Femtosecond laser processing method of optical fiber lens
A technology of femtosecond laser processing and fiber optic lens, which is applied in the direction of cladding optical fiber, optical waveguide light guide, laser welding equipment, etc., can solve the problems of optical fiber end face deformation, etc., to avoid stress damage, high processing accuracy, and avoid long-pulse laser thermal effect Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0066] The embodiments of the present invention use a femtosecond laser with a repetition rate of 1 kHz combined with hydrofluoric acid chemical corrosion to prepare a spherical fiber optic lens, specifically as follows:
[0067] Original material: Single-mode silica fiber.
[0068] The preparation steps of the tapered optical fiber convex lens are described in detail as follows:
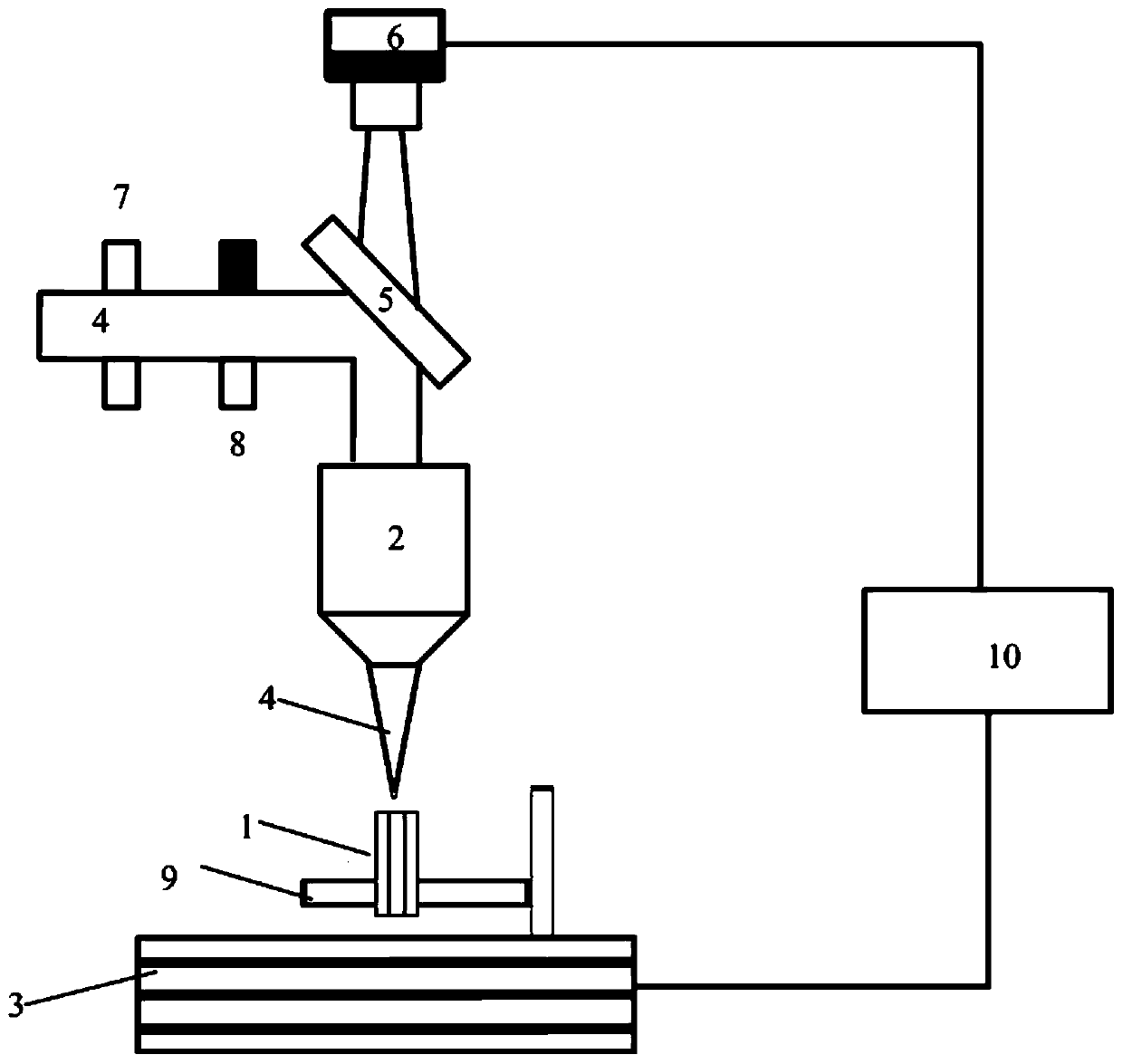
[0069] (1) The single-mode quartz optical fiber 1 is cut out with a cutting knife to form a flat fiber end face, and then fixed on the five-dimensional electric displacement stage 3, as figure 1 shown;
[0070] (2) The repetition frequency of the femtosecond laser 4 is 1 kHz, the pulse width is 50 fs, and the power is set to 5 mW. A microscopic objective lens 2 with 20× and a numerical aperture of 0.3 is selected to focus the femtosecond laser 4 inside the optical fiber 1 through the microscopic objective lens 2 . The focusing position of the femtosecond laser 4 in the optical fiber is controlled...
Embodiment 2
[0075] In the embodiment of the present invention, a fiber lens embryo is etched by layer-by-layer scanning with a femtosecond laser, and then etched to produce a fiber lens.
[0076] Original material: Single-mode silica fiber.
[0077] (1) Fixing of the silica optical fiber 1 refers to the corresponding process of the first embodiment.
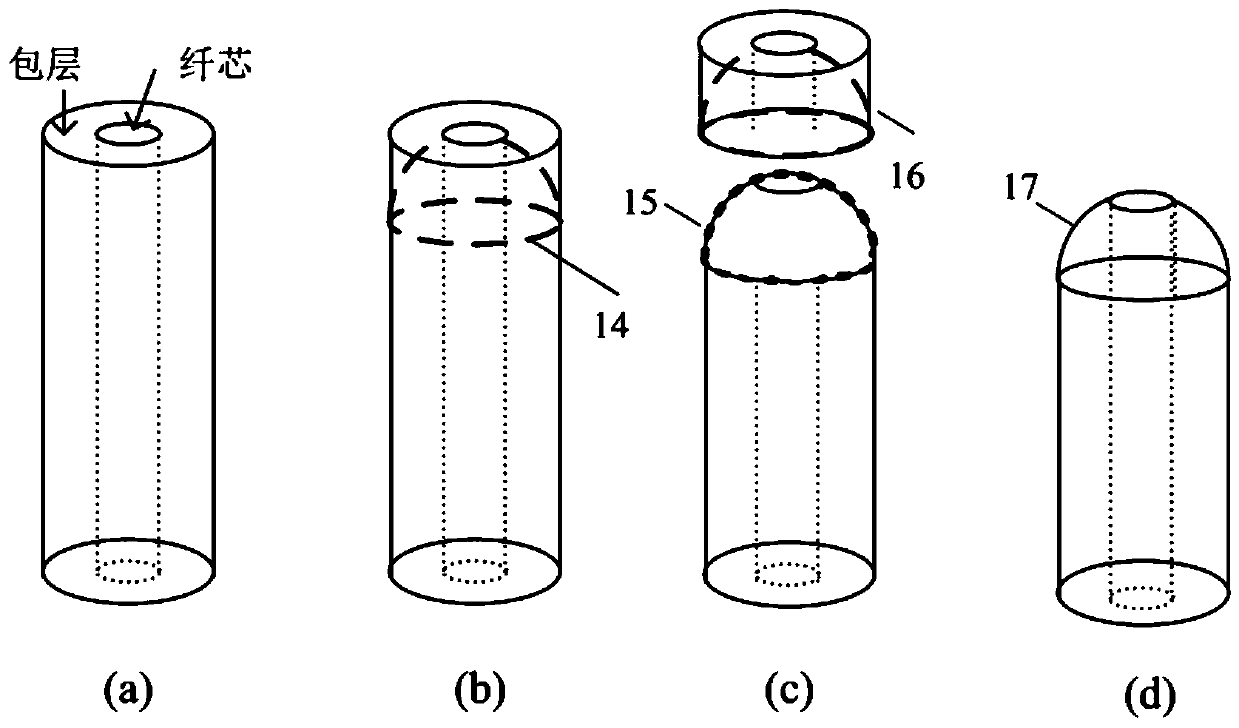
[0078] (2) The femtosecond laser 4 is focused on the end face of the fiber through the F-theta lens, and the femtosecond laser is scanned and processed on the end face of the fiber by means of a scanning galvanometer, and the end face of the fiber is removed layer by layer to form a tapered fiber lens embryo, see Figure 5 (a), the scanning speed is 50 μm / s, the cone angle is set to 30°, the laser power is 10 mW, and the repetition rate is 1 kHz.
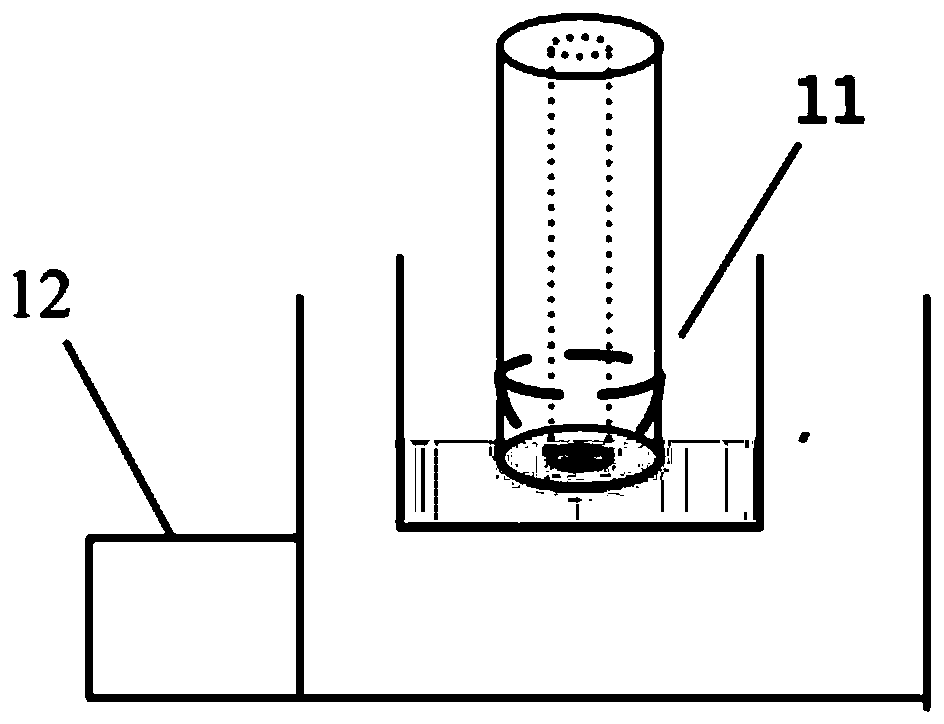
[0079] (3) The surface of the tapered fiber optic lens blank is still rough. Place the tapered fiber optic lens blank in 5% hydrofluoric acid and corrode for 20 minutes to form a tapered lens with ...
Embodiment 3
[0082] In the embodiment of the present invention, after using femtosecond laser to irradiate the end face of the optical fiber at a fixed point, the concave lens structure is processed by hydrofluoric acid corrosion, the details are as follows:
[0083] Original material: Single-mode silica fiber.
[0084] (1) Fixing of the silica optical fiber 1 refers to the corresponding process of the first embodiment.
[0085] (2) The femtosecond laser 4 is focused on the end face of the optical fiber 1 after being focused by the 20 times microscope objective lens 2. By controlling the five-dimensional electric displacement stage, the femtosecond laser is focused on the end face surface of the optical fiber 1 to be processed. Focus on the center of the fiber core, and control the fixed-point irradiation through the shutter 7 for 10s. The power of the femtosecond laser 4 is set to 10mW, and the numerical aperture of the 20x microscope objective lens 2 is 0.3. Grooves are formed in the fi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com