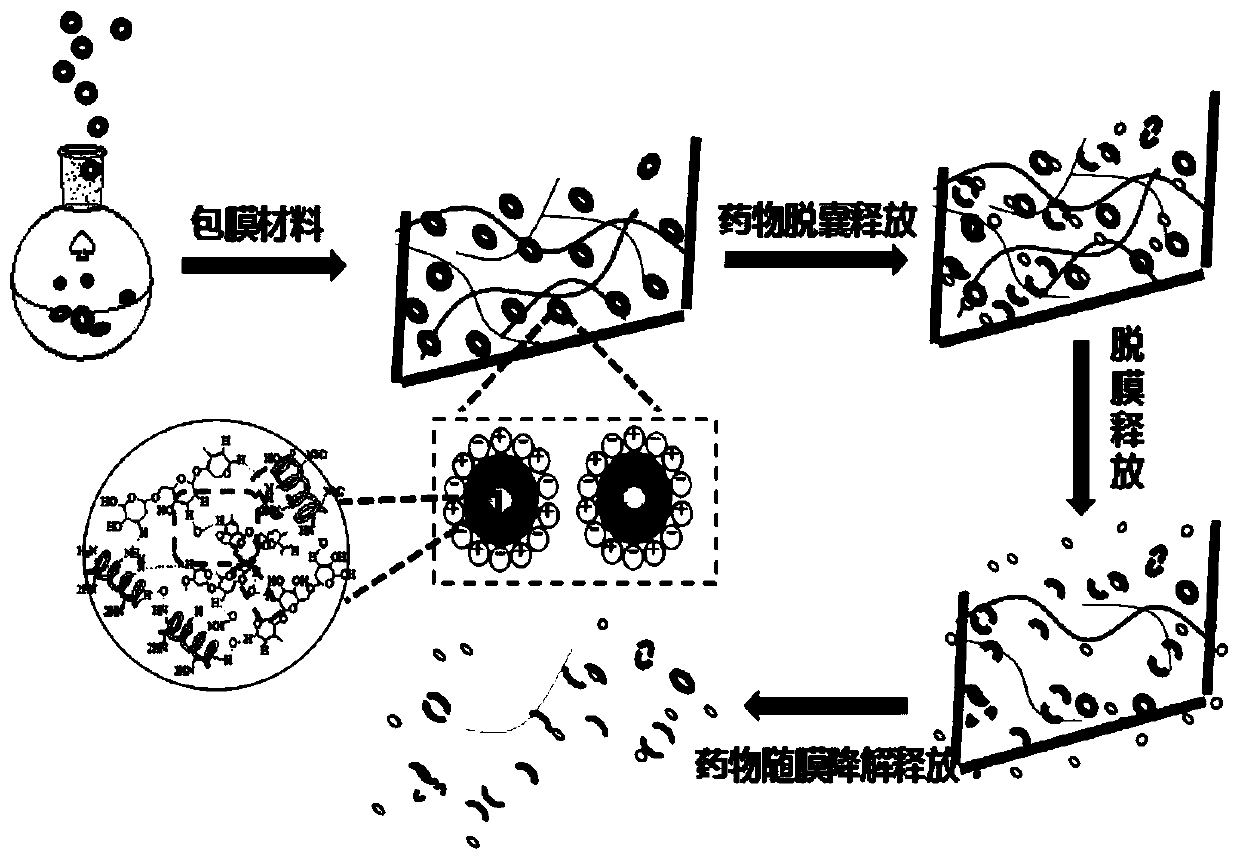
Degradable drug-loaded film material with step-by-step slow release function and preparation method and application of degradable drug-loaded film material
A drug-loaded film and functional technology, which is applied in the field of degradable drug-loaded film materials and its preparation, can solve the problems of limited sustained release requirements, long-lasting effect, and insufficient coating rate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Step 1: Weigh 0.5g of avermectin and dissolve it in 10mL of chloroform, and ultrasonically treat it at 20°C for 20 minutes to obtain a core material solution for use;
[0041]Step 2: Weigh 1g of gelatin at 50°C and stir at a speed of 200r / min, dissolve it in 20mL distilled water until it swells completely to obtain the first wall material solution; weigh 1g of gum arabic at 50°C and stir at 200r / min Stir at a high speed, dissolve in 20mL distilled water until fully swollen to obtain the second wall material solution;
[0042] Step 3: Emulsify the core material solution, the first wall material solution and 2mL sorbitan fatty acid ester at 30°C at a speed of 600r / min for 20min, then add dropwise to the second wall material solution, at 300r / min Stir at a high speed for 1.5h to obtain system A;
[0043] Step 4: Use hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH of system A to 4.0, stir at a speed of 500r / min for 15min, transfer to a cold water bath at 8°C for re-coagulation for 1h; ...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Step 1: Weigh 0.5g of avermectin and dissolve it in 5mL of chloroform, and ultrasonically treat it at 20°C for 20 minutes to obtain a core material solution for use;
[0048] Step 2: Weigh 1g of gelatin at 50°C, stir at a speed of 400r / min, dissolve in 50mL of distilled water until completely swollen to obtain the first wall material solution; weigh 1g of gum arabic at 50°C, stir at a speed of 400r / min Stir at a high speed, dissolve in 50mL distilled water until fully swollen to obtain the second wall material solution;
[0049] Step 3: Emulsify the core material solution, the first wall material solution and 2mL of sorbitan fatty acid ester at 30°C at a speed of 600r / min for 5min, then add dropwise to the second wall material solution, at 300r / min Stir at a high speed for 2 hours to obtain System A;
[0050] Step 4: Use hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH of system A to 5.0, stir at a speed of 500r / min for 15min, transfer to a cold water bath at 8°C for re-coagulation ...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Step 1: Weigh 0.5g of abamectin and dissolve it in 20mL of chloroform, and ultrasonically treat it at 20°C for 20min to obtain a core material solution for use;
[0055] Step 2: Weigh 1g of gelatin at 50°C, stir at a speed of 300r / min, dissolve in 60mL of distilled water until completely swollen to obtain the first wall material solution; weigh 1g of gum arabic at 50°C, stir at a speed of 300r / min Stir at a high speed, dissolve in 60mL distilled water until completely swollen to obtain the second wall material solution;
[0056] Step 3: Emulsify the core material solution, the first wall material solution and 2mL of sorbitan fatty acid ester at 30°C at a speed of 600r / min for 30min, then add dropwise to the second wall material solution, at 300r / min Stir at a high speed for 1h to obtain system A;
[0057] Step 4: Use tartaric acid to adjust the pH of system A to 4.5, stir at a speed of 500r / min for 15min, transfer to a cold water bath at 8°C for re-coagulation for 1h; ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com