Long-chain non-coding RNA gene ALEX1 and application thereof to improvement of bacterial blight resistance of rice
A long-chain non-coding, gene technology, applied in the field of plant genetic engineering, can solve problems such as the application of disease resistance and defense response is still blank, achieve important theoretical significance and application value, and enhance the effect of resistance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Example 1 Screening of differentially expressed rice lncRNA after bacterial blight infection
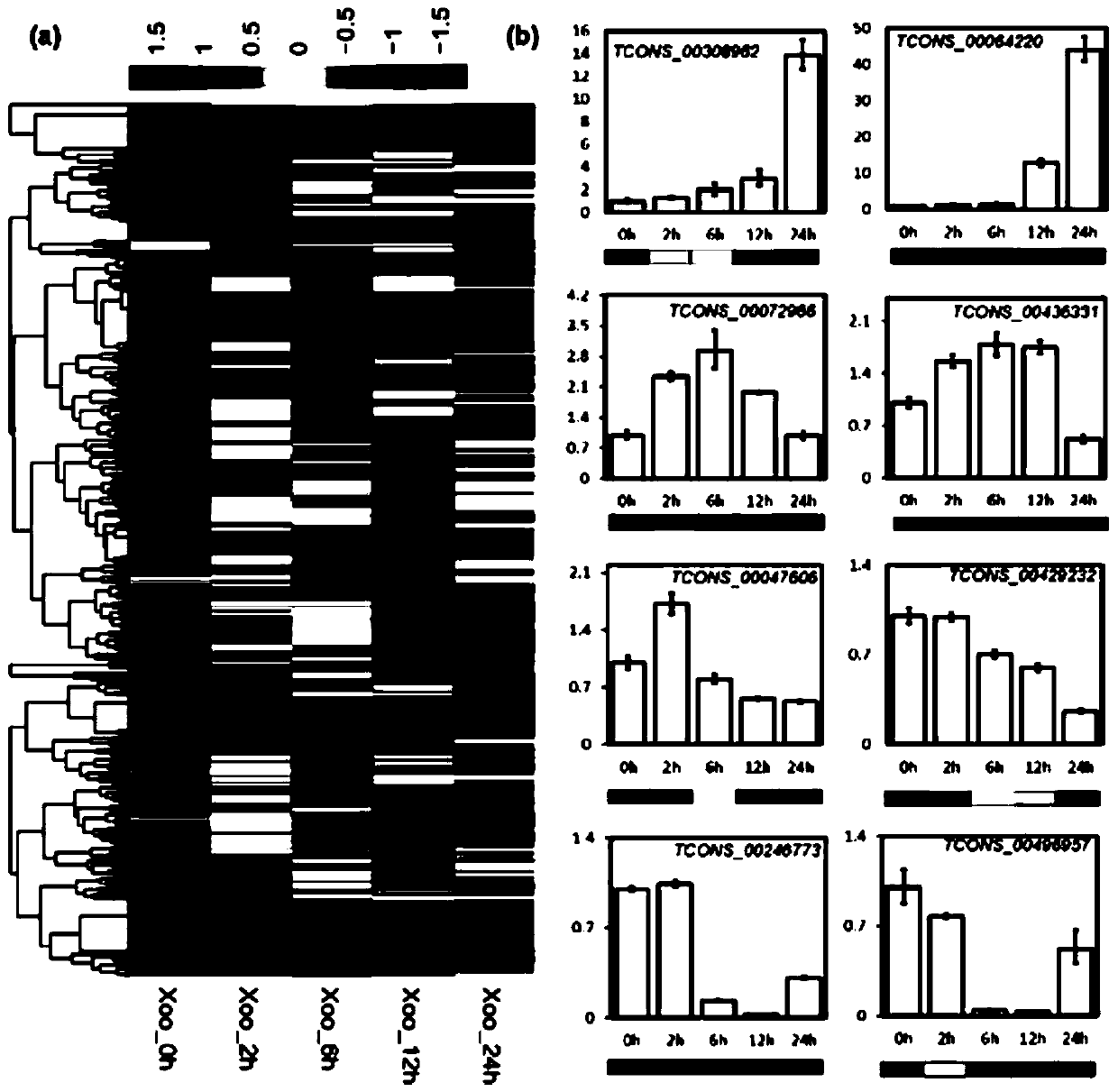
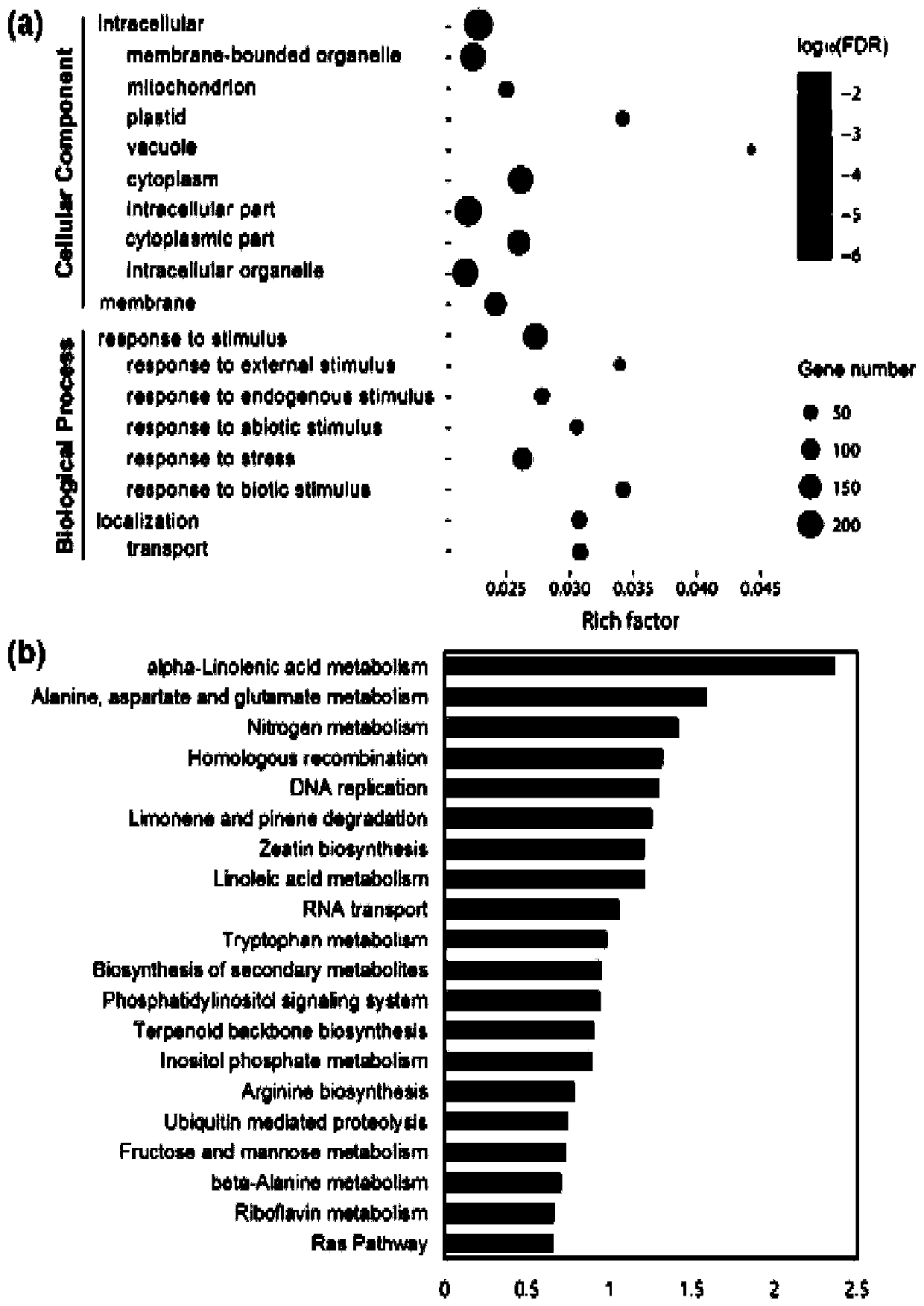
[0038] In order to study the role of lncRNA in rice disease resistance response, the inventors performed strand-specific lncRNA sequencing on rice leaf samples infected with bacterial blight PXO99A for 0, 2h, 6h, 12h and 24h, and obtained 5.7×10 8 reads, of which 4.9×10 8 The reads matched the reference genome of rice, accounting for 85.26% of the total data obtained. After splicing and assembly, a total of more than 700,000 transcripts were obtained. After five basic screening procedures and coding potential screening, 48,727 rice lncRNA transcripts with high reliability were finally obtained. The cuffdiff software was used to quantitatively analyze the screened lncRNAs to obtain the FPKM information of the lncRNAs of each sample. The expression levels of 567 lncRNAs were significantly changed due to bacterial blight infection ( figure 1 ). To confirm the reliability of de...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2 Acquisition and functional identification of plants activated by in situ expression of ALEX1
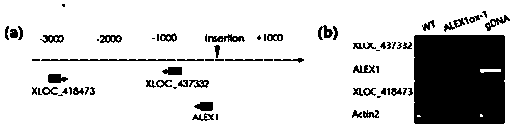
[0040] The 567 bacterial blight-responsive lncRNAs identified above are candidate genetic resources for regulating rice resistance to bacterial blight. In order to study whether the abnormal expression of these lncRNAs will affect the pathogenesis of rice bacterial blight, we searched the world's major rice mutant databases and identified a plant with activated lncRNA expression that exhibited obvious resistance to bacterial blight ( Figure 5 ). Since this lncRNA is highly specifically expressed only in leaves infected by bacterial blight, and is almost not expressed under normal physiological conditions ( Figure 4 ), so we named it ALEX1 (An LncRNA Expressed in Xoo-infected leaves), and the two activated expression lines of ALEX1 were named ALEX1ox-1 and ALEX1ox-2.
[0041] We have confirmed that ALEX1 is located on the antisense DNA strand of rice chromosome 8 ...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Example 3 In situ expression of ALEX1 activates plant exogenous methyl jasmonate treatment and determination of endogenous jasmonic acid content
[0047] In situ expression of wild-type Zhonghua 11 and ALEX1 activated rice seeds to germinate in water at 32°C for 3 days. Methyl jasmonate (Sigma Aldrich #392707) was diluted to the indicated concentrations in deionized water and used to treat 3-d-old seedlings as described above. The state of the roots was photographed after culturing for 6 days in a climate chamber at 27° C. and 70% humidity. Methyl jasmonate treatment experiments showed that JA signaling was enhanced in rice ALEX1-activated plants ( Figure 6 ).
[0048] JA, JA-Ile and OPDA were analyzed by liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (LC-MS / MS). Briefly, the tallest leaves of 3-week-old rice were homogenized in liquid nitrogen. A sample of a 200 mg powder sample of fresh tissue was added to 1,000 μL of 500:1 extraction buffer containing isopro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com