Co-editing marker ben-1sgRNA target site, CRISPR/Cas9 co-editing system and application of target site
A technology of ben-164sgrna and target sites, applied in the direction of DNA / RNA fragments, applications, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve problems such as inability to co-edit marker sites, achieve growth advantages, normal phenotypes, and save time Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Example 1: Finding effective ben-1 sgRNA target sites
[0049] The sgRNA site as a co-editing marker must itself be editable, and the editing efficiency is not lower than 10%. In order to find editable high-efficiency sgRNA sites in the ben-1 gene, the inventors selected 4 sgRNA target sites in the process of realizing the present invention, compared the editing efficiencies of these 4 sites, and searched for sites that can be regarded as co-editing marked site.
[0050] 1) Find the sgRNA site: download the coding sequence of ben-1 from the wormbase website, and check the sgRNA efficiency prediction website (such as http: / / crispor.tefor.net / ) to find specific sgRNA target sites with low off-target effects in the coding sequence of the first exon. In this example, the following 3 sgRNA sites were selected.
[0051] ben-1 29 sgRNA target sites:
[0052] ben-1 64 sgRNA target sites:
[0053] ben-1 112 sgRNA target sites:
[0054] The superscripted number i...
Embodiment 2
[0075] Example 2: Screening of F33A8.4 (Q82-, C83A) gene-edited nematodes by random screening method
[0076] Screening for F33A8.4(Q82-,C83A) gene editing by random screening
[0077] The purpose of F33A8.4 (Q82-, C83A) gene editing is to mutate the 82nd amino acid of the gene from glutamine to a stop codon, and to mutate the 83rd amino acid from cysteine to alanine. Such as Figure 4 As shown, the codons corresponding to the 82nd and 83rd amino acids are marked with upper bars. After editing, a Hind III restriction site is generated as shown in the box. Random screening methods such as Figure 5 As shown, the specific screening steps are as follows:
[0078] 1) Select the sgRNA target site: search for the sgRNA target site near the target mutation site Q83 and C84 on the http: / / crispor.tefor.net / website, select the sgRNA site with high specificity and high efficiency, Find the following sgRNA target sites, namely:
[0079] F33A8.4-sgRNA target site: CAAGTTCCGCAGTGCT...
Embodiment 3
[0095] Embodiment three: ben-1 64 sgRNA co-editing for screening F33A8.4(Q82-,C83A) gene editing
[0096] use ben-1 64 sgRNA co-editing method to screen F33A8.4(Q82-,C83A) gene-edited nematodes.
[0097] Compared with the random screening method, using ben-1 64 The sgRNA co-editing system screens heterozygous or homozygous target editing gene mutant nematodes, the steps are as follows:
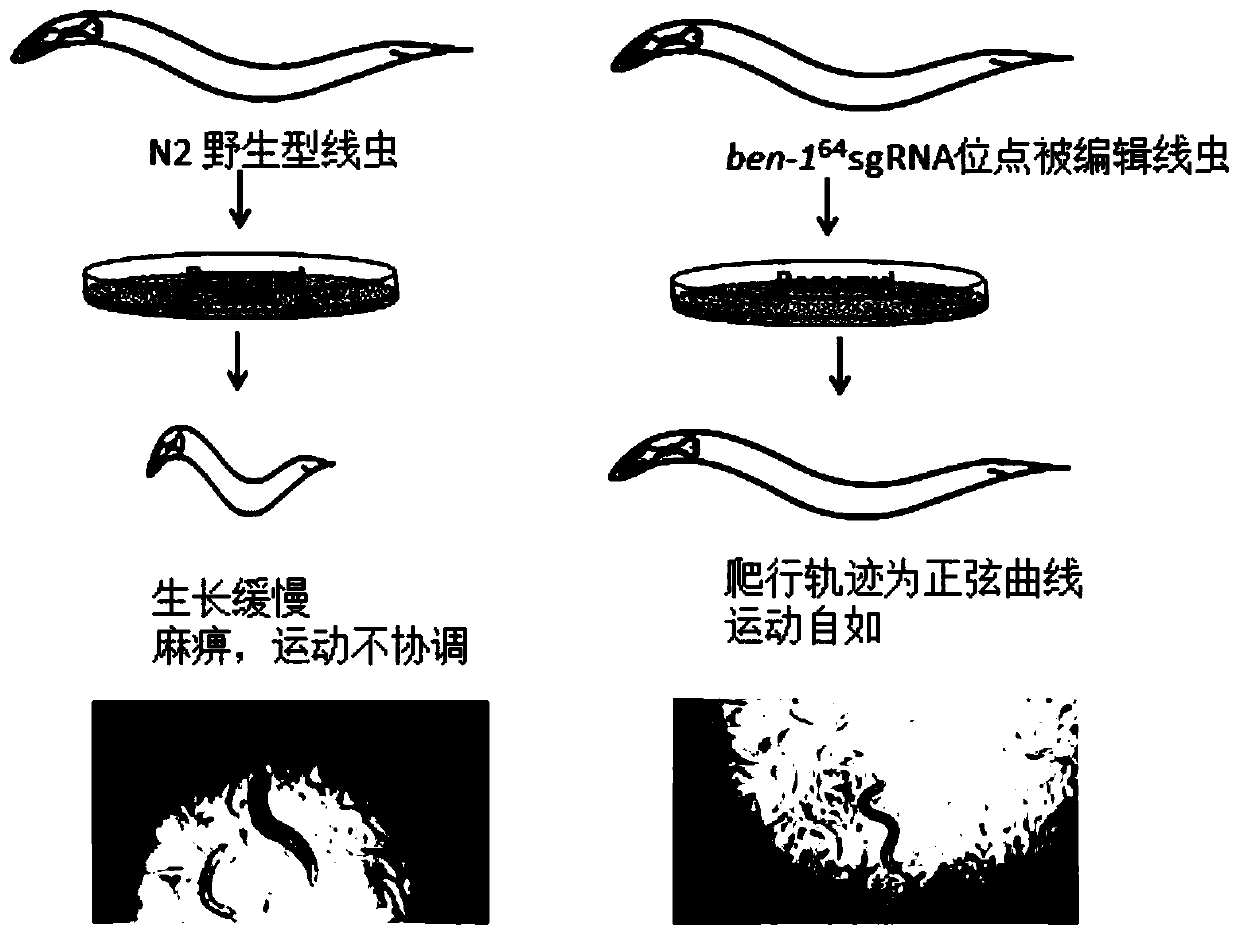
[0098] 1) Preparation of raw materials: The same raw materials as in Example 1 random screening method include: Cas9 plasmid, sgRNA plasmid that specifically recognizes the target mutation site of F33A8.4, reporter gene plasmid, repair template required to obtain the target mutation of F33A8.4, hermaphrodite Caenorhabditis elegans, common nematode culture plate. In addition, additional preparations are required: ben-1 64 sgRNA co-editing plasmids and nematode culture plates at a final concentration of 14 μM benomyl. ben-1 64 The sgRNA co-editing method for screening target editing metho...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com