Global optimization design method of photoelectric imaging system based on computational imaging
An optoelectronic imaging and computational imaging technology, applied in computing, image enhancement, image analysis, etc., can solve the problems of lack of depth information, bulky optical system, high processing and assembly costs, and reduce the difficulty of design.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
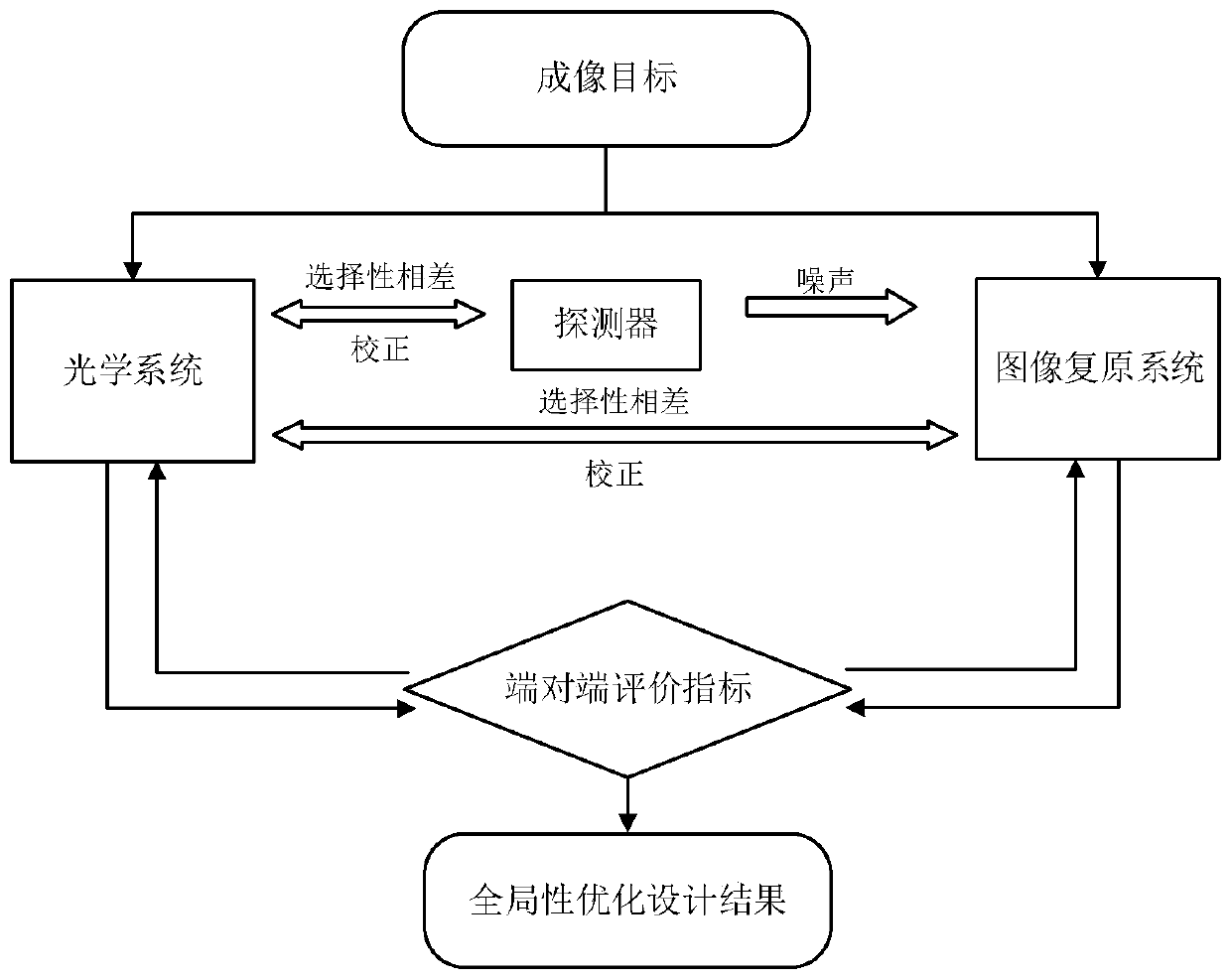
[0042] Please refer to figure 1 , figure 1 It is a flowchart of a global optimization design method for a photoelectric imaging system based on computational imaging provided by an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in the figure, a global optimal design method for a photoelectric imaging system based on computational imaging in this embodiment ,include:
[0043] S1: Design the initial structure of the lens of the optical system according to the imaging requirements, simulate and output the optical image, and obtain the PSF (point spread) function of the optical image;
[0044] S2: adding analog noise of the detector to the optical image to obtain a degraded image;
[0045] S3: Using an image restoration system to perform image restoration on the degraded image to obtain a restored image;
[0046] S4: Establishing an image quality evaluation index, and performing an end-to-end image quality evaluation on the restored image and the optical image, to obtain an eval...
Embodiment 2
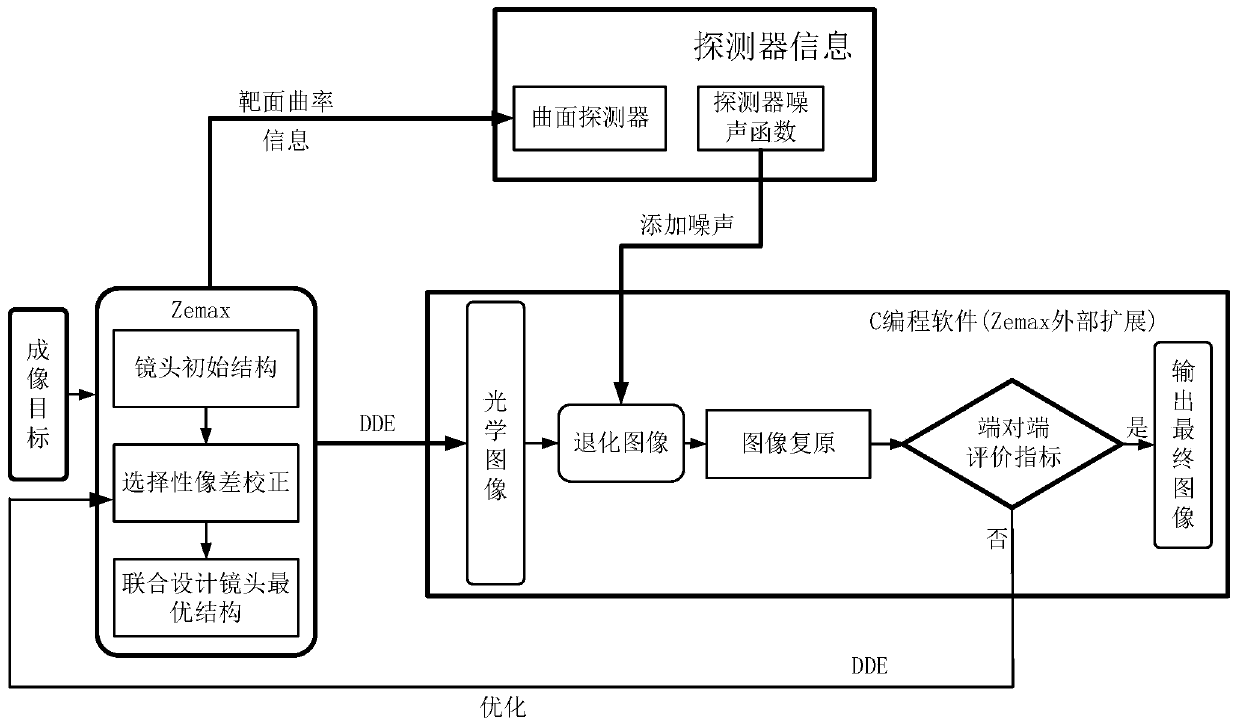
[0054] This embodiment is a specific description of the global optimization design method of the photoelectric imaging system based on computational imaging in the first embodiment, and the step S1 includes:
[0055] S11: the initial structure of the lens of the designed optical system is a simple lens optical structure, and according to the Zernike (Zernike) polynomial weighted summation, the PSF function and MTF (modulation transfer) function of the optical image are obtained,
[0056]
[0057]
[0058] In the formula, λ represents the central wavelength of the imaging band of the optical system, D represents the diameter of the exit pupil, and A p Represents the exit pupil area, FT represents Fourier transform, p(x,y) represents the exit pupil function, W(x,y) represents the wavefront optical path difference of each monochromatic geometric aberration;
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com