Method for screening bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus disease resistance with BmIML-2 gene
A technology of nuclear polyhedron and viral disease, which is applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, and microbial measurement/inspection, can solve the problems of silkworm mutual infection and easy pollution of silkworm breeding environment, so as to reduce the probability of mutual cross-infection, The effect of shortening the test period and improving the resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
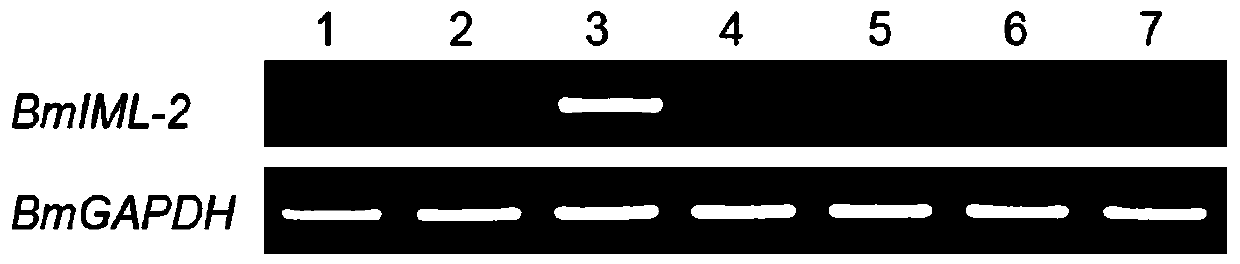
[0026] Example 1 Detection of the difference in transcription level of BmIML-2 gene in various tissues of larvae by RT-PCR
[0027] RNA was extracted from the head, midgut, fat body, silk gland, martensian tube, epidermis and trachea of the 5th instar larvae on the 3rd day of the silkworm, and reverse transcribed to obtain cDNA. Using the cDNA obtained by reverse transcription as a template, specific primers were designed, wherein the forward primer (SEQ ID NO. 1): 5'-AGAGTTCGTGTGGCATCTA-3', and the reverse primer (SEQ ID NO. 2): 5'-ACCATATGAGAGGCAGGGTT- 3'. The silkworm BmGAPDH gene is used as an internal reference gene, and its upstream and downstream primer sequences are F (SEQ ID NO. 3): 5'-TTCATGCCACAACTGCTACA-3', R (SEQ ID NO. 4): 5'-AGTCAGCTTGCCATTAAGAG-3', and BmIML-2 is detected Differences in the transcription level of genes in different tissues of silkworm larvae (as attached figure 1 Shown).
Embodiment 2
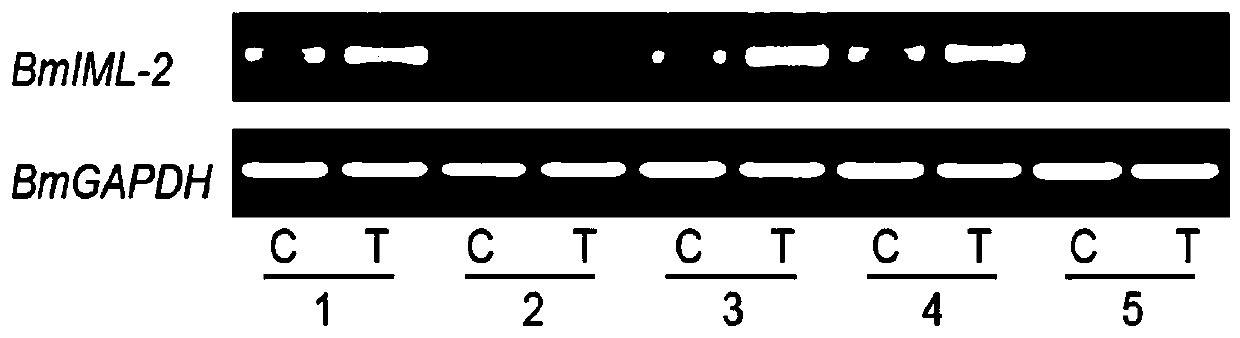
[0028] Example 2 Treating several silkworm species with feeding nuclear polyhedrosis virus and detecting changes in BmIML-2 transcription level
[0029] When the silkworm larvae were first fed to mulberries, several silkworm varieties were used as experimental materials, and each variety was divided into two groups for treatment. The treatment group was fed with nuclear polyhedrosis virus (concentration 1×10 7 Pieces / mL) fresh mulberry leaves after soaking, and the control group was fed fresh mulberry leaves without virus soaking. After adding the poison, weed out the dead silkworms in time, until the cocoons are formed on the upper swarms, and weed out the dead pupae. Take each group of silkworm moths after seed production, extract fat body RNA and reverse transcription to obtain cDNA. Design specific primers (same as Example 1), and use the cDNA obtained by reverse transcription as a template to detect the difference in the transcription level of the silkworm BmIML-2 gene befo...
Embodiment 3
[0030] Example 3 Continued screening of silkworm varieties with significantly up-regulated BmIML-2 transcription level after feeding virus
[0031] According to the test results in Example 2, the silkworm eggs laid by the individual silkworm species whose BmIML-2 transcription level was significantly up-regulated after the addition of nuclear polyhedrosis virus were selected for seeding and subculture, and the subcultured silkworm species were repeatedly screened . That is, when the silkworm larvae were fed to the mulberry last time, repeat the virus feeding treatment in the previous step, use the RT-PCR method to detect the difference in the transcription level of the BmIML-2 gene before and after feeding the virus, and screen the excellent male and female species Subgeneration. After screening by the above method, the resistance of Baiyu CB variety to nuclear polyhedrosis virus is increased by 10-100 times. When the second instar silkworm is raised, Baiyu CB and Jingsong are ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com