A method for in-situ electrocatalytic generation of sulfate radicals to oxidize pollutants
A technology of sulfate and free radicals, which is applied in the fields of environment, electrochemistry, and energy, to achieve the effects of small secondary pollution, efficient in-situ repair treatment, and easy automation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
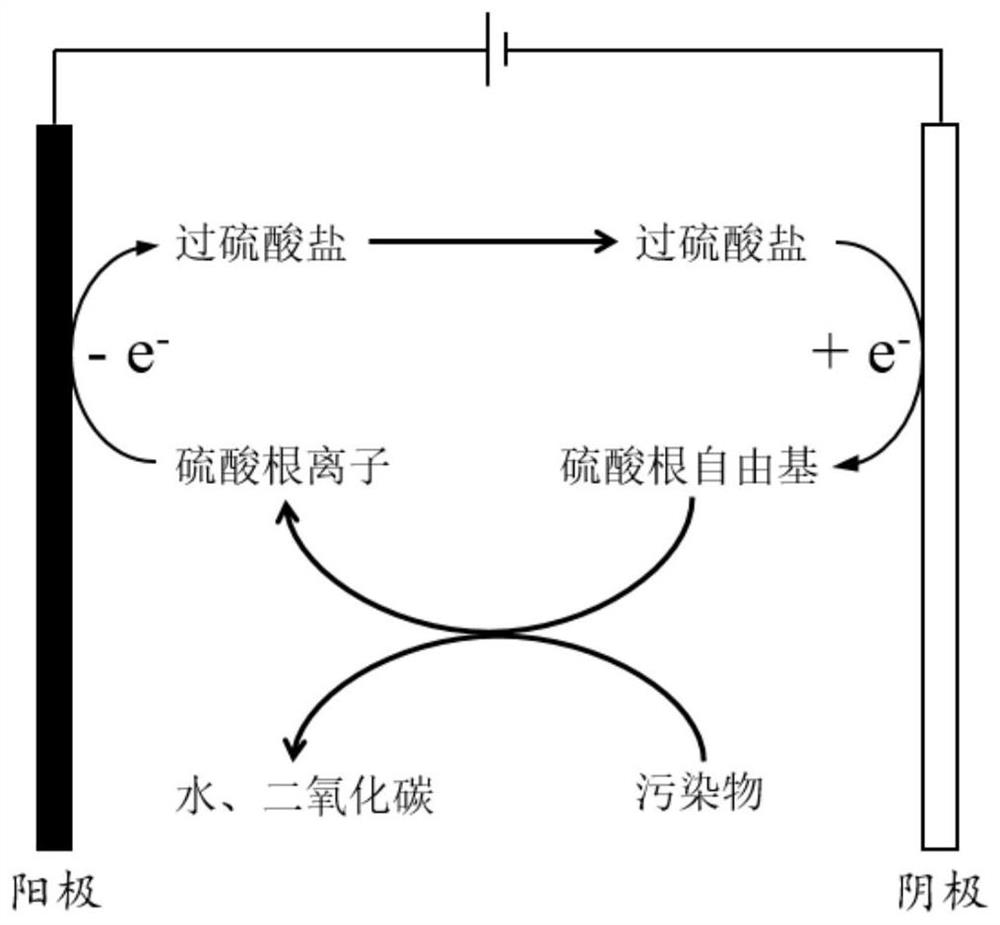
[0028] An electrochemical system for electrocatalytic in situ generation of strong oxidizing sulfate radicals for the oxidation and removal of pollutants. The principle of the system is as follows figure 1 As shown, its construction includes the following steps:
[0029] (1) The anode material used in the electrochemical system has the following characteristics. A boron-doped diamond electrode with an oxygen evolution potential of 2.4V (vs. SCE) is used as the anode, and Co 3 o 4 As the cathode material, a saturated calomel electrode was used as the reference electrode. The operating conditions of the electrochemical system are: the current density is 10mA / cm 2 , the electrode area is 0.1m 2 / t, the electrode spacing is 1cm, and the supporting electrolyte is 0.1M Na 4 SO 4 aqueous solution.
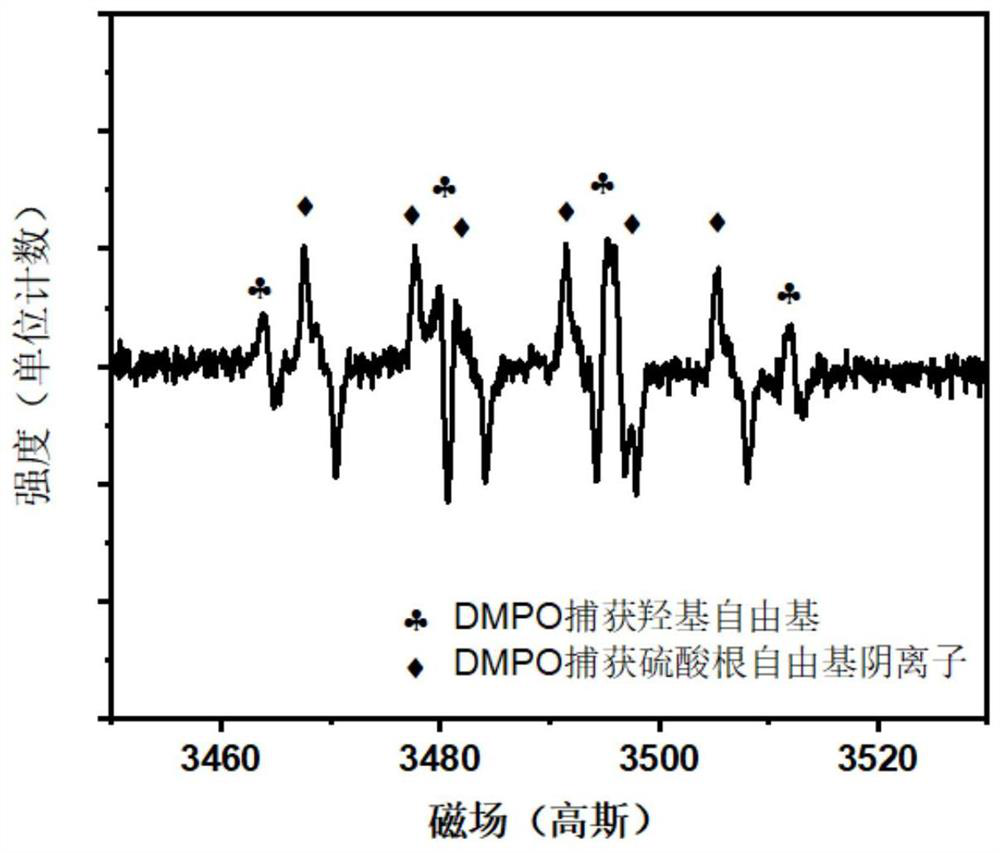
[0030] (2) Electron paramagnetic resonance technology is used to detect the free radical species produced in this electrochemical system, such as figure 2 As shown, it is found th...
Embodiment 2
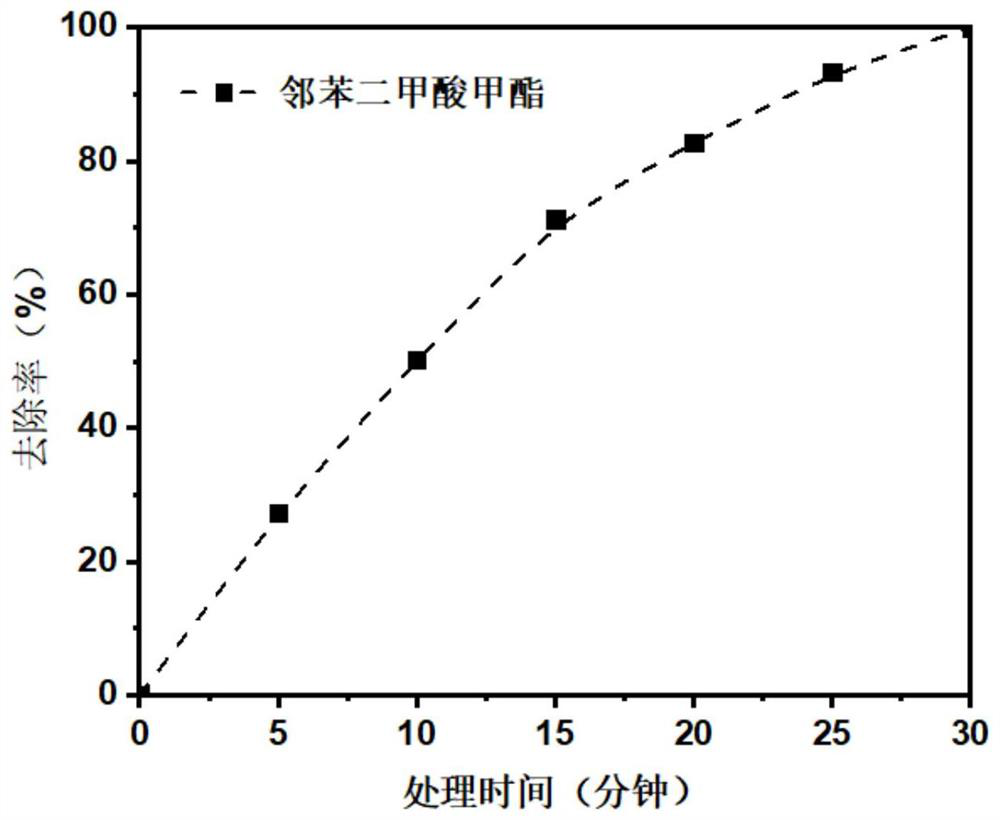
[0032] At room temperature, a boron-doped diamond electrode with an oxygen evolution potential of 2.4 V (vs. SCE) was used as the anode, and Co 3 o 4 As the cathode material, a saturated calomel electrode was used as the reference electrode. The operating conditions of the electrochemical system are: the current density is 10mA / cm 2 , the electrode area is 0.1m 2 / t, the electrode spacing is 1cm, and the supporting electrolyte is 0.1mol L -1 Na 4SO 4 Aqueous solution, add 10mg / L of dimethyl phthalate as a pollutant. Such as image 3 As shown, within 30 minutes, the degradation rate of dimethyl phthalate reached 99%, realizing the efficient removal of pollutants.
Embodiment 3
[0034] At room temperature, the boron-doped diamond electrode is used as the anode, the tricobalt tetroxide is used as the cathode, the saturated calomel electrode (SCE) is used as the reference electrode, and the supporting electrolyte solution is: 0.1mol L -1 Sulfate solution in water. The concentration of pollutants was detected by high performance liquid chromatography. This electrochemical system was used to degrade chemical oxygen demand (COD Cr ) is 500mg / L domestic wastewater, and the COD in the degradation process is measured by the national standard method Cr Variety. Such as Figure 4 As shown, COD within 2h Cr The removal rate has reached more than 80%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| electric potential / voltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com