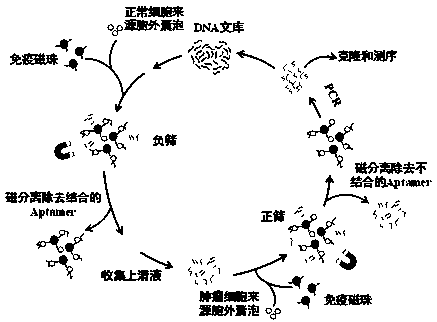
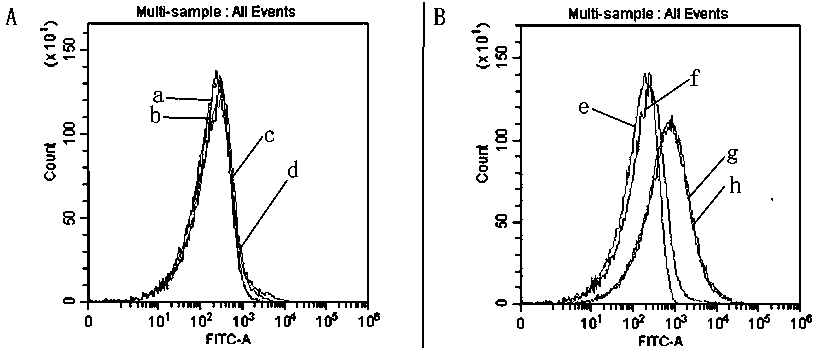
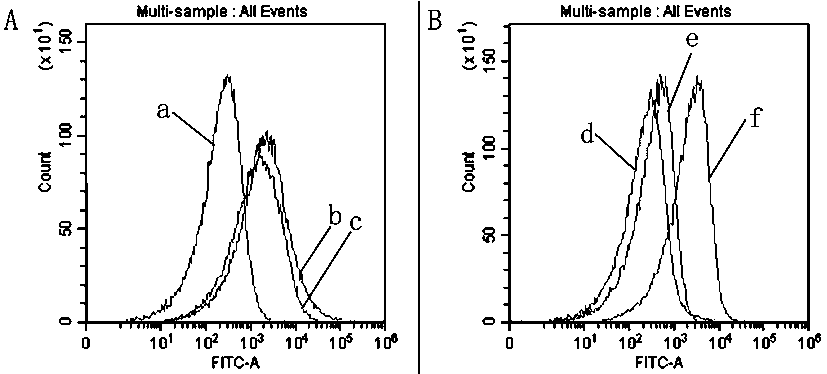
Extracellular vesicle surface protein specific aptamer screening technology based on magnetic-activated cell sorting
An immunomagnetic bead method and surface protein technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problem of rarely reported extracellular vesicle aptamer screening, achieve important social value and clinical significance, simple and rapid recovery rate, and reduce screening. effect of time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
[0052] The screening of specific aptamers for extracellular vesicle surface proteins in human lung adenocarcinoma cell A549 cells based on the immunomagnetic bead method comprises the following steps:
[0053] 1) Synthesize upstream and downstream primers and random libraries
[0054] The specific primer pair F / R and the random library sequence were synthesized by Shanghai Sangon Biotechnology Co., Ltd. The sequence of the upstream primer F is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, and the sequence of the downstream primer R is shown in SEQ ID NO: 2. The random library The sequence of is shown in SEQ ID NO: 3:
[0055] Upstream primer F (SEQ ID NO: 1): 5'-FAM-GTTGGTGAGGTAACGGCTCA-3'
[0056] Downstream primer R (SEQ ID NO: 2): 5'-biotin-CGGATAACGCTTGCCACCTA-3';
[0057] Random library: 35'-GTTGGTGAGGTAACGGCTCA-40nt-TAGGTGGCAAGCGTTATCCG-3';
[0058] Further, the random library in step 1) is an 80nt single-stranded oligonucleotide, the middle 40nt of the single-stranded oligonucleotide is 40...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com