SiC power device
A technology of power devices and N-type semiconductors, which is applied to semiconductor devices, electrical components, diodes, etc., can solve the problems of inability to adopt silicon-based conventional reverse conduction structures, slow turn-off speed of SiCIGBT, and large reverse recovery charge, etc., to achieve Elimination of minority carrier injection effect, small electric field reduction effect, and small leakage current effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
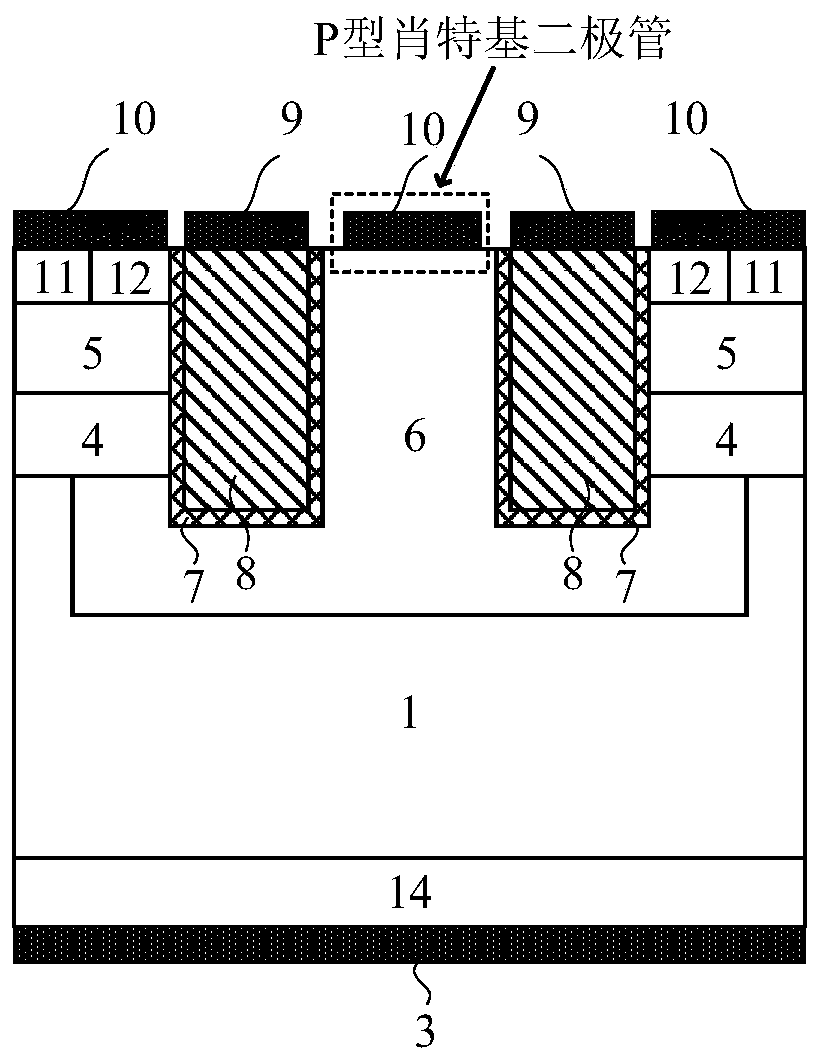
[0062] This embodiment provides a SiC MOSFET device integrating a PN junction body diode, and its cell structure is as follows figure 1 As shown, it includes: an N-type lightly doped region 1 as a withstand voltage region;
[0063]An N-type heavily doped ohmic contact region 14 disposed on the lower surface of the withstand voltage region 1, and an anode metal 3 covering the lower surface of the N-type heavily doped ohmic contact region 14;
[0064] Two separate gate deep grooves arranged on the upper surface of the withstand voltage region 1; the gate deep grooves are composed of an oxide layer 7 on the groove wall and a conductor 8 filled in the groove wall, and the conductor 8 is covered with Gate electrode metal 9; the semiconductor surfaces on the outside of the two gate deep grooves are respectively provided with a P-type semiconductor region base region 5, and the base region 5 is in contact with the groove wall; The contacted N-type heavily doped region 12 as the cat...
Embodiment 2
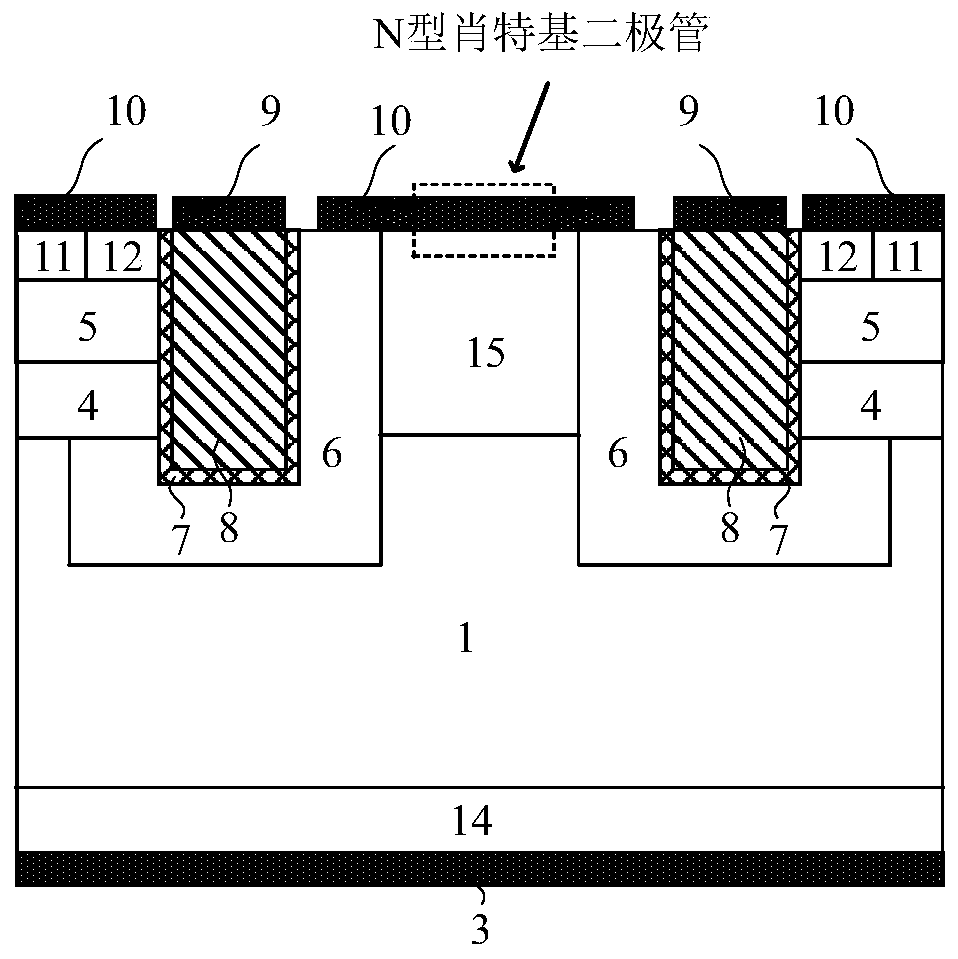
[0069] This embodiment provides a SiC MOSFET device integrating an N-type anti-parallel Schottky diode, and its cell structure is as follows: figure 2 As shown, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that: the P-type semiconductor region 6 is also provided with an N-type semiconductor region 15, and the N-type semiconductor region 15 is located between two gate deep grooves, and the P-type semiconductor region The region 6 is divided into two parts, and the lower surface of the N-type semiconductor region 15 is in contact with the withstand voltage region 1, and the upper surface forms a Schottky contact with the cathode metal 10;
[0070] When the MOSFET conducts in the reverse direction, since the conduction voltage drop of the N-type Schottky diode is lower than that of the PN junction diode, only the N-type Schottky diode participates in conduction, thus avoiding the minority carrier injection effect and reducing the Conduction loss and reverse recovery loss, EMI, etc.
Embodiment 3
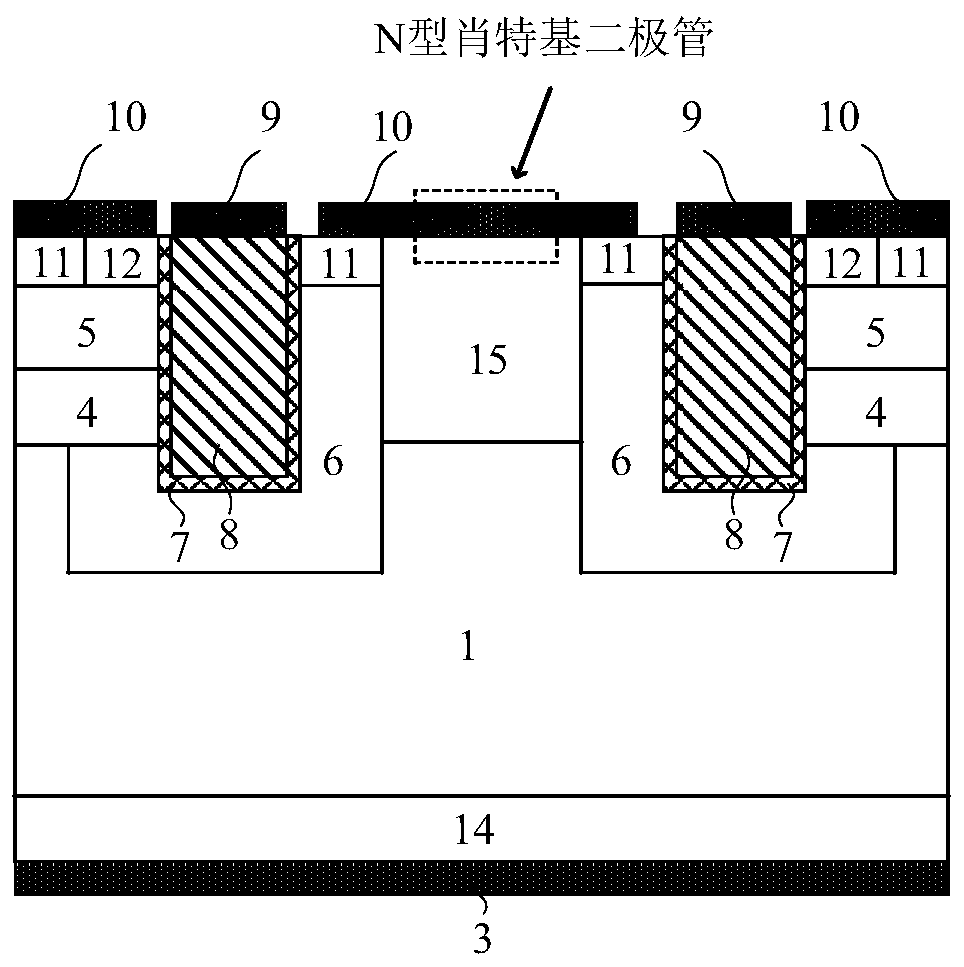
[0072] This embodiment provides a SiC MOSFET device integrating an N-type anti-parallel Schottky diode, and its cell structure is as follows: image 3 As shown, it differs from Embodiment 2 in that the two parts of the P-type semiconductor region 6 located on both sides of the N-type semiconductor region 15 respectively form ohmic contacts with the cathode metal 10 through the P-type heavily doped region 11 at the semiconductor surface.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com