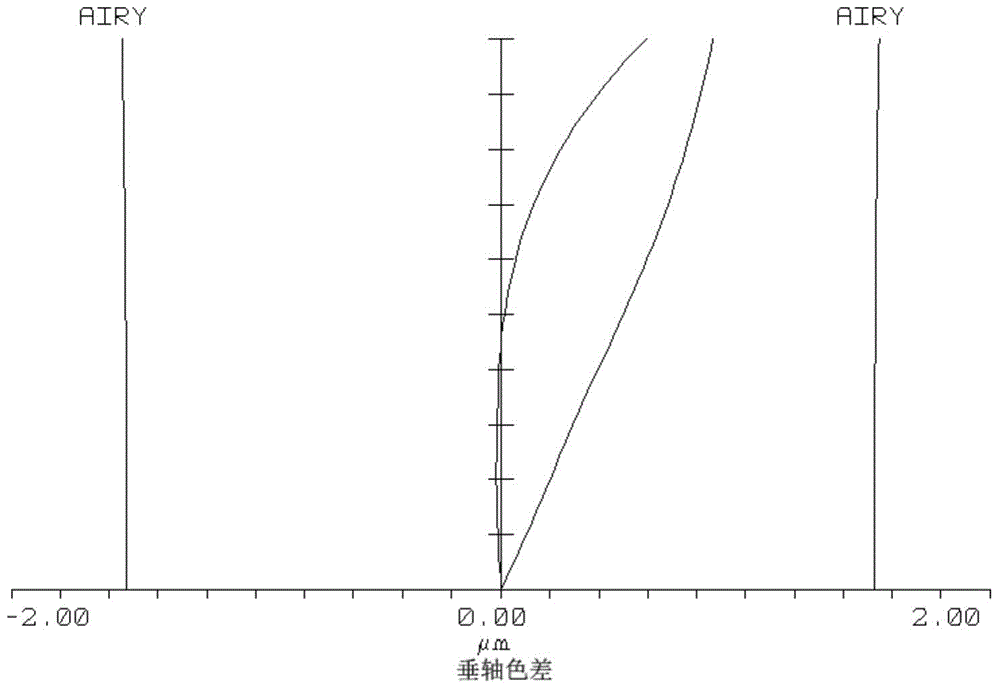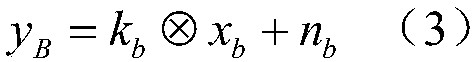Patents
Literature
63 results about "Simple lens" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In optics, a simple lens or singlet lens is a lens consisting of a single simple element. Typical examples include a magnifying glass or a lens in a pair of simple reading glasses. Simple lenses are prone to aberrations, especially chromatic aberration. They cannot be used for precise imaging and make poor camera lenses. They are commonly used for laser applications, however, where the beams are both monochromatic (minimizing chromatic aberration) and narrow (minimizing spherical aberration).
Semiconductor light source with optical feedback
InactiveUS20070063125A1Avoid mistakesReduce sensitivityPhotometry using reference valueLaser detailsBeam splitterPhotodiode
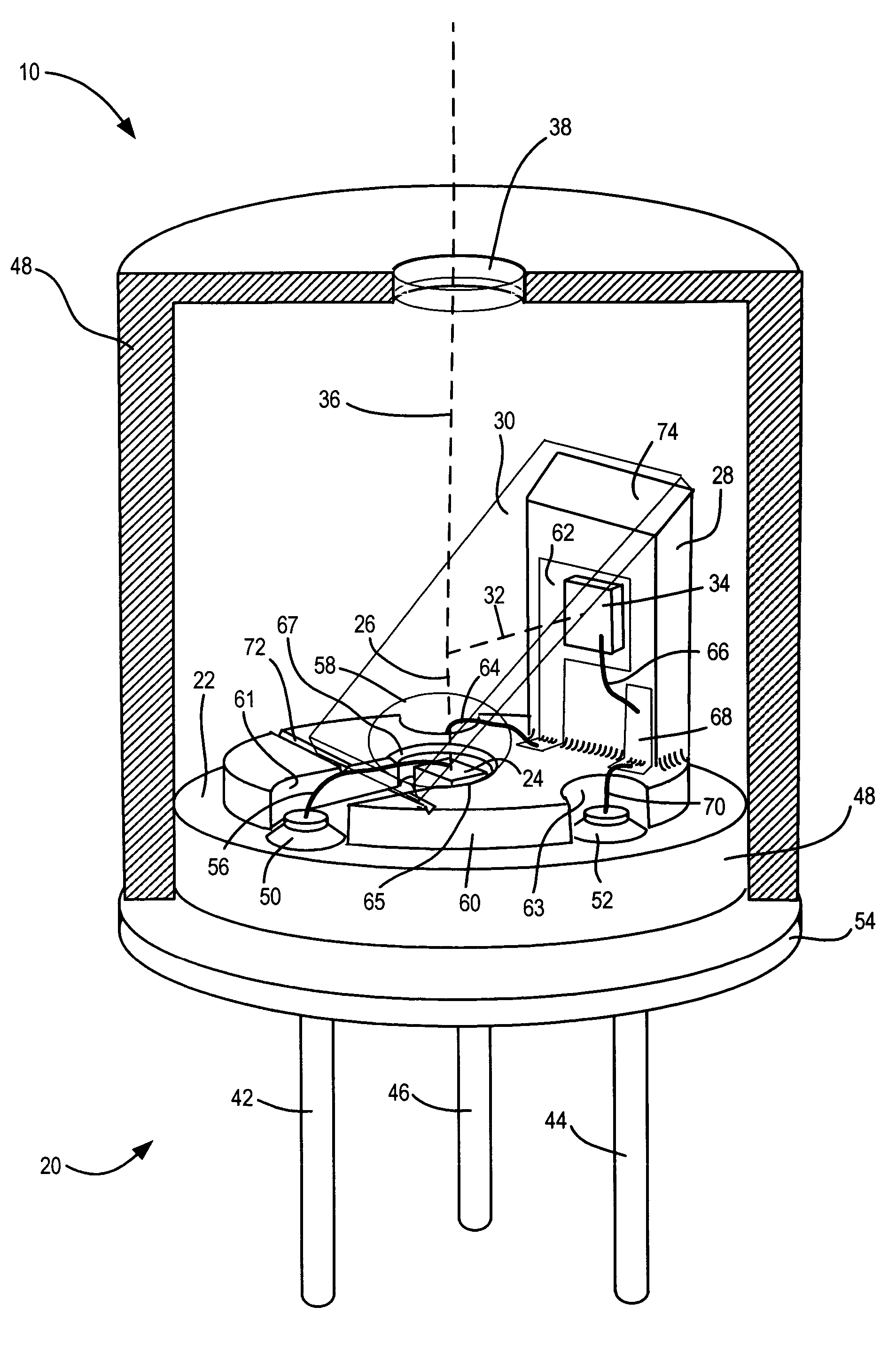
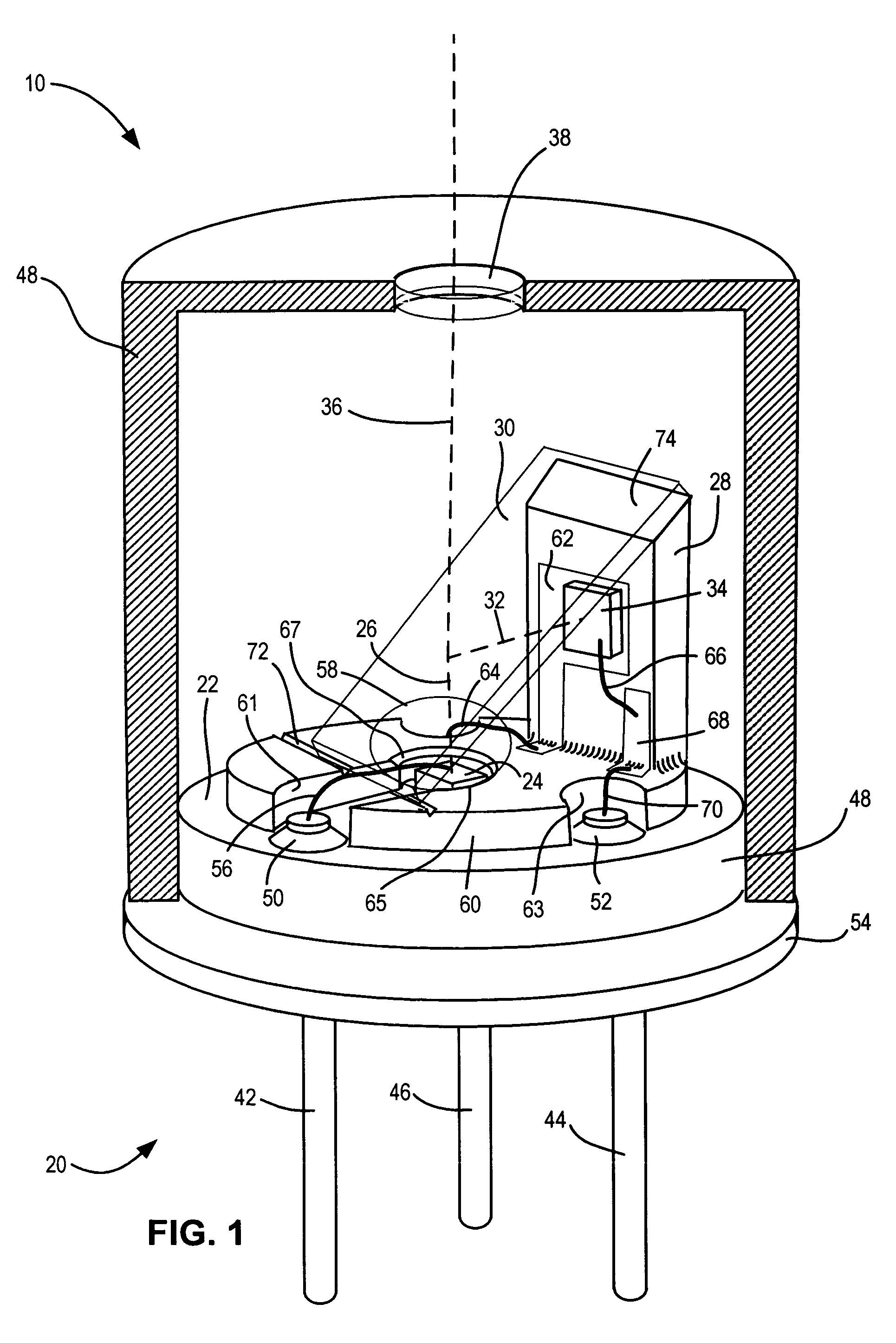
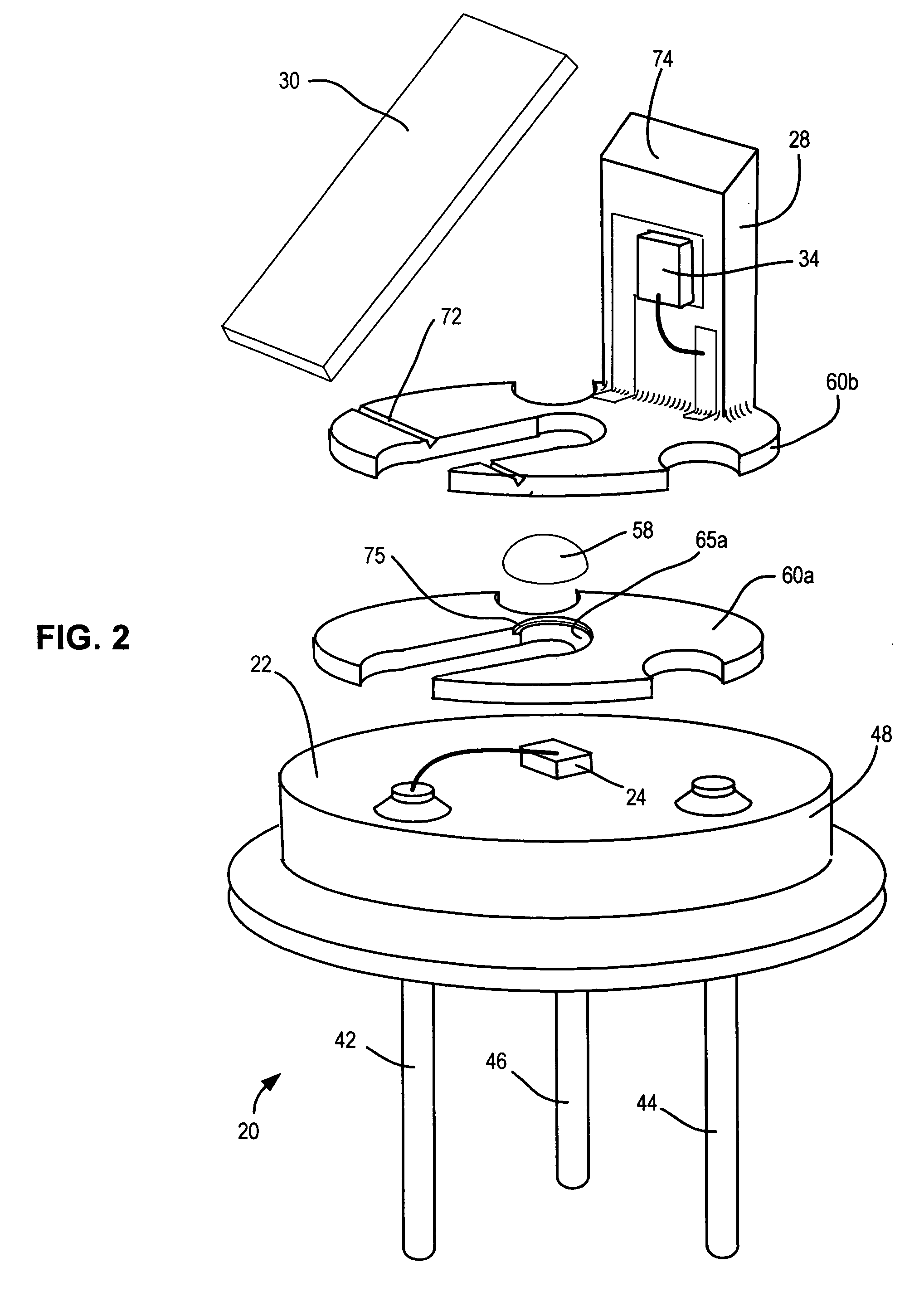
A semiconductor light source with optical feedback includes a vertical member extending upward from an upper horizontal surface of a header parallel to a vertical beam projected from a semiconductor light-emitting element mounted on the horizontal surface of the header wherein the vertical member supports a light-sensing element for receiving light reflected transversely from the vertical beam by a beam splitter supported by the vertical member. The vertical beam passing through the beam splitter passes through a window or filter in a cap mounted on the header and covering the light-emitting element, the light-sensing element, the beam splitter, and the vertical member. Substantially all of the transversely reflected light impinges on the light-sensing element and can be used to control the power to the light-emitting element. A simple lens can by used to collimate the beam. Interior portions of the unit are formed from light absorbing materials such as black ceramic, black plastic, anodized aluminum, etc. The combined effect of the non-reflective interior of the assembly, the orientation of the photo-diode to have an acceptance cone perpendicular to the beam axis, the small entrance pupil, and the optical filter reduces ambient radiation in the unit by as much as −75 dB of the level outside the device. This reduces noise and drift in the automatic power control loop to produce constant intensity in the output light beam.
Owner:USL TECH
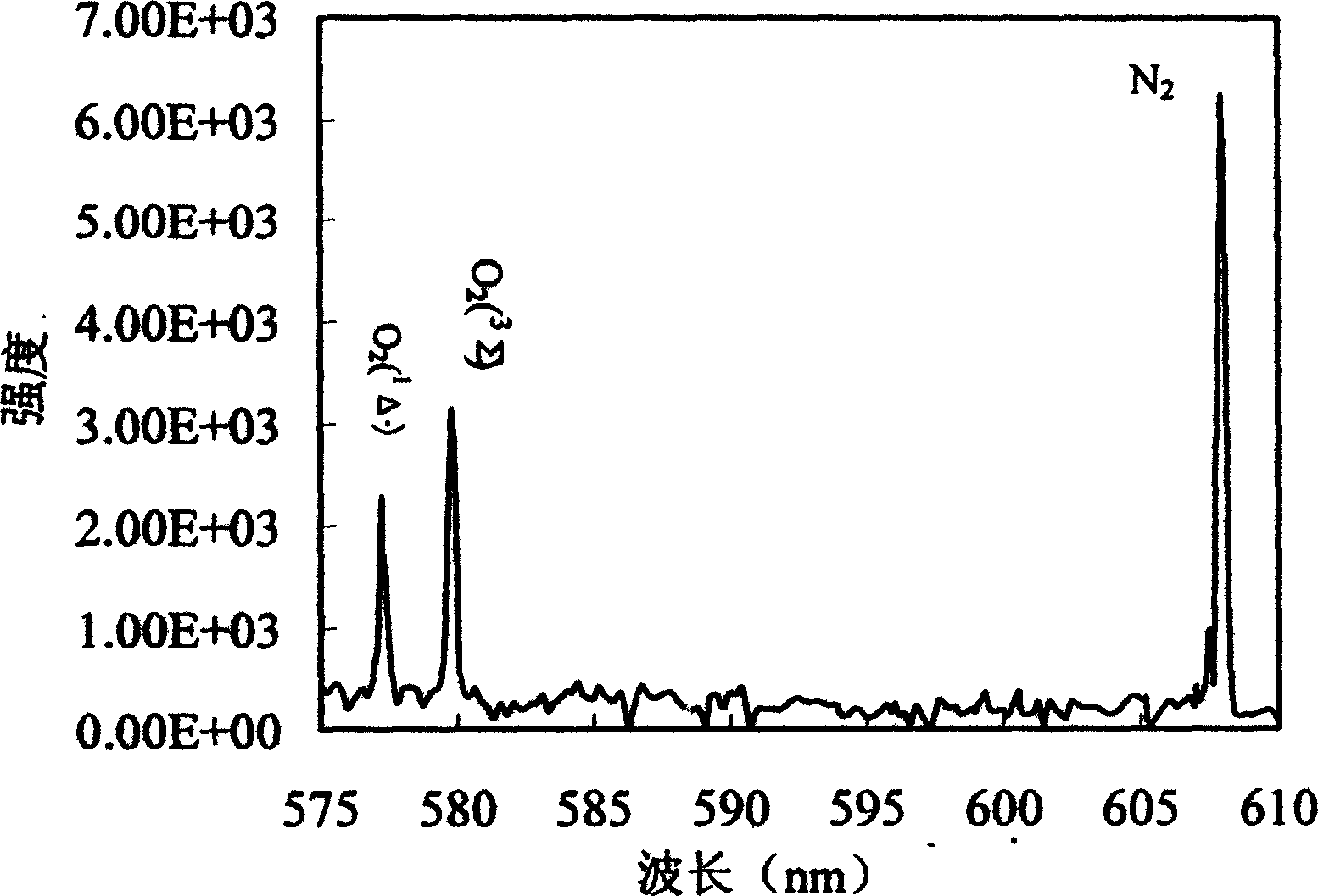
Testing method and system for measuring gas component concentration using spontaneous Raman scattering technology
InactiveCN1467492AHigh strengthImprove signal-to-noise ratioRaman scatteringCollection systemData treatment
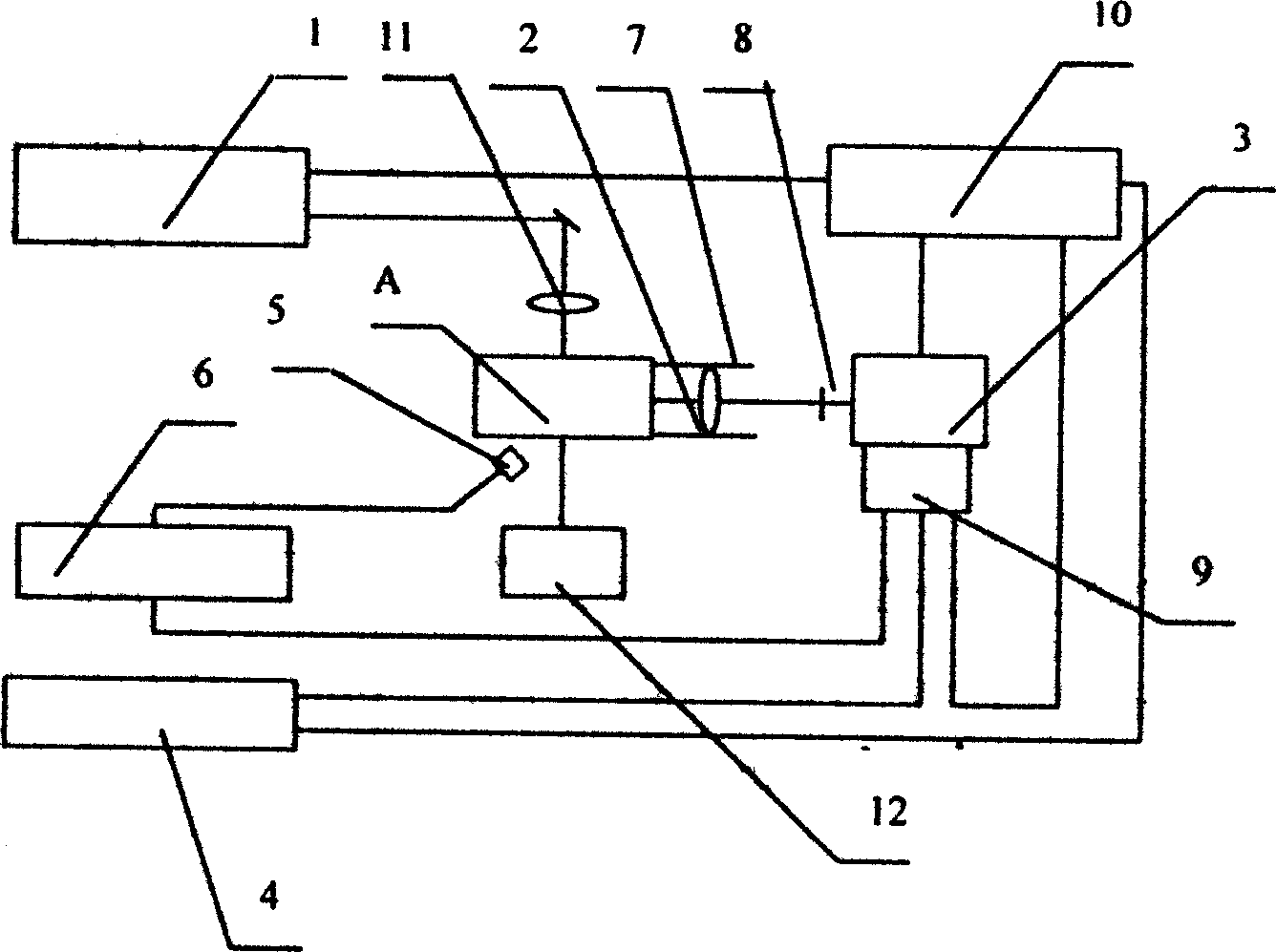
The present invention discloses the method and system for measuring the gas component by the spontaneous Raman dissemination process wherein the system comprises a laser, a collecting system, a detection system and a data processing system, the laser device sends linear polarization laser, the collecting system is a lens, the detecting system is a grating optical spectrum device with a ICCD array detector which can be used to regulate the optical spectrum of the sampled article. The invention can greatly increase the signal-to-noise ratio, and the detecting system can enable the grating and central wavelength to be regulated at any time according the requirement of the test, thus facilitating the acquisition of the Raman spectrum of the different components.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
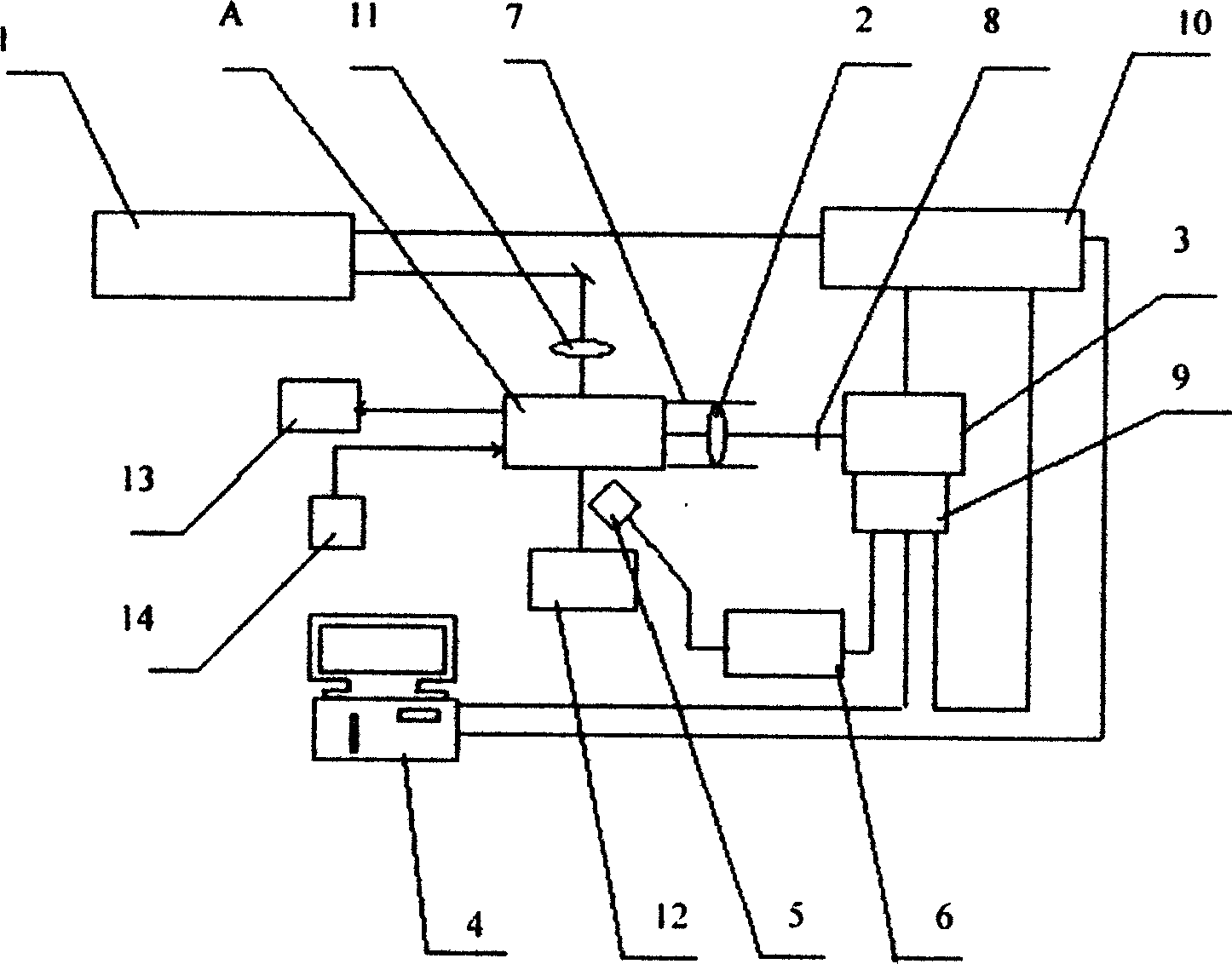
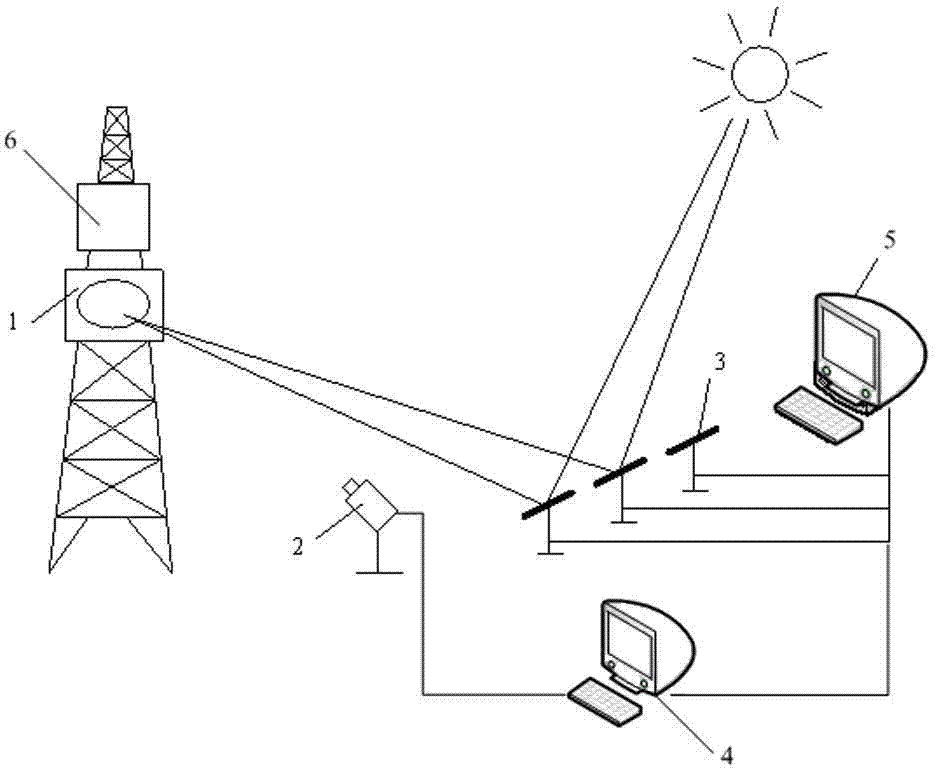
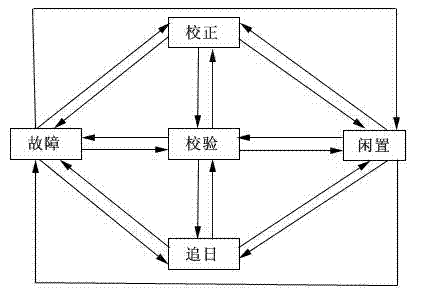
Mirror field dispatching system and method for tower type solar thermal power generation system
ActiveCN102778899AOvercome subjectivityOvercome limitationsControl using feedbackTesting optical propertiesHeliostatImaging processing
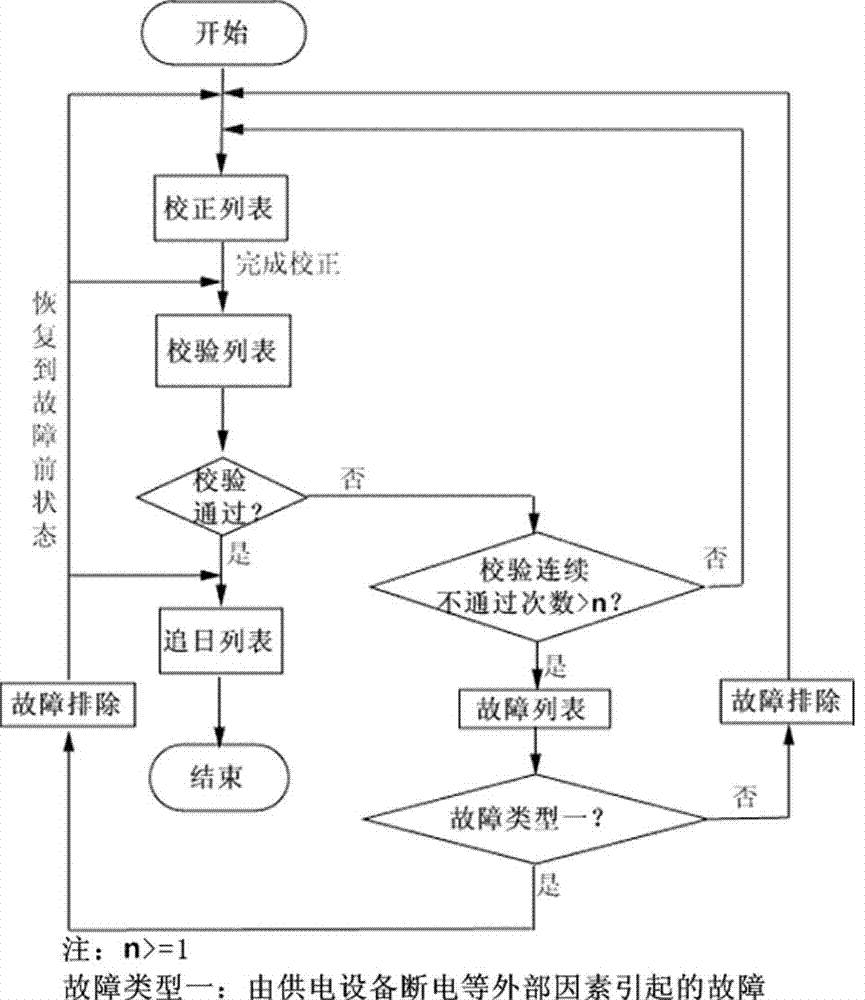
The invention discloses a mirror field dispatching system and method for a tower type solar thermal power generation system. The system comprises a receiver, a heliostat, a light spot imaging device, a light spot collection device, an image processing device and a mirror field control system for switching or regulating the single mirror state of the heliostat to control the whole mirror field. The method comprises the following steps of: correcting the heliostat successfully installed in the mirror field; verifying the corrected heliostat, judging whether the heliostat is verified or not, and seeking the sun by the verified heliostat; repeatedly correcting an unverified heliostat, and taking the heliostat continuously unverified many times as a fault heliostat, wherein the heliostat during sun seeking is needed to be regularly verified so as to solve the problem that the accuracy is lowered due to long term running of the heliostat. Through scientifically and reasonably dispatching the heliostat, correction, verification as well as fault detection and diagnosis of the heliostat are finished on the premise of ensuring the sun seeking efficiency of the mirror field to the maximum, and safe and efficient operation of the mirror field is ensured.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SUPCON SOLAR TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
General surgery three-dimensional micrography camera shooting presentation device
ActiveCN103340686AEasy to adjust the distanceEasy to adjust the angleDiagnosticsSurgeryDigital videoFiber
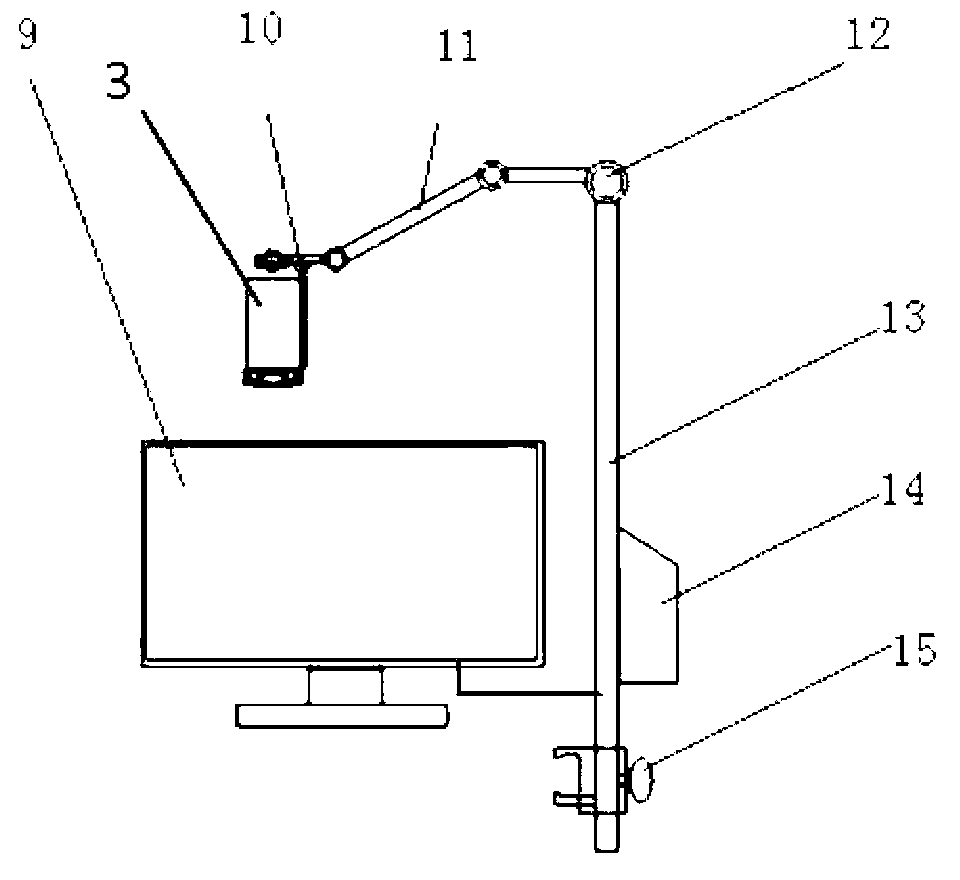
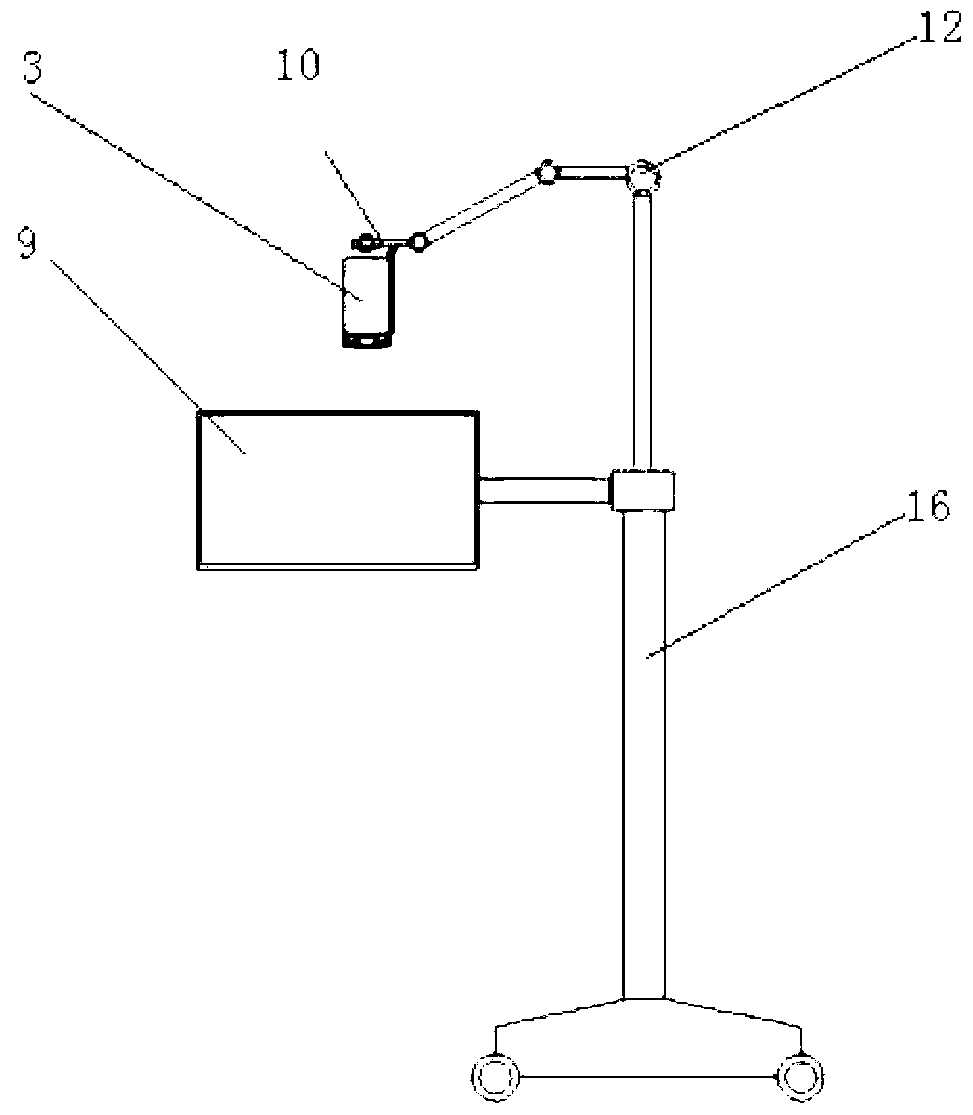
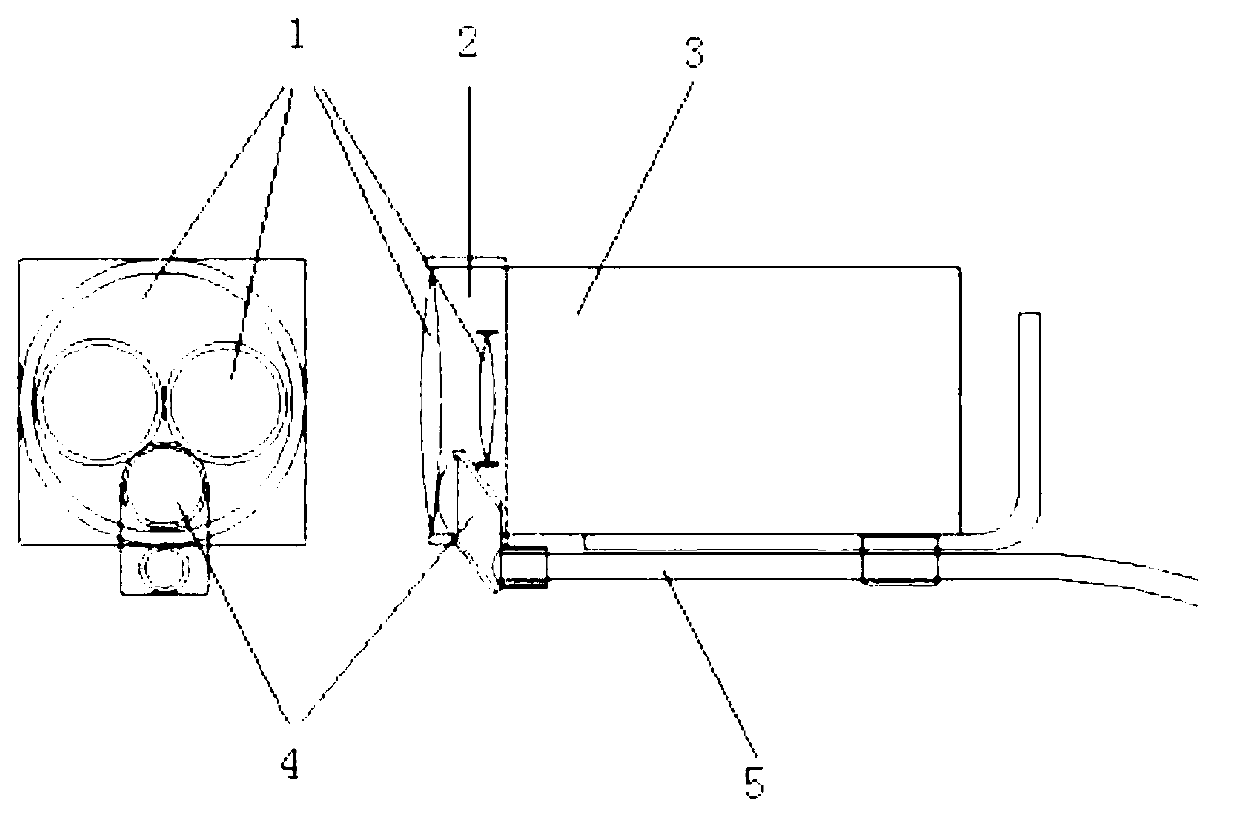
The invention relates to a general surgery three-dimensional micrography camera shooting presentation device which is formed by a 3D high-definition digital video, a 3D high-definition liquid crystal displayer and an adjusting support. The 3D high-definition digital video is a small integrated 3D high-definition digital video, a micrography adapter, a micrography pick-up lens and a focus light source are additionally arranged in front of an original lens of the small integrated 3D high-definition digital video, and the small integrated 3D high-definition digital video is fixed by the bed side type, suspension type or floor stand type adjusting support and connected with the 3D high-definition liquid crystal displayer. The micrography pick-up lens is composed of a single lens or a plurality of lenses, and the focal length of the micrography pick-up lens is 250mm to 500mm. The focusing light source is a cold light source which connected through light fibers or an LED light source, a focusing lens is additionally arranged at the front end of the focusing light source, and the optical axis focus of the focusing light source is identical with the focus of the 3D micrography pick-up lens. The general surgery three-dimensional micrography camera shooting presentation device is small and light, has the functions of surgery lighting, 3D real-time high-definition camera shooting, videotaping, recording, displaying, image transmitting and the like, and is suitable for multidiscipline micrography surgeries and general open surgeries in surgery systems.
Owner:上海昌宁医疗科技有限公司
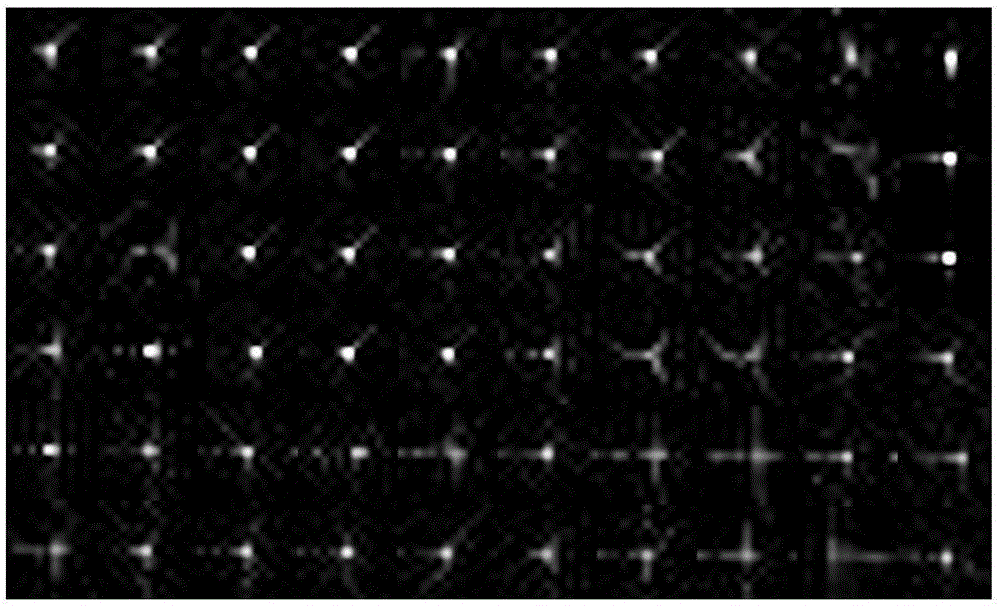
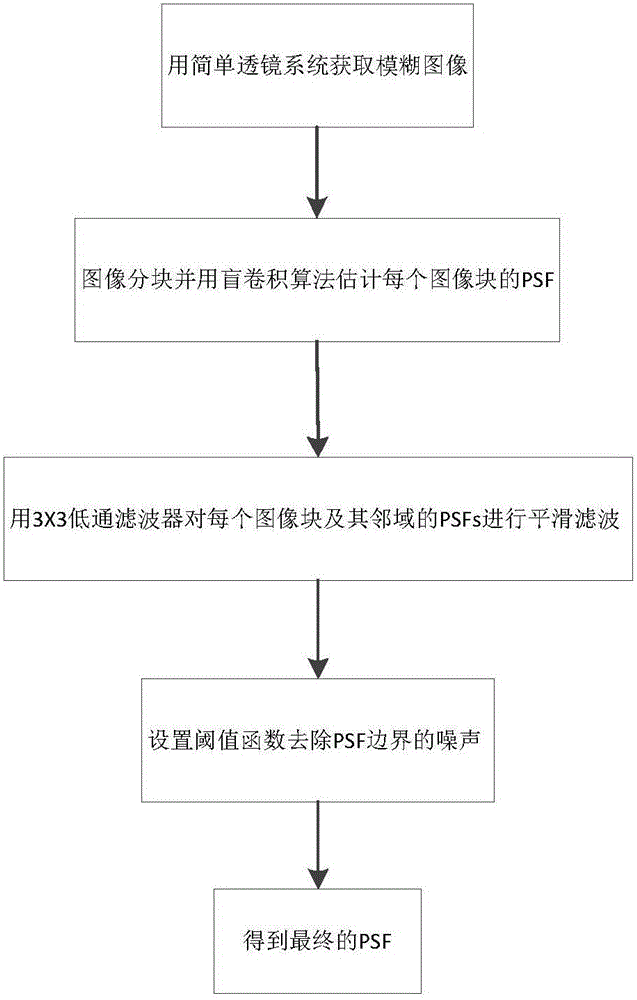
Spatial variation point diffusion function smoothing method based on simple lens calculating imaging
ActiveCN106709879AReduced stabilityImprove robustnessImage enhancementImage analysisDiffusion functionSimple lens
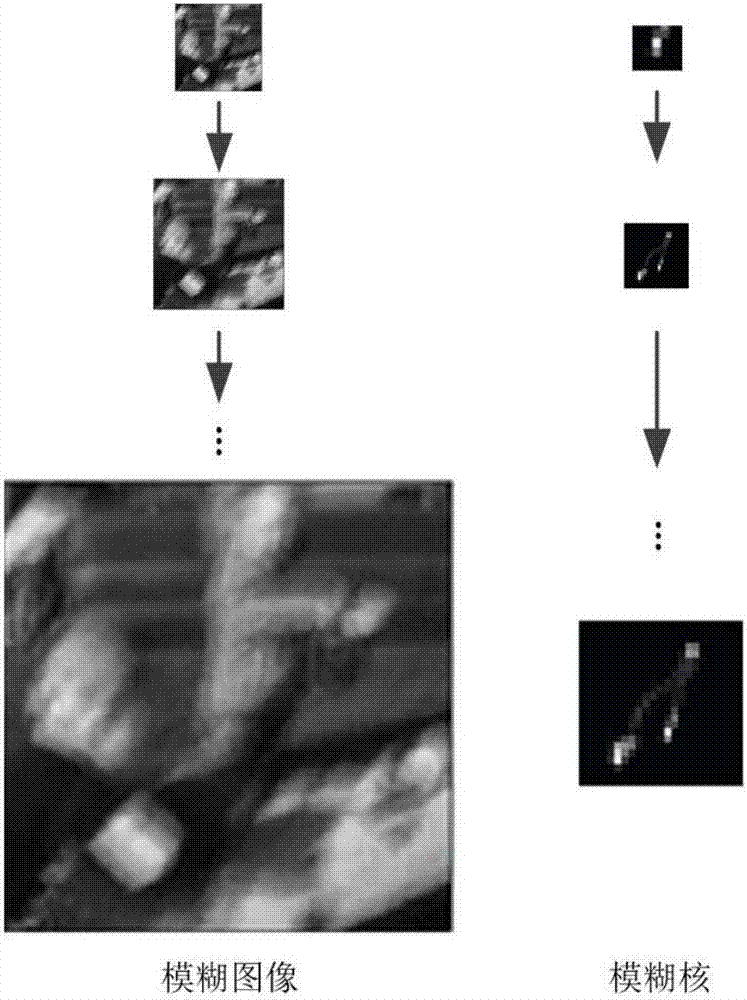
The invention provides a spatial variation point diffusion function smoothing method based on simple lens calculating imaging. The method is characterized by fully using characteristics of sparsity, similarity and the like of a single lens fuzzy kernel; firstly, using a blind convolution algorithm to estimate a fuzzy kernel of each image block, and combining fuzzy kernel TV priori; and then carrying out smoothing and de-noising processing on the fuzzy kernel, and based on a filtered PSF of neighborhood information, replacing an existing PSF. Compared to the prior art, by using the method of the invention, a complex experiment environment and equipment are not needed, the spatial variational PSF can be estimated through combining a correlation algorithm based on a simple lens system; robustness of a deconvolution process is increased; and a noise, a ringing effect and the like are restrained.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
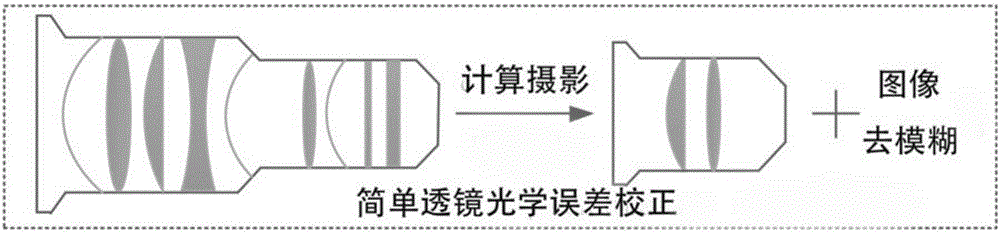
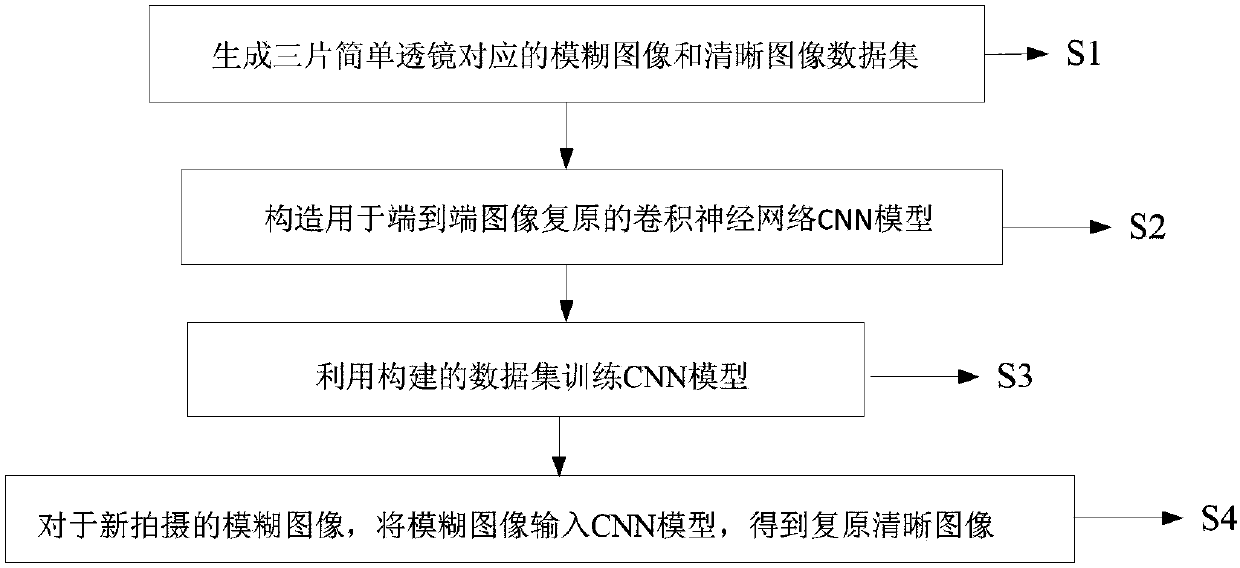
Three-sheet simple lens image restoration method based on convolution neural network CNN
InactiveCN107730469AProcessing speedAvoid blind convolutionImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImaging processing
The invention discloses a three-sheet simple lens image restoration method based on a convolution neural network CNN. The method comprises steps of firstly, generating a blurred image and clear imagedata set corresponding to three sheets of simple lenses; constructing a convolution neural network CNN model used for end-to-end image restoration; by use of the generated data set to train the CNN model; and for newly shot blurred images, by use of the trained CNN model, directly obtaining restored clear images. According to the invention, a large number of optimization iteration processes of blind convolution and non-blind convolution image restoration in the current method can be avoided; there is no need to independently estimate the PSF of the simple lenses, so the image restoration process of the three sheets of simple lenses are quite simple and convenient; the image processing speed is fast; and the method is very important in simple lens calculation and imaging field.
Owner:CHANGSHA PANODUX TECH CO LTD
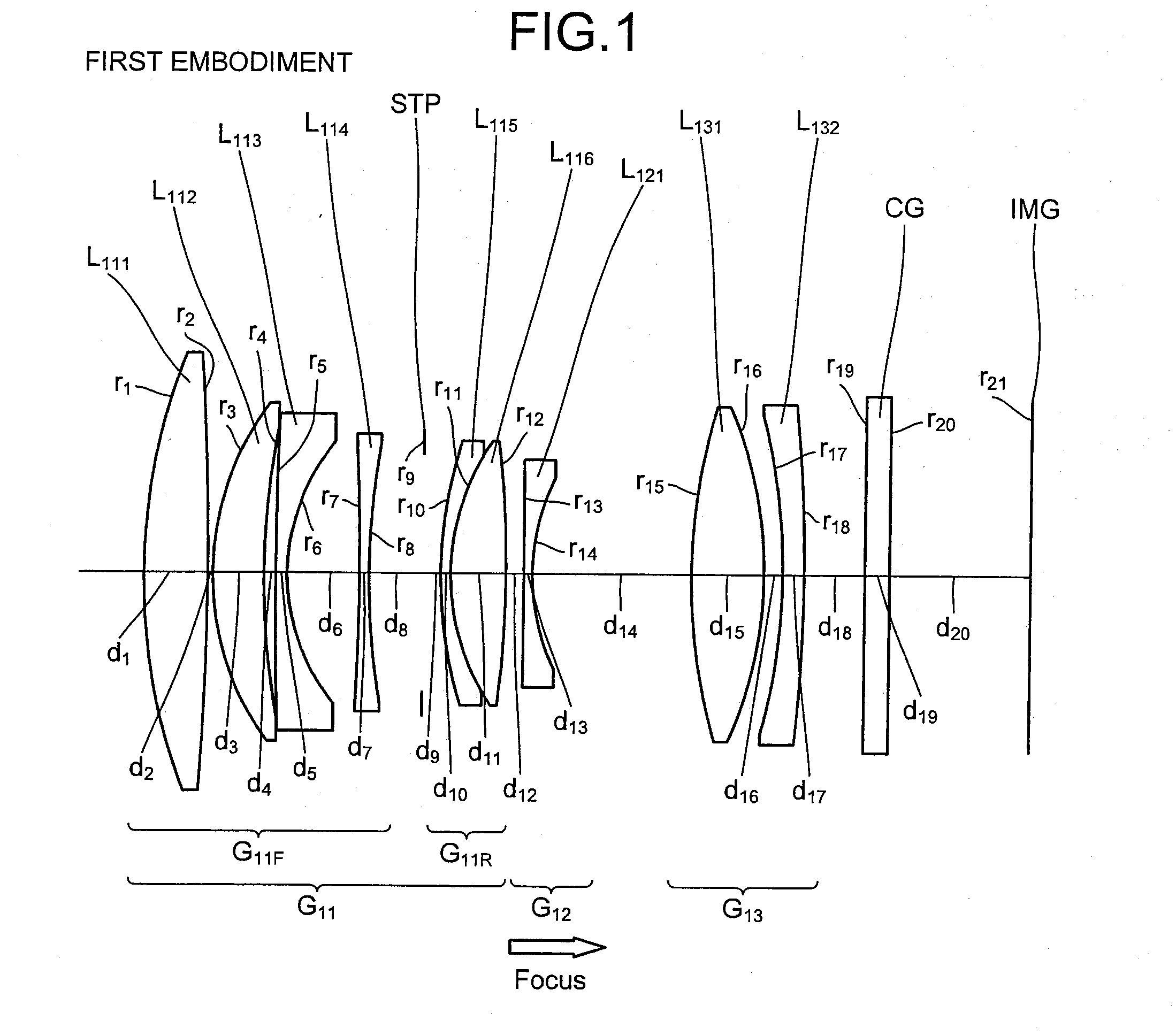
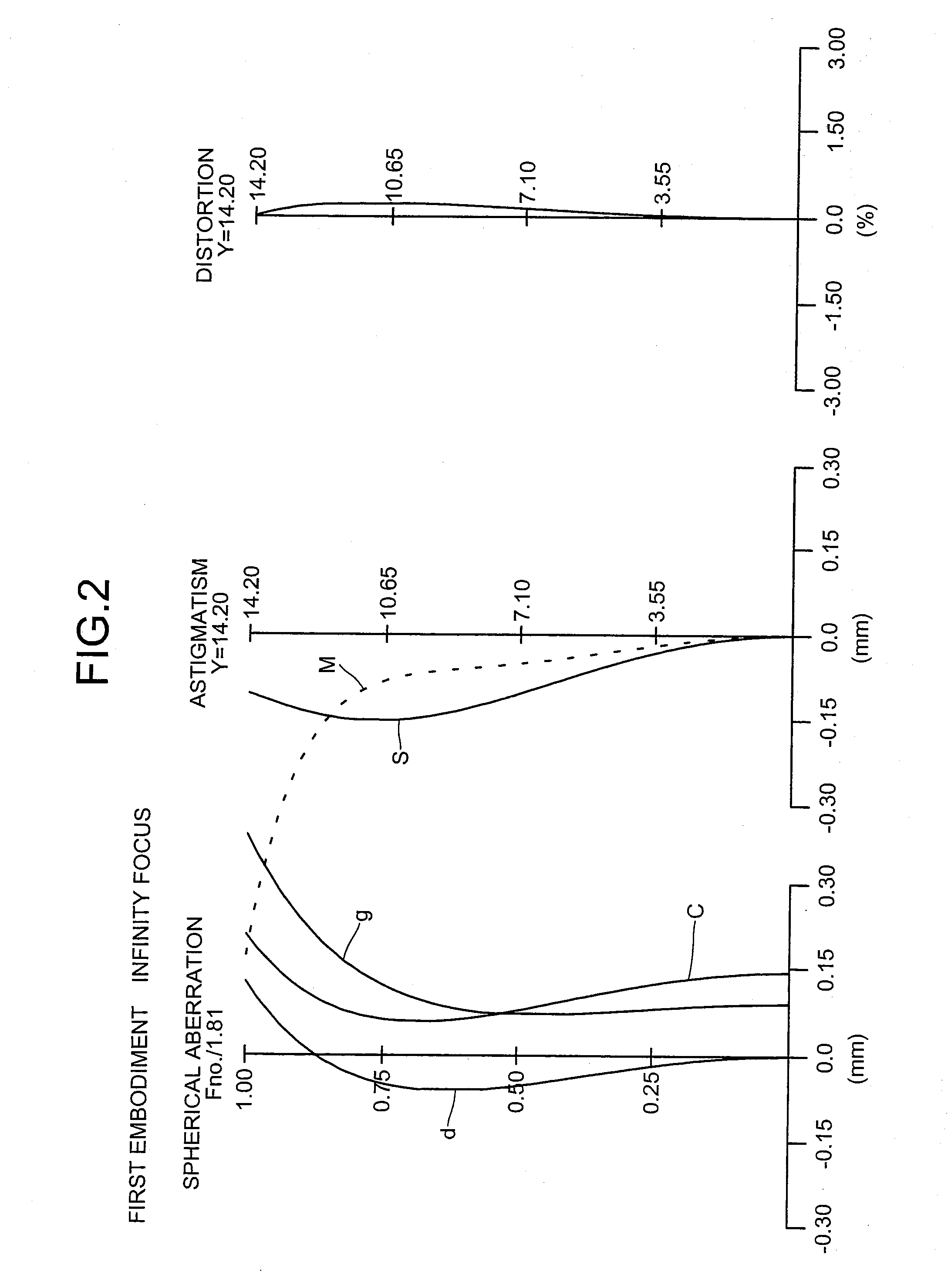
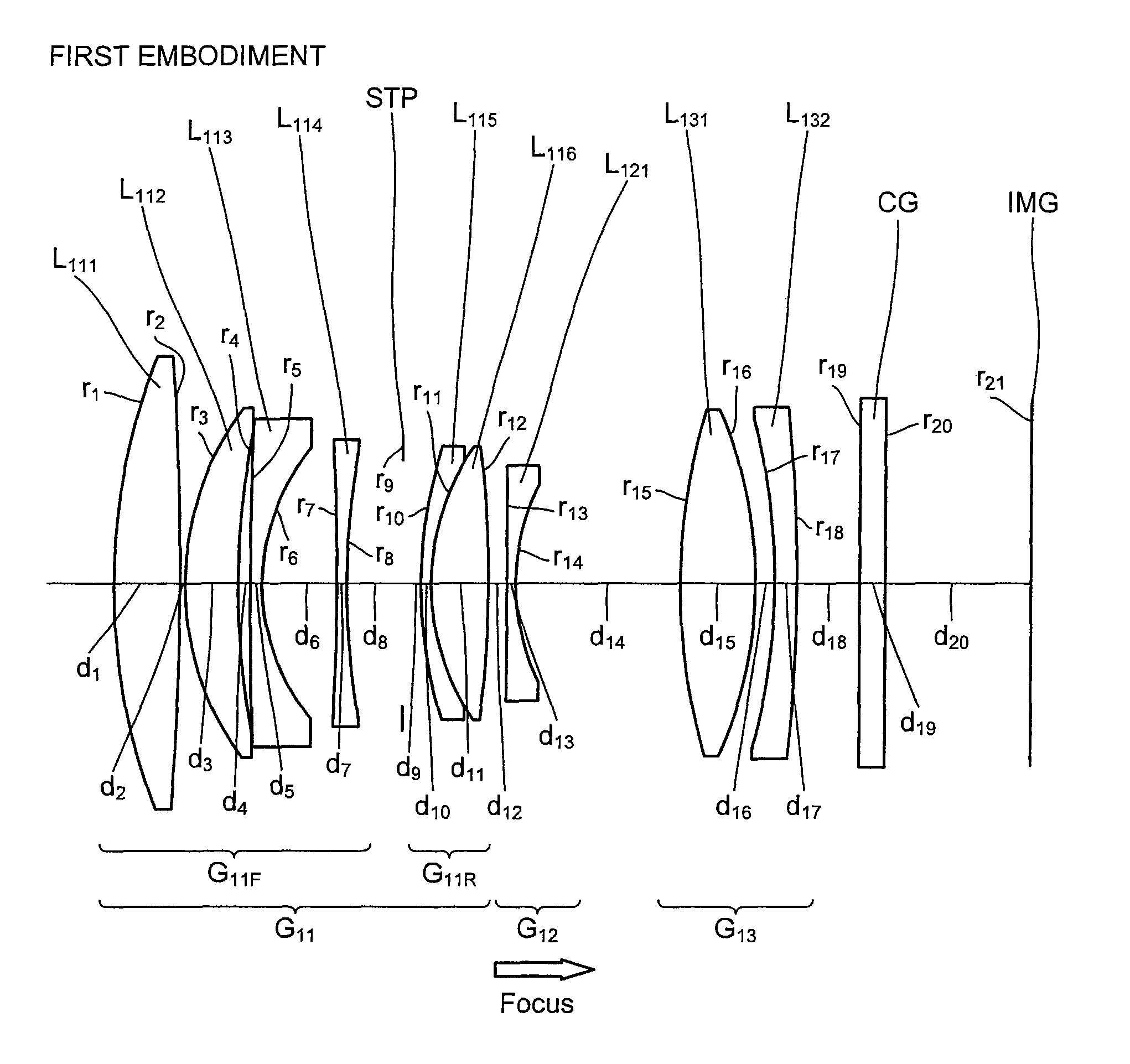
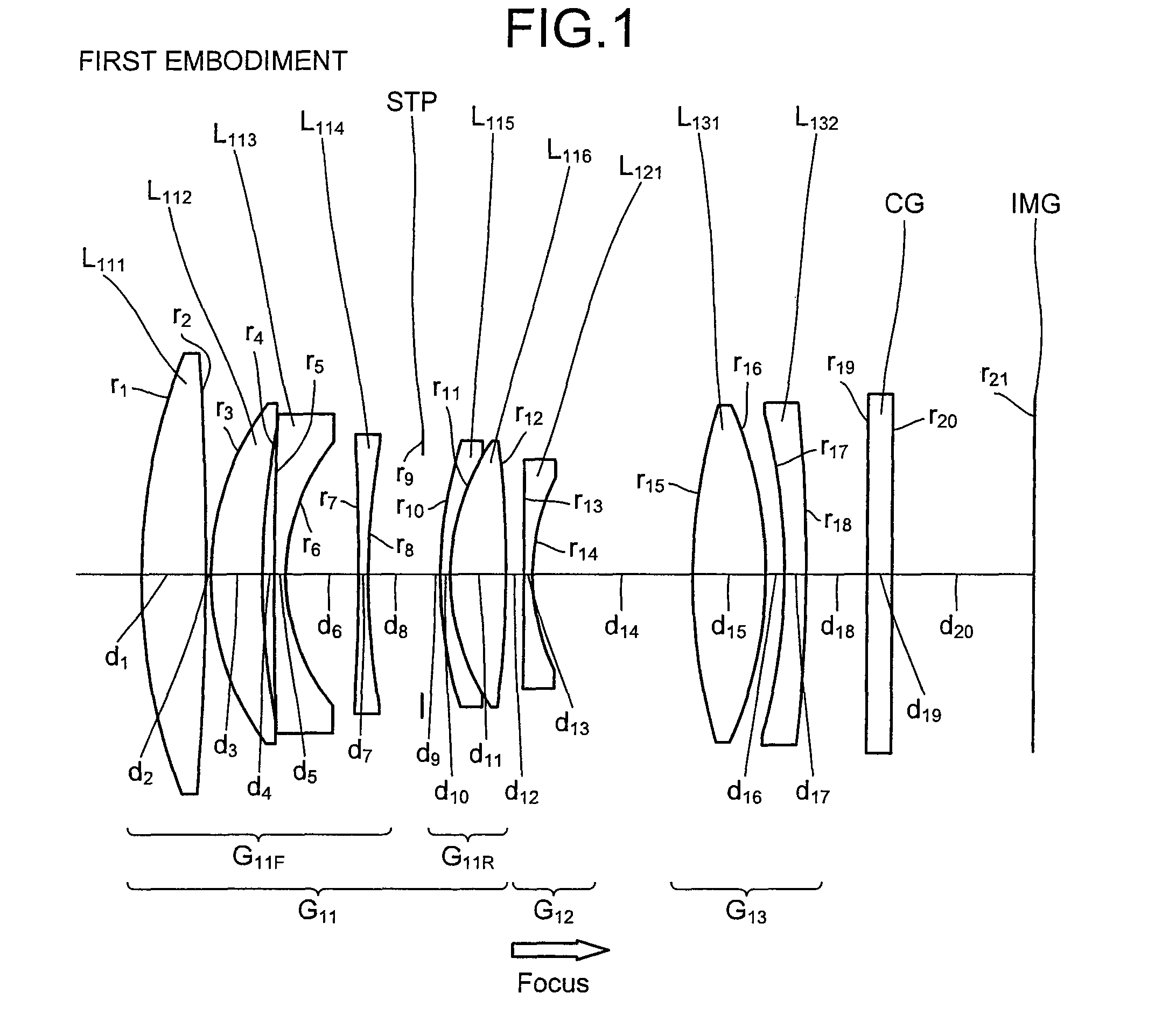
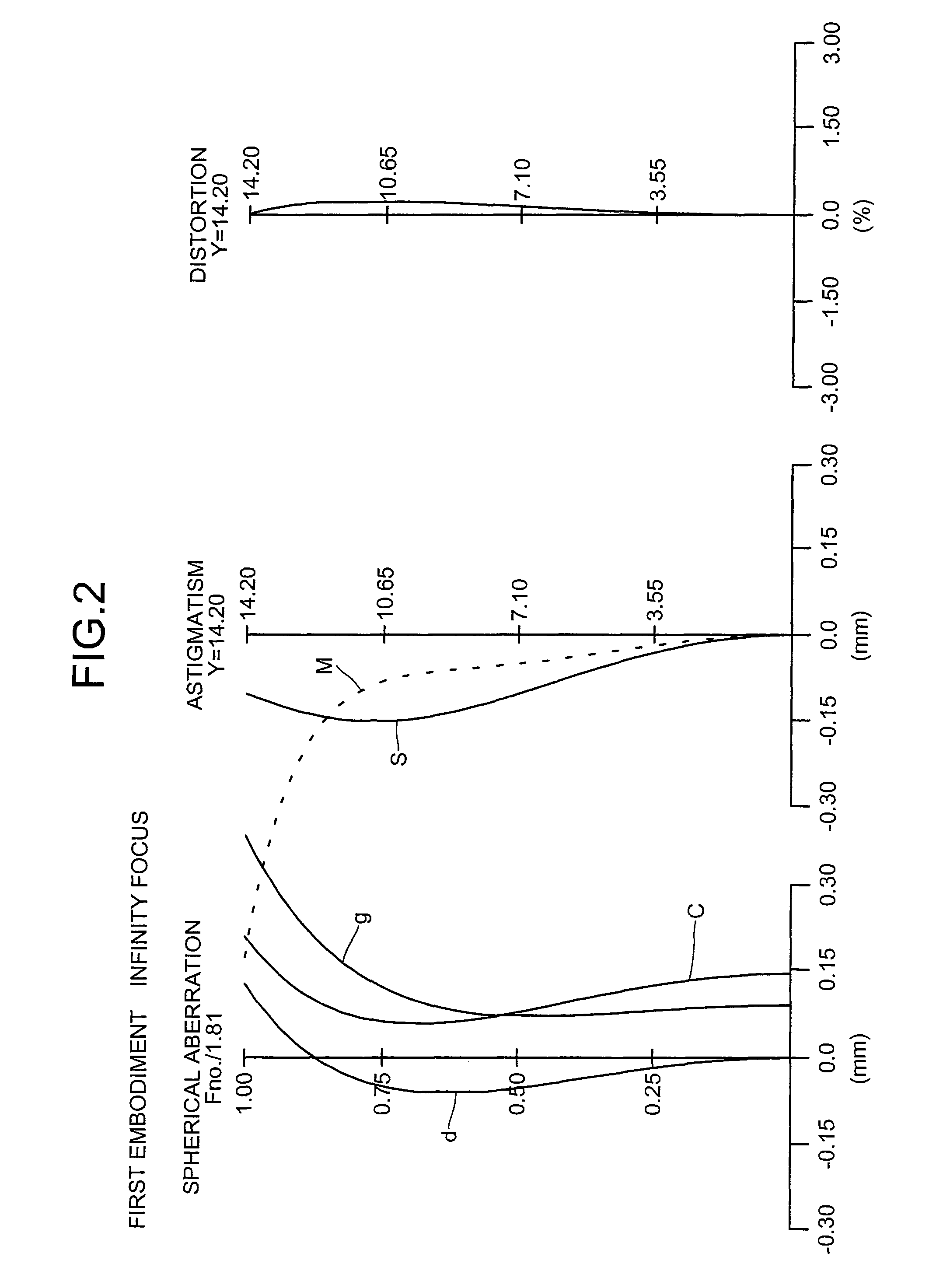
Imaging lens, optical apparatus equipped therewith, and method for manufacturing imaging lens
ActiveUS20110176215A1Good optical performanceDownsizingMetal rolling stand detailsMountingsSimple lensOptical axis
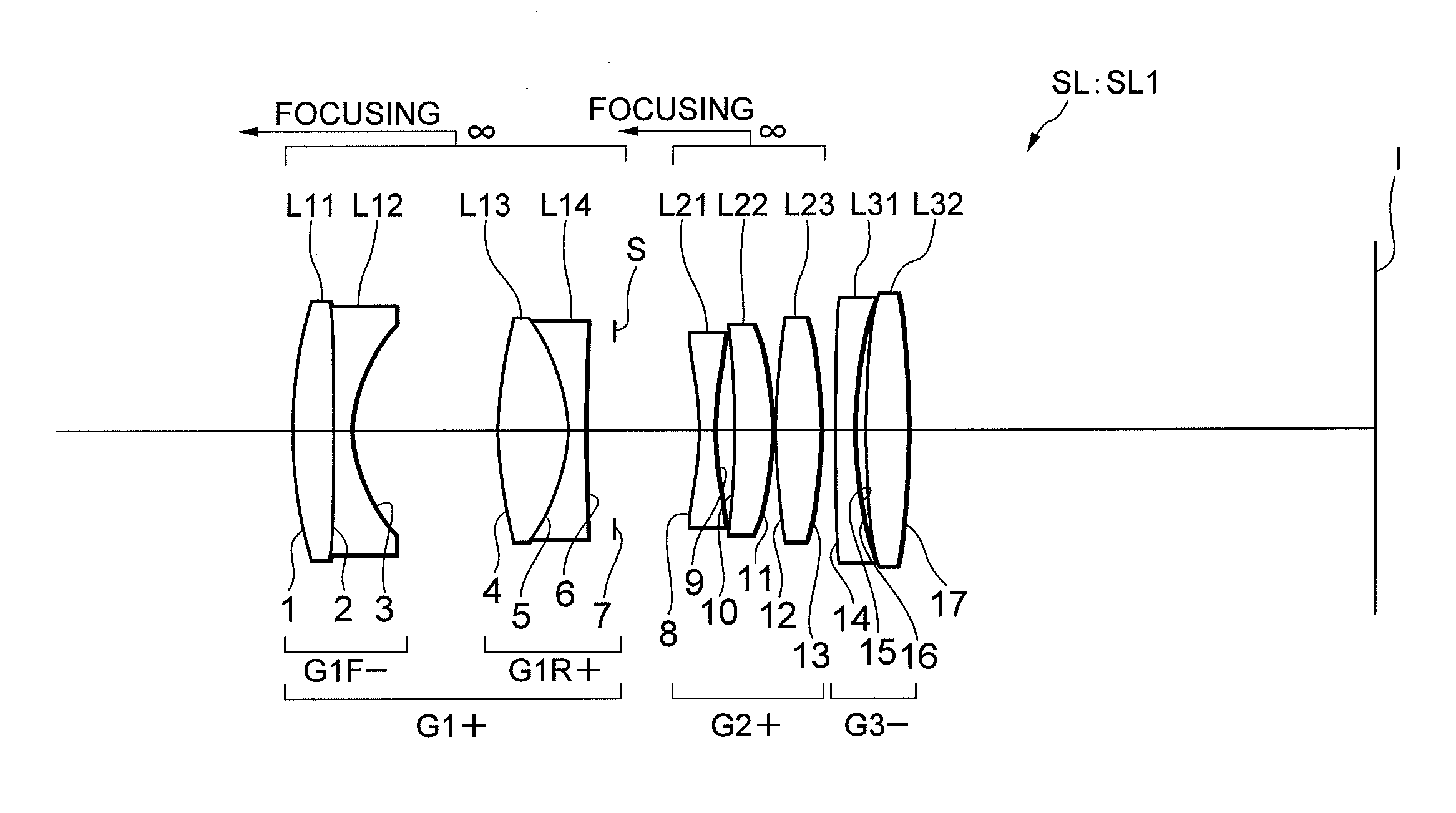
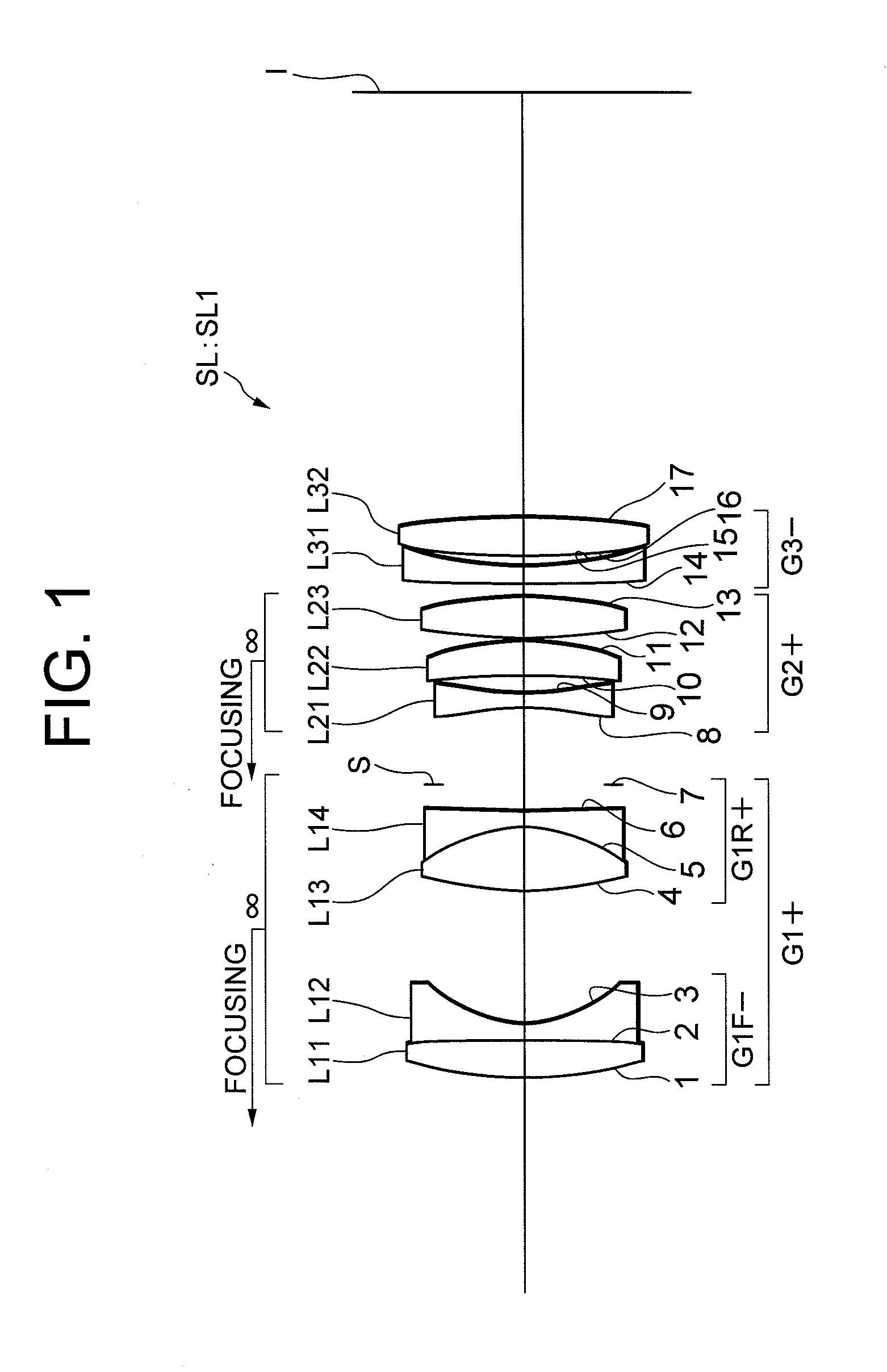
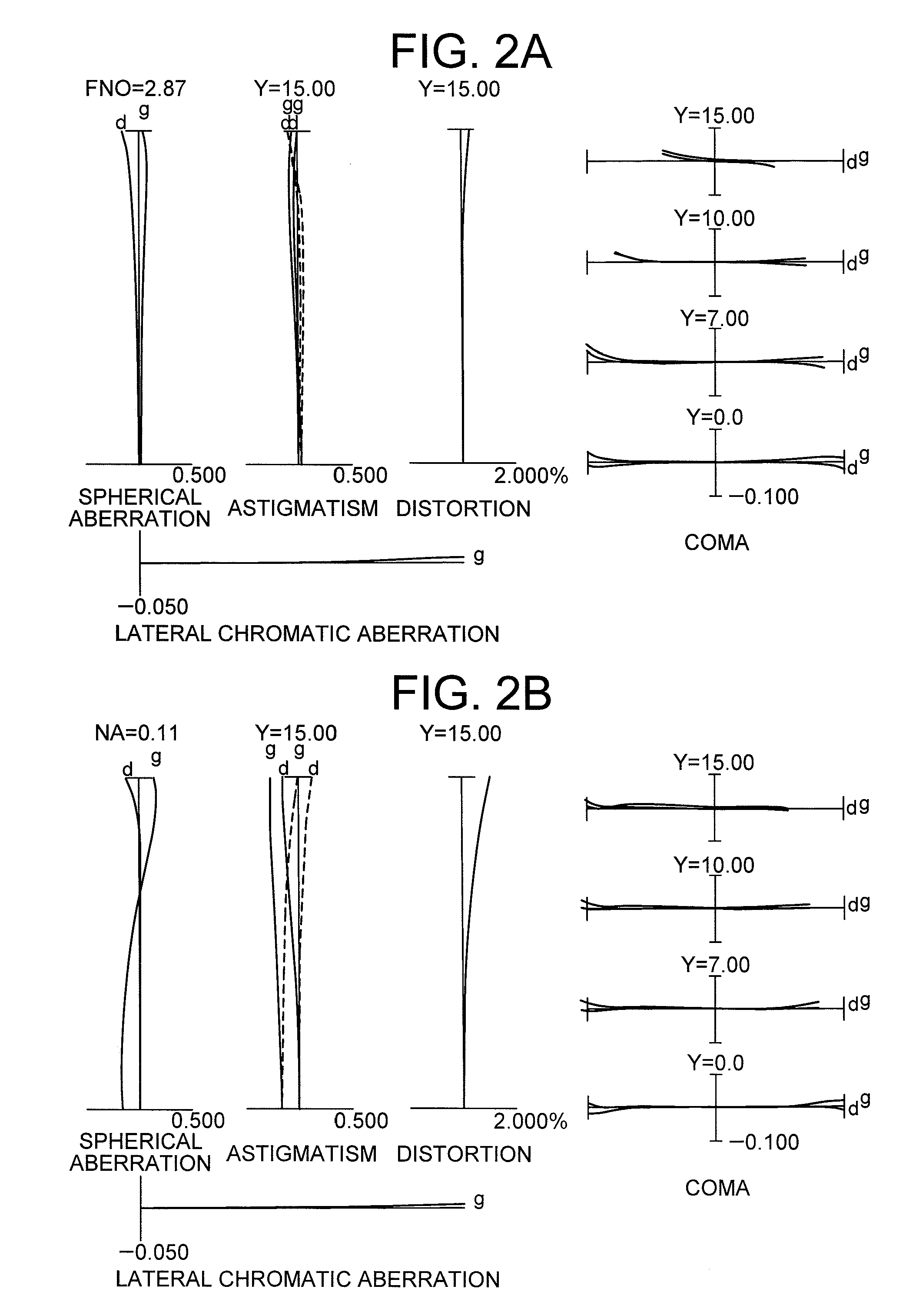
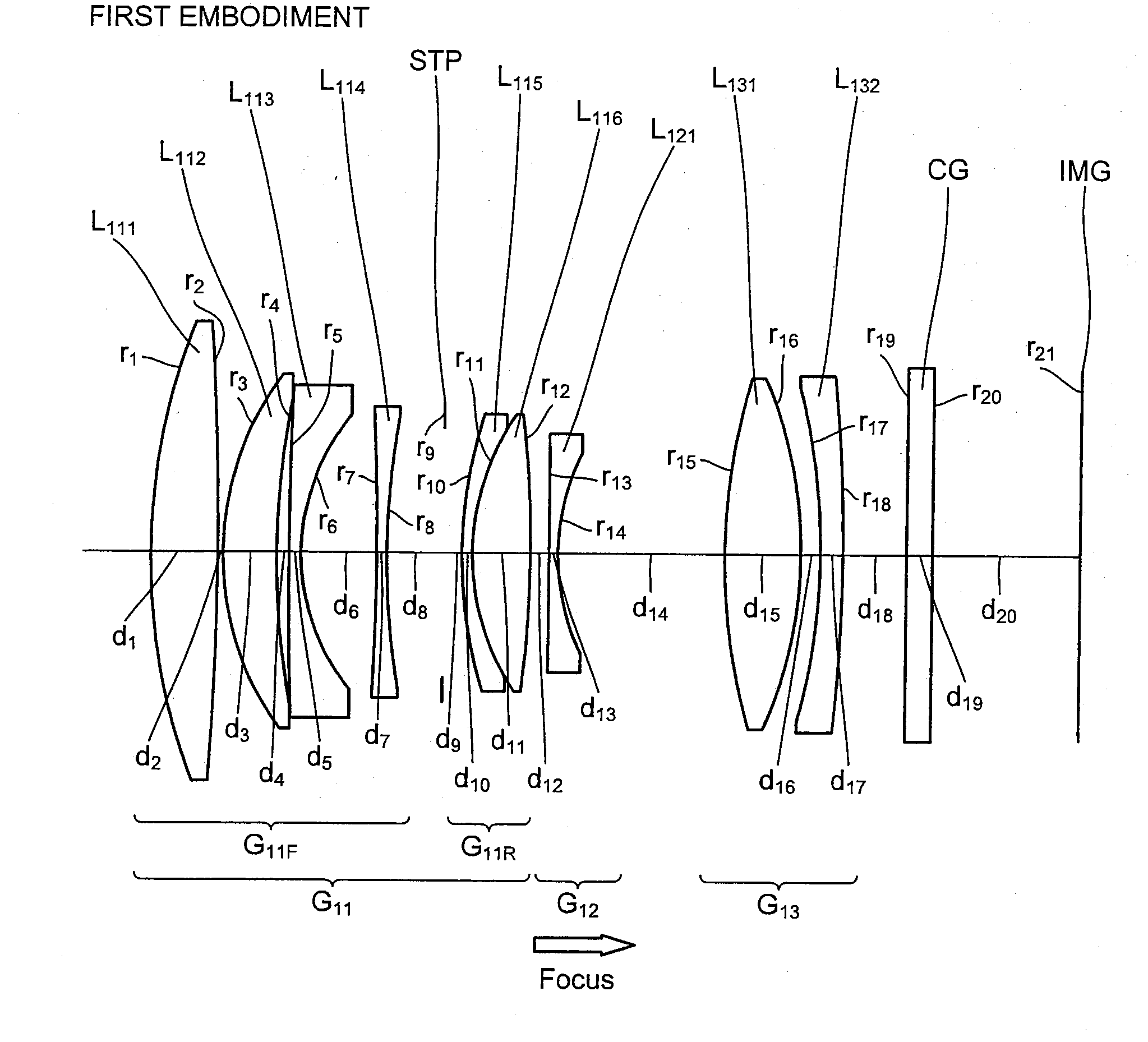
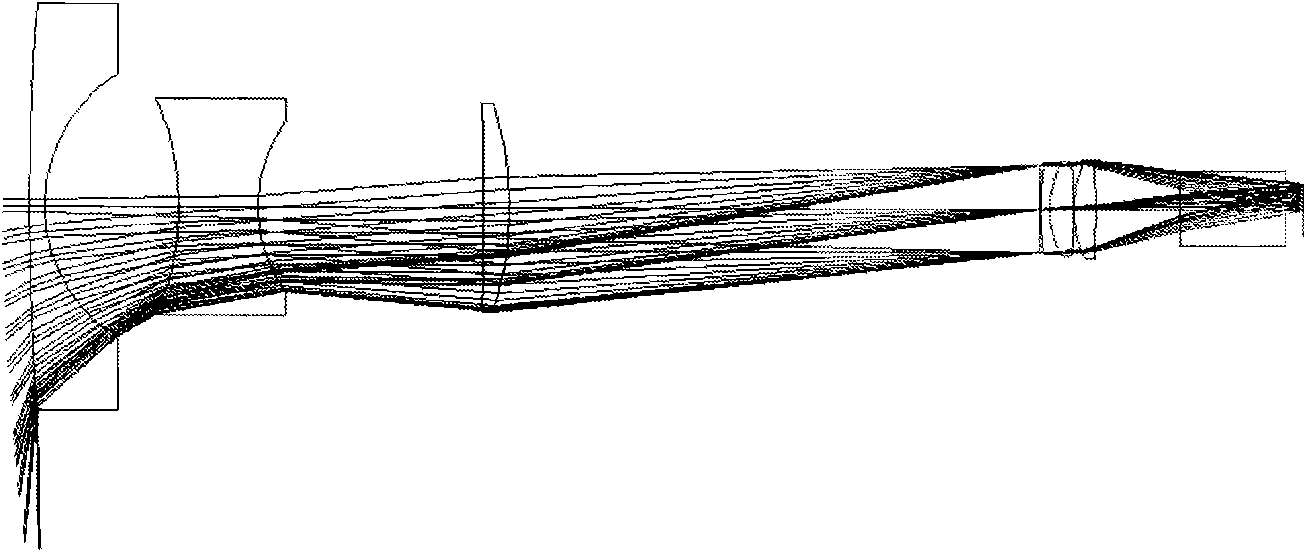
An imaging lens SL comprising, in order from an object side: a first group G1 having positive refractive power; an aperture stop S; a second group G2 having positive refractive power; and a third group G3 having negative refractive power; upon focusing from infinity to a close object, the first group and the second group moving independently along an optical axis toward the object side, the first group including, in order from the object side, a front group having negative refractive power, and a rear group having positive refractive power, and the front group consisting of, in order from the object side, a positive lens and a negative lens, thereby providing an imaging lens capable of obtaining excellent optical performance upon focusing from infinity to a close object, with downsizing the optical system with a simple lens construction, an optical apparatus and a method for manufacturing the imaging lens.
Owner:NIKON CORP
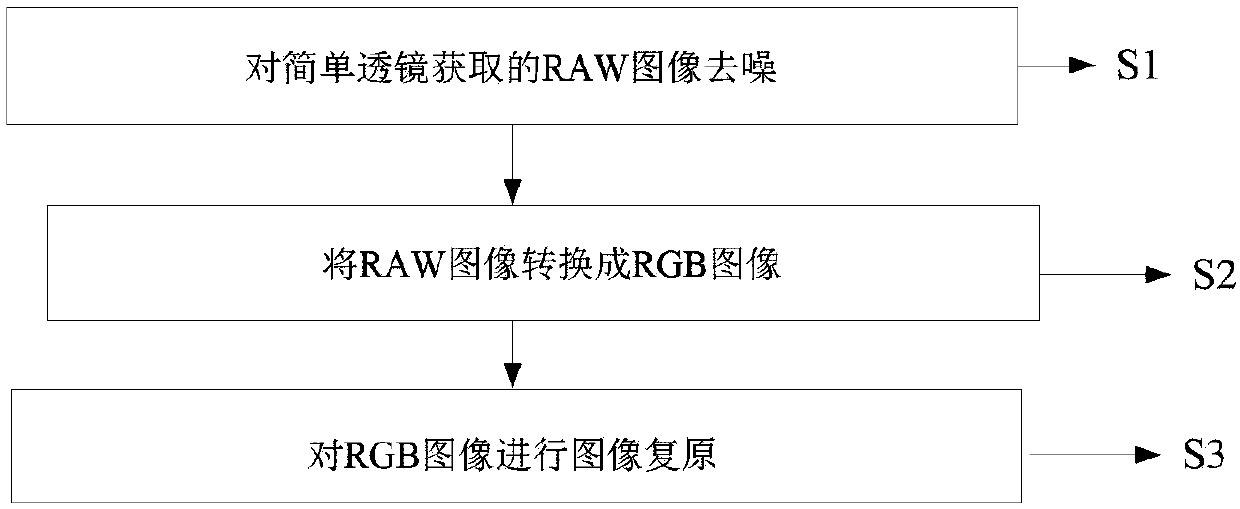
Simple lens image restoration method combined with RAW image denoising
InactiveCN107833194AImprove image restoration qualityEffectively filter out noiseImage enhancementImage analysisCamera lensImage denoising
The invention discloses a simple lens image restoration method combined with RAW image denoising, which firstly denoises a RAW image directly captured by a simple lens, then converts the RAW image into an RGB image, and then performs blind convolution image restoration on the RGB image to get a final clear restoration image. The method of the invention can effectively filter the noise of the sensor when acquiring the image data when correcting the image blur caused by lens aberration and dispersion, and can further improve the image restoration quality of the simple lens computational imaging.
Owner:CHANGSHA PANODUX TECH CO LTD
DMD comprising nonparallel mirror deflection axes
The digital mirror device (DMD) is an array of single mirrors, which are deflectable on mirror deflection axes (MDAs, as e.g. characterized by their orientation with the array raster). In the state of the art, all single mirrors on a DMD have parallel MDAs. In our invention, the array is made of different classes of mirrors. These classes differ by the orientation of their MDAs. The invention relates to the simultaneous processing of different characteristics of light (e.g. color) by a single DMD-chip.
Owner:MAYER MAX +1
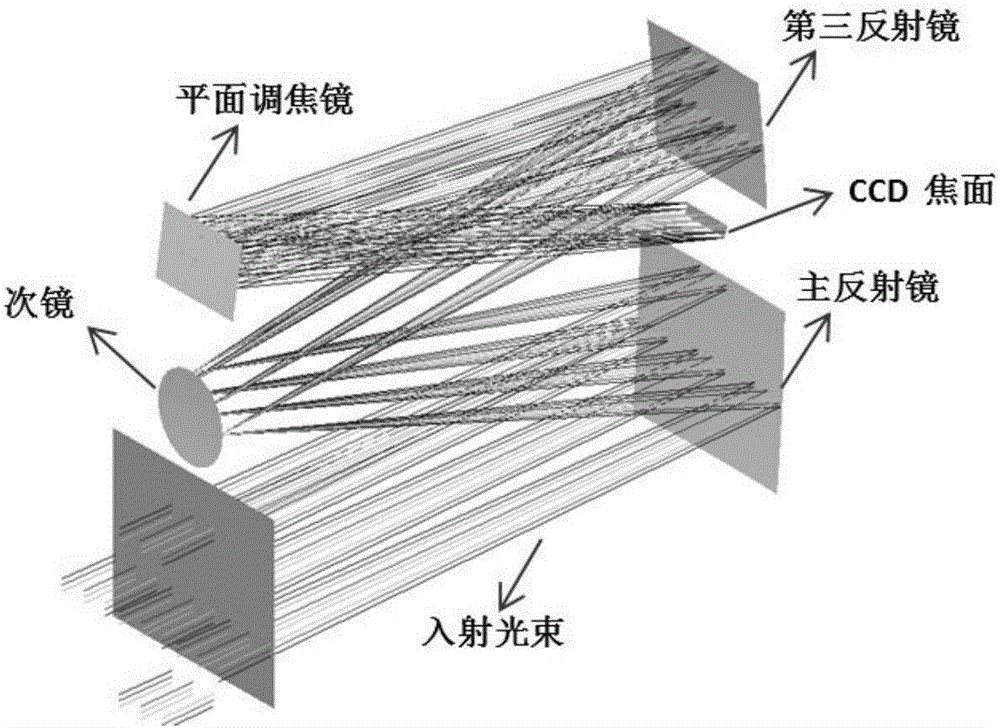
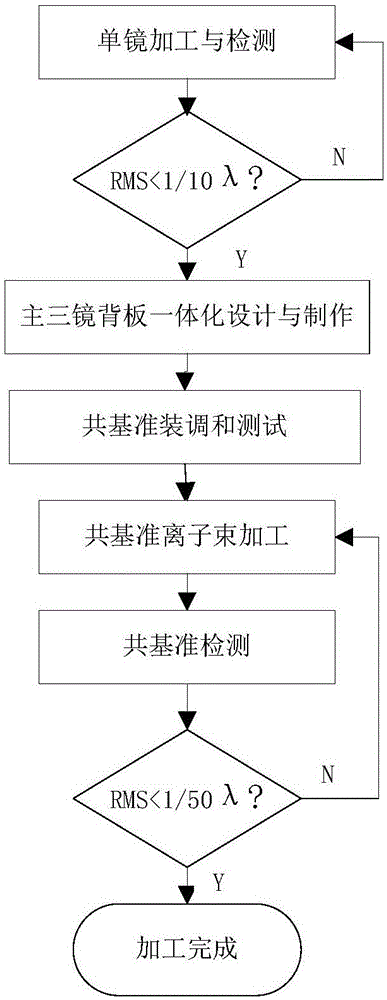
Common-reference detection and machining method of off-axis three-mirror aspheric optical system
InactiveCN106225712AShorten follow-up assembly timeHigh precisionUsing optical meansSimple lensIon beam
The invention discloses a common-reference detection and machining method of an off-axis three-mirror aspheric optical system. The method includes: firstly, machining of a main reflecting mirror and a third reflecting mirror are respectively performed until the RMS value of the full-aperture interference detection surface shape of each single reflecting mirror is greater than 1 / 10[Lambda], wherein Lambda refers to the laser interferometer operating wavelength; secondly, according to design parameters, an integrated backboard used for fixing the main reflecting mirror and the third reflecting mirror is designed and machined; thirdly, the main reflecting mirror and the third reflecting mirror are fixedly arranged on the integrated backboard, common-reference detection of the main reflecting mirror and the third reflecting mirror is performed, and the surface shapes of the main reflecting mirror and the third reflecting mirror are respectively obtained; fourthly, based on the surface shapes of the main reflecting mirror and the third reflecting mirror, which are obtained by common-reference detection, ion beam machining of the main reflecting mirror and the third reflecting mirror fixed on the integrated backboard is performed according to the design requirement; and fifthly, common-reference detection of the main reflecting mirror and the third reflecting mirror after ion beam machining is performed until the design requirement is satisfied. According to the method, the complicated assembling and adjusting processes of the off-axis three-mirror aspheric optical system can be avoided.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical configuration for improved lens performance
InactiveUS6614957B2Simple and inexpensiveImprove performanceIntegrated optical head arrangementsRecord information storageCamera lensWide field
Owner:LEIDOS
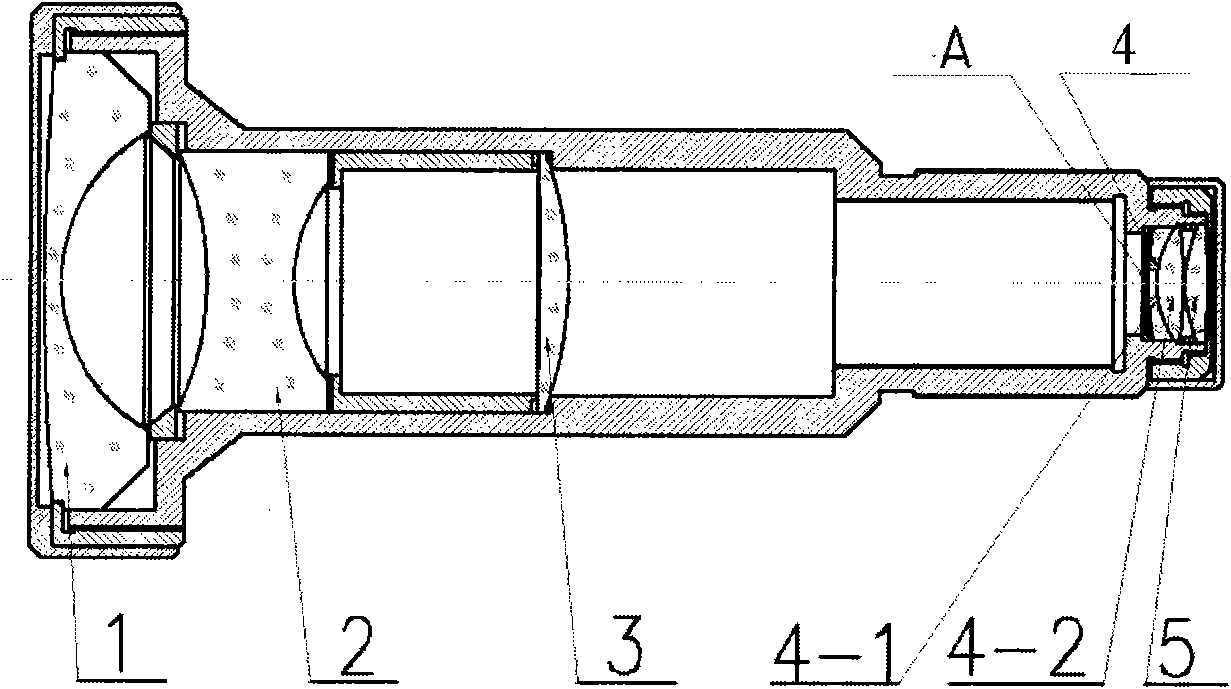
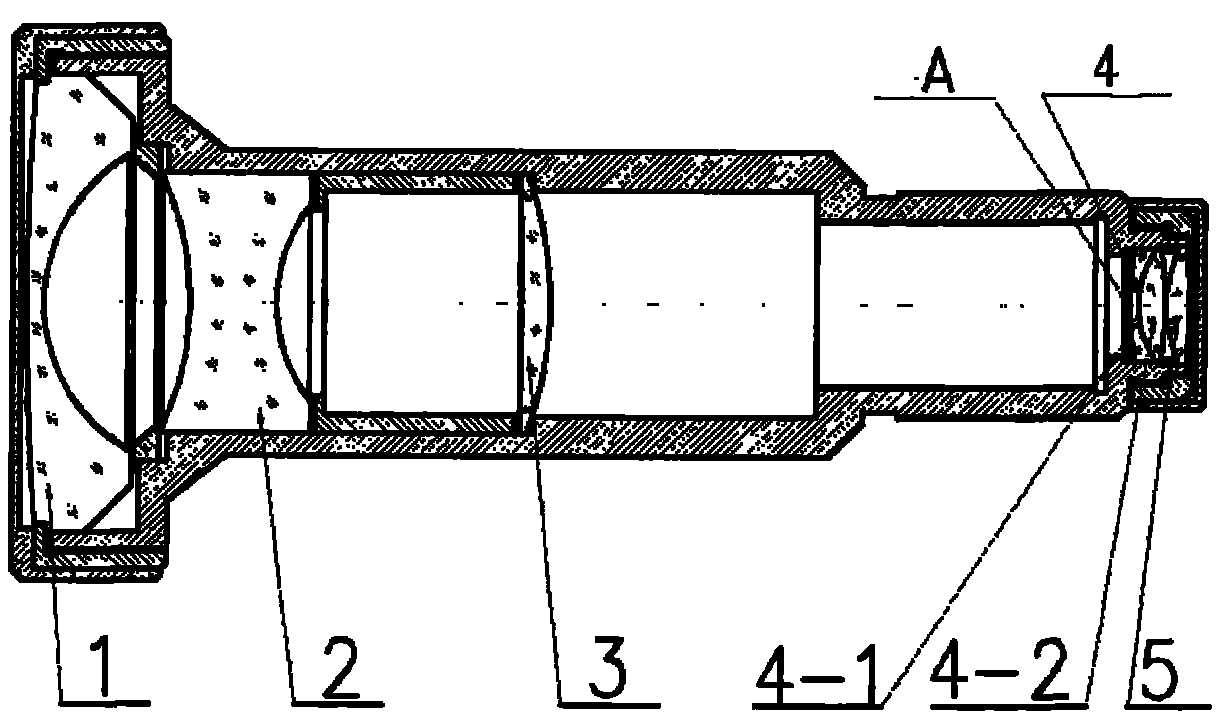
F19 mm type vehicle-mounted far-infrared mechanical athermal lens
The invention discloses a f19 mm type vehicle-mounted far-infrared mechanical athermal lens. The lens comprises a housing, a front main cylinder, a rear main cylinder and a thermal compensation telescopic ring. The front main cylinder and the rear main cylinder are sequentially arranged along the light incident direction of a light path. One end of the thermal compensation telescopic ring is fixed to the housing, and the other end of the thermal compensation telescopic ring is connected with the front main cylinder. A front main cylinder positive lens is fixed in the front main cylinder. A rear main cylinder negative lens and a rear main cylinder positive lens are sequentially arranged in the rear main cylinder along the light incident direction. The air space between the rear main cylinder negative lens and the rear main cylinder positive lens is over five times the distance between the front main cylinder and the rear main cylinder. When the telescopic phenomenon of the thermal compensation telescopic ring occurs due to temperature change in the light path direction, the front main cylinder is driven to move by the thermal compensation telescopic ring. Therefore, the distance between the front main cylinder and the rear main cylinder is changed. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the temperature self-adaption of an infrared lens can be realized based on a simple lens structure.
Owner:FUJIAN FUGUANG TIANTONG OPTICS
Internal focus lens
An internal focus lens comprising sequentially from an object side a first lens group having a positive refractive power; a second lens group having a negative refractive power; and a third lens group having a positive refractive power. The second lens group is configured by a simple lens element and is moved along an optical axis to perform focusing. The internal focus lens satisfies condition expressions (1) 0.48<|f3| / f<0.73 and (2) 1.05<Fno×f1 / f<1.42, where f3 is the focal length of the third lens group, f is the focal length of the entire optical system, f1 is the focal length of the first lens group, and Fno is the F number of the entire optical system.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
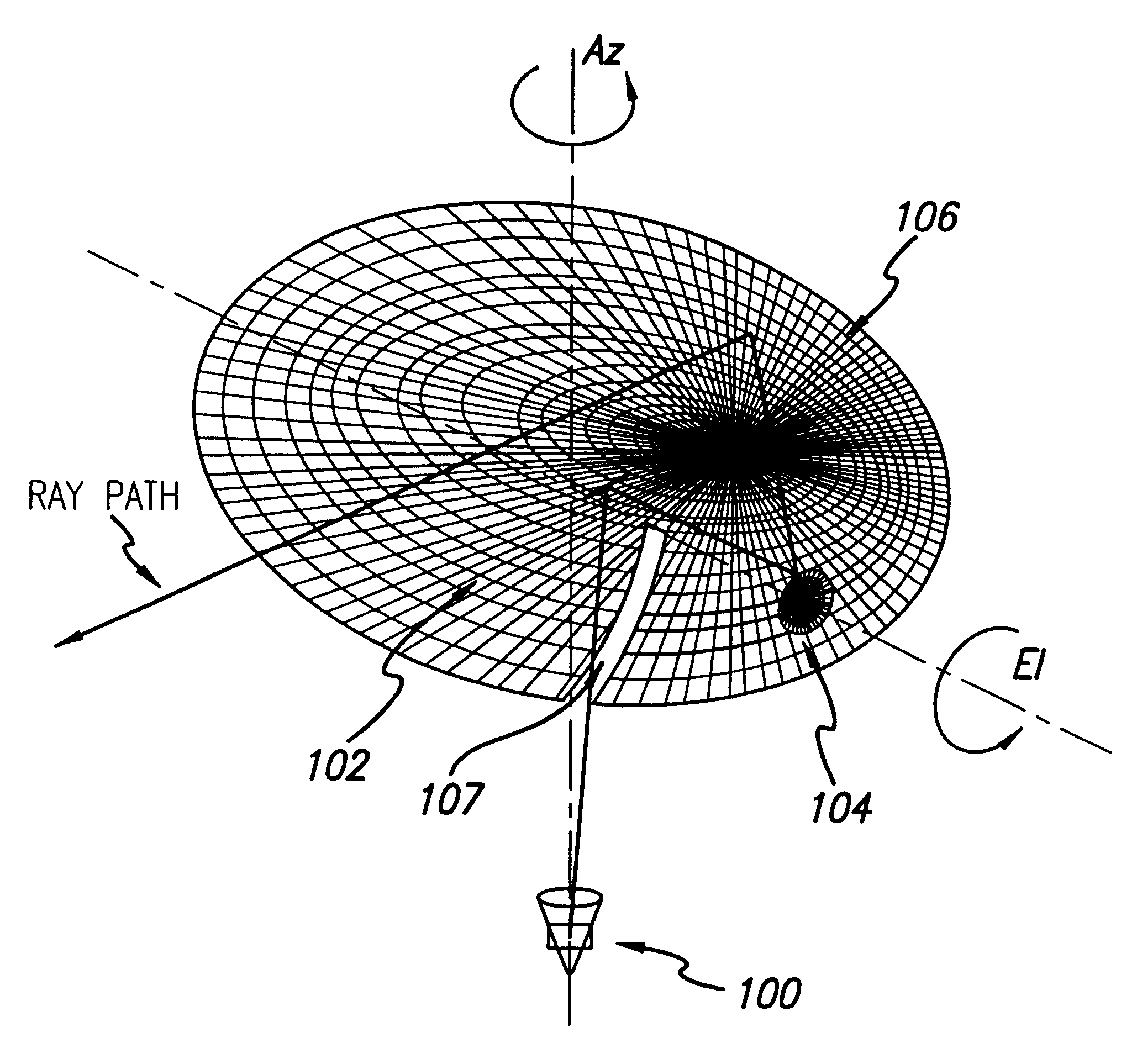
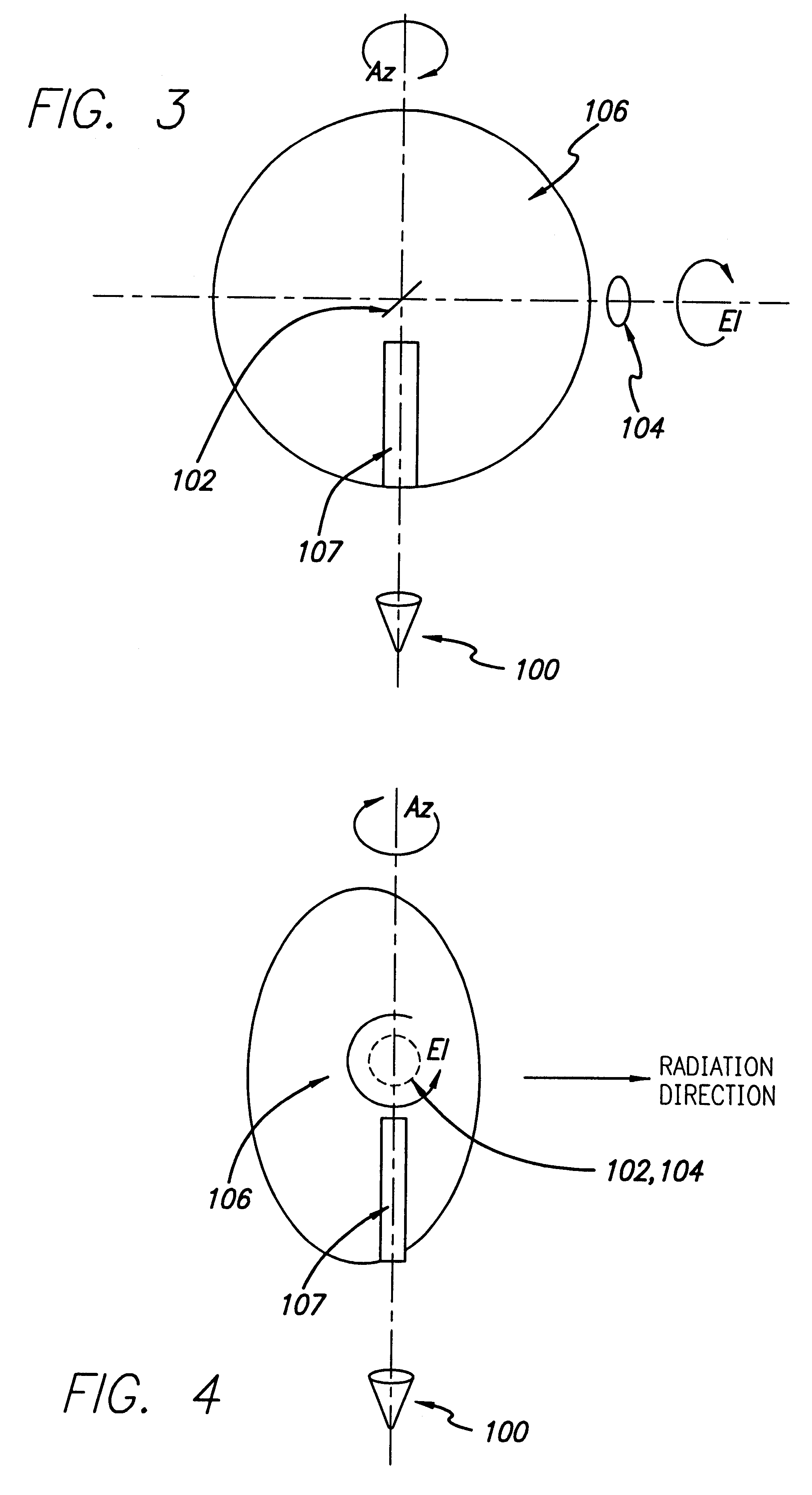
Single mirror dual axis beam waveguide antenna system
A dual axis beam waveguide antenna system includes a radiator generating a beam, a mirror which directs the beam to a subreflector, which receives the beam, and a main reflector illuminated by the subreflector, which generates a collimated output. The beam waveguide of the antenna system is characterized by an azimuth axis defined by the radiator and the mirror and an elevation axis defined by the mirror and the subreflector.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
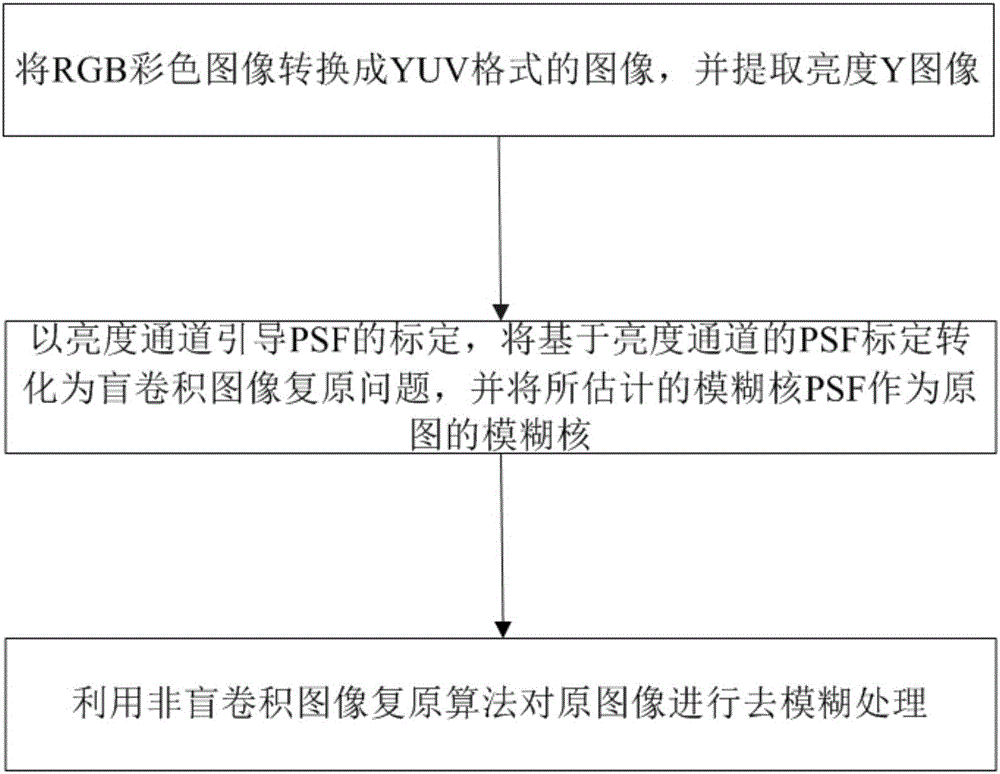
Brightness channel guided simple lens imaging blurring removing method
ActiveCN106651811AHigh precisionQuality improvementImage enhancementImage analysisCamera lensRgb image
The invention discloses a brightness channel guided simple lens imaging blurring removing method and relates to the technical field of image restoration. The method comprises the steps of converting an RGB colour image into a YUV format image; extracting brightness Y image; taking the brightness Y as a guide image; through utilization of a blind convolution image restoration algorithm, PSF (Point Spread Function) calibration of a simple lens is carried out; and through utilization of a non-blind convolution image restoration algorithm, deblurring processing is carried out on a blurring image, thereby obtaining a final clear image. Compared with the traditional method of directly carrying out PSF calibration through utilization of the RGB image, the method has the advantages that a brightness Y channel does not contain chrominance information, the influence of the dispersion of the simple lens on the PSF calibration precision can be avoided by taking the brightness Y channel as guide, and the restoration quality of the final image is improved.
Owner:CHANGSHA PANODUX TECH CO LTD
Pixel array of CMOS image sensor
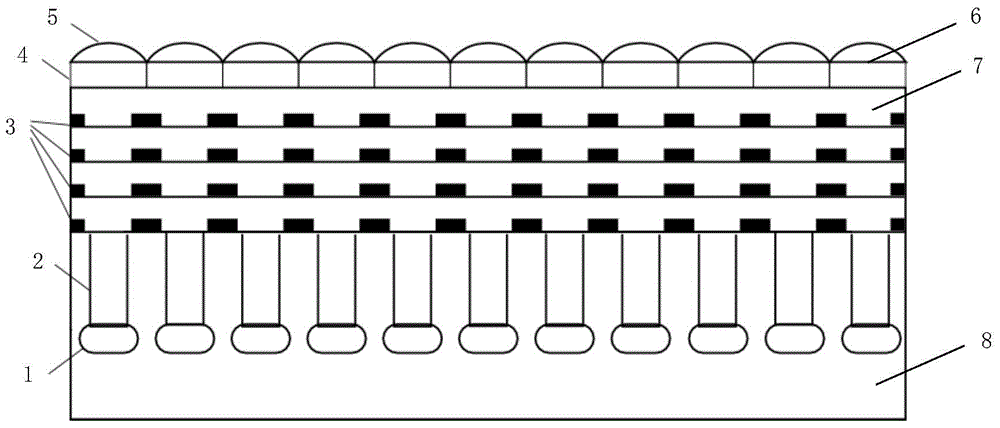
InactiveCN104091814AAvoid loss of light intensityIncrease profitRadiation controlled devicesCamera lensCMOS
The invention discloses a pixel array of a CMOS image sensor. A filter layer is in a concave hook face shape facing a camera lens and is supported by a supporting layer, a photosensitive coating and a metal layer are in a plane shape, an increased incident angle can be obtained when inclined light rays emitted into through the camera lens enter the filter layer on the edge portion close to the filter layer, the inclined light rays are conducted into a photosensitive diode through an optical fiber, obvious light intensity loss of the incident light in an optical channel can be avoided, incident optical signals can be efficiently transmitted, the imaging quality is greatly improved, the crosstalk of pixels can be effectively restrained, simpler lens design can be further matched for an optical structure, the flange focus of a main lens can be shortened, and the size of the whole imaging system can be reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI INTEGRATED CIRCUIT RES & DEV CENT +1
Optical imaging lens
The present invention provides an optical imaging lens which comprises a lens set. The lens set comprises the following components which are coaxial and are successively arranged from an object side to the image side: a first lens with a negative diopter, a second lens with a negative diopter, a third lens with a positive diopter, and a fourth lens with a positive diopter. Furthermore the lens set satisfies the following relationships: L / F>13, -15<f1 / F<-12, Lh / F>1.5; wherein the focal length of the first lens is set to f1, the focal length of the lens set is set to F, the optical total length of the optical imaging lens is set to L, and an optical back focal length is set to Lh. The optical imaging lens provided by the invention can be matched with an imaging chip more easily, and has an super-large view field which has a horizontal-direction full view field that is not smaller than 180 DEG and a diagonal full view field that is not smaller than 219 DEG. The optical imaging lens has the following advantages: small number of adopted lens, simple lens structure, effective lens volume reduction and high imaging quality.
Owner:深圳市合力泰光电有限公司
Internal focus lens
An internal focus lens comprising sequentially from an object side a first lens group having a positive refractive power; a second lens group having a negative refractive power; and a third lens group having a positive refractive power. The second lens group is configured by a simple lens element and is moved along an optical axis to perform focusing. The internal focus lens satisfies condition expressions (1) 0.48<|f3| / f<0.73 and (2) 1.05<Fno×f1 / f<1.42, where f3 is the focal length of the third lens group, f is the focal length of the entire optical system, f1 is the focal length of the first lens group, and Fno is the F number of the entire optical system.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Single mirror optical scanner
The present disclosure is directed to a device having an optical scanner, the optical scanner structured to include a mirror, a first actuator that rotates the mirror around a first axis of rotation, a first angular position sensor that senses an angular position of the mirror around the first axis of rotation, a second actuator that rotates the mirror around a second axis of rotation, a second angular position sensor that senses the angular position of the mirror around the second axis of rotation, and a controller coupled to the first and second drivers and structured to drive the respective first and second actuators to rotate the mirror into respective specific angles around the axes of rotation as sensed by the respective first and second angular position sensors.
Owner:INTENZITY INNOVATION APS
Optical lens
The invention discloses an optical lens for a simple lens structure to improve the resolution. The optical lens is orderly provided with a first lens group with negative focal power and a second lens group with positive focal power along a direction from an object side to an image side. The first lens group comprises a lens 1 with negative focal power, a lens 2 with negative focal power, and a lens 3 with positive focal power. The second lens group comprises a lens 4 with negative focal power, a lens 5 with positive focal power, a lens 6 with positive focal power, a lens 7 with positive focal power, a lens 8 with positive focal power, and a lens 9 with negative focal power. The effective focal length of the optical lens and the effective focal length of the lens 1 satisfy a first setting relation, and the effective focal length of the optical lens and the effective focal length of the second lens group satisfy a second setting relation. In this way, since the structure is simple, the optical lens of the embodiment of the invention has a low cost.
Owner:ZHEJIANG DAHUA TECH CO LTD
Optical configuration for improved lens performance
InactiveUS20020071635A1Simple and inexpensiveImprove performanceIntegrated optical head arrangementsRecord information storageCamera lensWide field
Described herein is a system and method for extending the performance of a simple lens system with curvature of field to image a set of optical light guide sources extended over a wide field of view. Embodiments are applicable to systems using integrated optical light guides as the sources for imaging. Further, the systems and methods allow for a wide field of view using simple aspheric lenses with resulting savings in complexity, size, mass, and cost.
Owner:LEIDOS
Basic structure consisting of five groups of six fisheye lenses for digital projector
ActiveCN101840057AMeet the use requirementsSimple production processOptical elementsCamera lensLiquid-crystal display
The invention discloses a basic structure consisting of five groups of six fisheye lenses for a digital projector, which comprises five lens groups consisting of six lenses with standard spherical surfaces. The five lens groups consist of four single lens groups and a double-glued lens group; an aperture diaphragm is arranged between the double-glued lens group and the single lens group in front of the double-glued lens group; the absolute values of the focal power of the lenses are in a ratio of 1:1.51:0.485:0.14:1.51 from front to back in turn; the sum of the focal power of the lenses in front of an aperture diaphragm A is a negative value; the sum of the focal power of the lenses behind the aperture diaphragm A is a positive value; and the ratio of the absolute value of the negative value to the absolute value of the positive value is 1:1.539. The basic structure is simple, lowers the production cost and assembling difficulty and enhances the stability of a lens structure. Moreover, the fisheye lens structure can zoom out the focal length in proportion to adjust full-field image height so as to adapt to different sizes of digital projectors with three liquid crystal displays (LCDs) or one digital mirror device (DMD).
Owner:秦皇岛视听机械研究所有限公司
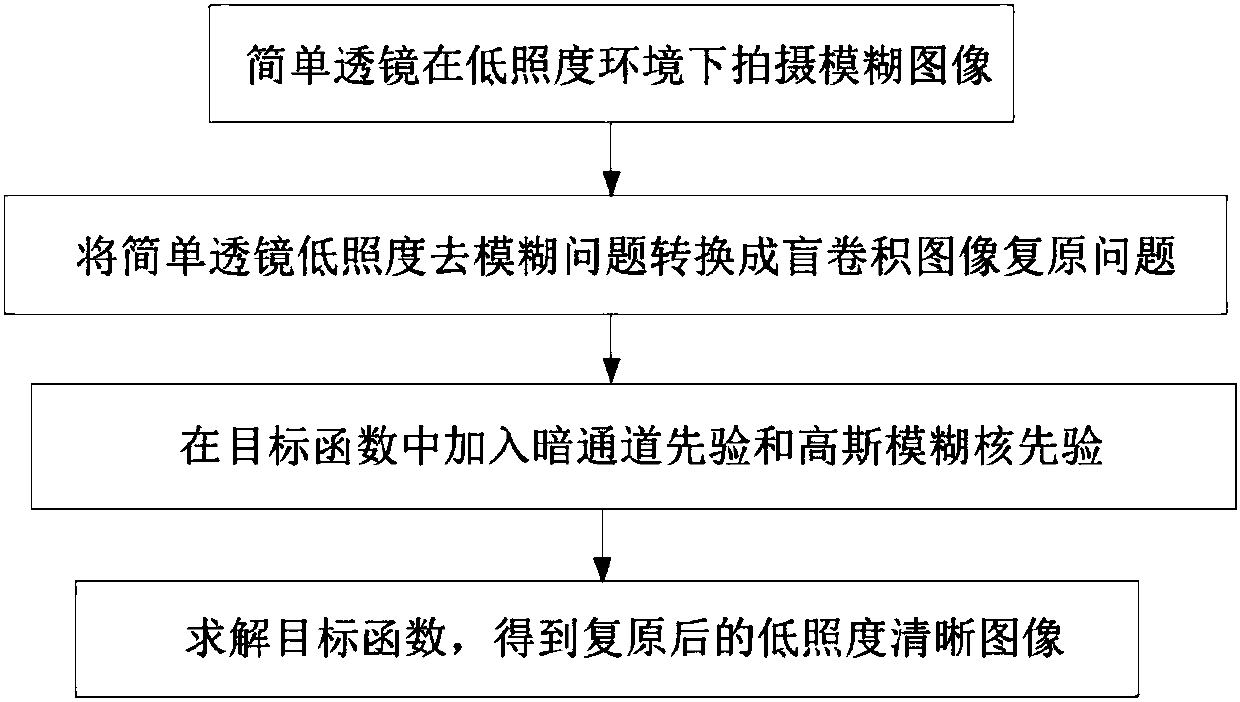
Dark channel and Gaussian combined prior art-based low-illuminance blind convolution image restoration method
InactiveCN107451971APromote recoveryImprove adaptabilityImage enhancementImage analysisIlluminanceSimple lens
The invention discloses a dark channel and Gaussian combined prior art-based low-illuminance blind convolution image restoration method and belongs to the image restoration technical field. The method comprises the following steps that: a simple lens is utilized to shoot a blurred image under low illuminance; the restoration problem of the low-illuminance blurred image is transformed into the problem of blind convolution image restoration; dark channel prior art and Gaussian blurring kernel prior art are added to the objective function of a blind convolution image restoration algorithm; and a corresponding optimization algorithm is adopted for the objective function of the blind convolution image restoration algorithm, so that a restored clear image can be obtained. According to the method of the invention, the dark channel prior art and the Gaussian blurring kernel prior art are combined to solve the image restoration problem of the imaging of the simple lens under low illuminance; the dark channel prior art aims at a low-illuminance image, and the Gaussian blurring kernel prior art aims at an actual situation that the imaging blurring kernel of the simple lens is disk-shaped, and therefore, the dark channel prior art and the Gaussian blurring kernel prior art can be combined to well solve the restoration problem of a blurred image which is shot by the simple lens under low illuminance.
Owner:湖南鸣腾智能科技有限公司
Method and apparatus for a camera having simple lens
InactiveUS20140071297A1High resolutionMake up bulkyImage enhancementImage analysisCamera lensSimple lens
In an image capturing and processing system, a device and method is provided. The lens is made of simple lens with high diffractive materials and known strong color aberrations. The method includes the steps of: calibrating or measuring a Point Spread Function (PSF) for each color components at a set of distances, capturing image data, and calculating the image obtained using a de-convolution method based on the PSF found.
Owner:YU JENNIFER JINGHAN
Dual-spot interpretation and tracking method for one-to-many simultaneous laser communication among satellites
InactiveCN110440913APhotometry using reference valueSatellite communication transmissionCommunications systemSimple lens
The invention relates to a dual-spot interpretation and tracking method for one-to-many simultaneous laser communication among satellites, and belongs to the technical field of information. The invention relates to the dual-spot interpretation and tracking method for the one-to-many simultaneous laser communication among the satellites. The characteristic of the method is that reflecting mirror tracking control is divided into single-mirror tracking and a double-mirror linkage mode. A tracking detector has the ability of energy detection and spot position extraction and can determine whether double spots are present. The problem that the reflecting mirror cannot be controlled due to the influence of the double spots during the double-mirror linkage by trajectory prediction open-loop follow-up combined with closed-loop tracking, and a system can complete the function of single-reflecting mirror tracking. The method is used to solve the problem that when two reflecting mirrors track thesame target, the double spots appear in the detector and a conventional tracking method cannot determine a corresponding relationship between the two spots and the two reflecting mirrors and cannot track, and so a spaceborne one-to-many laser communication system can control multiple reflecting mirrors to track the target.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Full-set focusing type optical passive athermalized long-wave infrared security lens
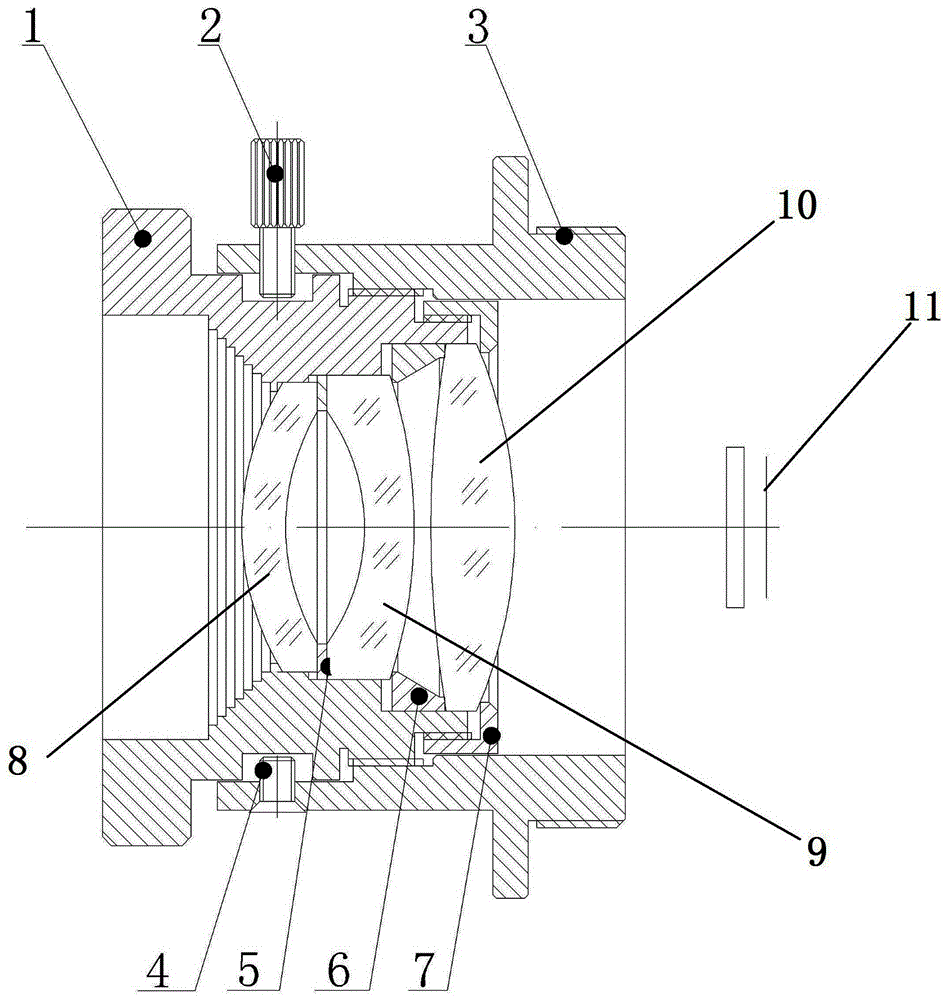
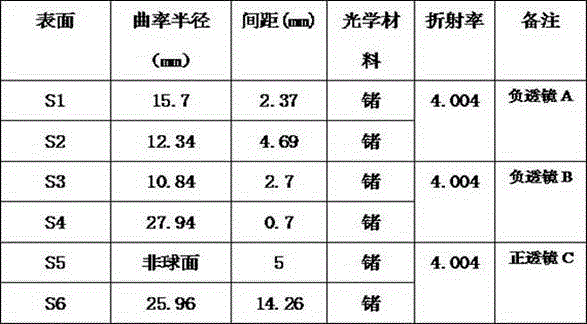
The invention provides a full-set focusing type optical passive athermalized long-wave infrared security lens. The lens comprises a main lens barrel, an outer cover and a lens group. The lens group is fixed in the main lens barrel. The main lens barrel is connected with the outer cover in the axially displaceable manner. The lends group comprises a negative lens A, a negative lens B and a positive lens C, wherein the three lenses are sequentially arranged in the light incidence direction. The negative lens A is made of the germanium glass. The negative lens B and the positive lens C are made of the chalcogenide glass. The air space between the negative lens A and the negative lens B is 4.69 mm. The air space between the negative lens B and the positive lens C is 0.7 mm. When the axial relative movement occurs between the main lens barrel and the outer over, the rear cut-off distance of the lens is changed. Therefore, a long-wave infrared non-cooled optical system can be realized based on the above simple lens structure.
Owner:FUJIAN FUGUANG TIANTONG OPTICS
RGBW mage demosaicing and deblurring combined method
InactiveCN107622477AImprove clarityImprove the accuracy of blur kernel estimationImage enhancementColor imageSimple lens
For the problems that, for an existing method, which is characterized by carrying out demosaicing processing on an RGBW mage first, and then, carrying out image deblurring processing, PSF estimation accuracy of is poor and it is easy to produce ringing phenomenon, the invention provides a method for carrying out demosaicing and deblurring simultaneously. The method comprises the following specificsteps: estimating an image fuzzy kernel on an RGBW single-channel image; carrying out demosaicing interpolation on the image fuzzy kernel; carrying out demosaicing on the RGBW image; and carrying outdeblurring on the image obtained after demosaicing to obtain a clear image. Compared with the prior art, the method can obviously improve PSF estimation accuracy and improve color imaging quality ofan RGBW image sensor under a simple lens system.
Owner:成都精工华耀科技有限公司
Method for sticking massively produced simple lenses and metal brackets
The invention discloses a method for sticking massively produced simple lenses and metal brackets, which comprises the following steps of: a. placing the metal bracket into a through hole in a positioning jig, and coating glue on the upper surface uniformly; b. placing the lens in a slot of the positioning jig, wherein the metal bracket is at the lower side, and the lens is completely positioned on the upside; and c, baking. The structure of the positioning jig comprises a bottom plate, wherein a plurality of through holes arranged linearly are formed on the bottom plate, a left upper plate and a right upper plate are symmetrically arranged on the bottom plate, a slot for accommodating the simple lens is formed at the contact joint face of the left upper plate and the right upper plate and positioned above each through hole, a lens support face is formed in the slot, symmetrical and vertical arc faces are arranged on the two sides of the slot, and the two ends of the slot have symmetric and vertical upper end faces and upper sides vertical to the upper end faces. The method has the advantages that: the structure is simple; the operation is easy; the efficiency is high; the positioning is accurate; the lens is not polluted; and the qualified rate is high.
Owner:大连艾科科技开发有限公司
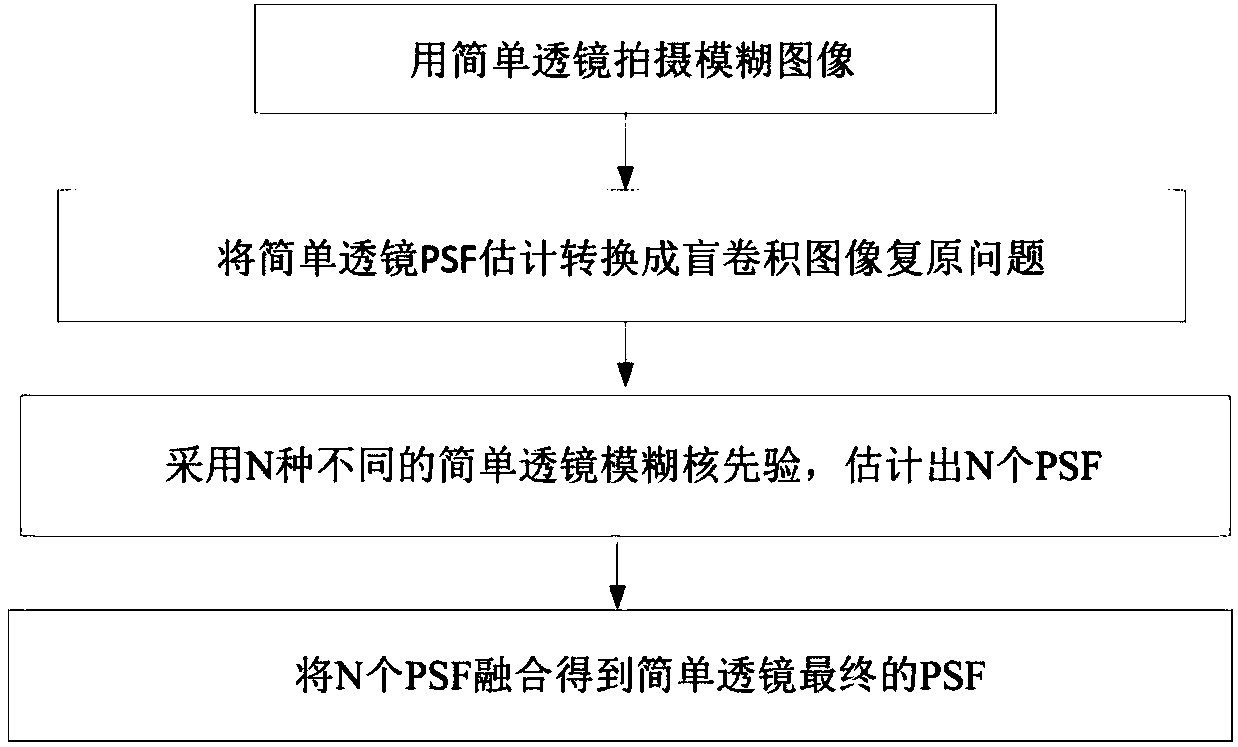
Simple lens PSF (Point Spread Function) mean value fusion method based on different fuzzy kernel priors
InactiveCN107610064AConducive to imaging subsequent image processingFusion PSF AccurateImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionSimple lens
The invention discloses a simple lens PSF (Point Spread Function) mean value fusion method based on different fuzzy kernel priors, and relates to the technical field of image restoration. The method comprises the following steps that: utilizing a simple lens camera to obtain a fuzzy image; converting a simple lens PSF estimation problem into a blind convolution image restoration problem; adoptingN types of different simple lens fuzzy kernel priors to estimate N pieces of PSF of the simple lens; and carrying out mean value fusion on the N pieces of PSF to obtain a final PSF. The PSF estimatedwith the method can simultaneously own characteristics embodied by different fuzzy kernel priors. Compared with the PSF estimated by single fuzzy kernel prior, the fused PSF is more accurate and is favorable for the subsequent processing of simple lens imaging.
Owner:CHANGSHA PANODUX TECH CO LTD
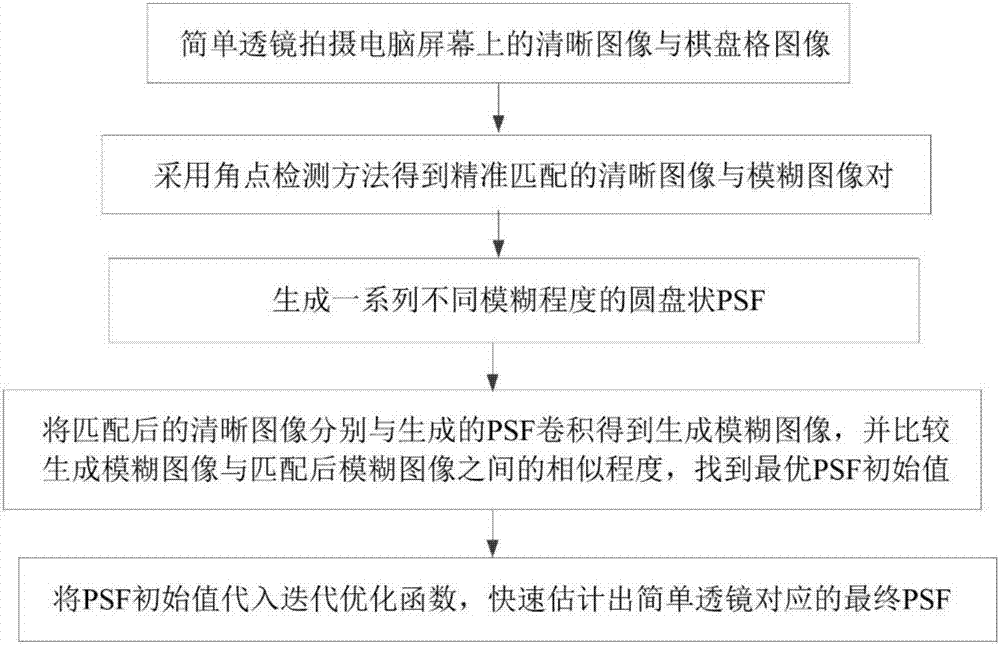
Corner detection-based simple lens PSF iterative optimization initial value method
InactiveCN107392882AAffect accuracyShorten the timeImage enhancementImage analysisLocal optimumSimple lens
The present invention discloses a corner detection-based simple lens PSF iterative optimization initial value method, and relates to the image restoration field. The method comprises the steps of using a simple lens to shoot a clear image and a checkerboard image to obtain a fuzzy image and the checkerboard image; based on the checkerboard image, adopting a corner detection method to obtain the accurately matched clear image and fuzzy image pairs; according to the prior knowledge of a simple lens PSF, generating a series of disc-shaped PSF of different fuzzy degrees; convoluting the matched clear images and the generated series of PSF separately to obtain the generated fuzzy images, comparing the similar degrees between the generated fuzzy images and the matched fuzzy images, taking the PFS corresponding to the most similar generated fuzzy image as the initial value of a simple lens PSF estimation iterative optimization process; putting the selected PSF initial value in a PSF estimation optimization algorithm, and estimating the PSF corresponding to the simple lens rapidly. The method of the present invention can avoid the influence of the local optimal solution of an optimization algorithm on the PSF precision, and enables the final image restoration quality to be improved.
Owner:湖南鸣腾智能科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com