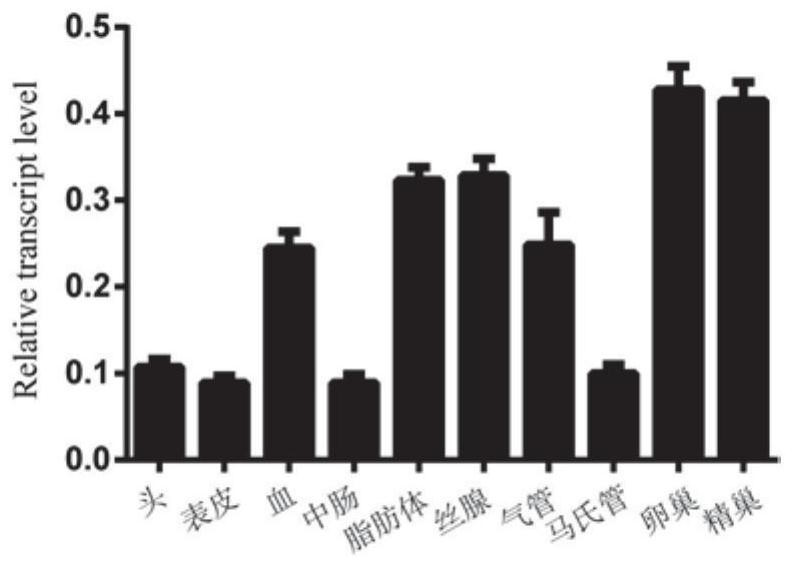
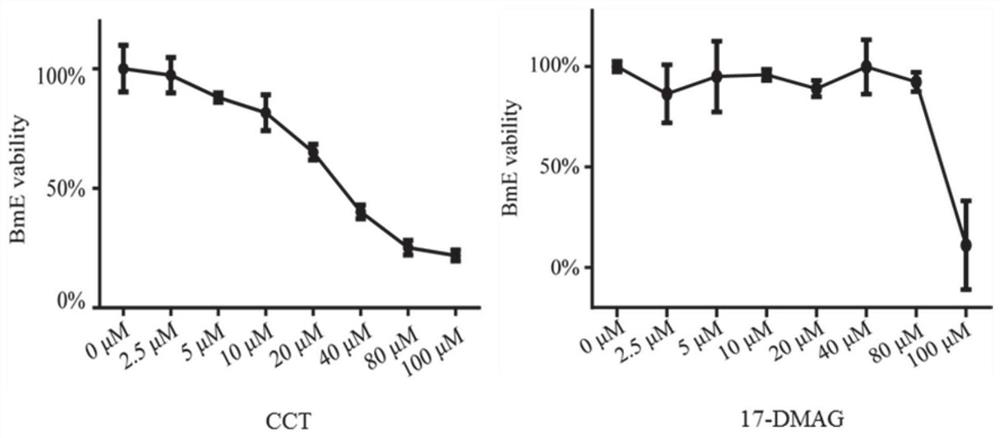
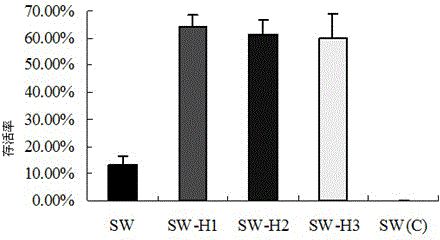
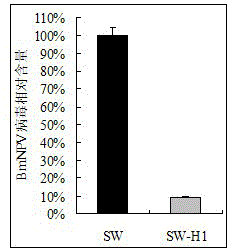
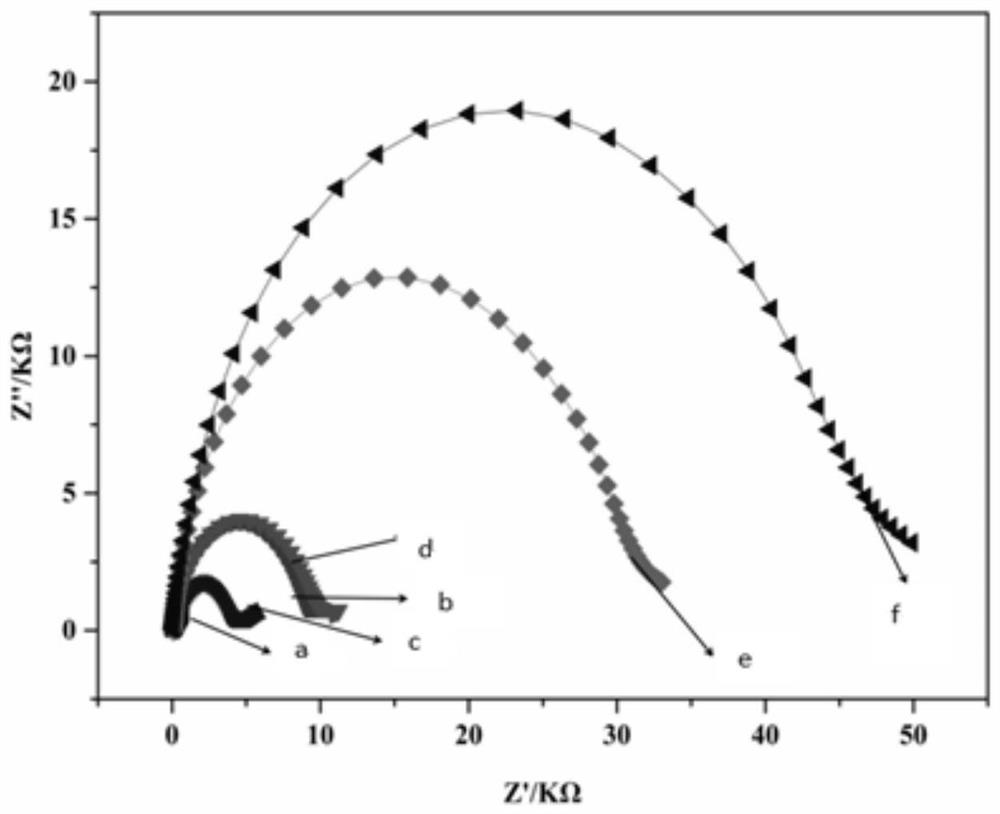
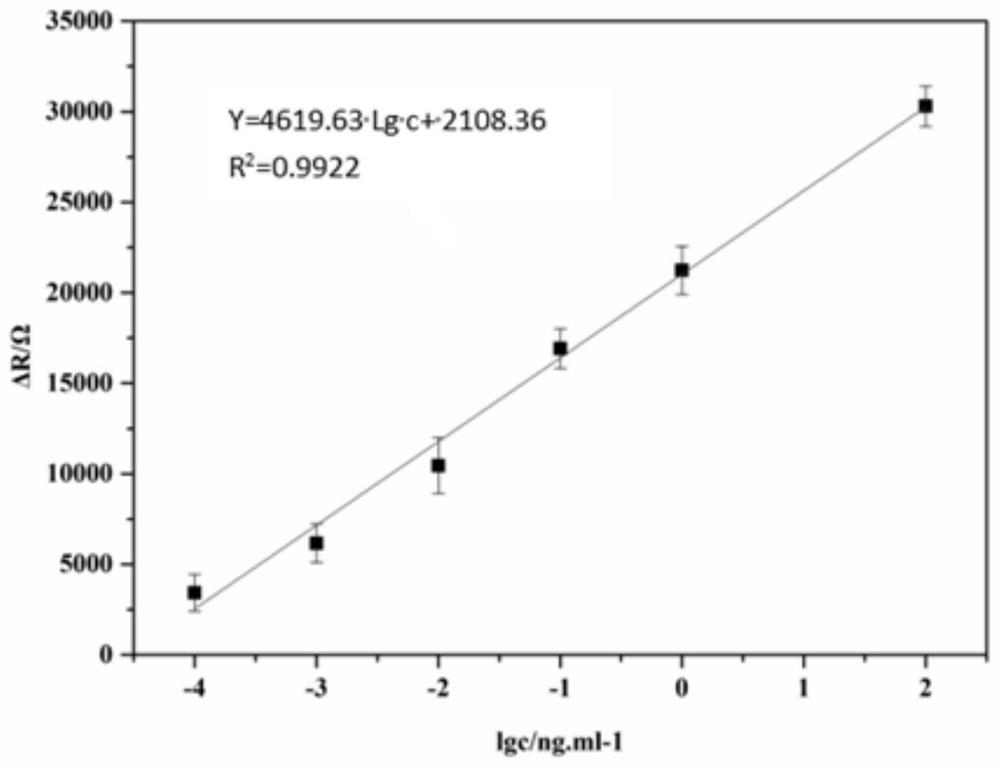
Patents
Literature
33 results about "Bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus BmNPV" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Rapid detection kit and detection method for bombyx mori nuclear polyhydrosis virus
InactiveCN104450957AStrong specificityHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementBombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus BmNPVNucleic acid detection
The invention relates to a rapid detection kit and a detection method for bombyx mori nuclear polyhydrosis virus, specifically relates to a quick and convenient detection kit for detecting the bombyx mori nuclear polyhydrosis virus by combining the loop-mediated isothermal amplification technology and the nucleic acid detection lateral chromatography test paper, and a detection method of the detection kit, and belongs to the technical field of viral epidemic disease diagnosis. The detection kit is characterized by comprising a BmNPVLAMP pre-reaction liquid, wherein the desired primer and probe are designed according to the conserved region of the genomic sequence of the bombyx mori nuclear polyhydrosis virus published by GenBank; the kit is capable of effectively and quickly detecting the bombyx mori nuclear polyhydrosis virus; the steps of virus DNA extraction and BmNPVLAMP reaction system amplification are performed, and after the reaction ends, the result is judged by use of the quick nucleic acid detection test paper to obtain that the BmNPV virus DNA is efficiently and specifically amplified; the detection method is simple, convenient and quick, good in specificity, and high in sensitivity, and is suitable for farmers to use daily and advantageous for diagnosing and preventing the bombyx mori nuclear polyhydrosis virus disease.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Application of prodiginine (PG) in prevention and control of bombyx morinuclear polyhedrosis virus
InactiveCN103690534AAccelerated deathPrevent and effectively control the spread ofOrganic active ingredientsAnimal feeding stuffBombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus BmNPVAssay
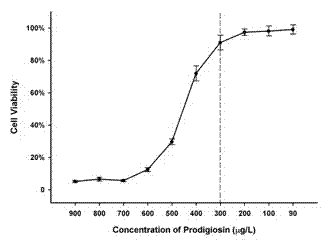
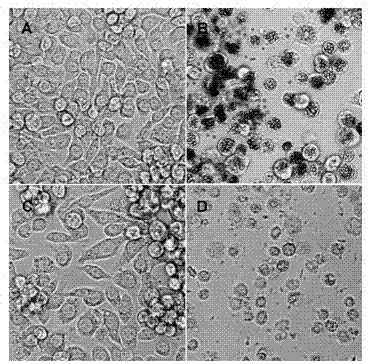
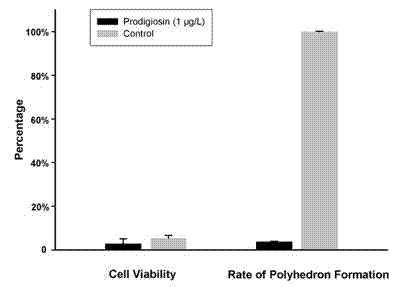
The invention relates to the effect of small molecule compound prodiginine (PG) for inhibiting BmNPV (bombyx mori nuclear polyhydrosis virus), and application thereof in prevention and control of BmNPV. Cell assay indicates that PG can interfere with proliferation of BmNPV in cells in a concentration range of 0.01-0.8 mu g / L to stop formation of virus polyhedron, and can selectively cause death of silkworm cells infected with BmNPV in a concentration range of 1-300 mu g / L with the death rate being over 97 percent; PG does not show toxicity to normal cells of silkworm in the application ranges. Individual tests indicate that the silkworms infected with BmNPV stop taking food and prematurely die, infected silkworms can be removed easily, and prodiginine does not show toxicity to healthy cells when prodiginine is used for orally feeding silkworm in a concentration range of 1-10mg per silkworm. Proliferation of BmNPV and formation of polynedron can be inhibited by utilizing PG, and PG has the effect of accelerating death of BmNPV, and can prevent and effectively control spread of BmNPV.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Bombyx mori nuclear polyhydrosis virus (BmNPV) 39k inducible promoter and application thereof
InactiveCN101914537APriming activityPrevent proliferationFungiBacteriaVirus multiplicationBombyx mori
The invention discloses a bombyx mori nuclear polyhydrosis virus (BmNPV) 39k inducible promoter and application thereof. A nucleotide sequence of the promoter is shown as SEQ ID No.1; the promoter has obvious BmNPV inducible promotion activity and can make cells start foreign gene expression when the cells are subjected to the BmNPV infection; an RNAi vector using a BmNPV multiplication essential gene as a target can be built by utilizing the promoter; the abundant expression of shRNA can be performed when the bombyx mori is subjected to the BmNPV infection; the shRNA is cut into siRNA in a cell by an enzyme; specific degradation is performed on the BmNPV multiplication essential gene mRNA to initiate the BmNPV multiplication essential gene to be transcribed and then silenced, so the aim of inhibiting the virus multiplication is fulfilled, and the promoter can be used for preventing and controlling the BmNPV infection of the bombyx mori, performing genetic engineering breeding of bombyx mori anti-BmNPV strains and providing a good reference mode for transgenic therapy of other biologic virus diseases.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
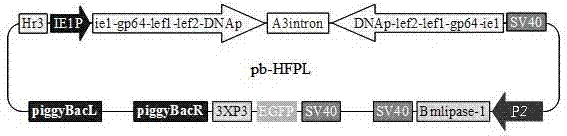
Application and recombinant vector of bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus polygene inverted repeat sequence and bombyx mori lipase-1 gene
ActiveCN102925484AControlled reproductionReduce contentVector-based foreign material introductionInverted Repeat SequencesEnzyme Gene
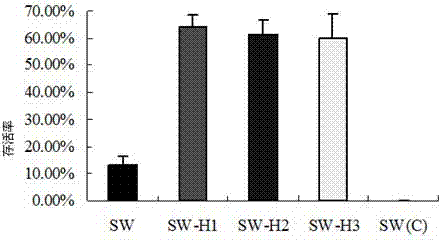
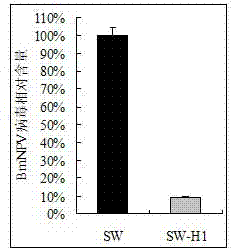
The invention discloses an application of a bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus (BmNPV) polygene inverted repeat sequence and a bombyx mori lipase-1 gene and specifically an application of the BmNPV polygene inverted repeat sequence and the bombyx mori lipase-1 gene to the construction of a recombinant vector; the vector can express a hairpin RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) for interfering with BmNPV multiple genes and bombyx mori lipase-1; BmNPV is inactivated by the incremental expression of bmlipase-1 (bombyx mori lipase-1) in the intestinal juice of a bombyx mori, and the number of BmNPV which invades intestinal cells of the bombyx mori is reduced; the expressed hairpin RNA can degrade the mRNA (Messenger Ribonucleic Acid) of a BmNPV gene and inhibit the replication and the proliferation of the virus in the Bombyx mori; and after the vector is used for producing a transgenic bombyx mori, the proliferation of BmNPV in the transgenicbombyx mor can be effectively inhibited, and the virus content is reduced, so that the survival rate of the bombyx mori infected with BmNPV is greatly increased.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
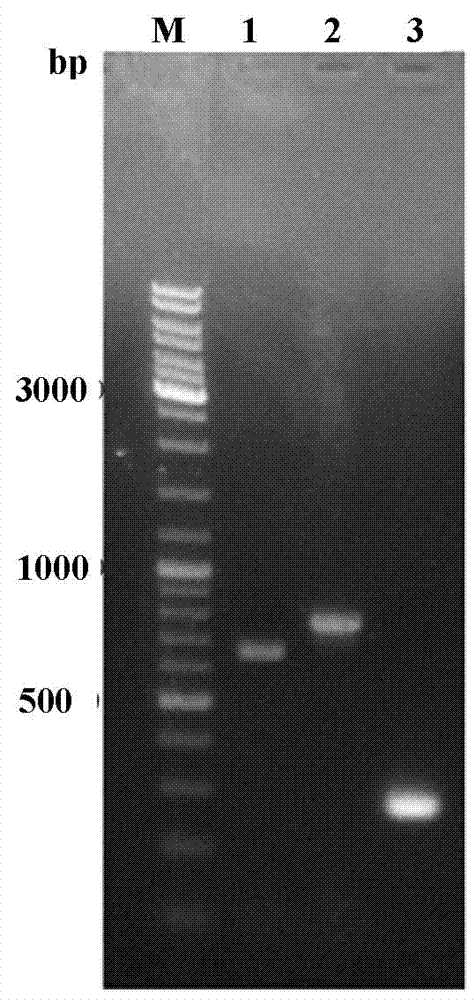
Method for targeted knockout of non-essential genes for Bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus replication
ActiveCN103589745AEasy accessObtain intuitivelyDsDNA virusesVector-based foreign material introductionPUC19Genomic DNA
The present invention relates to a method for targeted knockout of non-essential genes for replication of the Bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus BmNPV. The method is as below: using BmNPV as a material to amplify a homologous sequence at both ends of a non-essential region for replication by PCR and cloning it into a vector pUC19; splicing successively an IE1 early promoter, a marker gene (EGFP) and a termination sequence SV40polyA of BmNPV by an overlapping PCR method and cloning them to the abovementioned vector pUC19 to obtain a recombinant transfer vector pUC19-lef7-IE1-EGFP-SV40polyA-gp64; co-transfecting BmN cells using the vector and the genome of wild BmNPV and carrying out homologous recombination to obtain a recombinant virus RBmNPV-EGFP with a fluorescent marker; and co-transfecting BmN cells using genomic DNA thereof and a transfer vector pUC19-lef7-gp64 without marker gene and carrying out homologous recombination to obtain a recombinant virus RBmNPV without fluorescent marker gene. The present invention solves the problem of the presence of marker genes in recombinant virus genomes and improves the screening efficiency of positive recombinant viruses, and thus the marker genes can be reused.
Owner:TIANJIN YAOYU BIOLOGICAL TECH
Genetic modification method capable of enhancing disinsection efficiency of baculovirus
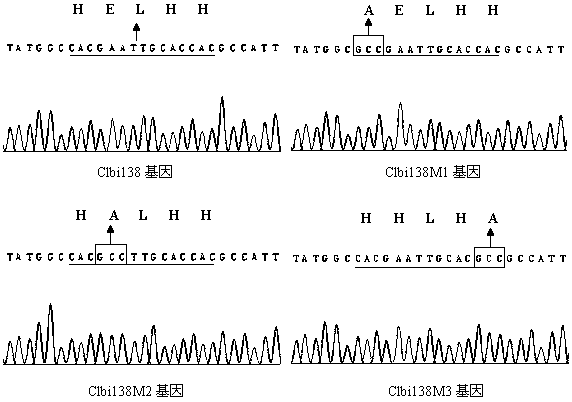
InactiveCN104911201AImprove insecticidal efficiencyReduce half-lethal timeBiocideMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEnzyme digestion
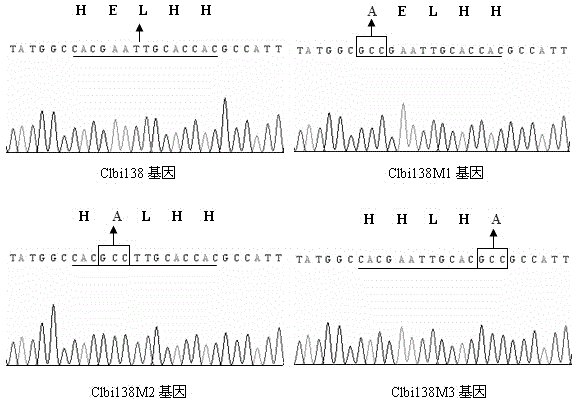
The invention relates to a genetic modification method capable of enhancing disinsection efficiency of baculovirus, belonging to the field of gene engineering. The method comprises the following steps: amplifying EGFP gene by using a pEGFP-N1 vector as a template, carrying out double enzyme digestion, and connecting into a plasmid pFastBacDUAL to obtain a recombinant plasmid pDUAL-EGFP; designing and synthesizing primers according to the Clbi138 gene sequence and open reading frame thereof; carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification by using greenish brown hawk moth karyotype polyhedrosis virus genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) as a template, recovering the target segment, carrying out enzyme digestion, and connecting into the recombinant plasmid pDUAL-EGFP subjected to double enzyme digestion to obtain a recombinant plasmid pDUAL-EGFP-Clbi138; and transforming a Escherichia coli strain containing silkworm karyotype polyhedrosis virus, culturing, purifying, inoculating into an LB (Langmuir-Blodgett) liquid culture medium, carrying out shake culture, and extracting DNA of the recombinant BmNPV. The experiment proves for the first time that the disinsection efficiency of the recombinant BmNPV is obviously enhanced, the median lethal concentration is reduced by 11 times as compared with the control group, the median lethal time is shortened by 42.9% as compared with the control group, and the liquefaction in the sick polypide is more severe, thereby achieving the effect of enhancing control effects on pests. The recombinant BmNPV has obvious economic and ecological benefits, and has wide application prospects.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
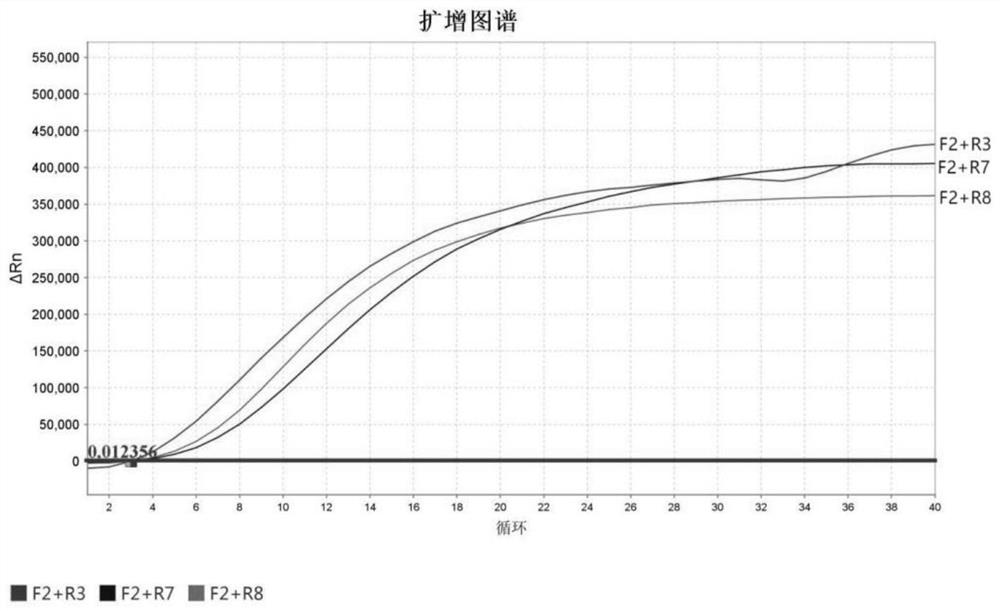
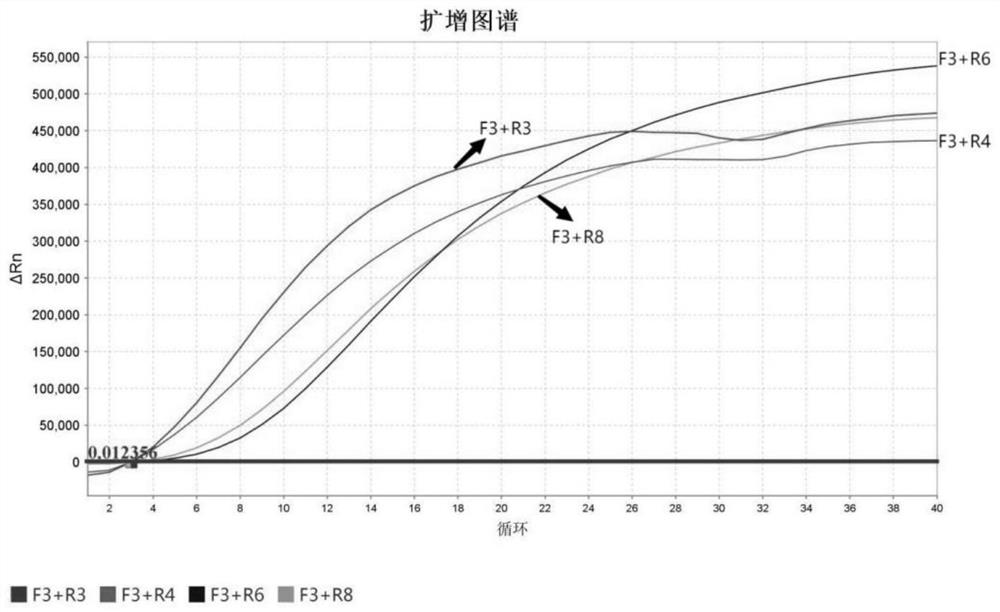
LAMP primer combination for detecting Bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus and kit
InactiveCN105803117ARapid early diagnosisEarly diagnosis is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virusTissue sample
The invention discloses an LAMP primer combination for detecting Bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus and a kit. The primer combination comprises external primers, internal primers and a loop primer, wherein the external primers F3 and B3, the internal primers FIP and BIP and the loop primer LF have base sequences of a sequence list from SEQ.ID.No.1 to SEQ.ID.No.5. The primer combination is contained in the kit. By means of the LAMP primer combination for detecting Bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus and the kit, Bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus can be detected only by performing DNA extraction and loop-mediated isothermal amplification on a tissue sample, thus early diagnosis of Bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus in a production field can be carried out quickly, accurately and easily. Compared with the prior art, the LAMP primer combination for detecting Bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus and the kit have the advantages of high specificity, high sensitivity, quick result obtaining and no pollution.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
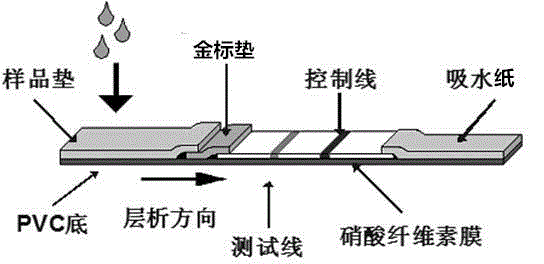
Immune colloidal gold test strip and detection method for karyotype polyhedrosis viruses of bombyx mori
The invention relates to an immune colloidal gold test strip and a detection method for karyotype polyhedrosis viruses of bombyx mori, particularly relates to an immune colloidal gold diagnosis test strip for detecting the karyotype polyhedrosis viruses of the bombyx mori by adopting an immunochromatography technology, and a preparation method of the immune colloidal gold diagnosis test strip, and belongs to the technical field of virus epidemic disease diagnosis. The immune colloidal gold test strip comprises a colloidal gold pad marked with an antigen BmNPV-Lef4 antibody and a coated nitrocellulose membrane, wherein an upper detection line of the nitrocellulose membrane is coated by rabbit-anti BmNPV-Lef4; and a quality control line at the lower part of the nitrocellulose membrane is coated with goat-anti-mouse IgG. The immune colloidal gold test strip is used for detecting the karyotype polyhedrosis viruses of the bombyx mori; compared with a traditional colloidal gold detection method, a double-antibody sandwich method is adopted when the colloidal gold test strip is prepared and a concentration proportion of two virus antibodies is regulated, so that the specificity, the sensitivity and the stability of a detection result can be effectively guaranteed; the detection sensitivity is high and the detection method is simple and convenient and is applied to the detection of the karyotype polyhedrosis viruses of the bombyx mori for the first time.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
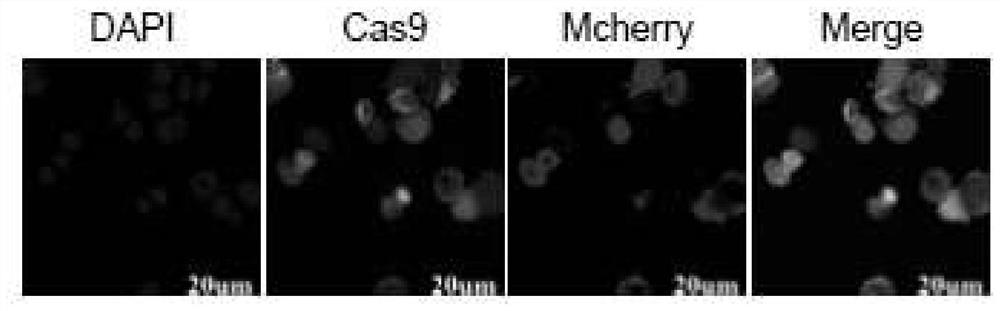
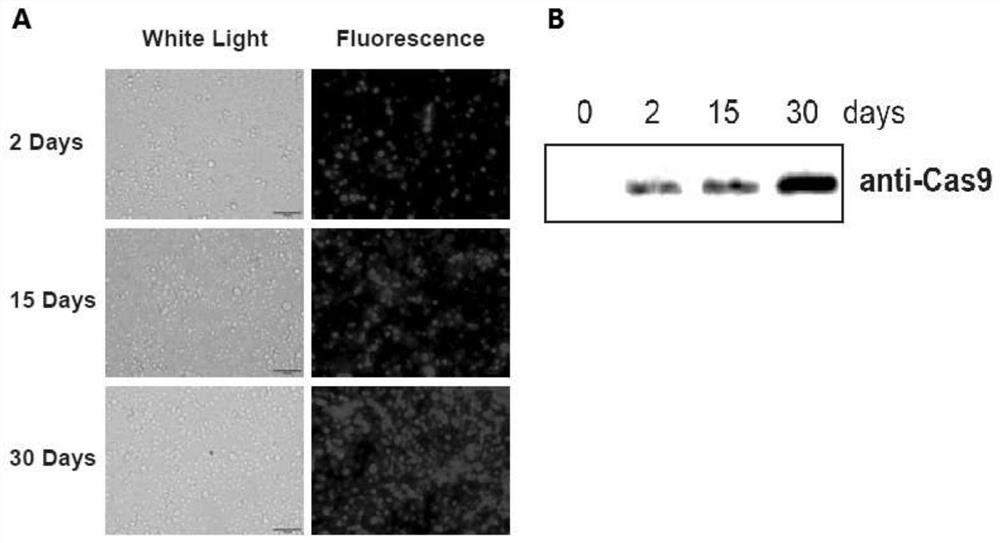
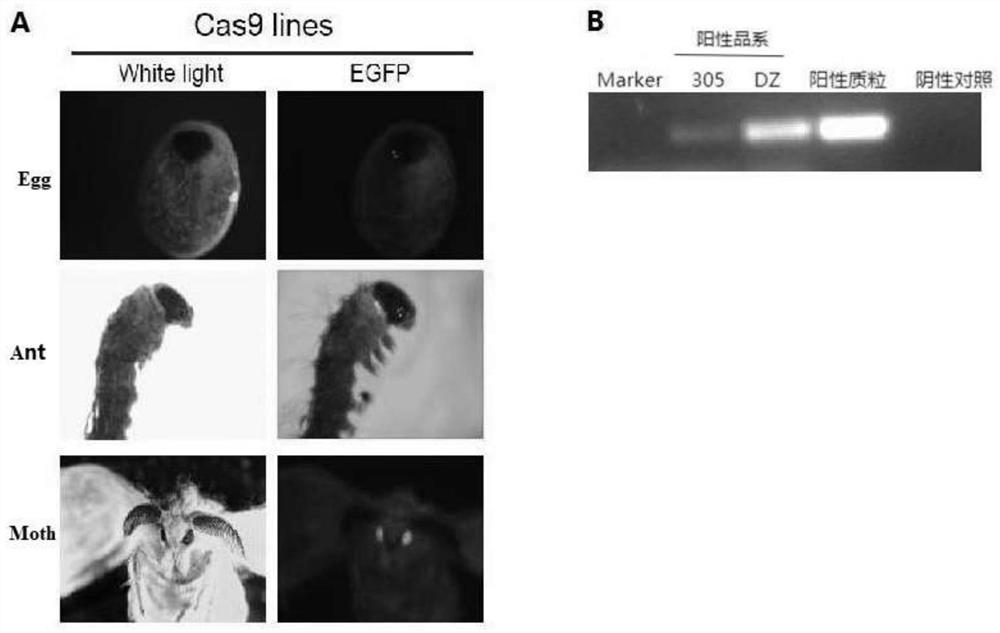
Cas9 system for efficiently editing bombyx mori genome and application of Cas9 system
PendingCN112852871AImprove securityEfficient editingHydrolasesNucleic acid vectorPromoterRecombinant virus
The invention discloses a Cas9 system for efficiently editing a bombyx mori genome and an application of the Cas9 system. The system comprises a bombyx mori transgenic expression vector for expressing a Cas9 gene and bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus packaging virion containing an expression cassette U6-sgRNA expressed by a U6 promoter regulating sgRNA. A bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus (BmNPV) genome is used as a vector, the U6-sgRNA expression cassette is recombined to the virus genome through Bac-to-Bac transposition, a recombinant virion is constructed, a Cas9 cell line or Cas9 bombyx mori is infected with the recombinant virus, and a target gene can be effectively edited. The established Cas9 system does not need a transfection process, is high in transfection efficiency and good in safety, can stably and efficiently edit a target gene, and can be suitable for research on functions of viral genes and related host genes, a baculovirus expression system and the like.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
A genetic modification method for improving the insecticidal efficiency of baculovirus
InactiveCN104911201BImprove insecticidal efficiencyReduce half-lethal timeBiocideMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEnzyme digestion
The invention relates to a genetic modification method capable of enhancing disinsection efficiency of baculovirus, belonging to the field of gene engineering. The method comprises the following steps: amplifying EGFP gene by using a pEGFP-N1 vector as a template, carrying out double enzyme digestion, and connecting into a plasmid pFastBacDUAL to obtain a recombinant plasmid pDUAL-EGFP; designing and synthesizing primers according to the Clbi138 gene sequence and open reading frame thereof; carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification by using greenish brown hawk moth karyotype polyhedrosis virus genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) as a template, recovering the target segment, carrying out enzyme digestion, and connecting into the recombinant plasmid pDUAL-EGFP subjected to double enzyme digestion to obtain a recombinant plasmid pDUAL-EGFP-Clbi138; and transforming a Escherichia coli strain containing silkworm karyotype polyhedrosis virus, culturing, purifying, inoculating into an LB (Langmuir-Blodgett) liquid culture medium, carrying out shake culture, and extracting DNA of the recombinant BmNPV. The experiment proves for the first time that the disinsection efficiency of the recombinant BmNPV is obviously enhanced, the median lethal concentration is reduced by 11 times as compared with the control group, the median lethal time is shortened by 42.9% as compared with the control group, and the liquefaction in the sick polypide is more severe, thereby achieving the effect of enhancing control effects on pests. The recombinant BmNPV has obvious economic and ecological benefits, and has wide application prospects.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
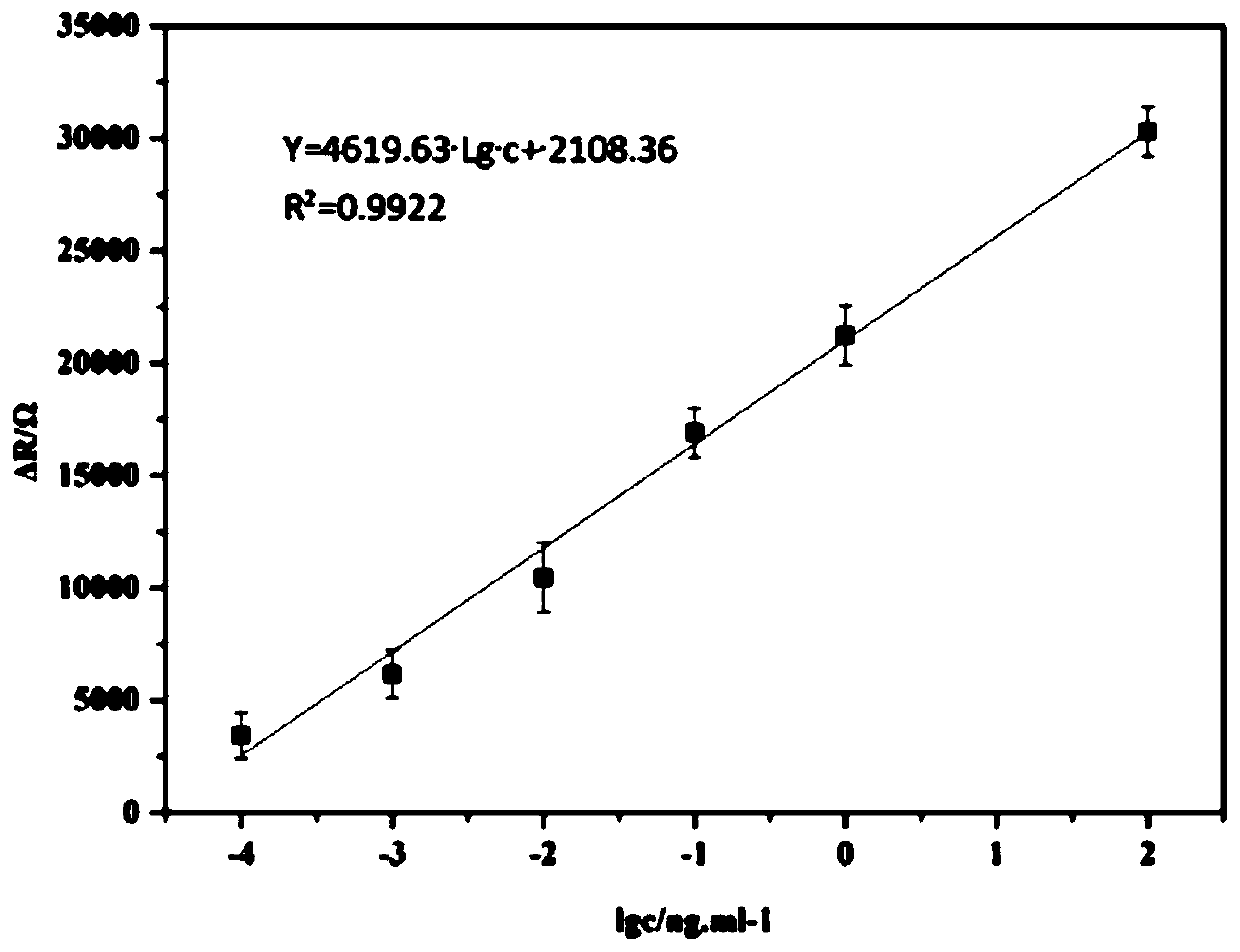
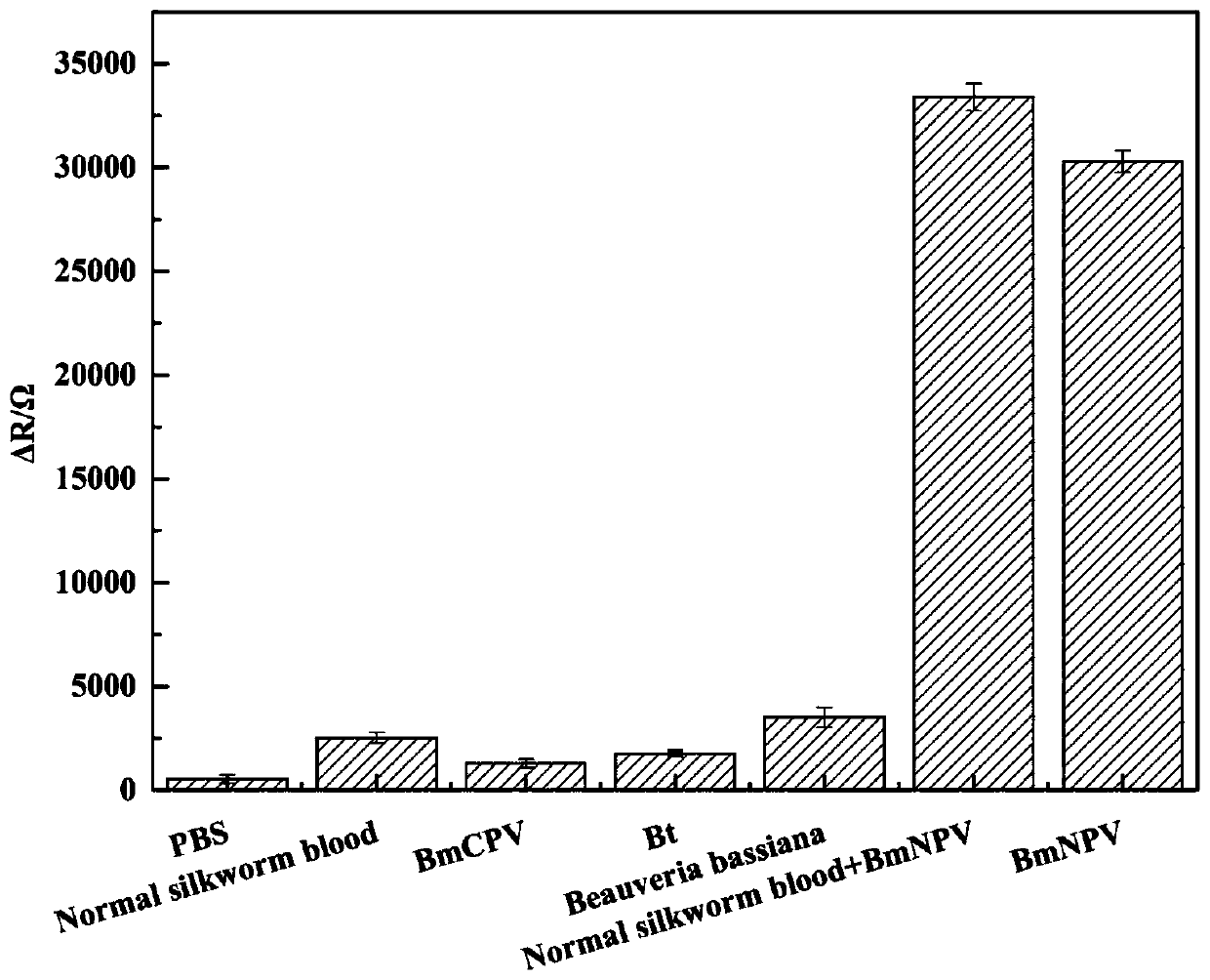
Electrochemical immunosensor for detecting bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus and detection method thereof
ActiveCN111380933AHigh sensitivityGood biocompatibilityMaterial impedanceMaterial electrochemical variablesAntigenBombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus BmNPV
The invention discloses an electrochemical immunosensor for detecting a bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus and a detection method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: modifying a gold electrode by using an undecylmercaptoundecanoic acid / beta-mercaptoethanol mixed self-assembled membrane, wherein the hybrid self-assembly membrane is used for immobilizing a BmNPV polyhedrosis protein antibody; completing the capturing of BmNPV polyhedrosis protein through specific binding of an antigen and the antibody, and achieving the ultra-sensitive detection of the bombyx morinuclear polyhedrosis virus based on the electro-catalysis effect of the hybrid self-assembly membrane. The detection method has the characteristics of simplicity, convenience, quickness, good specificity and high sensitivity, the linear range is 0.0001-100ng / mL, the detection limit is 14.54 fg / mL, and the detection method is suitable for early-stage quick diagnosis and prevention of the bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
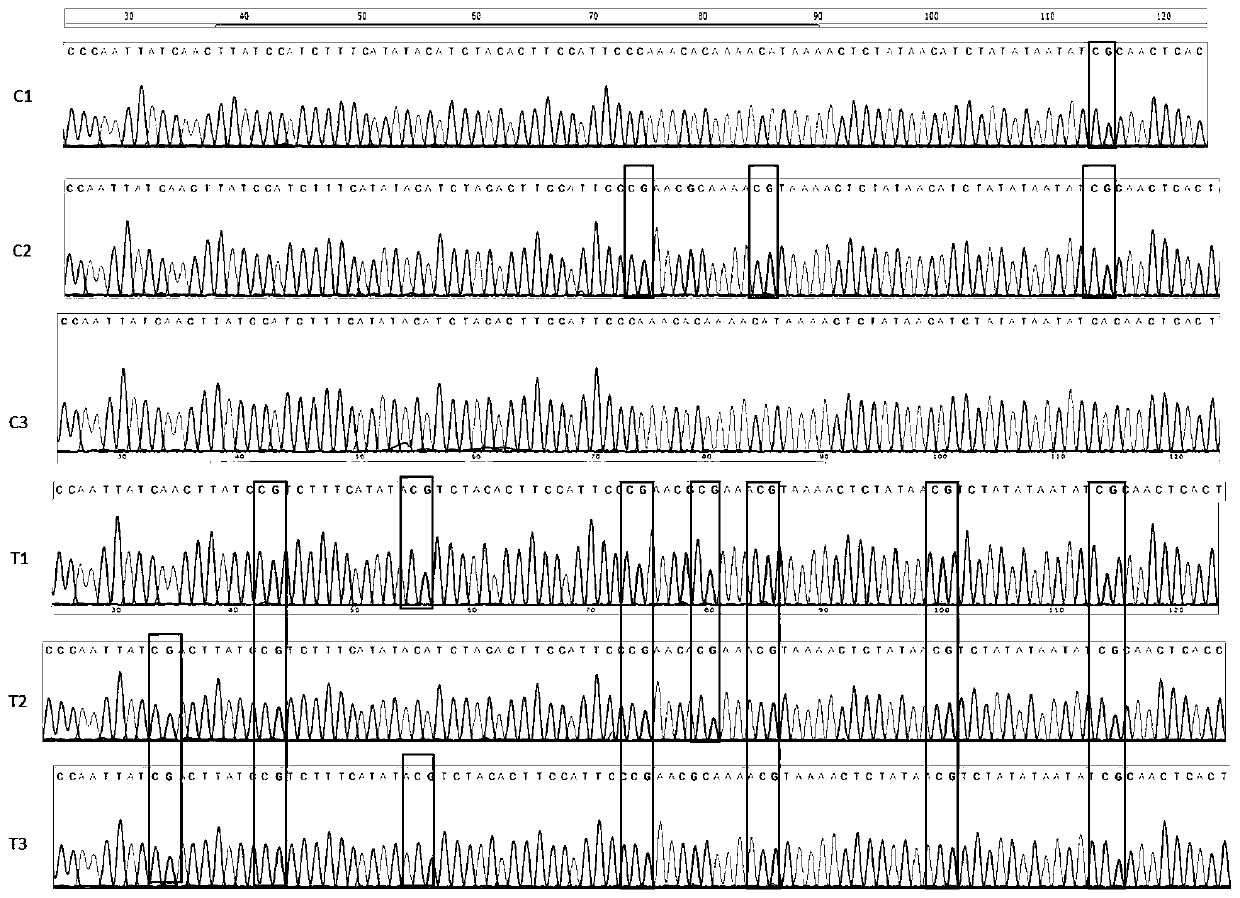
Bombyx mori actin 6A gene and application in detection of methylation level of bombyx mori actin 6A gene
InactiveCN111471688AStrong specificityImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptidesDNA methylationNucleotide
The invention discloses a bombyx mori actin 6A gene and application in detection of methylation level of the bombyx mori actin 6A gene. The CG methylation level of the gene in a 1884-2071bp nucleotideregion is obviously higher than that of normal cells in silkworm cells infected with nuclear polyhedrosis viruses, and the nucleotide sequence of the region is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. The inventionalso provides a primer pair, a kit and a detection method for specifically detecting the CG methylation level in the region. The forward sequence of the primers is shown as SEQ ID NO.2, and the reverse sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.3. The invention provides a new research direction for researching the interaction mechanism of bombyx mori DNA methylation and the nuclear polyhedrosis virus. The primers and the detection kit for detecting the methylation level of the gene disclosed by the invention have important practical application value for detecting the bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Probe, kit and detection method for rapidly detecting bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus
ActiveCN114231666AQuick checkHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus BmNPVVirus
The invention discloses a probe for rapidly detecting a bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus. The bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus can be rapidly detected through an RAA technology. The invention further discloses a kit for rapidly detecting the bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus, and the kit is rapid in detection and high in sensitivity. The invention further discloses a detection method of the kit for rapidly detecting the bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus, the steps of reagent mixing and sample adding are reduced, operation is convenient, and time is saved.
Owner:广西壮族自治区蚕业技术推广站
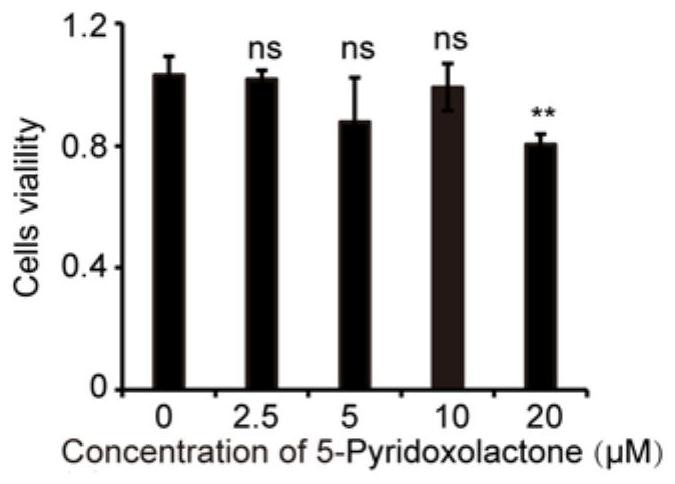
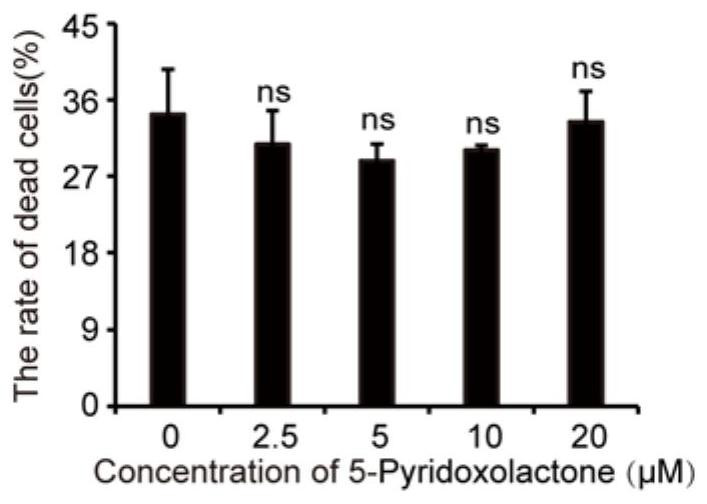
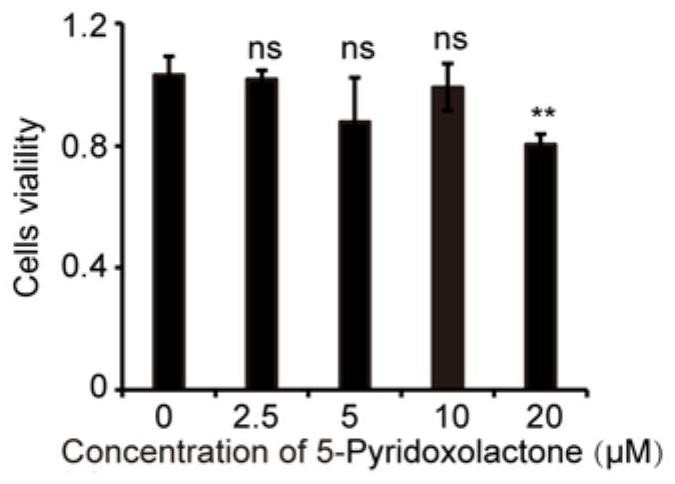
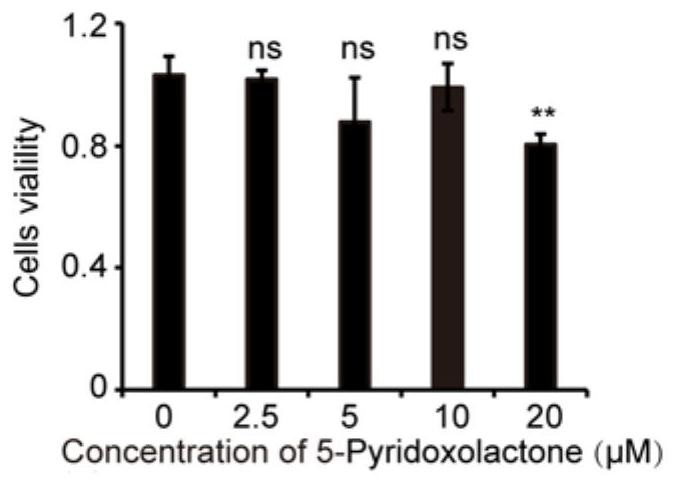
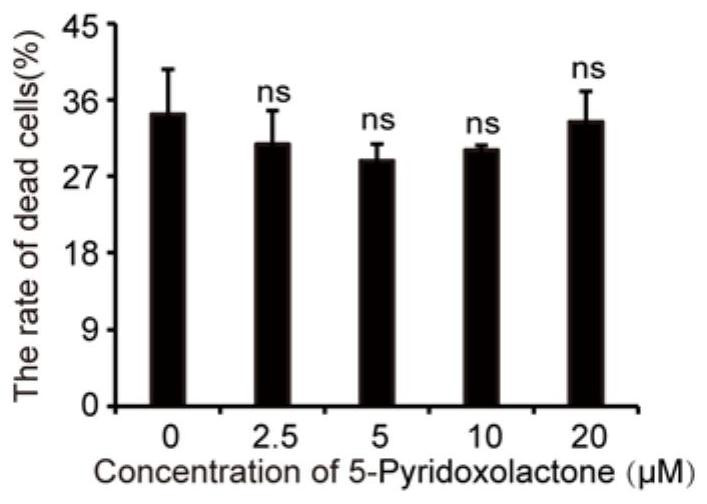
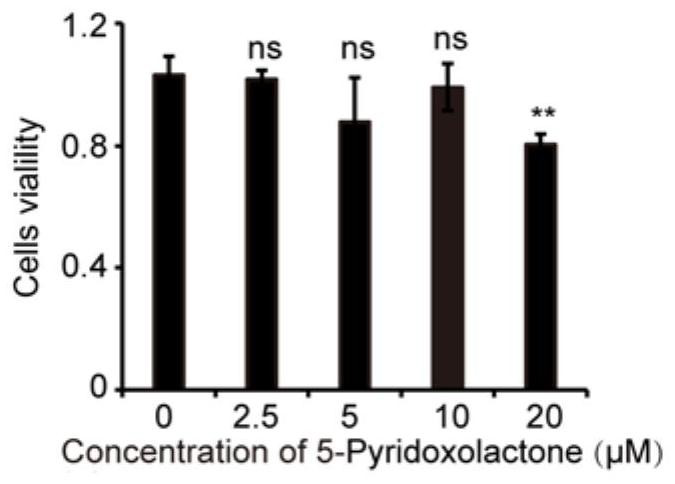
Application of 5-pyridoxolactone in the preparation of medicines for inhibiting silkworm nuclear polyhedrosis virus
ActiveCN113116890BInhibition of replicationPrevent proliferationOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsBombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus BmNPVSericulture
The invention discloses the application of 5-Pyridoxolactone in the preparation of medicines for inhibiting the nuclear polyhedrosis virus of silkworm, by rationally utilizing the small molecule 5-Pyridoxolactone in the host cell of the anti-BmNPV virus to inhibit its replication in the cell, that is, when the cell is infected After BmNPV virus infection, adding 5‑Pyridoxolactone first inhibits the replication of BmNPV virus, which provides a new idea for the treatment of BmNPV infection in cells, and also lays a foundation for the prevention and treatment of virus infection in sericulture production.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Method for targeted knockout of non-essential genes for Bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus replication
ActiveCN103589745BEasy accessObtain intuitivelyDsDNA virusesVector-based foreign material introductionPUC19Genomic DNA
The invention relates to a method for targeted knockout of non-essential genes for Bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus BmNPV replication. The method uses BmNPV as a material to amplify and clone homologous sequences at both ends of a non-essential fragment for replication by PCR into the vector pUC19; the IE1 early promoter, marker gene (EGFP), and termination sequence SV40polyA of BmNPV were sequentially spliced by overlapping PCR method, and cloned into the above-mentioned vector pUC19 to obtain the recombinant transfer vector pUC19-lef7-IE1-EGFP-SV40polyA-gp64; The vector and wild BmNPV genome were co-transfected into BmN cells, and the recombinant virus RBmNPV-EGFP with fluorescent marker was obtained through homologous recombination; its genomic DNA was co-transfected with the transfer vector pUC19-lef7-gp64 without marker gene BmN cells were transfected, and the recombinant virus RBmNPV without fluorescent marker gene was obtained by homologous recombination. The invention solves the problem of the marker gene in the genome of the recombinant virus, improves the screening efficiency of the positive recombinant virus, and the marker gene can be used repeatedly.
Owner:TIANJIN YAOYU BIOLOGICAL TECH
Method for preparing analgesic polypeptide from silkworms
InactiveCN105255945AStrong analgesic activityOptimize gene sequencePeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticChemical synthesisBombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus BmNPV
The invention discloses a method for preparing analgesic polypeptide from silkworms and belongs to the field of gene engineering. The preparation method comprises steps as follows: a conotoxin omega-MVIIA gene sequence is optimized according to BmNPV (Bombyx mori Nucleopolyhedrovirus) codon usage frequency, genes obtained after chemical synthesis are linked to a donor plasmid pFastBacDual and introduced to EGFP (enhanced green fluorescent protein) genes, and a recombinant donor plasmid pFBD-MVIIA / EGFP is established. MVIIA / EGFP is transposed to BmNPV with a Bac-to-Bac method, and a recombinant virus vBmMVIIA / EGFP is formed. DNA of the recombinant virus is transfected to cells of the silkworms, BV particles are obtained and injected into the silkworms at 200 pfu after the titer of the BV particles is tested by the aid of green fluorescence, and blood of the silkworms is collected after five days of transfection. Acetic-acid-induced mouse writhing experiments show that the blood of the silkworms infected with expressed conotoxin omega-MVIIA has remarkable analgesic activity, and the number of the average writhing times is only 3.55 and is remarkably higher than 37.30 in a control group of mice injected with normal saline. A new method is provided for expression of conotoxin omega-MVIIA with analgesic activity, and has potential application value.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Application of bmuap56 gene in silkworm
ActiveCN113057146BGood antiviral effectPrevent proliferationOrganic active ingredientsHydrolasesGenes mutationBombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus BmNPV
The invention discloses the application of the silkworm BmUAP56 gene, and specifically discloses the application of the silkworm BmUAP56 gene in cultivating silkworm varieties resistant to silkworm nuclear polyhedrosis virus and preparing medicines for inhibiting the proliferation of silkworm nuclear polyhedrosis virus. The nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.3, and the expression level of the BmUAP56 gene in the silkworm body can be reduced by RNA interference or / and gene editing, or a reagent that inhibits the binding of the silkworm UAP56 protein to the BmNPV viral protein 25K can also be passed through the BmUAP56 gene The mutation weakens the binding force between silkworm UAP56 protein and BmNPV virus protein 25K, thereby obtaining the ability to resist silkworm nuclear polyhedrosis virus, which has good application value.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
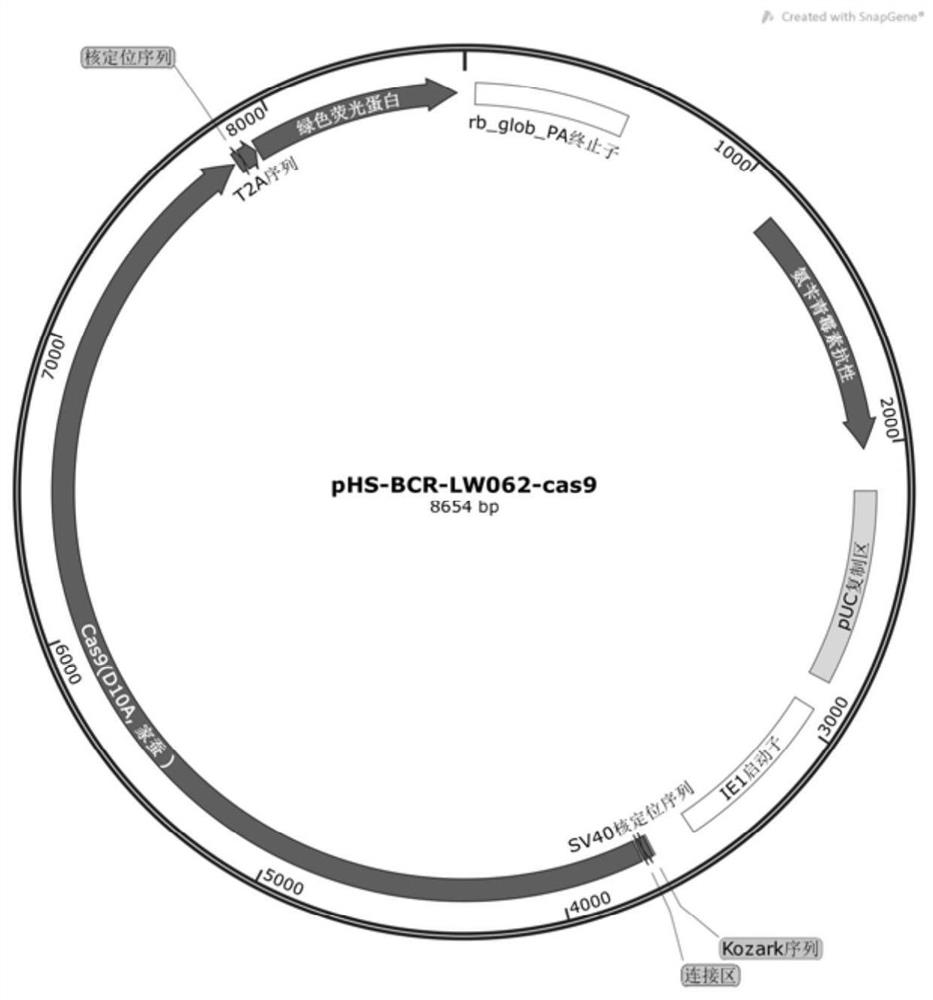
Silkworm gene precise knockout system based on CRISPR/cas9 double nickase technology and its application
ActiveCN109136262BImprove expression efficiencyImprove accuracyStable introduction of DNAPeptidesLigationPromoter
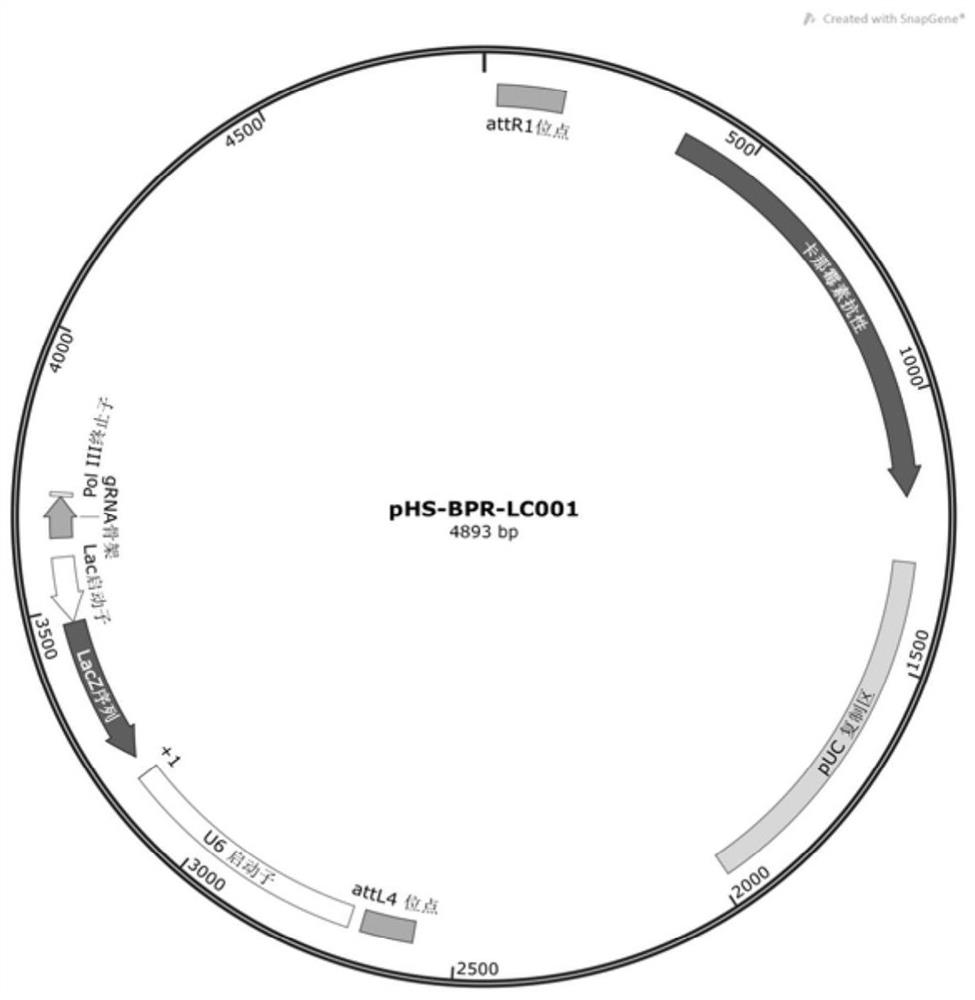
The invention discloses a silkworm gene precise knockout system based on CRISPR / Cas9 double nickase technology. The system includes a Cas9 mutant expression vector pHS-BCR-LW062-cas9 (full length 8654bp) and a sgRNA (guide sequence) production vector pHS ‑BPR‑LC001 (full length 4893bp). The silkworm gene precise knockout system based on CRISPR / Cas9 double nickase technology of the present invention can target and knock out silkworm functional genes, and greatly reduce the off-target rate, at least 50 times, or even 1500 times; the system is extremely The accuracy rate of gene knockout is greatly improved, and the reaction process is simple; the Cas9 mutant expression vector pHS-BCR-LW062-cas9 in the system of the present invention introduces the strong promoter IE1 of the silkworm nuclear polyhedrosis virus and silkworm codons The optimized cas9D10A greatly increases the expression efficiency of the enzyme; the pHS-BPR-LC001 in the system of the present invention uses the U6 promoter of Bombyx mori, and is inserted into the IIS type Bsa I enzyme cleavage site, and the golden gate ligation method can be used. The rapid construction of sgRNA expression vector greatly saves the operation steps.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A kind of induced mulberry leaves for preventing and treating silkworm bmnpv disease and its application
ActiveCN107114561BAltered secondary metabolite contentReduce mortalityAnimal feeding stuffAntiviralsDiseaseBombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus BmNPV
The invention discloses induced mulberry leaves for preventing bombyx mori from suffering from BmNPV diseases and an application of the induced mulberry leaves. Bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis viruses (BmNPV) are one of viruses causing largest damage to bombyx mori, and at present, an explicit treatment method for the BmNPV diseases is not developed. According to the induced mulberry leaves disclosed by the invention, fresh mulberry leaves are subjected to ultraviolet illumination, wherein ultraviolet rays are one or more of UVA wave bands, UVB wave bands and UVC wave bands, the ultraviolet illumination intensity is 10-1000W, the ultraviolet illumination time is 0.05-3h, and the humidity in the illumination process is kept to be 10-100%. The mulberry leaves have important pharmacological activity and a main food source for the bombyx mori. According to the induced mulberry leaves, the content of mulberry leaf secondary metabolism products can be notably changed, the mortality rate of the bombyx mori after being infected with viruses is reduced, and the bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis viruses can be resisted.
Owner:开化明阳健康科技有限公司
Enhanced bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus inducible promoter En39k and application thereof
ActiveCN103642807BGood induction of priming activityInduced priming activity increasedBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus BmNPVKaryotype
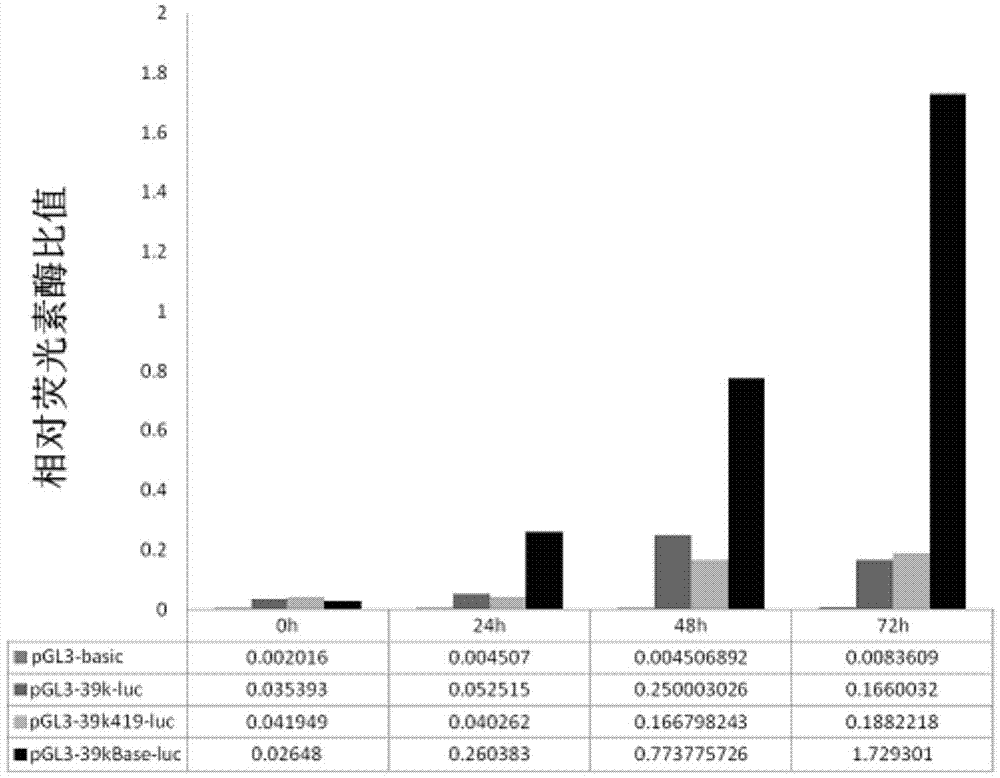
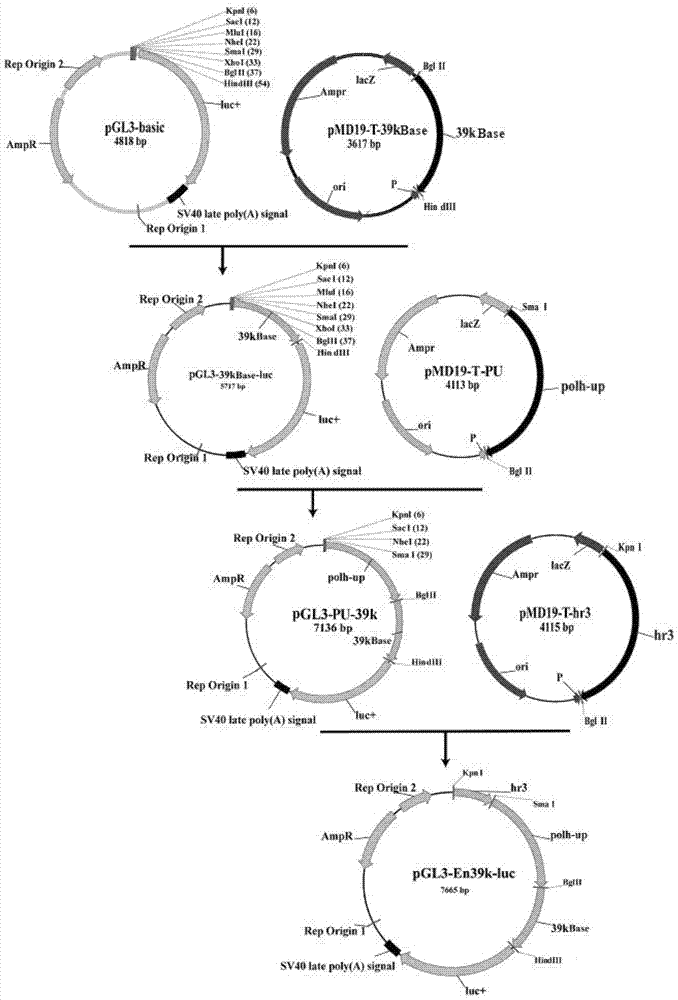
The invention discloses enhanced bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus (BmNPV) inducible promoter En39k and an application thereof. According to the invention, the optimal sequence of a promoter for delaying the early gene 39k through BmNPV is used as a parent promoter, then the parent promoter is serially connected with a BmNPV-sourced hr3 sequence and a PU sequence serving as enhancing elements so as to obtain the promoter which is a recombinant promoter (SEQ ID NO.1). The promoter has strong BmNPV inducible promotion activity (which is about 155 times the activity of the BmNPV39k inducible promoter in ZL201010231957.9), an exogenous gene can be driven to be efficiently expressed in an insect cell or in a single insect body after being infected with BmNPV or induced by relevant factors, the promoter is not only applicable to equimolecular biology theoretical study such as the gene function analysis, but also suitable for improvement of the silkworm variety by utilizing the gene engineering technology and especially suitable for breeding of the high-efficiency BmNPV-resisting variety of silkworm and breeding of the silkworm variety capable of eliminating the disease spreading through the expression of exogenous lethal gene or marker gene.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
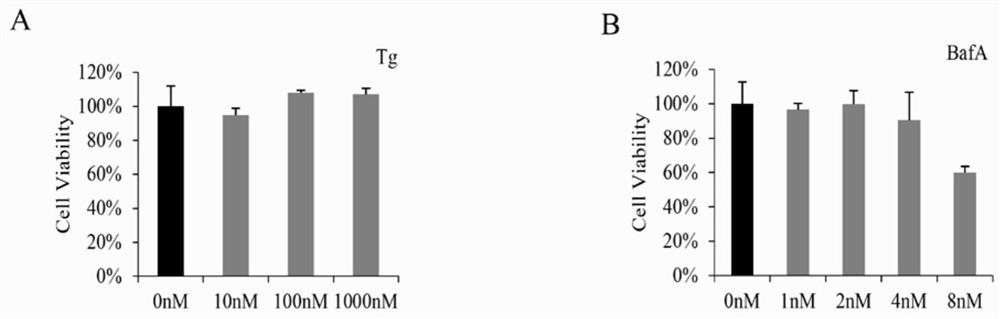
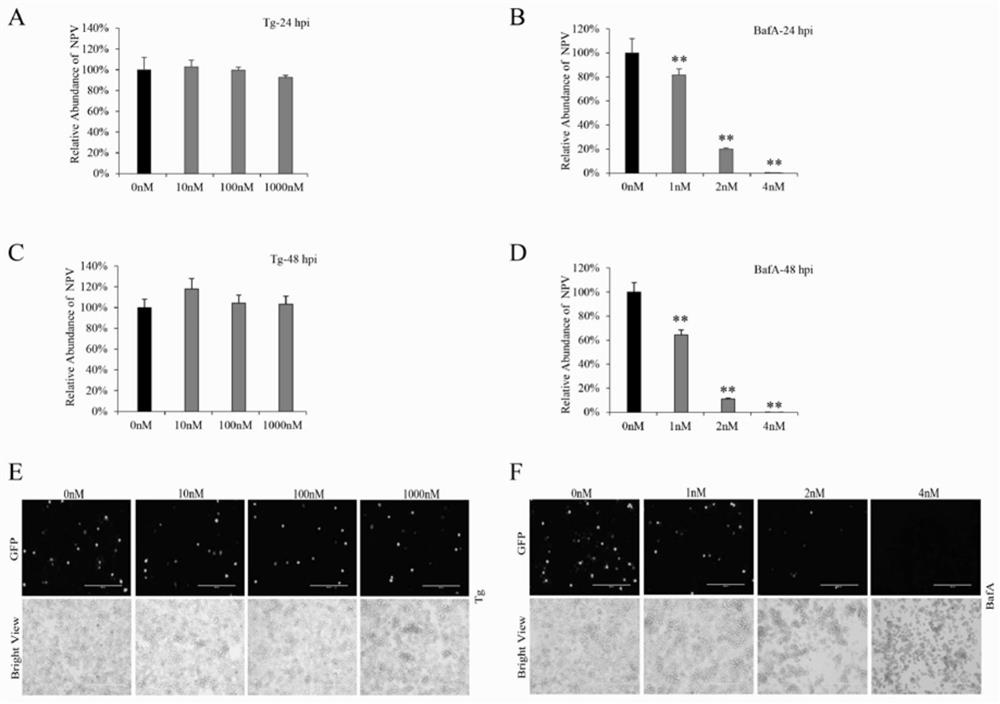
Method for improving bombyx mori baculovirus infection resistance
ActiveCN113068661AInhibition of replicationPrevent proliferationFermentationAnimals/human peptidesATPaseBombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus BmNPV
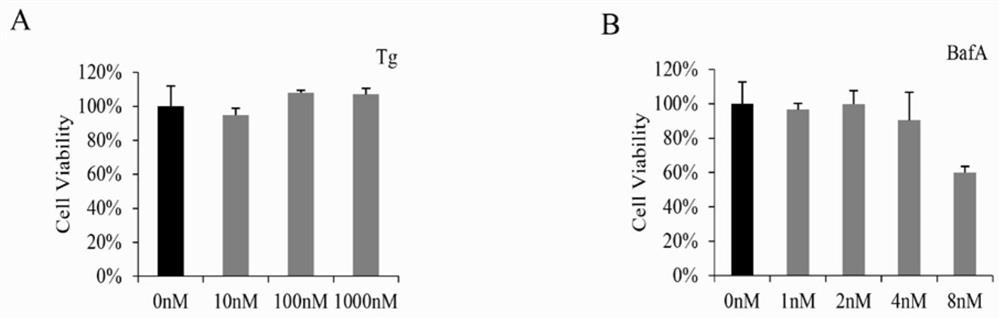
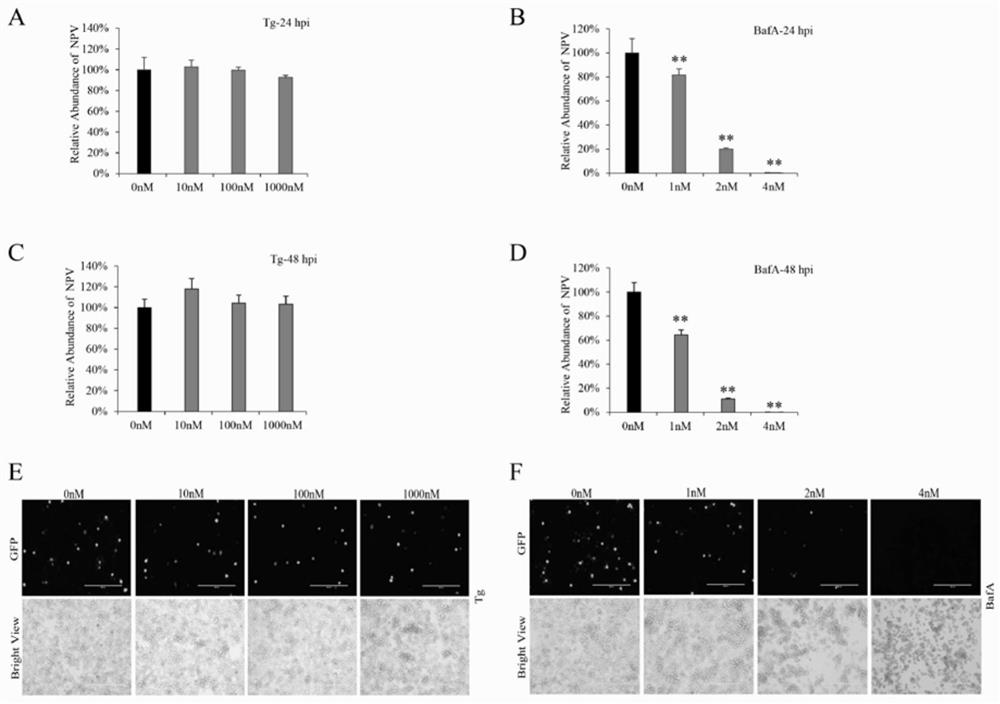
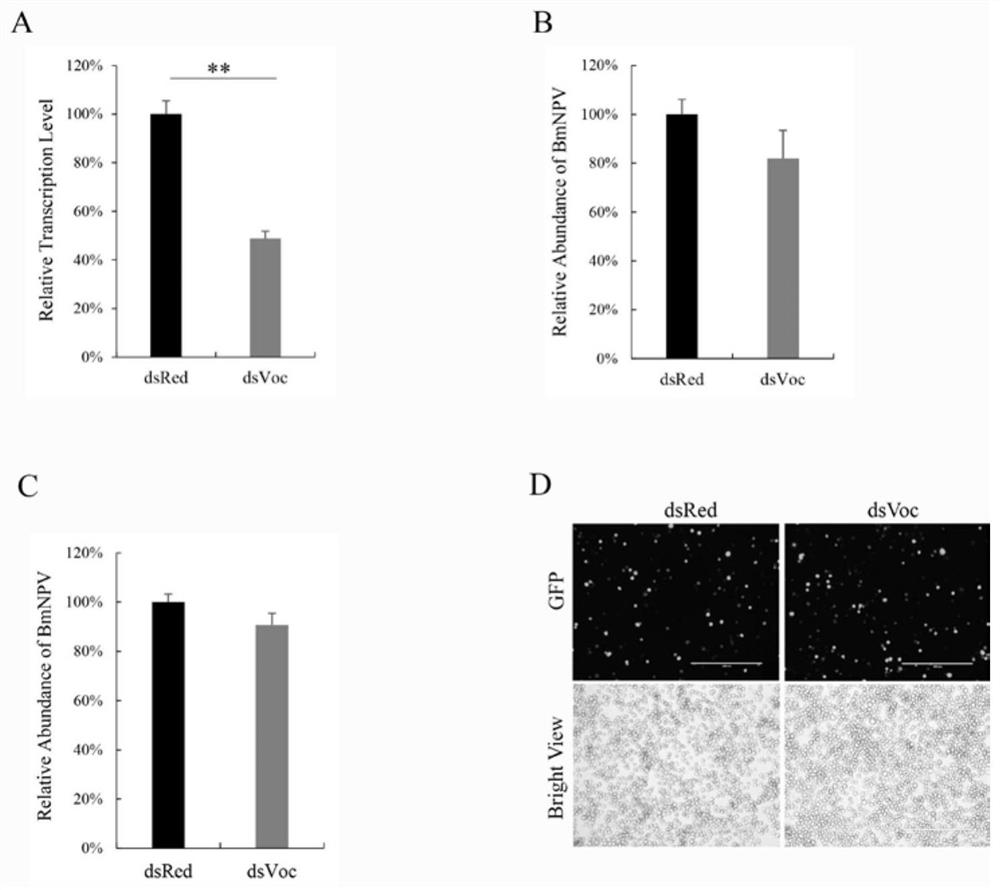
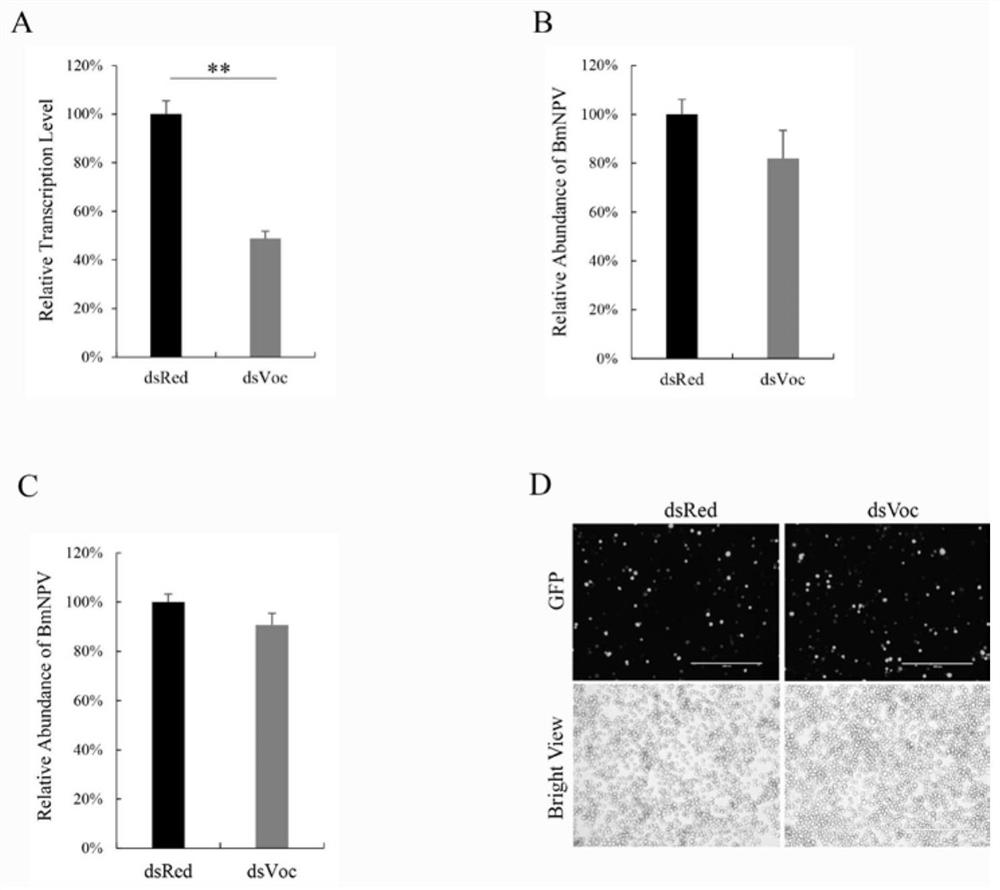
The invention discloses a method for improving bombyx mori baculovirus infection resistance. The method comprises the steps that bombyx mori is treated by specifically using a V-ATPase Vo complex inhibitor, and by reducing the expression of a Bm Voa4 gene in the bombyx mori or mutating the Bm Voa4 gene to cause function loss, the research shows that virus replication can be completely inhibited by using 4nM bafilomycin A1 for treatment; and then, a target gene of the bafilomycin A1 is selected for research to find that the virus content in cells interfering with the Bm Voa4 is remarkably reduced, the virus contents 24 hours and 48 hours after infection are 74% and 68% of those of a control group correspondingly, but the virus contents cannot be reduced by interfering with the Bm Voa3 and the Bm Voc, so that the Bm Voa4 is the target gene of the bafilomycin A1. A reagent targeting the Bm Voa4 gene can be used for research, development and production of drugs for preventing and treating bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus infection, and has popularization value.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
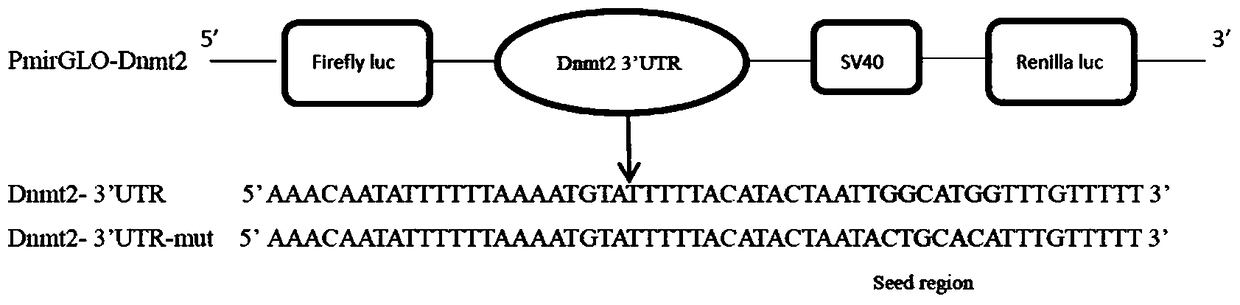
Application of microRNAs associated with nuclear polyhedrosis virus infection in silkworm
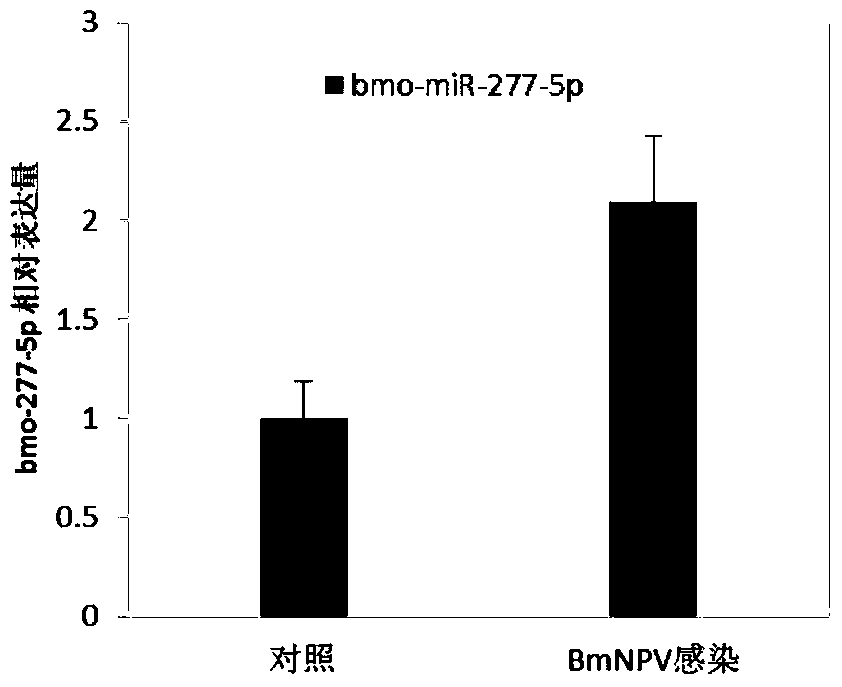
ActiveCN105483269BEnsure consistencyEasy to useMicrobiological testing/measurementBombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus BmNPVNuclear Polyhedrosis Virus
The invention discloses an application of microRNA related to silkworm nuclear polyhedrosis virus infection. The application is the application of bmo-miR-277-5p in the preparation of a kit for detecting the infection of silkworm nuclear polyhedrosis virus, or the application of bmo-miR-277-5p in the inhibition of gene expression, The mRNA after gene transcription has a 3'UTR of the sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.12. The present invention opens up the new application of silkworm microRNA, especially bmo-miR-277-5p, which can provide a new research direction for the study of the interaction mechanism between silkworm and nuclear polyhedrosis virus, and at the same time provide a new method for the diagnosis and treatment of silkworm nuclear polyhedrosis virus. Prevention provides new ideas.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
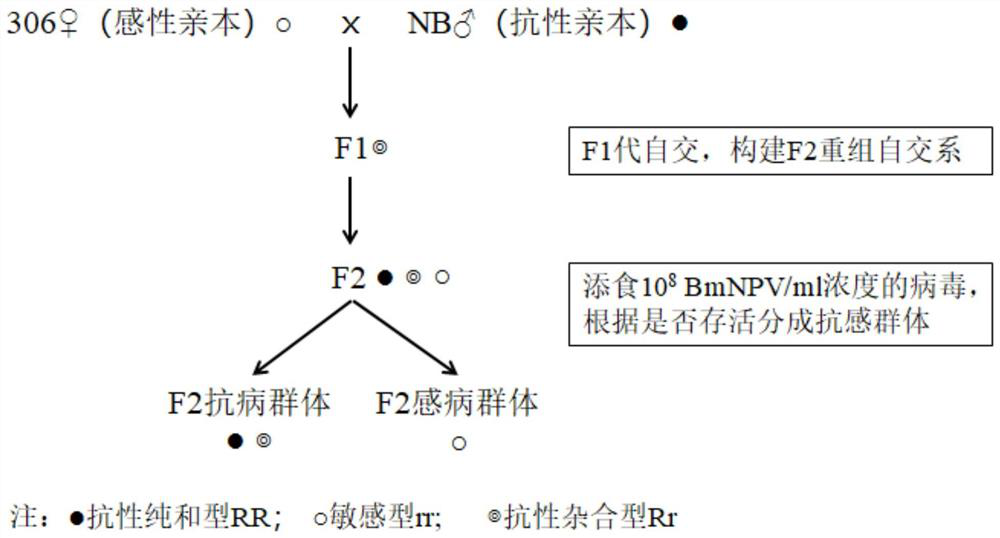
SNP molecular marker related to bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus resistance and application thereof
PendingCN114854876AReduce false positive rateValid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesBombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus BmNPVKaryotype
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology and molecular breeding, and particularly relates to an SNP molecular marker related to bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus (BmNPV) resistance and application of the SNP molecular marker. The SNP molecular marker comprises a combination of a Chr3-746 marker and a Chr27-5071 marker, and the combination of the Chr3-746 marker and the The Chr3-746 marker is located at the 14951064th site of a No.3 chromosome sequence of a silkworm p50T genome, and the base polymorphism is G / A; the Chr27-5071 marker is located at the 9462596th site of a chromosome sequence 27 of a silkworm p50T genome, and the base polymorphism of the Chr27-5071 marker is C / G. The SNP molecular marker can effectively distinguish BmNPV-resistant silkworms, reduce the false positive rate of detection, improve the accuracy rate, realize rapid and high-throughput screening, solve the technical problem of traditional breeding of silkworms and accelerate breeding of BmNPV-resistant varieties of silkworms.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Application of 5-Pyridoxolactone in preparation of medicine for treating bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus (BmNPV)
ActiveCN113116890AInhibition of replicationPrevent proliferationOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsBombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus BmNPVIntracellular
The invention discloses application of 5-Pyridoxolactone in preparation of a medicine for treating bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus (BmNPV). Micromolecule 5-Pyridoxolactone in an anti-BmNPV host cell is reasonably utilized to inhibit the replication of BmNPV in the cell, that is, after the cell is infected by the BmNPV, the 5-Pyridoxolactone is firstly added to inhibit the replication of the BmNPV, so that a new thought is provided for treating the BmNPV infection of the cell, and a foundation is laid for virus infection prevention and treatment in sericulture production.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
A kind of method to improve resistance to silkworm baculovirus infection
ActiveCN113068661BInhibition of replicationPrevent proliferationFermentationAnimals/human peptidesGenes mutationATPase
The invention discloses a method for improving resistance to Bombyx mori baculovirus infection, specifically treating Bombyx mori with a V-ATPase Vo complex inhibitor, reducing the expression of Bm Voa4 gene in Bombyx mori or making Bm Voa4 gene mutation to cause loss of function, Studies have shown that bafilomycin A1 treatment with 4nM can completely inhibit virus replication, and then the target gene of bafilomycin A1 was selected for research. The virus content at and 48h were 74% and 68% of the control, respectively, but the interference of Bm Voa3 and Bm Voc could not reduce the virus content, indicating that Bm Voa4 is the target gene of bafilomycin A1, and by targeting the Bm Voa4 gene The reagent can be used for the research, development and production of drugs for preventing and treating Bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus infection, and has promotion value.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Bombyx mori nuclear polyhydrosis virus (BmNPV) 39k inducible promoter and application thereof
InactiveCN101914537BPriming activityPrevent proliferationFungiBacteriaVirus multiplicationNucleotide
The invention discloses a bombyx mori nuclear polyhydrosis virus (BmNPV) 39k inducible promoter and application thereof. A nucleotide sequence of the promoter is shown as SEQ ID No.1; the promoter has obvious BmNPV inducible promotion activity and can make cells start foreign gene expression when the cells are subjected to the BmNPV infection; an RNAi vector using a BmNPV multiplication essential gene as a target can be built by utilizing the promoter; the abundant expression of shRNA can be performed when the bombyx mori is subjected to the BmNPV infection; the shRNA is cut into siRNA in a cell by an enzyme; specific degradation is performed on the BmNPV multiplication essential gene mRNA to initiate the BmNPV multiplication essential gene to be transcribed and then silenced, so the aim of inhibiting the virus multiplication is fulfilled, and the promoter can be used for preventing and controlling the BmNPV infection of the bombyx mori, performing genetic engineering breeding of bombyx mori anti-BmNPV strains and providing a good reference mode for transgenic therapy of other biologic virus diseases.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Application and recombinant vector of bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus polygene inverted repeat sequence and bombyx mori lipase-1 gene
ActiveCN102925484BControlled reproductionReduce contentVector-based foreign material introductionBombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus BmNPVInverted Repeat Sequences
The invention discloses the application of the Bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus BmNPV multi-gene inverted repeat sequence and the silkworm lipase 1 gene, specifically, the BmNPV multi-gene inverted repeat sequence and the silkworm lipase 1 gene are used to construct a recombinant vector, and the carrier It can express hairpin RNA and silkworm lipase 1 that interfere with multiple genes of BmNPV, and inactivate BmNPV in silkworm intestinal fluid by increasing expression of Bmlipase-1, reducing the number of BmNPV viruses that invade silkworm midgut cells; the expressed hairpin RNA can degrade The mRNA of the BmNPV virus gene can inhibit the replication and proliferation of the virus in the silkworm. After the transgenic silkworm is prepared by using the vector, it can effectively inhibit the proliferation of BmNPV in the transgenic silkworm and reduce the virus content, so that the survival rate of the silkworm after infection with BmNPV is greatly improved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
An electrochemical immunosensor for detecting silkworm nuclear polyhedrosis virus and its detection method
ActiveCN111380933BHigh sensitivityGood biocompatibilityMaterial impedanceMaterial electrochemical variablesAntigenBombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus BmNPV
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Application of bombyx mori BmUAP56 gene
ActiveCN113057146AGood antiviral effectPrevent proliferationOrganic active ingredientsHydrolasesBombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus BmNPVBombyx mori protein
The invention discloses application of a bombyx mori BmUAP56 gene, and particularly discloses application of the bombyx mori BmUAP56 gene in cultivation of bombyx mori varieties resisting bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis viruses and preparation of drugs for inhibiting bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus proliferation. The nucleotide sequence of the BmUAP56 gene is shown in SEQ ID NO.3. The expression quantity of the BmUAP56 gene in bombyx mori is reduced through RNA interference or / and gene editing, or a reagent for inhibiting the binding of the bombyx mori UAP56 protein and the BmNPV virus protein 25K is used, and the binding force of the bombyx mori UAP56 protein and the BmNPV virus protein 25K can be weakened through BmUAP56 gene mutation, so that the capability of resisting bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus is obtained, and the bombyx mori UAP56 protein has a very good application value.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
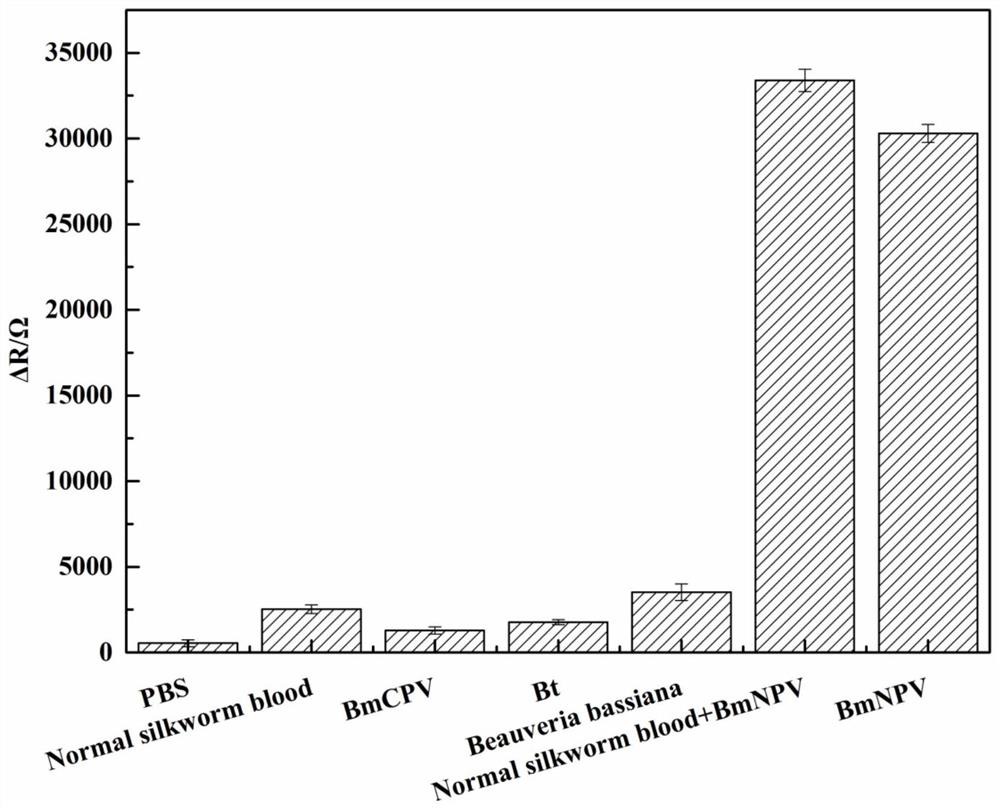
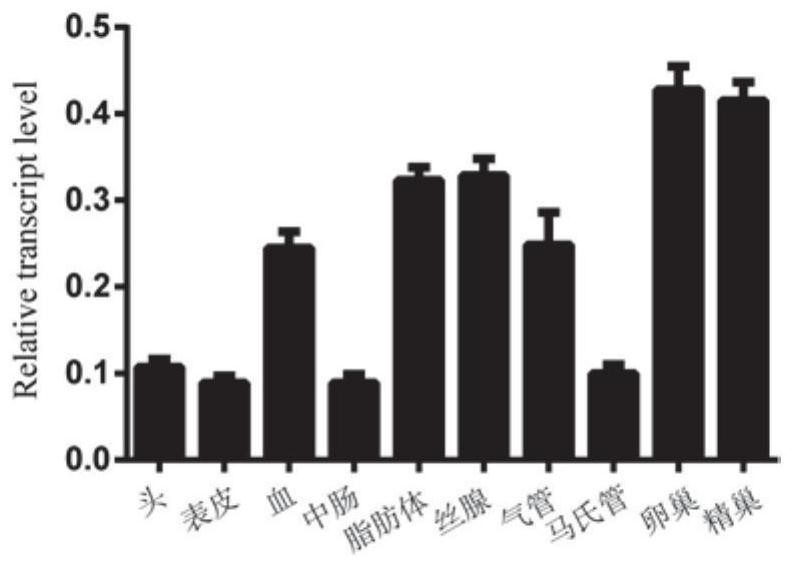
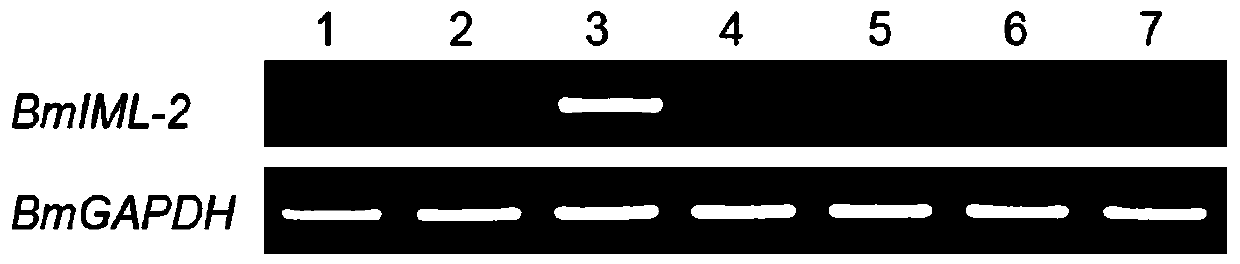
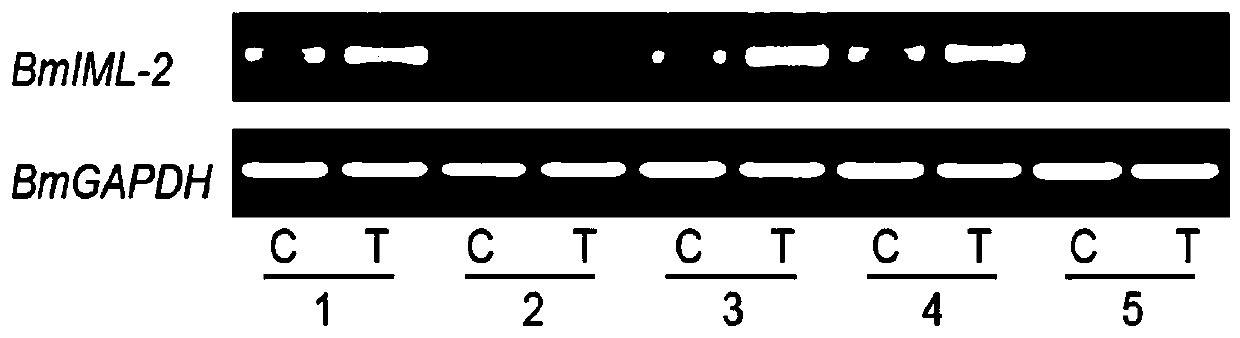
Method for screening bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus disease resistance with BmIML-2 gene
PendingCN111004852AResistanceShort experiment cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseBombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus BmNPV
The invention discloses a method for screening bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus disease resistance with a BmIML-2 gene. According to the method, nuclear polyhedrosis virus is added during the last mulberry leaf feeding before mounting, and the transcription level of the BmIML-2 gene is adopted as the detection index to judge the resistance strength of bombyx mori to the virus. Compared withthe prior art, the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that: (1) the virus is added before 5-instar mounting, so that the test period can be shortened, the workload is small, and theprobability of cross infection among bombyx mori is reduced; (2) the resistance of the bombyx mori variety screened by the method to the nuclear polyhedrosis virus is improved by 10-100 times; and (3)the bombyx mori variety screened by the method is stable in resistance and vigorous in physique after multi-generation feeding.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com