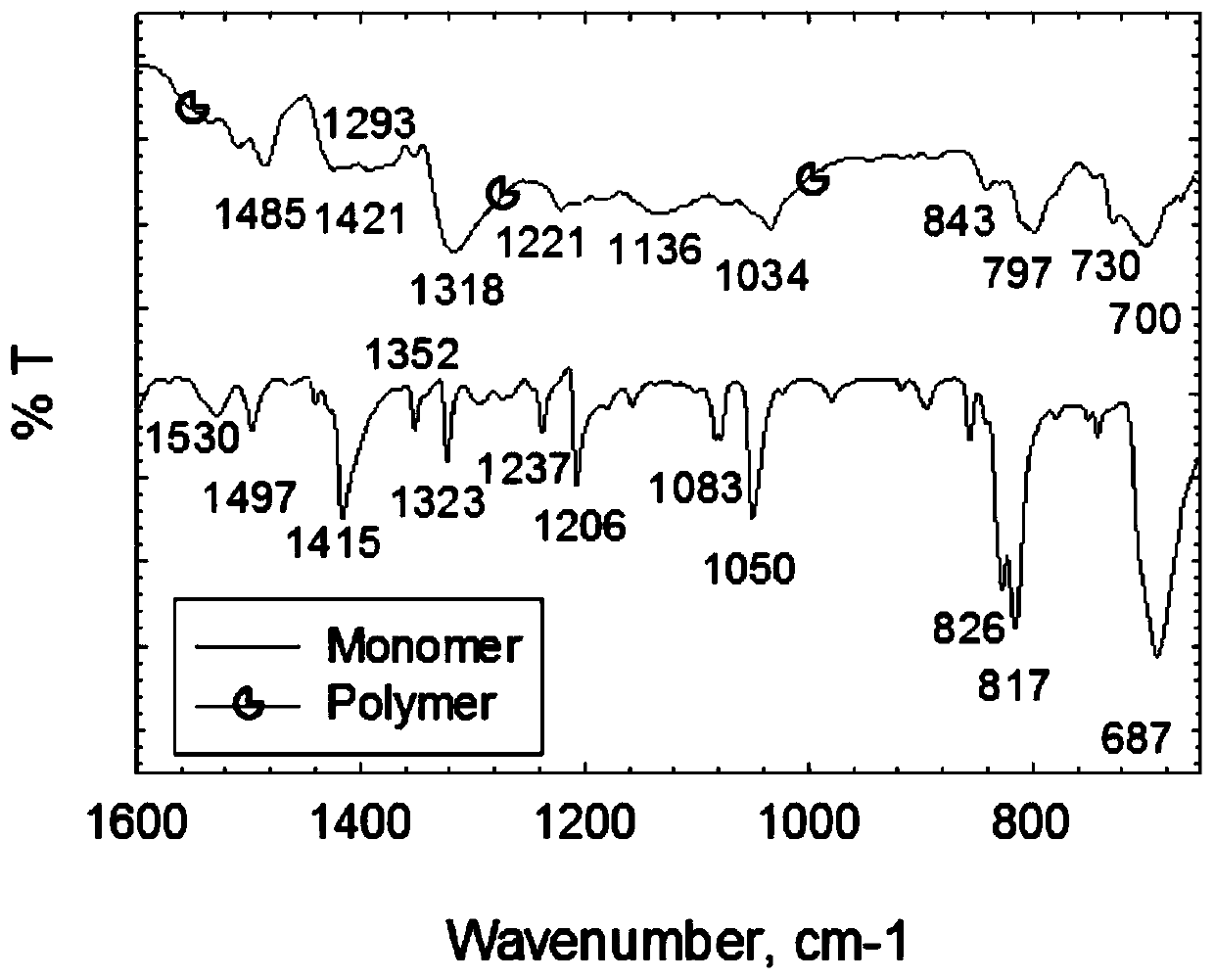
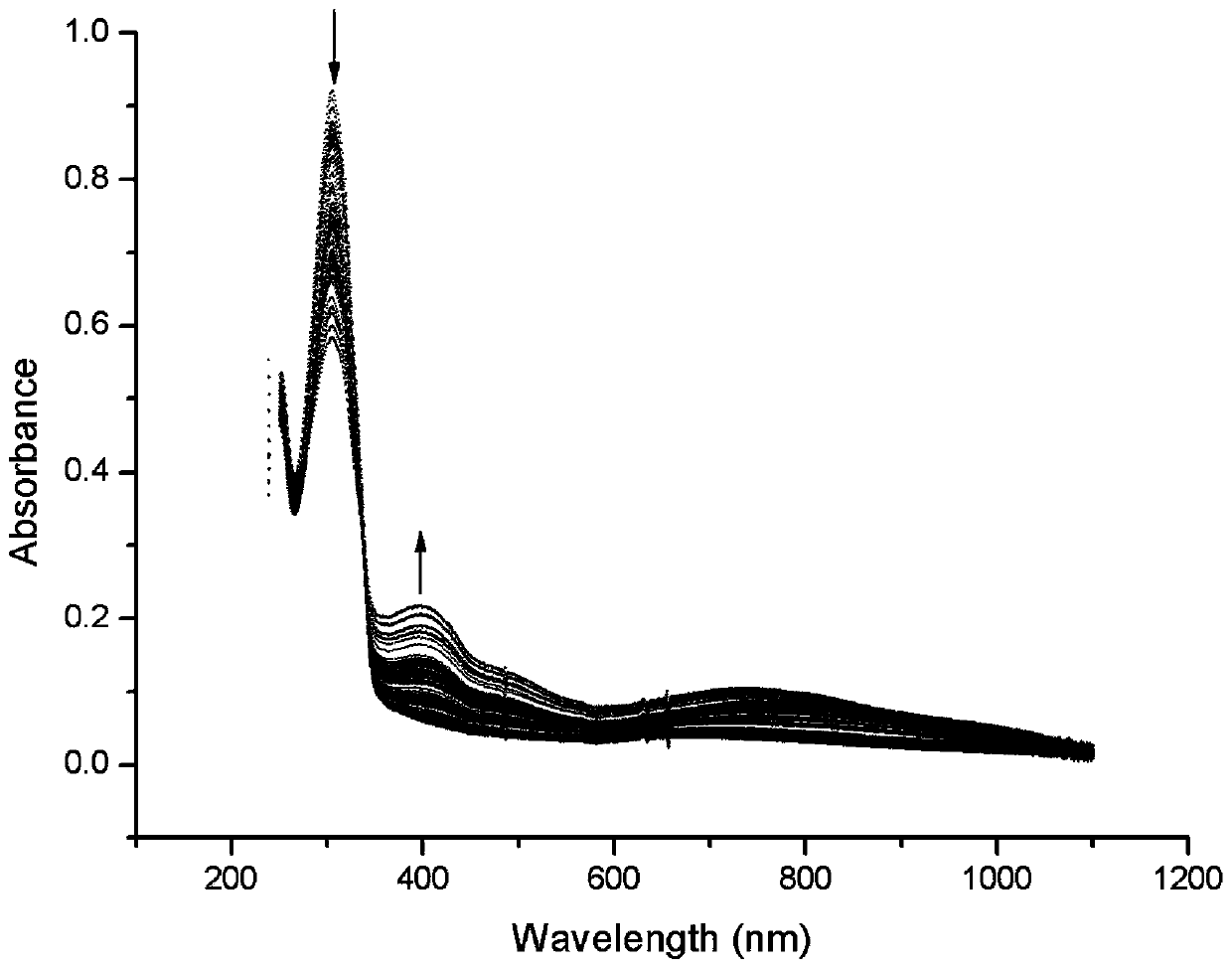
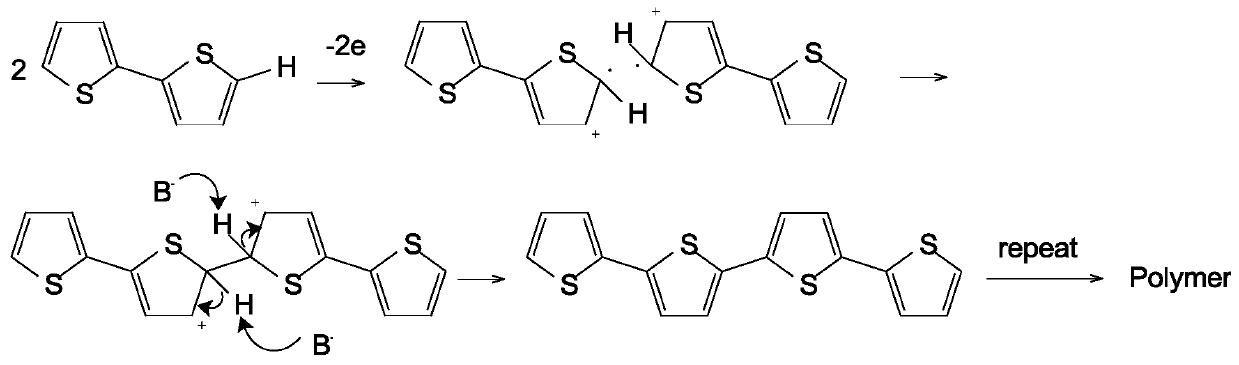
Method for preparing conductive polythiophene and conductive paper through atmospheric pressure plasma in-situ solid-state polymerization
A plasma and solid-state polymerization technology, which is used in the addition of non-polymeric organic compounds, papermaking, textiles and papermaking. , The effect of strong combination and stable performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] A method for preparing conductive polythiophene by atmospheric pressure plasma in-situ solid-state polymerization, comprising the steps of:
[0040]S1. Fully dissolve 2,2'-bithiophene, which is solid at room temperature, in a volatile organic solvent. Specifically, dissolve 200 mg of 2,2-bithiophene in 1 mL of ethanol (without iodine addition), and centrifuge at 10,000 rpm 10 minutes to fully dissolve, the clarified solution was used for spin coating, spin coating 5 times with 750rpm on the quartz substrate, placed 5-10min, after the solvent was volatilized, a solid monomer film (thickness approx. is 0.10mm);
[0041] S2. The monomer film in S1 was placed under the atmospheric pressure plasma of the dielectric barrier discharge device for in-situ solid-state polymerization. The discharge gap <1cm) adopts nanosecond pulse power supply with variable voltage and variable voltage frequency. When the dielectric barrier discharge device is working, the power supply parameter...
Embodiment 2
[0043] A method for preparing conductive polythiophene by atmospheric pressure plasma in-situ solid-state polymerization, comprising the steps of:
[0044] S1. Fully dissolve 2,2'-bithiophene and iodine, which are solid at room temperature, in a volatile organic solvent, specifically 200mg 2,2-bithiophene and 200mg I 2 Dissolve together in 1mL ethanol, centrifuge at 10000rpm for 10 minutes to fully dissolve, use the clarified solution for spin coating, spin coating 5 times on the quartz substrate at 750rpm, place for 5-10min, after the solvent is evaporated, the quartz substrate A solid monomer film (thickness is about 0.10mm) is formed on the upper surface;
[0045] S2. The monomer film in S1 was placed under the atmospheric pressure plasma of the dielectric barrier discharge device for in-situ solid-state polymerization. The discharge gap <1cm) adopts nanosecond pulse power supply with variable voltage and variable voltage frequency. When the dielectric barrier discharge de...
Embodiment 3
[0047] A method for preparing conductive polythiophene by atmospheric pressure plasma in-situ solid-state polymerization, comprising the steps of:
[0048] S1. Fully dissolve 2,2'-bithiophene and iodine, which are solid at room temperature, in a volatile organic solvent, specifically 200mg 3,3'-dibromo-2,2'-bithiophene and 200mg I 2 Dissolve together in 1.5mL chloroform, centrifuge at 10000rpm for 10 minutes to fully dissolve, use the clear solution for spin coating, spin coating 6 times on the quartz substrate at 550rpm, place for 10-15min, after the solvent is evaporated, the quartz substrate A solid monomer film (thickness is about 0.20mm) is formed on the upper surface of the bottom;
[0049] S2. Place the monomer film in S1 under the atmospheric pressure plasma of dielectric barrier discharge device to carry out in-situ solid-state polymerization, dielectric barrier discharge device adopts nanosecond pulse power supply with variable voltage and variable voltage frequency,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com