Method for selectively removing arsenic and recycling valuable metals from white smoke dust
A technology for recovery of valuable metals, applied in chemical instruments and methods, arsenic compounds, arsenic oxide/arsenic hydroxide/oxyacid arsenic, etc., can solve the problem of lack of perfect treatment process, low arsenic removal rate, and poor process versatility and other problems, to avoid long wet treatment process, high arsenic removal selectivity, and strong adaptability of raw materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
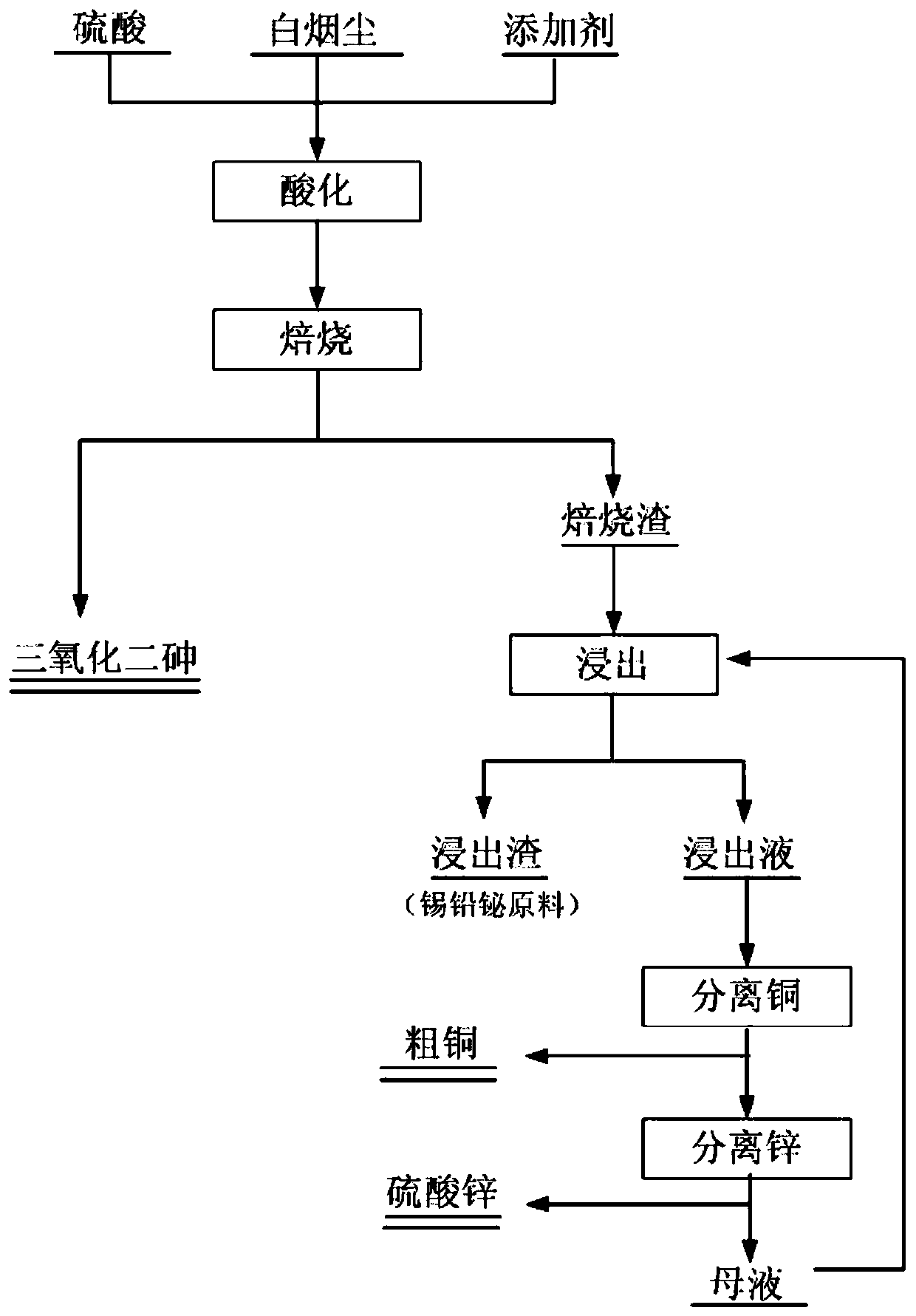
[0036] 1) 500kg of arsenic-containing copper smelting smoke and dust, 75kg of additive sulfur and mix evenly, add 85L of sulfuric acid and stir in the acidification tank;
[0037] 2) Put the acidified material into 30cm×20cm×10cm iron pan and stack it on the material rack, put it into the muffle furnace flue gas hood and heat it up to 500°C for 3 hours, and discharge the material; the arsenic-containing smoke generated by roasting Collected by the dust collection system and sold as arsenic trioxide;
[0038]3) Add water to the roasted slag at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:6, leach in a stirring tank, adjust the leaching pH to ≤4 with sulfuric acid, control the leaching temperature at 80-95°C, and leaching for 3 hours. After the leaching is completed, plate and frame filtration;
[0039] 4) The filtrate is replaced with zinc powder to recover copper, the copper removal solution is concentrated to recover zinc sulfate, and valuable metals such as tin, lead and bismuth are recover...
Embodiment 2
[0042] 1) 500kg of arsenic-containing copper smelting smoke and dust, 230kg of additive pyrite and mixing, add 145L of sulfuric acid and stir in the acidification tank;
[0043] 2) Put the acidified materials into 30cm×20cm×10cm iron pans and stack them on the material rack, put them into the muffle furnace flue gas hood and heat up to 575°C for 5 hours, and discharge the materials; the arsenic-containing smoke generated by roasting Collected by the dust collection system and sold as arsenic trioxide;
[0044] 3) Add water to the roasted slag according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:7, leaching in the stirring tank, and adjust the leaching pH to ≤5 with sulfuric acid, control the leaching temperature at 90-95°C, leaching for 4 hours, and filter the plate and frame after the leaching is completed;
[0045] 4) The filtrate is replaced with zinc powder to recover copper, the copper removal solution is concentrated to recover zinc sulfate, and valuable metals such as tin, lead ...
Embodiment 3
[0048] 1) Mix 500kg of arsenic-containing copper smelting dust, 45kg of additive charcoal powder, add 100L of sulfuric acid and stir in the acidification tank;
[0049] 2) Put the acidified materials into 30cm×20cm×10cm iron pans and stack them on the material rack, put them into the muffle furnace flue gas hood and heat up to 425°C for 4 hours, and discharge the materials; the arsenic-containing smoke generated by roasting Collected by the dust collection system and sold as arsenic trioxide;
[0050] 3) Add water to the roasted slag according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:4, leaching in the stirring tank, and adjust the leaching pH to ≤6 with sulfuric acid, control the leaching temperature at 80-95°C, leaching for 4 hours, and filter the plate and frame after leaching;
[0051] 4) The filtrate is replaced with zinc powder to recover copper, the copper removal solution is concentrated to recover zinc sulfate, and valuable metals such as tin, lead and bismuth are recovered ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com