Treating agent for jointly removing heavy metal ions in industrial wastewater
A technology for heavy metal ions and industrial wastewater, applied in the field of water treatment, can solve problems such as complex treatment process, and achieve the effect of stabilizing metal precipitates
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
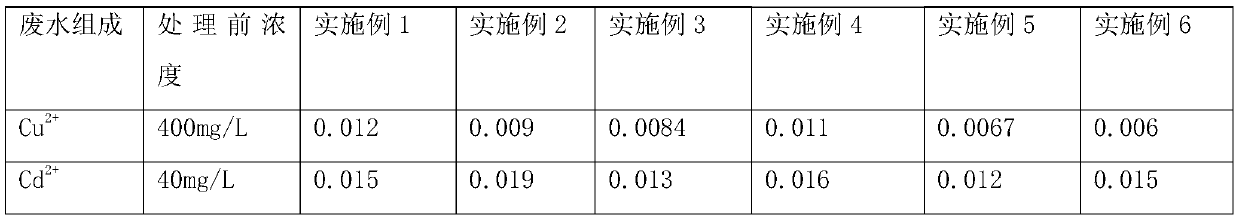
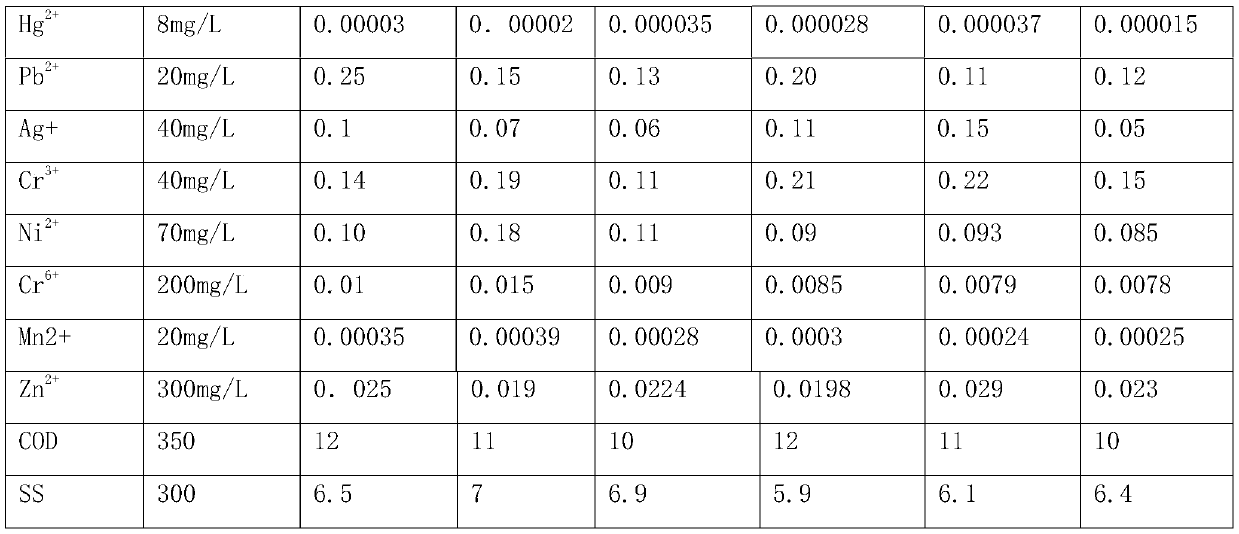
[0017] The treatment agent for the combined removal of heavy metal ions in industrial wastewater in this embodiment, the raw materials include the following components by weight: 40 parts of polystyrene divinylbenzene resin microspheres, 5 parts of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, dithiocarbamic acid 5 parts of salt, 5 parts of polyethyleneimine, 10 parts of glutaraldehyde, 5 parts of black wattle tannin, 10 parts of poly(2-acrylamide-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid), 8 parts of maleic anhydride, 4 parts of hydrocarbyl dithiophosphate, 10 parts of polyaspartic acid, 5 parts of 2-amino-3-mercaptopropionyl chitosan, 2 parts of sodium polyethyleneimine xanthate, 2 parts of thioglycolic acid, ortho 1 part of dibutyl phthalate, 6 parts of polyepoxysuccinic acid, 1 part of dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate, 1 part of crosslinking agent, and 1 part of coupling agent.
Embodiment 2
[0019] The treatment agent for the joint removal of heavy metal ions in industrial wastewater of this embodiment, the raw materials include the following components by weight: 50 parts of polystyrene divinylbenzene resin microspheres, 15 parts of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, dithiocarbamic acid 12 parts of salt, 15 parts of polyethyleneimine, 20 parts of glutaraldehyde, 12 parts of black wattle tannin, 15 parts of poly(2-acrylamide-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid), 12 parts of maleic anhydride, 12 parts of hydrocarbyl dithiophosphate, 20 parts of polyaspartic acid, 15 parts of 2-amino-3-mercaptopropionyl chitosan, 6 parts of sodium polyethyleneimine xanthate, 6 parts of thioglycolic acid, ortho 6 parts of dibutyl phthalate, 12 parts of polyepoxysuccinic acid, 5 parts of dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate, 3 parts of crosslinking agent, and 3 parts of coupling agent.
Embodiment 3
[0021]The treatment agent for the combined removal of heavy metal ions in industrial wastewater of this embodiment, the raw materials include the following components by weight: 40 parts of polystyrene divinylbenzene resin microspheres, 15 parts of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, dithiocarbamic acid 5 parts of salt, 15 parts of polyethyleneimine, 10 parts of glutaraldehyde, 12 parts of black wattle tannin, 10 parts of poly(2-acrylamide-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid), 12 parts of maleic anhydride, 4 parts of hydrocarbyl dithiophosphate, 20 parts of polyaspartic acid, 5 parts of 2-amino-3-mercaptopropionyl chitosan, 6 parts of sodium polyethyleneimine xanthate, 2 parts of thioglycolic acid, ortho 6 parts of dibutyl phthalate, 6 parts of polyepoxysuccinic acid, 5 parts of dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate, 1 part of crosslinking agent, and 3 parts of coupling agent.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com