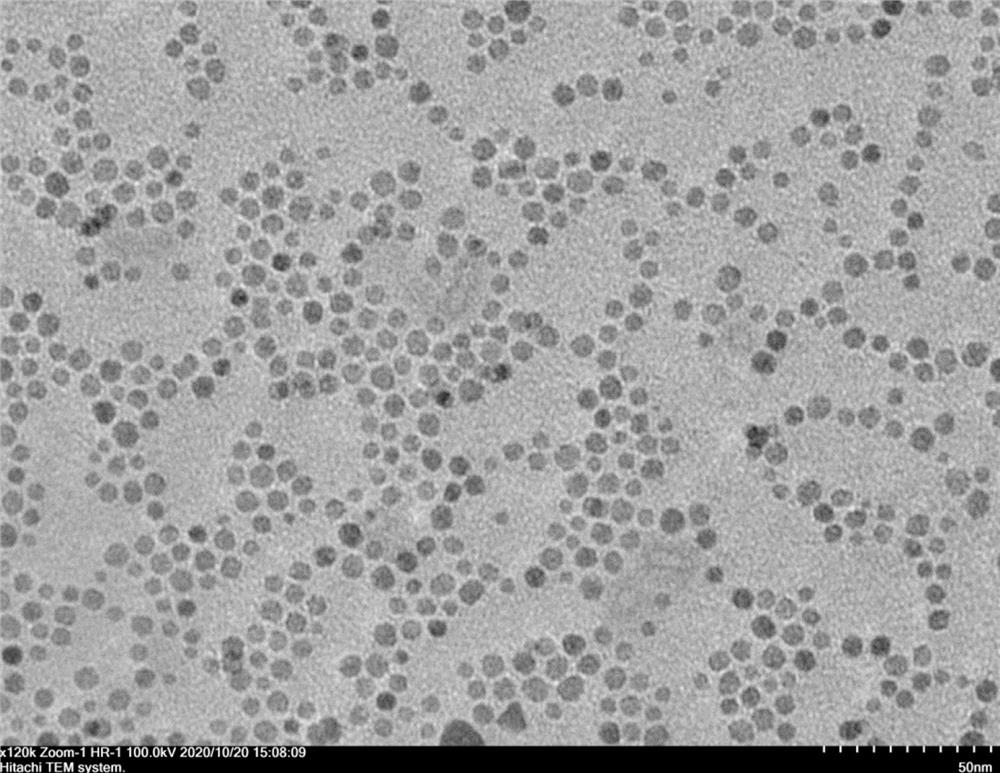
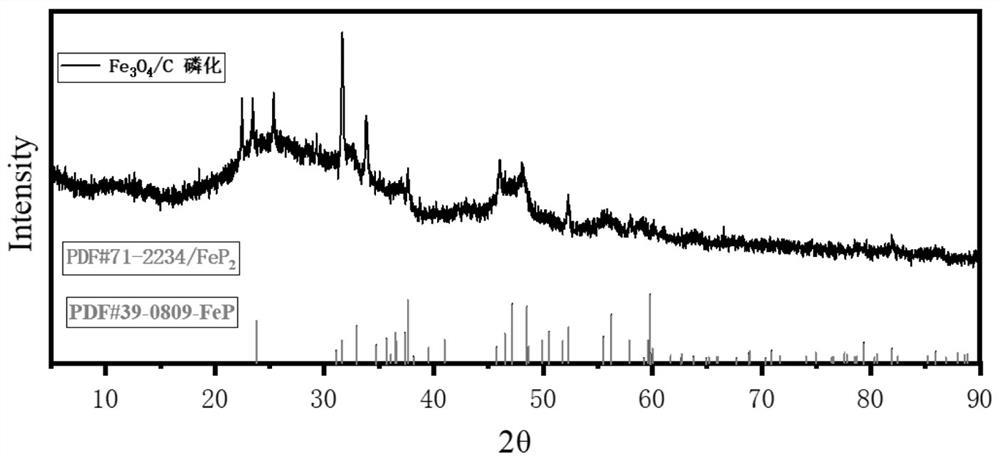
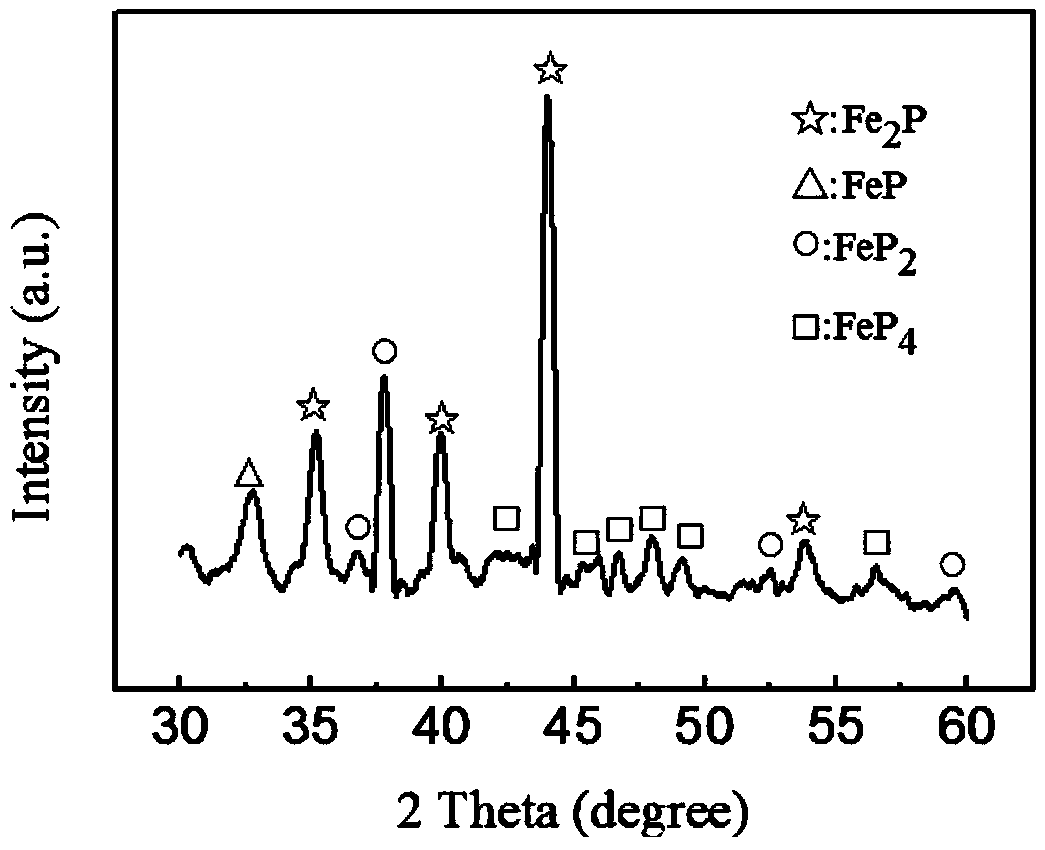
Patents
Literature
123 results about "Iron phosphide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Iron phosphide is a chemical compound of iron and phosphorus, with a formula of Fe₃P. Its physical appearance is grey, hexagonal needles. Manufacturing of iron phosphide takes place at elevated temperatures, where the elements combine directly. Iron phosphide reacts with moisture and acids producing phosphine (PH₃), a toxic and pyrophoric gas.
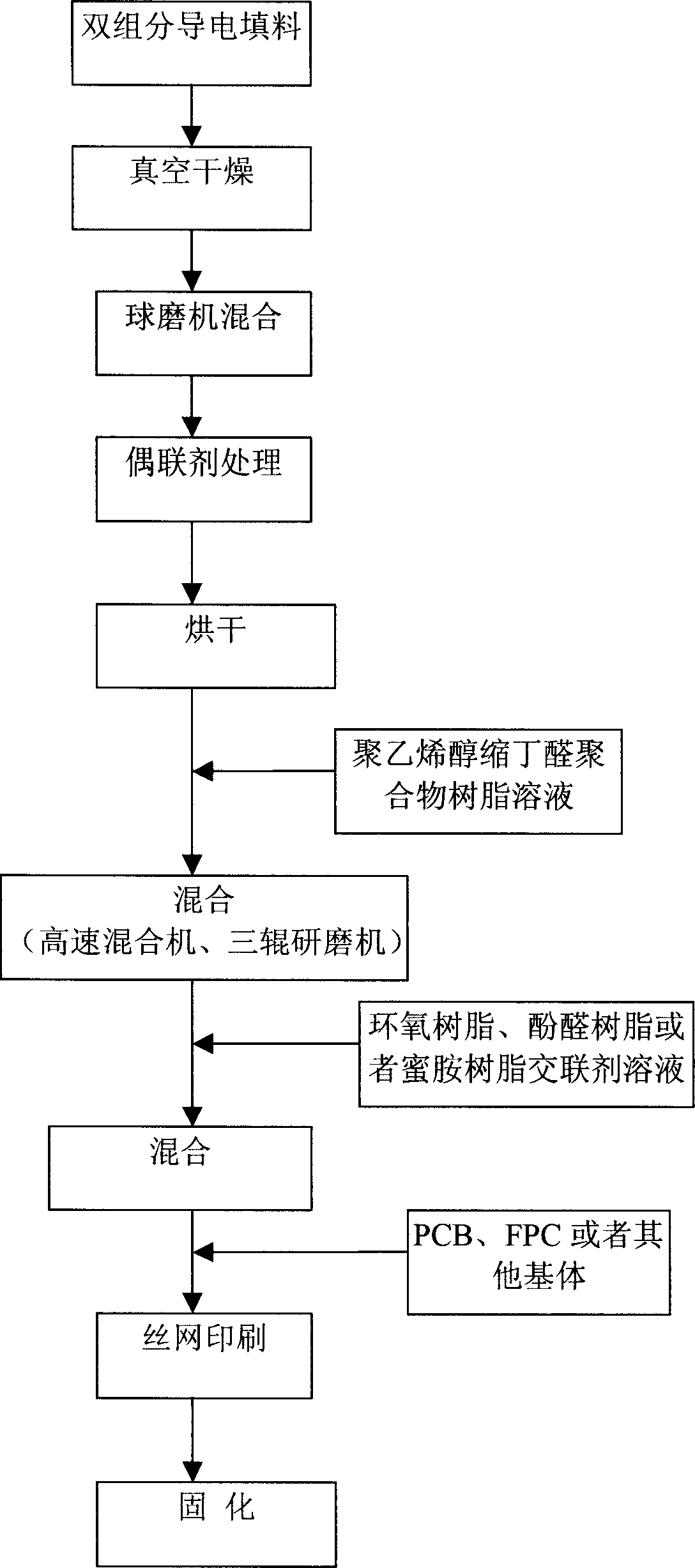
Preparation method of Li2FeSiO4 cathode material used for controlling Fe3P
InactiveCN101734675ALow costWide variety of sourcesCell electrodesAlkali metal silicatesPhosphorous acidWater baths
The invention relates to a preparation method of Li2FeSiO4 cathode material used for controlling Fe3P. The technical scheme comprises the following steps: weighting lithium salt or hydrate of lithium salt, ferrous salt or hydrate of ferrous salt, silicon compound and phosphorous acid or aqueous solution of phosphorous acid according to a molar ratio of the reactants that Li<+>:Fe<2+>:Si:H3PO3=0.95-1.10:0.95-1.10:0.70-0.999:0.001-0.429, mixing the reactants, then adding carbon-containing compound which accounts for 1wt%-20wt% of anhydrous reactants and wet grinding medium which accounts for 0.10-10 times of anhydrous reactants by volume, mixing with a ball mill, heating with water bath, mixing with a ball mill again, heating and drying in vacuum, and then using the two-stage sintering process or temperature programmed two-stage sintering process to prepare Li2FeSiO4 with controllable Fe3P under inert atmosphere or weak reduction atmosphere. The material prepared by the method of the invention has better discharge performance, the discharge capacity is significantly increased in 2.9V zone and the cycle performance is good under 0.3C current.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Coating composition and resin-coated metal sheets
InactiveUS6126730AImprove solderabilityImprove adhesionLiquid surface applicatorsConductive materialInorganic pigmentsChemical conversion
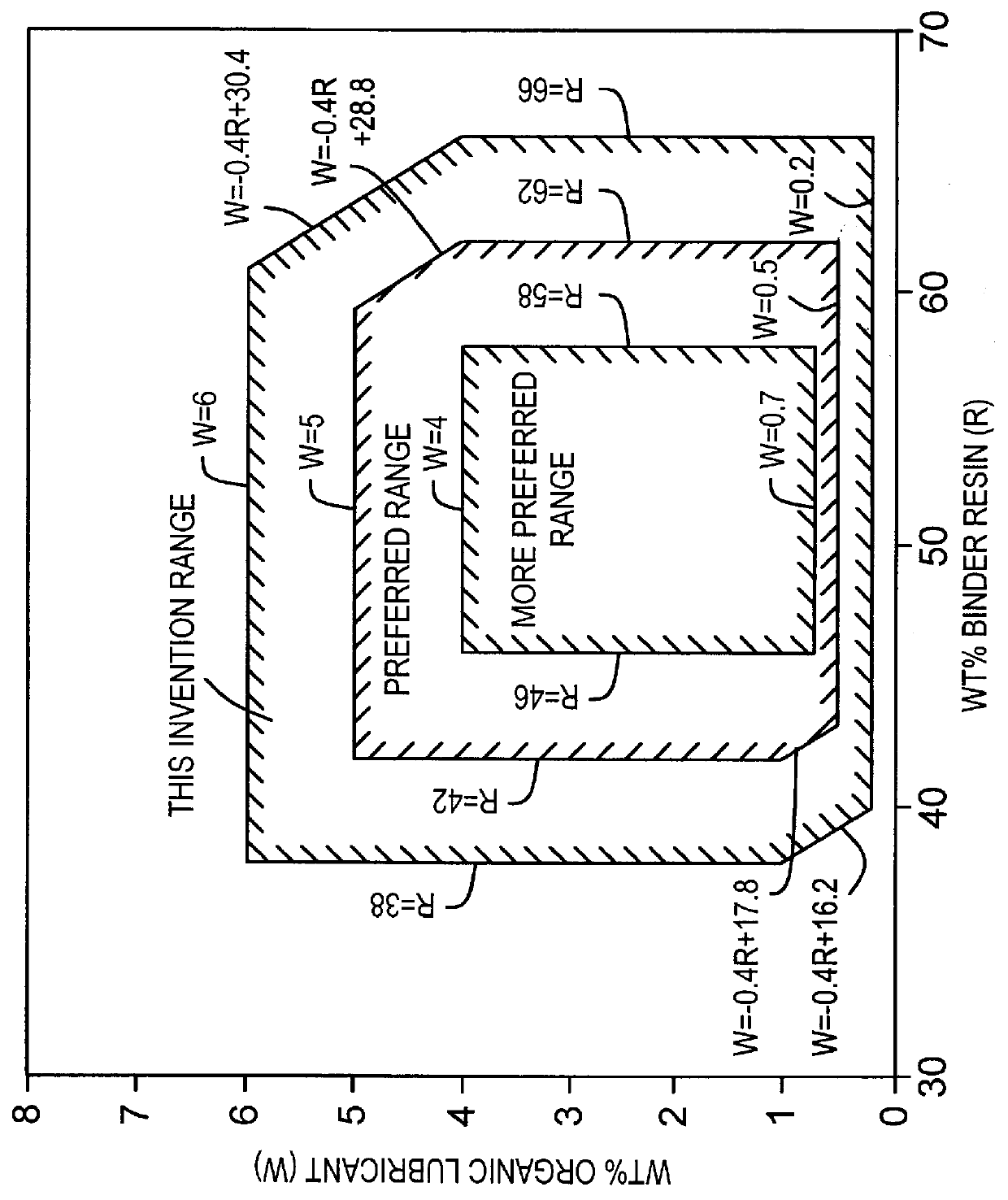
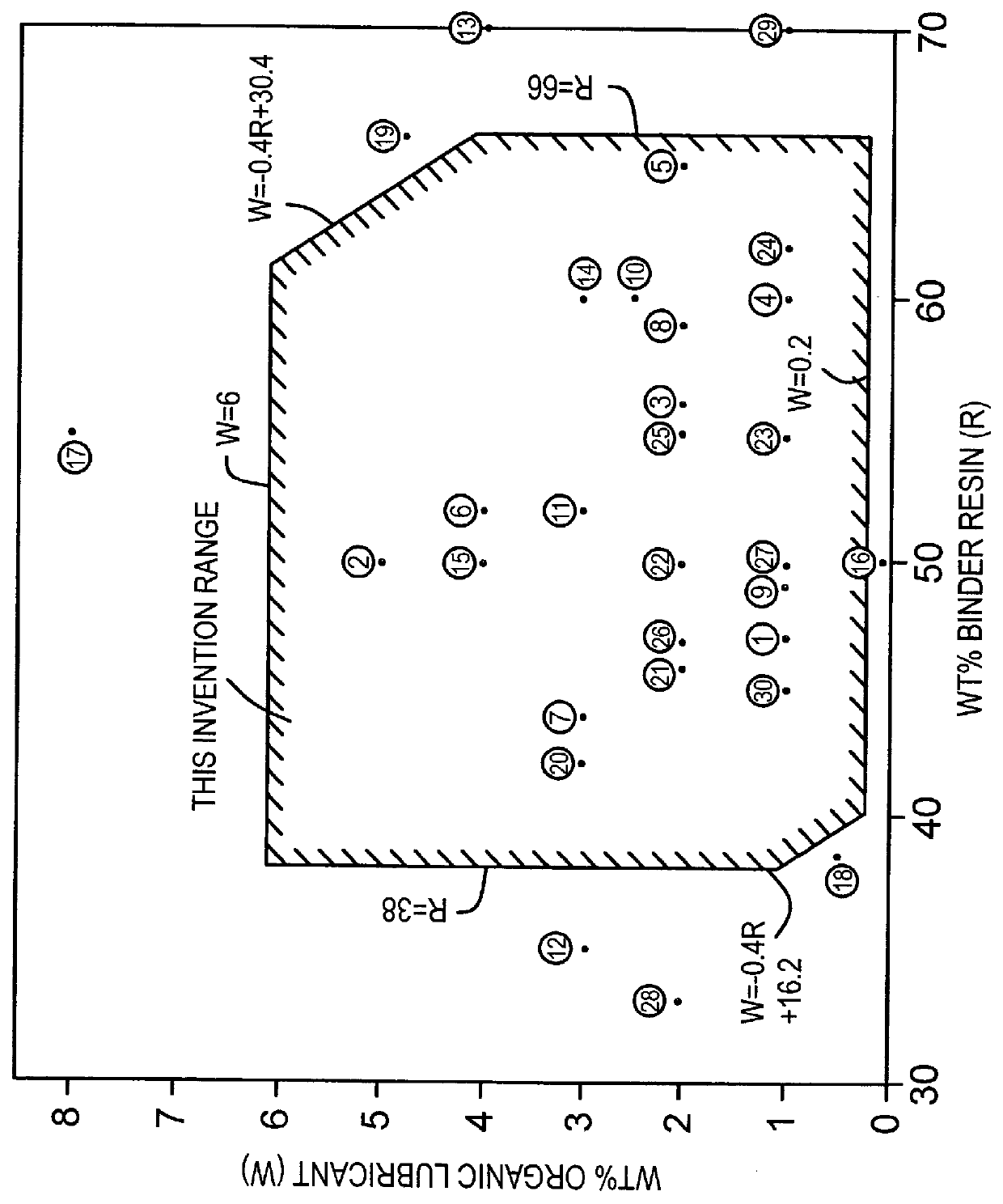
A coating composition comprising 38%-66% of a binder resin (including a curing agent), 0.2%-6% of an organic lubricant, 20%-50% of an iron phosphide-based electrically conductive pigment, and 3%-25% of one or more other inorganic pigments including anticorrosive pigments (the total content of these pigments being between 31% and 56%), wherein the content of the binder resin (including a curing agent) (R) and that of the organic lubricant (W) satisfy the following inequality: -0.4R+16.2< / =W< / =-0.4R+30.4, and wherein the coating composition further comprises a curing catalyst in an amount of from 0.7% to 10% based on the solids of the binder resin (including a curing agent). The coating composition can be applied to a plated metal sheet having a zinc- or aluminum-based plated coating after the plated metal sheet has been subjected to chemical conversion treatment such as chromating treatment, to form a resinous coating thereon having a thickness of 2-9 mu m, thereby resulting in the production of a resin-coated metal sheet having improved overcoat adhesion, weldability, edge face corrosion resistance, and formability, which is suitable for use as a material for automotive repair parts.
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL IND LTD +1
High density spherical nano lithium iron phosphate material, a preparation method thereof, and lithium ion battery containing same
ActiveCN106229505ATightly boundImprove liquidityCell electrodesSecondary cellsSodium-ion batteryLithium-ion battery
A high density spherical nano lithium iron phosphate material, a preparation method thereof, and a lithium ion battery containing the same are provided. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) pre-sintering a lithium resource, iron phosphides, adulterant, and a carbon source with protective gas after dry mixing; (2) mixing a pre-sintering material, dispersant, and deionized water, and performing ultra fine grinding; (3) performing spray drying on a sizing agent obtained by ultra fine grinding, to obtain a spherical nano lithium iron phosphate precursor; and (4) performing chemical vapor deposition coating on the spherical nano lithium iron phosphate precursor obtained in step (3), to prepare the high density spherical nano lithium iron phosphate material. A primary particle size of the lithium iron phosphate material prepared in the present invention is not large, and a powder conductivity may reach 10.1 S / cm, so that a material capacity, low temperature, rate performance, and fabrication and cycling performance may be well balanced.
Owner:江苏贝特瑞纳米科技有限公司
Ferrite ductile iron used at low temperature and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN102634723AEasy to controlSolve the problem of impuritiesProcess efficiency improvementChemical compositionFerrosilicon
The invention discloses chemical compositions of ferrite ductile iron used at low temperature and a manufacturing method of the ferrite ductile iron, determines the range of the chemical compositions of the ferrite ductile iron used at low temperature being minus 40 DEG C and provides a quality standard for the production of qualified and stable ductile iron workpieces. The manufacturing method comprises the steps of adopting pure iron, a carburant and silicon iron as raw materials, synthesizing and melting the raw materials in an electric furnace, conducting spheroidization on the raw materials by utilizing a low-rare-earth spheroidizing agent, and producing the ferrite ductile iron by adopting a combined inoculation method. According to the method, the purity of molten iron is improved stably, and the difficulties of high phosphorus, sulphur, titanium, other imputies and interference elements contents in the molten iron, large fluctuation and instability are solved. According to the method, a novel technical scheme is provided for the production of ferrite ductile iron workpiece which contains small, circular and smooth ductile iron and does not contain cementite and iron phosphide eutectic basically, the ferrite ductile iron can meet the demands of high-performance ferrite ductile iron workpiece in electrical industry, high-speed rail industry and the like, the dependence on imported products can be broken; and the running safety of nuclear power and the high-speed rail can be improved substantially.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU RES INST OF MECHANICAL ENG CO LTD
Wear-resistant spheroidal graphite cast iron and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a wear-resistant spheroidal graphite cast iron and a prepration method thereof, and the cast ion contains the following chemical elements by weight percent: 3.5-3.7% of C; 2.8-3.3% of Si; not more than 0.5% of Mn; less than 0.02% of S; 0.15-0.4% of P and the balance of iron. The preparation method comprises the working procedures of material preparation, smelting and interrupted front treatment. Compared with the prior art, rare earth elements are utilized in the method for obtaining the spheroidal graphite cast iron with a binary iron phosphide eutectic structure, and the spheroidal graphite cast iron has uniform and continuous distribution and high hardness, and can not reduce the elongation rate of the cast ion, thereby being particularly applicable to delivering solid powder and granular substances.
Owner:WUHU JINMAO FLUID TECH CO LTD
Surface carbon coating method of lithium iron phosphate positive electrode material
ActiveCN103794788AAvoid high temperature heat treatmentCoated evenlyCell electrodesCarbon coatingChemical vapor deposition
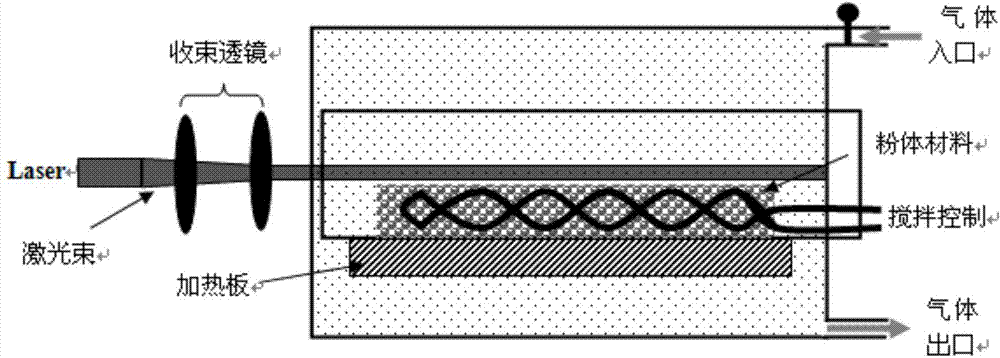
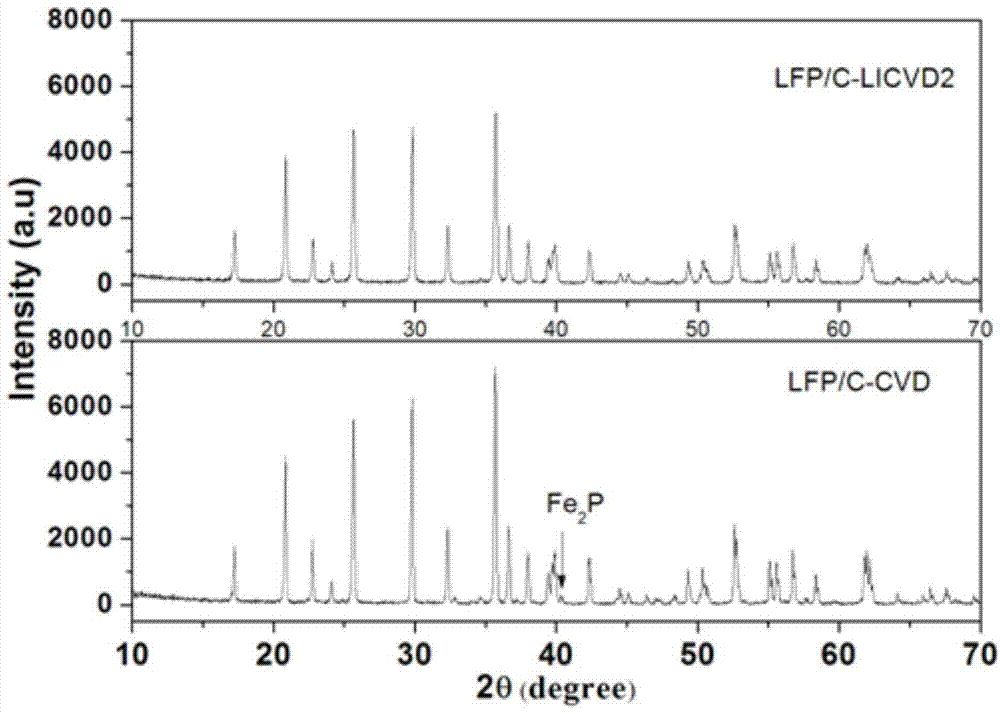
The invention discloses a surface carbon coating method of a lithium iron phosphate positive electrode material. The uniform carbon coating on the surface of the lithium iron phosphate material is realized at a low thermal treatment temperature by a laser chemical vapor deposition method for overcoming the shortcomings of an existing coating technology of the lithium iron phosphate material; in the synthesis process, the surface of the lithium iron phosphate material is subjected to uniform carbon coating treatment by selecting appropriate laser wavelength, carbon source gas proportion, gas flow rate and thermal treatment temperature under the dynamic condition of the lithium iron phosphate powder material; moreover, because the temperature is low in the coating process, the generation of an iron phosphide impurity phase is prevented. The obtained lithium iron phosphate material is pure in phase; the surface coating layer is uniform and complete; the lithium iron phosphate positive electrode material has excellent multiplying power charging and discharging performance.
Owner:HEFEI GUOXUAN HIGH TECH POWER ENERGY
Method for preparing mixing phase positive pole material of iron phosphide and lithium iron phosphate by reaction method
The invention relates to a method for preparing ferrous phosphide and lithium iron phosphate mixed phase cathode materials by reduction method and is characterized in that the preparing process includes the following steps: lithium salt, ferrous salt, phosphate, and hypophosphorous acid or hypophosphite are taken by weighing while the mol ratio of Li: Fe: PO4<3->: hypophosphorous acid or hypophosphite is x: y (1-z): k. The ferrous salt is uniformly blended with medium strong reducing agent and then mixed with a strong reducing agent. The lithium salt, phosphate, hypophosphorous acid or hypophosphite, carbon-containing compound or carbon powder and wet milling liquid are added, ball milling is carried out for 3-15 hours, and the mixture is dried in atmospheric pressure or vacuum at 55-105 DEG C. The dried powder is put in inert atmosphere or weakly reducing atmosphere for preparing the ferrous phosphide and lithium iron phosphate mixed phase cathode materials by two-stage sintering process or temperature programmed two-stage sintering process.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Centrifugally-cast burr cylinder sleeve and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a centrifugally-cast burr cylinder sleeve and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of cylinder sleeves. The centrifugally-cast burr cylinder sleeve comprises,by weight, 2.8%-3.7% of carbon, 0.03%-0.08% of sulfur, 1.7%-2.8% of silicon, more than zero and no more than 0.5% of phosphorus, 0.5%-1.0% of manganese, more than zero and no more than 0.4% of chromium, 0.1%-0.6% of copper, and the balance iron. A-type graphite is no less than 80% in the metallographic phase of the cylinder sleeve, the length of the A-type graphite is at 4-7 grades, the matrix structure is fine lamellar pearlite, ferrite is no more than 3%, the amount of carbide and iron phosphide eutectic is no more than 5%, and the carbide and the iron phosphide eutectic are in discontinuous network distribution or even distribution. Customer requirements to mechanical performance can be met, the condition of pull of the inwall of a pipe mould is reduced obviously, the life of the mouldis prolonged greatly, and the processing performance of the cylinder sleeve is better.
Owner:ZYNP GRP
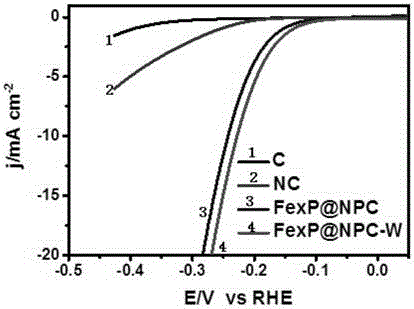
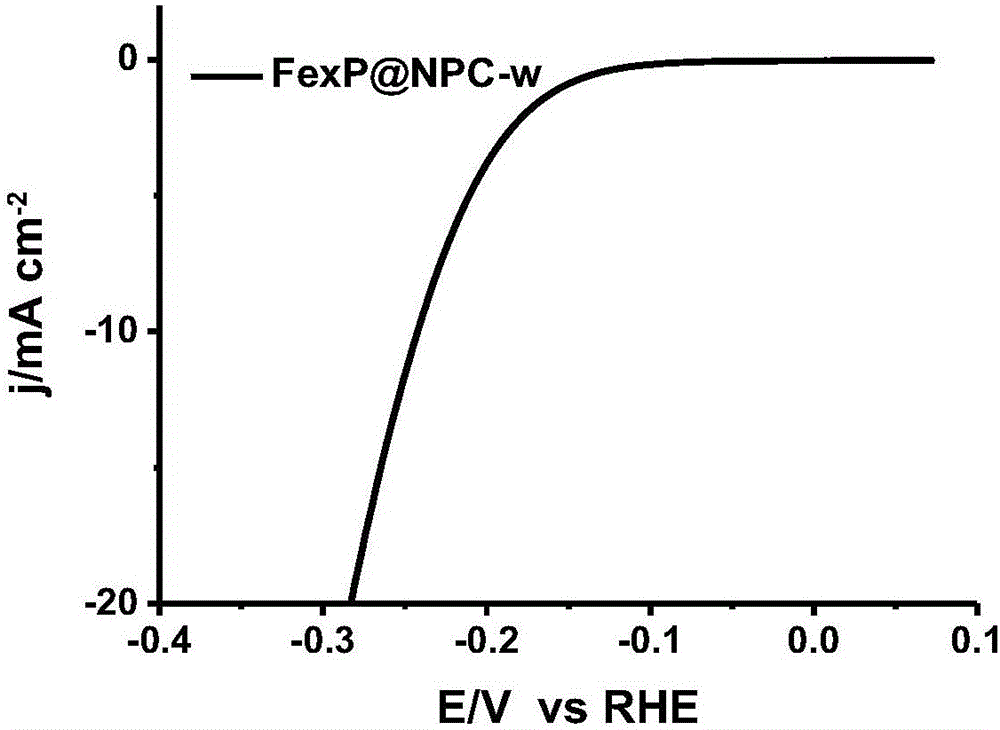
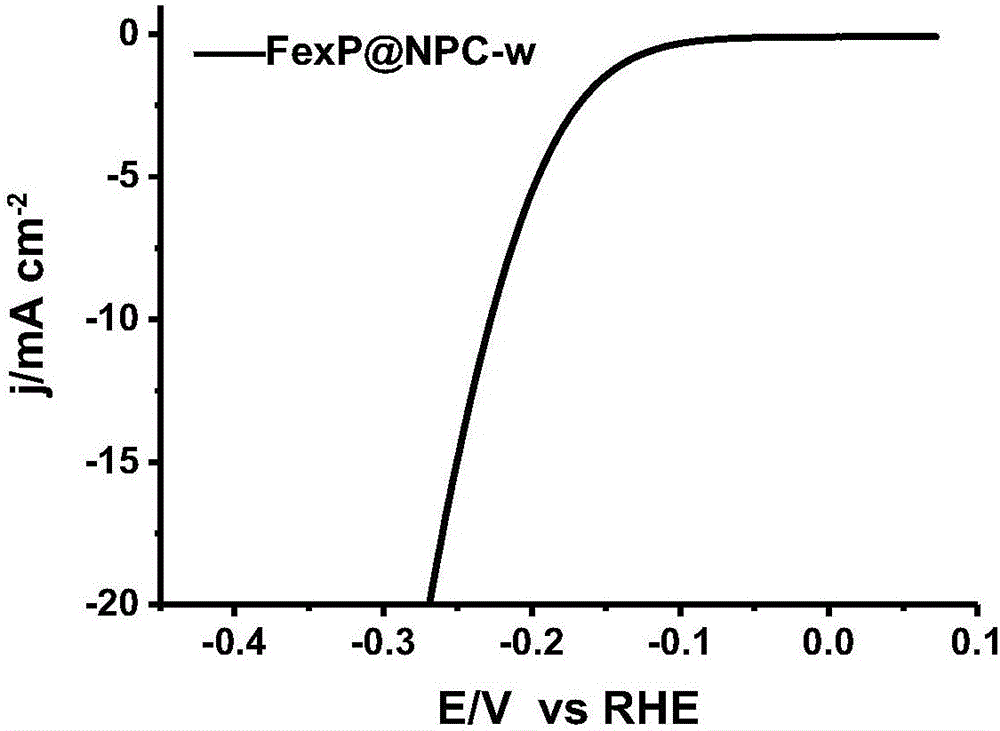
Hydrogen evolution catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106215964AHigh hydrogen evolution electrocatalytic activityImprove conductivityCatalyst activation/preparationOver potentialCarbonization
A hydrogen evolution catalyst and a preparation method thereof belong to the field of catalysis. Provided are a novel nitrogen-and-phosphor-codoped hollow carbon / iron phosphide composite catalyst and a preparation method thereof. According to the method, uniform mixing of a nitrogen source, a carbon source, a phosphor source, an iron source in a precursor are ensured, and a process of nitridation, phosphatization and carbonization is achieved through one-step high-temperature pyrolysis to prepare a phosphide having a hollow carbon inner wall inlaid with transition metal. The catalyst is high in catalytic activity, low in hydrogen evolution over potential, and prolonged in cycle life. The catalyst is low in cost of raw materials and easy to prepare.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Iron phosphide film hydrogen evolution catalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107999101ALow costThe preparation of raw materials is safe and environmentally friendlyCatalyst activation/preparationIron saltsIron oxyhydroxide
The invention provides a preparation method of an iron phosphide film hydrogen evolution catalyst and belongs to the field of catalysis. The preparation method comprises a step of preparing an iron oxyhydroxide precursor, namely weighing an iron salt, dissolving the iron salt into a glycerin / water mixed solution, then, mixing the iron salt with the glycerin / water mixed solution, transferring the mixture into a reactor, raising the temperature to 100-140 DEG C to carry out a reaction, cleaning the product by using water and ethanol, and drying the product to obtain a film-like iron oxyhydroxideprecursor. The preparation method further comprises a step of preparing an iron phosphide film, namely placing the film-like iron oxyhydroxide precursor at the downstream of a tube furnace, placing sodium dihydrogen phosphate at the upstream of the tube furnace, and carrying out temperature-controlled phosphorization in an inert atmosphere to obtain an iron phosphide film catalyst. The preparation method has the characteristics of controllable synthesis of the film-like iron oxyhydroxide precursor and low-temperature controllable shape-preserving phosphorization and has the advantages such assafe and environment-friendly preparation raw materials, low price, simple preparation process and easiness in operation. The catalyst shows efficient hydrogen evolution activity and circulation stability in acidic, alkaline and neutral water solutions.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Vanadium-titanium gray cast iron and production technique thereof
The invention particularly relates to a vanadium-titanium gray cast iron and a production technique thereof. The vanadium-titanium gray cast iron contains 3.2-3.6% of C, 1.6-1.9% of Si, 0.7-0.9% of Mn, 0-0.10% of P, 0.07-0.12% of S, 0.15-0.20% of V, 0.07-0.12% of Ti, 0.25-0.35% of Cr, and the balance of Fe and other minor elements and inevitable impurities. The vanadium-titanium gray cast iron has the advantages of high tensile strength, favorable heat resistance and favorable wear resistance; and the type-A graphite content in the metallurgical structure is higher than 85%, the graphite length is Grade 3-5, the pearlite content in the matrix structure is greater than or equal to 98%, and the total content of carbides and iron phosphide eutectic is less than or equal to 2%.Late inoculation treatment is adopted to enhance the inoculation effect, improve the graphite form, eliminate the carbides and ferrite and increase the pearlite content. By using cheap vanadium-titanium pig iron as the raw material and avoiding adding noble alloys, the vanadium-titanium gray cast iron has the advantages of low cost and high performance.
Owner:陈国
Preparation method of nitrogen doped carbon nano-array loaded iron phosphide/cobalt phosphide
InactiveCN109433240AImprove hydrogen production performanceImprove stabilityPhysical/chemical process catalystsElectrodesShielding gasMetal-organic framework
The invention provides a preparation method of nitrogen doped carbon nano-array loaded iron phosphide / cobalt phosphide. The method includes the steps: calcining polyaniline-iron cobalt metal organic framework in protective gas to obtain a precursor; performing phosphorization on the precursor in the protective gas under the heating condition to obtain the nitrogen doped carbon nano-array loaded iron phosphide / cobalt phosphide. A catalyst prepared by the method for loading a prepared novel phosphide on a nitrogen doped carbon nano-array is excellent in hydrogen producing performance, a materialmanufacturing process is easily controlled, long-time stability is good, low is lower as compared with an existing noble metal catalyst, and the catalyst can be applied to production of electrochemical cell hydrogen evolution electrodes.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Method for preparing transition metal phosphide Fe2P
The invention discloses a novel method for preparing transition metal phosphide Fe2P. The method comprises the following steps: taking ferric phosphate as precursor, taking potassium borohydride as reductant, grinding phosphate of ferrum and reductant in a mortar at molar ratio of 1:1.5 to 1:2, and uniformly mixing, and reacting for 30 min under the argon protection at 500 DEG C to 600 DEG C; the product being porphyrized, rinsing for three times respectively with distilled water and absolute ethyl alcohol, then drying with vacuum under 60 DEG C for 12h, and obtaining the product Fe2P. The invention has the advantages that the source of required main material is rich, the price is cheap, and the cost is lower; the synthesis method is novel, the process is simple, the complex steps of high temperature, high pressure and the like can be avoided, the preparation process is simplified, and the energy consumption is reduced; and the environment pollution can not be caused during the preparation process of the adoptedemployed method, and the invention is suitable for mass production.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV +1
Flexible ferrous phosphide/carbon nanofiber membrane, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111188126AEasy to prepareRealize large-area continuous productionNegative electrodesSecondary cellsCarbon layerSpinning
The invention discloses a flexible ferrous phosphide / carbon nanofiber membrane, and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of (1) preparingferric phytate nanoparticles by using phytic acid and ferric chlorides as raw materials; (2) dispersing the ferric phytate nanoparticles prepared in the step (1) into an organic solvent; then, addingpolyacrylonitrile to prepare a spinning solution; and performing electrostatic spinning to prepare a ferric phytate / PAN nanofiber membrane; and (3) pre-oxidizing the ferric phytate / PAN nanofiber membrane prepared in the step (2), and performing carbonization treatment in an inert atmosphere to prepare the flexible ferrous phosphide / carbon nanofiber membrane. The preparation method provided by theinvention is simple, convenient, green and safe, and can realize large-area continuous production. Through a phosphorus doped carbon material in a prepared flexible electrode material, the electricalconductivity is improved, and the volume change of FeP in the charging-discharging process is reduced; through a carbon layer on the FeP, the formation of a stable SEI membrane is improved; and the structure integrity is maintained.
Owner:JIAXING UNIV
Carbon oil in use for making carbon resistance element, preparation method, and prepared element of carbon resistance
InactiveCN1797614ASimple processNarrow distribution range of square resistanceNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialResistor manufactureCross-linkCrazing
The carbon oil is composed of current conducting padding, rosin joint material, cross-linking agent, and solvent. The padding includes carbon black, metal powder or mixture of powder of electroconductive metallic compound. The said metal powders can be powders of nickel, silver, gold, aluminum, zinc, tin or stainless steel. Mixture of powder can be nickel oxide, tin oxide, indium oxide, niobium oxide or iron phosphide. Features are: simple technique, narrow distribution range of numerical value of resistance in mean square. The invention overcomes defects of pinholes, cracks etc. in final product so as to raise capability of product and stability of carbon resistance element.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
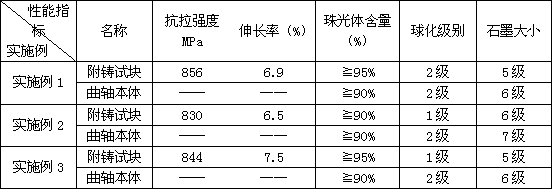
As-cast high-strength nodular cast iron for crankshaft and preparation method of as-cast high-strength nodular cast iron
ActiveCN108396219AImprove performanceDense heart tissueProcess efficiency improvementHigh intensityPearlite
The invention provides as-cast high-strength nodular cast iron for a crankshaft and a preparation method of the as-cast high-strength nodular cast iron. The as-cast high-strength nodular cast iron consists of the following elements by weight percent: more than or equal to 4.2 and less than or equal to 4.5 of CE, 3.5-3.9% of C, 1.8-2.2% of Si, less than or equal to 0.5% of Mn, less than or equal to0.03% of P, 0.005-0.02% of S, 0.4-0.8% of Cu, 0.002-0.01% of Sb and the balance of Fe and inevitable micro-elements. The as-cast high-strength nodular cast iron has the tensile strength of 800-850 Mpa, the ductility of more than or equal to 6% and the nodularity of 90%. A metallographic structure has the matrix of more than or equal to 90% of pearlite. Cementite and iron phosphide eutectic are less than or equal to 2%. The nodularity is 2-level or above. The sizes of graphite nodules are 5-8 levels. The tensile strength Rm is more than or equal to 800 MPa. The elongation is more than or equalto 6%. Such key parts as the crankshaft prepared by the preparation method are reliable in quality and superior in performance.
Owner:FIRST TRACTOR
Transition metal phosphide iron phosphide negative electrode material
InactiveCN110304614ASmall volume expansionImprove conductivitySecondary cellsNegative electrodesN dimethylformamideRetention ratio
The invention discloses a transition metal phosphide iron phosphide negative electrode material. The transition metal phosphide iron phosphide negative electrode material is prepared from the following steps that (1) water and N,N-dimethylformamide are mixed evenly; (2) an iron source and an organic ligand are added, stirring is conducted, and thus a mixed solution is formed; (3) sealing, heatingreaction, cooling, filtering, washing and drying are conducted to obtain yellow powder; (4) in inert atmosphere, roasting and cooling are conducted to obtain black powder; and (5) sodium hypophosphiteand the black powder are placed at the upstream part and the downstream part of a tubular furnace, in the inert atmosphere, roasting and cooling are conducted, and thus the transition metal phosphideiron phosphide negative electrode material is formed. The particle size of the negative electrode material is 400-600 nm, the transition metal phosphide iron phosphide negative electrode material isassembled into a battery, under the situation that the voltage is within the range of 0.1-3 V and the testing current is 100 mA.g<-1>, the first charge specific capacity reaches 1241 mAh.g<-1>, the first discharge specific capacity reaches 672 mAh.g<-1>, the capacity retention ratio after 100 cycles of circulating is greater than or equal to 95%, the preparation technique is simple in process, thereaction temperature is low, the cycle is short, and the cost is low.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Composite inoculant
The invention relates to a composite inoculant, which contains the following ingredients of: by weight, 20-30% of carbon, 40-50% of silicon, 6-9% of rare earth, 0.6-0.8% of strontium, 2.2-2.8% of barium, 0.1-0.2% of calcium, 0.1-0.2% of aluminium, and the balance being iron. In addition, 0.06-0.08 wt% of tin is added in the composite inoculant. The composite inoculant provided by the invention can effectively prolong graphitization depression time, substantially increase casting hardness and eliminate white castings, is especially in favor of improving the morphology and distribution of graphite in thin-walled castings, lowers the difference between crystal structures of positions with different thicknesses, reduces shrinkage tendency of castings, improves compactness of castings, raises cold-hot fatigue resistance and mechanical fatigue of castings, minimizes segregation of phosphor in cast iron, and makes phosphor become fine and uniformly-distributed binary iron phosphide eutectic in cast iron.
Owner:王萍
Method for preparing iron phosphide and carbon composite structure by utilizing carbothermic reaction
InactiveCN104084224AWell mixedMix well and evenlyPhysical/chemical process catalystsCarbon compositesPhosphate
The invention relates to a method for preparing an iron phosphide and carbon composite structure by utilizing carbothermic reaction, and particularly relates to a simple and easy method for preparing the iron phosphide and carbon composite structure. The method is suitable for preparing a composite structure of iron phosphide, other metal phosphides and carbon in large scale. The method comprises the following steps: soaking melamine by a mixed solution of ferric chloride hexahydrate and ammonium dihydrogen phosphate by adopting a soaking method in which the ferric chloride hexahydrate, the ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and the melamine are used as raw materials, then carrying out high-temperature pyrolysis on melamine under inert gas by adopting a high-temperature pyrolysis method, reducing metal phosphates into metal phosphides, thereby obtaining the iron phosphide and carbon composite structure. According to the method, the uniform refining of the iron phosphide and carbon composite structure can be achieved by changing the ratio of the ferric chloride hexahydrate to the melamine and conditions of the pyrolysis reduction, such as warming velocity, holding temperature, temperature holding time, so that the iron phosphide and carbon composite structure which is uniform in granule and excellent in catalytic performance can be obtained.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Heteroatom-doped carbon nanotube-loaded iron phosphide nanoparticle oxygen reduction catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108927185AUniform one-dimensional structureUniform sizeMaterial nanotechnologyPhysical/chemical process catalystsNano catalystCarbonization
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of new nano materials, and relates to a heteroatom-doped carbon nanotube-loaded iron phosphide nanoparticle oxygen reduction catalyst. The nanocatalyst takes polyphosphazene nanotubes as a heteroatom-doped carbon nanotube precursor and an organic iron salt or inorganic iron salt as an iron element precursor. The iron element precursor isadsorbed by the polyphosphazene nanotubes, one-step high temperature carbonization is performed in an inert atmosphere, and the heteroatom-doped carbon nanotube-loaded iron phosphide nanoparticle composite material is obtained. The composite material has excellent oxygen reduction catalytic performance, the catalytic activity of the oxygen reduction catalyst is close to that of a commercial Pt / C catalyst, and the oxygen reduction catalyst is cheaper and easier to obtain; at the same time, the catalytic durability, the methanol toxicity resistance and other characteristics are better than thoseof the commercial Pt / C catalyst.
Owner:LINYI UNIVERSITY
Iron phosphide-based photocatalyst and synthesis method thereof
InactiveCN107126968ACatalyst activation/preparationHydrogen productionPhotocatalytic water splittingHydrogen
The invention relates to a photocatalytic material and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the field of inorganic photocatalytic materials. The photocatalytic material is prepared from iron phosphide and a mixture of the iron phosphide and other photocatalytic materials. The photocatalytic material prepared by the preparation method has photocatalytic activity in a wavelength range of 400nm to 1000nm; the photocatalytic material can be radiated by visible light or natural light and be subjected to photocatalytic hydrolysis to generate hydrogen.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Preparation method of iron phosphide nano material and application of iron phosphide nano material as electrocatalyst
PendingCN113101955AConsistent appearanceComplete size and shapeElectrolysis componentsPhysical/chemical process catalystsPtru catalystPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a preparation method of an iron phosphide nano material and application of the iron phosphide nano material as an electrocatalyst, during preparation, oxide particles of iron are prepared by adopting a hydrothermal method, then the oxide particles are loaded on carbon powder, and finally, the iron oxide particles are converted into iron phosphide particles by adopting a high-temperature gas phase phosphating method. The preparation process is simple to operate, easy to control and low in cost. According to the method, the precursor morphology is regulated and controlled, the optimal phosphating condition is explored, and the initial appearance morphology is reserved. The components of the material are FeP and FeP4 or FeP and FeP2, and the hydrogen evolution reaction can be continuously, efficiently and stably catalyzed.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES CORPORATION
Preparation method of iron phosphide nanosheet and biomass carbon composite material and application
ActiveCN108807941AImprove cycle lifeSimple processCell electrodesSecondary cellsBiomass carbonSodium-ion battery
The invention discloses a preparation method of an iron phosphide nanosheet and biomass carbon composite material. The method comprises the following steps: compositing the iron phosphide nanosheet and a biomass carbon membrane through using an electrochemical method, to obtain an iron phosphide / biomass carbon integrated electrode without a binder. The method is simple, and convenient to operate,and the preparation cost of materials is low. The iron phosphide is firstly composited with the biomass carbon material so as to obtain the composite material for the negative electrode material of asodium-ion battery. The composite material electrode is excellent in sodium storage performance, and stable in structure.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Creeping agent for pearlite type vermicular cast iron member
The invention discloses a vermiculizer for pearlite type vermicular cast iron. The vermiculizer comprises the following components in weight percentage: 10 to 30 percent of rare earth, 2 to 8 percent of magnesium, 35 to 50 percent of silicon, 1 to 3 percent of aluminum, 10 to 15 percent of phosphorus, 10 to 30 percent of copper, and the balance being iron. The adoption of phosphorus and iron aims to form evenly distributed iron phosphide eutectic in the vermicular cast iron, which improves the wearing resistance of the vermicular cast iron; and the addition of electrolytic copper aims to increase the pearlite content of the vermicular cast iron. By using the vermiculizer, the high strength and high hardness vermicular cast iron of which the vermicular graphite percentage is more than 80 percent and the basal body is the pearlite can be effectively produced. The vermiculizer has the advantages of simple use, obvious effect and stable vermicular graphite.
Owner:上海市机械制造工艺研究所有限公司
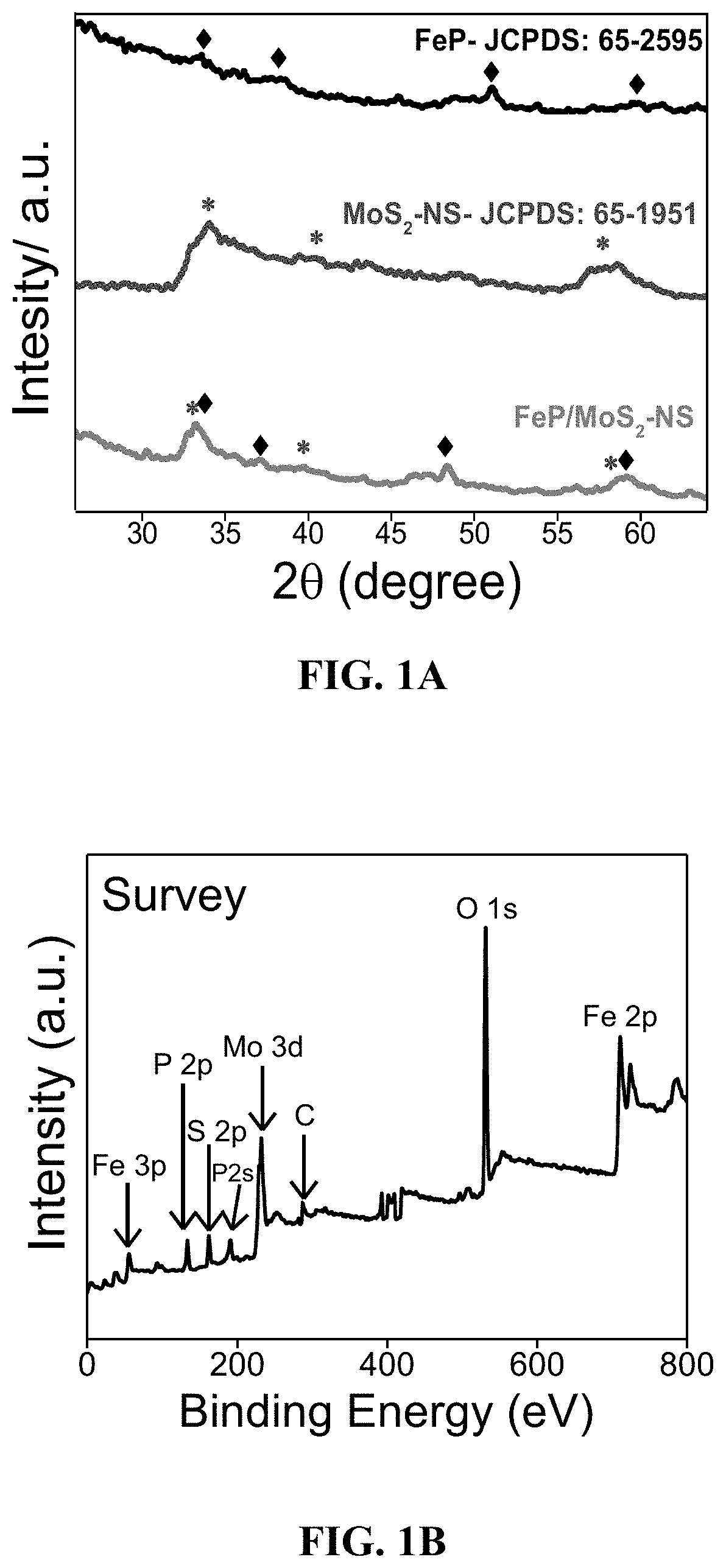
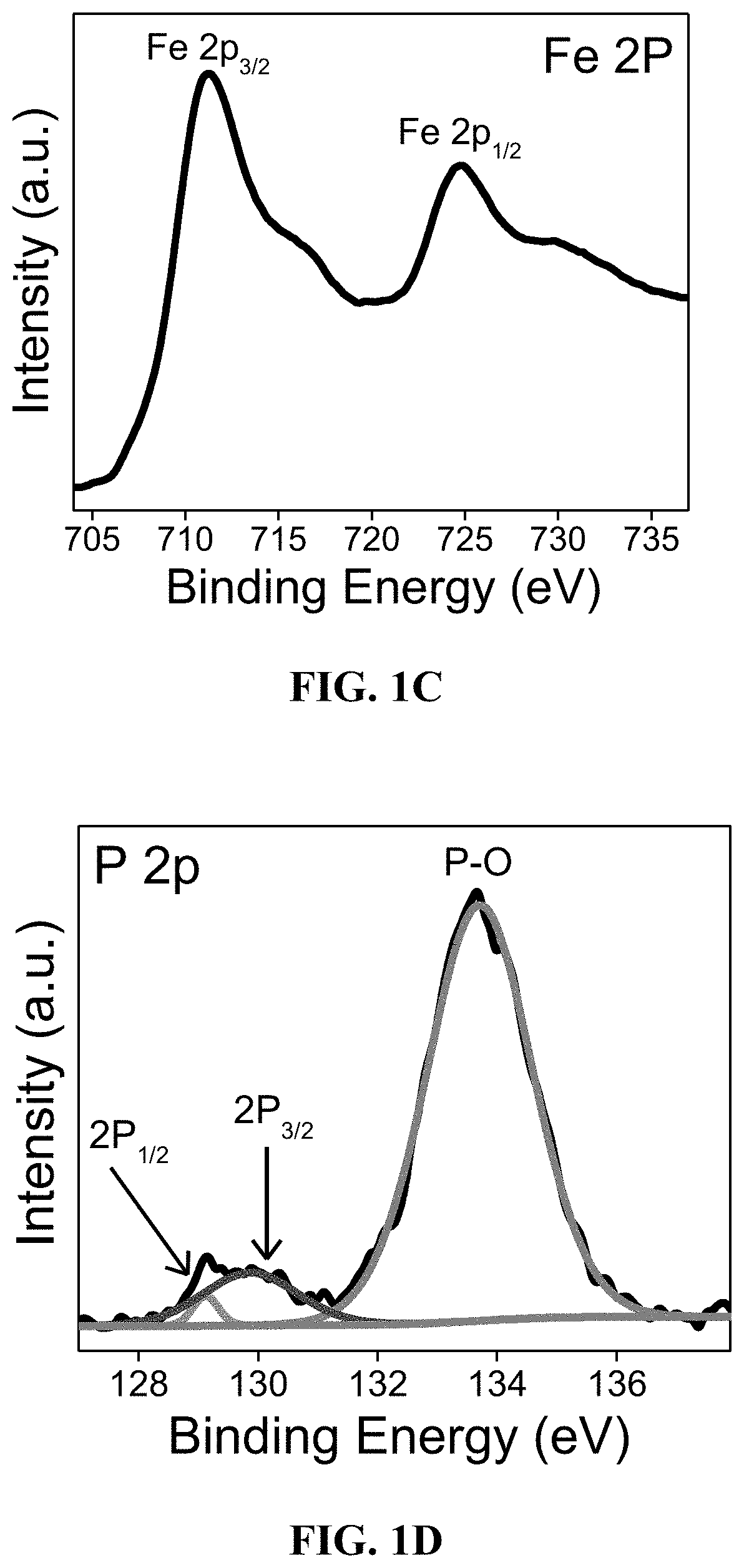
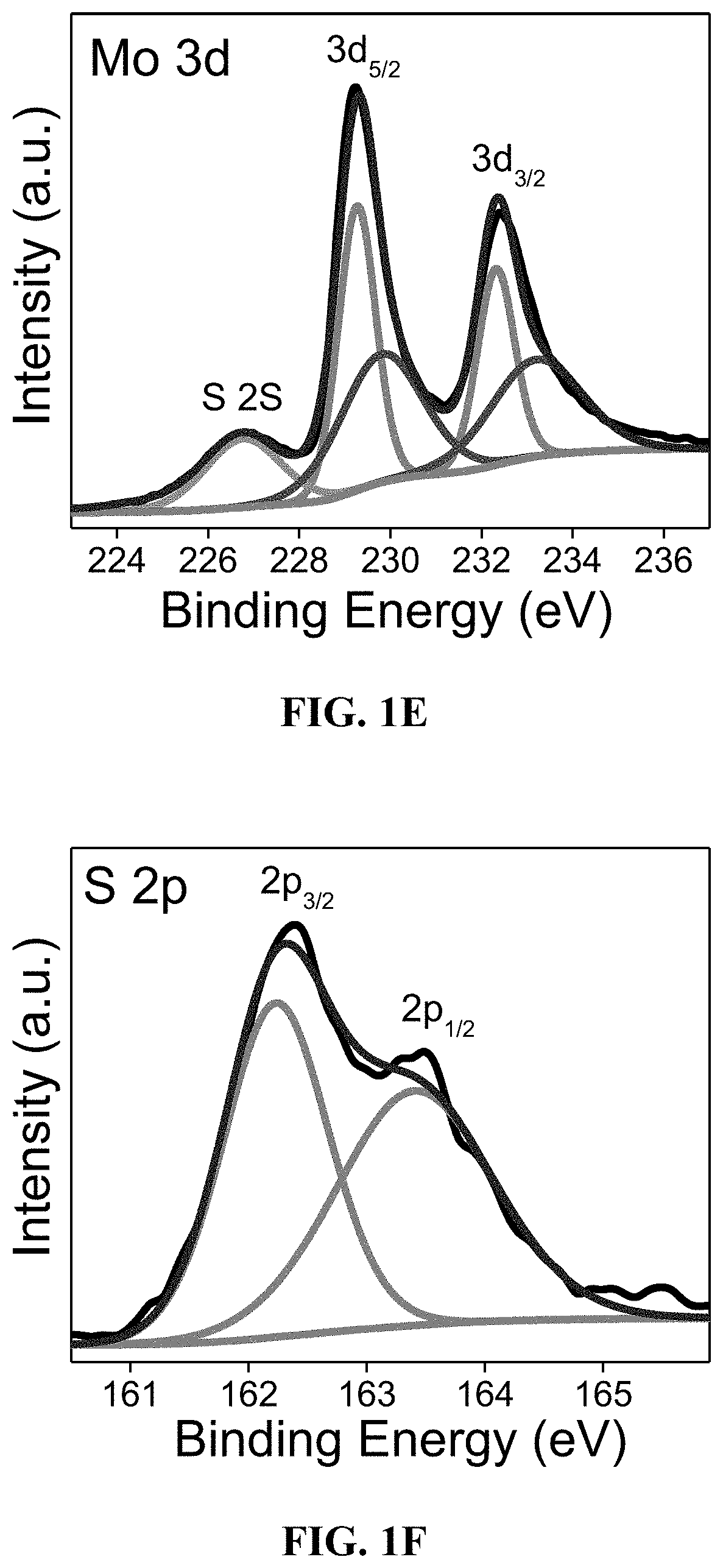
Molybdenum sulfide nanosheets decorated with iron phosphide for hydrogen gas evolution
ActiveUS20210170384A1Material nanotechnologyPhysical/chemical process catalystsPtru catalystPhotochemistry
An electrocatalyst comprising molybdenum disulfide nanosheets with dispersed iron phosphide nanoparticles is described. The molybdenum disulfide nanosheets may have an average length in a range of 300 nm-1 μm and the iron phosphide nanoparticles may have an average diameter in a range of 5-20 nm. The electrocatalyst may have an electroactive surface area in a range of 10-50 mF·cm−2 when deposited on a working electrode for use in a hydrogen evolution reaction.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Bismuth-containing inoculating agent for cast iron and preparation method of inoculating agent
InactiveCN109811247AInhibition of anti-allogueReduced section sensitivityRare earthMechanical property
The invention discloses a bismuth-containing inoculating agent for cast iron and a preparation method of the inoculating agent. The inoculating agent comprises, by weight percentage, 60-70% of silicon, 1-5% of bismuth, 1-3% of calcium, 1-5% of aluminum, 2-7% of a mixed rare earth metal element, and 20-30% of iron. The bismuth-containing inoculating agent for the cast iron can be applied to variousgray iron casting production processes; by adding in the bismuth element, iron phosphide eutectic is decreased and decomposed, the reverse chill effect of a casting is inhibited, the fracture surfacesensitivity of the casting after inoculating is lowered, the graphite form is changed, the rate of spheroidization is increased, and the ferrite content in a casting matrix structure is remarkably increased; by adding in the rare earth metal element, the effects of evolving molten iron, increasing the supercooling degree, and promoting pearlite forming and refining crystalline grains are achieved; and by controlling the content of aluminum and calcium, aluminum and calcium oxide in the molten iron is within a reasonable content range, inoculating interference of the aluminum and calcium oxideon other elements is prevented, and the mechanical performance and the easy-to-machine performance of the casting are effectively improved.
Owner:JIANGSU YAFENG ALLOY MATERIAL
Gray pig iron air cylinder sleeve and gas nitriding production process thereof
ActiveCN105369121AShorten the timeLow costPositive displacement pump componentsSolid state diffusion coatingNitrationManganese
The invention discloses a gray pig iron air cylinder sleeve and a gas nitriding production process thereof and belongs to the technical field of air cylinder sleeves. The air cylinder sleeve is composed of, by weight, 3.0%-3.6% of carbon, 2.0%-2.8% of silicon, 0.1%-0.4% of phosphorus, more than 0% but less than 0.12% of sulfur, 0.5%-1.0% of manganese, 0.2%-0.5% of copper, more than 0% but less than 0.06% of titanium, more than 0% but less than 0.04% of vanadium, and the balance iron. The structure of the gray pig iron air cylinder sleeve is flaky graphite (the content of A type graphite is greater than 50%), and the substrate is pearlite (the amount is greater than 95%)+ferrite+a small amount of dispersively distributed carbide and iron phosphide eutectic. The cylinder sleeve is subjected to nitriding treatment, and the air cylinder sleeve with a nitration layer 0.15-0.35 mm thick and the nitration layer 600-800 HV hard is obtained. The nitridation gray pig iron air cylinder sleeve has the advantages of being high in hardness and abrasion resistance, good in anti-abrasion property and the like.
Owner:ZYNP GRP
Method for producing mixed matrix structure as-cast spheroidal graphite cast iron
InactiveCN106868395AHigh strengthImprove impact toughnessProcess efficiency improvementIntermediate frequencyHardness
The invention discloses a method for producing mixed matrix structure as-cast spheroidal graphite cast iron. A proper smelting technology and proper chemical components are selected for control, wherein an intermediate frequency furnace is used in molten iron smelting for single smelting, and a pig iron and scrap steel recarburization technology is adopted for producing base iron; a sandwich type package is used in a ladle, and the mass percents of Si, Mn, Cu, Ca and Ba in a casting are controlled; and after casting forming is conducted, high-temperature box opening is conducted. By the adoption of the method, the content range of pearlite ranges from 55% to 75%, the content of ferrite ranges from 25% to 45%, the content of cementite is zero, iron phosphide eutectic is in the first level, the graphite spheroidal rate reaches the second level, and the graphite sphere size is in the sixth level. According to the mechanical performance of a casting body of the mixed matrix structure as-cast spheroidal graphite cast iron, the tensile strength of the casting body can be larger than or equal to 600 Mpa, the ductility of the casting body is larger than or equal to 10%, the impact toughness of the casting body is larger than or equal to 25 J / cm<2>, the hardness HB of the casting body ranges from 180-250, and iron is used for replacing steel. In addition, technological processes are simple, control is easy, and the cost is reduced.
Owner:GUANGXI YUCHAI MACHINE PARTS MFG CO LTD
Bottom ring material DPR-D5 of piston rings of marine diesel engine and casting method thereof
The invention discloses a bottom ring material DPR-D5 of piston rings of a marine diesel engine and a casting method of the bottom ring material DPR-D5 of the piston rings of the marine diesel engine. A small amount of copper, molybdenum and nickel are added to cast iron, pearlite can be refined, and graphite can also be refined; chromium is added, so that the mechanical property and the heat resistance can be improved and enhanced; and manganese is added and can be dissolved in a matrix and a carbide, the matrix can be reinforced, the stability of the carbide can be improved, and formation of fine pearlite can be promoted. The graphite form of the cast alloy iron DPR-D5 is flaky graphite IA3-5, the matrix structure of the cast alloy iron DPR-D5 is the pearlite, a small amount of ferrite and a hard phase (comprising cementite and iron phosphide eutectic); detection results show that the cast alloy iron DPR-D5 has the advantages of being moderate in hardness, high in bending strength, good in wear resistance and corrosion resistance and the like, various technical indexes of the cast alloy iron DPR-D5 all reach the CF5 standard requirements of the MAN-B&W material standard, and the cast alloy iron DPR-D5 can replace the imported material CF5 to be used for casting of a bottom ring of the piston rings of the MAN-B&W diesel engine; and in this way, the manufacturing cost is reduced, and the order cycle time is shortened.
Owner:大连锦航新能源设备有限公司
Nitrogen-phosphorus-doped carbon composite iron phosphide three-dimensional rod-like porous material, lithium battery diaphragm, preparation method of lithium battery diaphragm, lithium-sulfur battery and electric equipment
ActiveCN111285348AImprove adsorption capacityStop the spreadSecondary cellsCarbon preparation/purificationCarbon compositesElectrical battery
The invention provides a nitrogen-phosphorus-doped carbon composite iron phosphide three-dimensional rod-like porous material, a lithium battery diaphragm, a preparation method of the lithium batterydiaphragm, a lithium-sulfur battery and electric equipment. A preparation method of the nitrogen-phosphorus-doped carbon composite iron phosphide three-dimensional rod-like porous material comprises the following steps: mixing raw materials including an iron source, a nitrogen-containing organic matter, phytate and an organic solvent, and drying to obtain a precursor; and carrying out heating treatment on the precursor to obtain the nitrogen-phosphorus-doped carbon composite iron phosphide three-dimensional rod-like porous material for the lithium-sulfur battery diaphragm. The preparation method of the lithium battery diaphragm comprises the following steps: mixing raw materials including the nitrogen-phosphorus doped carbon composite iron phosphide three-dimensional rod-like porous material, a binder and a solvent and dispersing to obtain coating slurry; and coating the surface of a diaphragm base material with the coating slurry to obtain the lithium battery diaphragm. According to the nitrogen-phosphorus-doped carbon composite iron phosphide three-dimensional rod-like porous material, the lithium battery diaphragm, the preparation method of the lithium battery diaphragm and thelithium-sulfur battery, the shuttle effect can be effectively solved, and the electrochemical performance of the lithium-sulfur battery is improved.
Owner:湖南桑瑞新材料有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com