Method for leaching vanadium, titanium and chromium from vanadium, titanium and chromium raw materials by hydrothermal organic acid
A technology of organic acid and hydrothermal method, which is applied in the field of metallurgy, can solve the problems of no co-extraction and difficult production of titanium dioxide, and achieve the effects of high-efficiency co-extraction, universal raw material applicability, and low energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
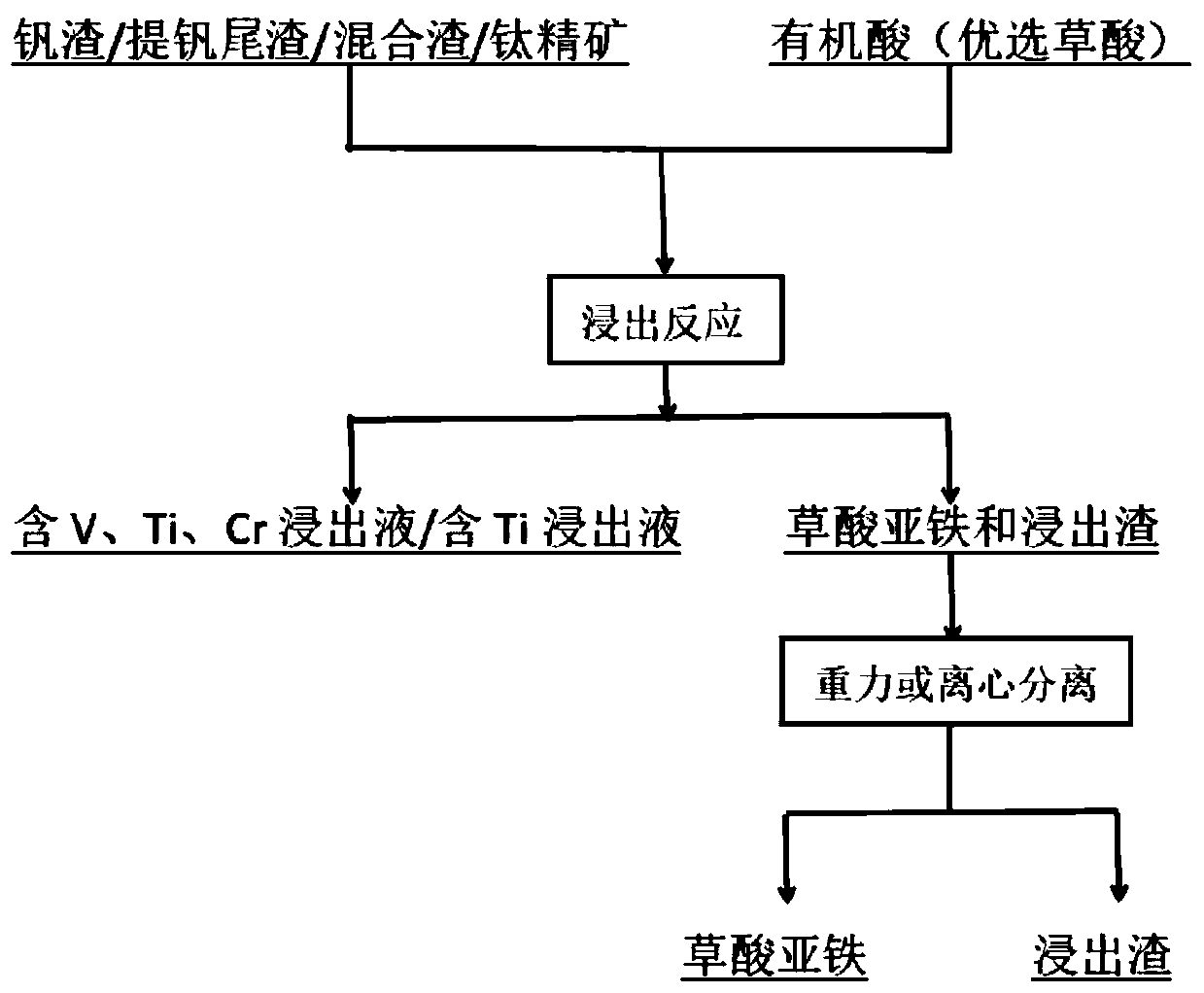
[0038] (1) Weigh 1.25g of vanadium slag, the concentration is 30% oxalic acid solution, the liquid-solid ratio is 20:1, mix it into a slurry, and add it into the reaction kettle. Reaction conditions: the reaction temperature is 125°C, the reaction time is 3h, the reaction pressure is 0.3-0.9MPa, and the stirring speed is 500r / min. After the reaction is finished, the reactant is cooled to room temperature, filtered and washed to obtain a leaching solution containing vanadium, titanium and chromium, ferrous oxalate and leaching residue. Through centrifugal separation, the ferrous oxalate and the leaching residue are fully separated.
[0039] After ICP-AES detection, in the obtained leaching solution, the V leaching rate was 98.3%, the Ti leaching rate was 98%, and the Cr leaching rate was 96.5%. The separation rate of ferrous oxalate and leaching residue is 95%.
Embodiment 2
[0041] (1) Weigh 1.25g of vanadium slag, the concentration is 15% oxalic acid and 10% formic acid solution, the liquid-solid ratio is 15:1, mix it into a slurry, and add it into the reaction kettle. Reaction conditions: the reaction temperature is 130°C, the reaction time is 2.5h, the reaction pressure is 0.3-0.7MPa, and the stirring speed is 500r / min. After the reaction is finished, the reactant is cooled to room temperature, filtered and washed to obtain a leaching solution containing vanadium, titanium and chromium, ferrous oxalate and leaching residue. Through centrifugal separation, the ferrous oxalate and the leaching residue are fully separated.
[0042] After ICP-AES detection, in the obtained leaching solution, the V leaching rate was 97.5%, the Ti leaching rate was 97%, and the Cr leaching rate was 95.8%. The separation rate of ferrous oxalate and leaching residue is 96%.
Embodiment 3
[0044] (1) Weigh 1.25g of vanadium slag, the concentration is 10% oxalic acid, 5% formic acid and 10% citric acid solution, the liquid-solid ratio is 20:1, mix it into a slurry, and add it into the reaction kettle. Reaction conditions: the reaction temperature is 135°C, the reaction time is 4h, the reaction pressure is 1-2.0MPa, and the stirring speed is 500r / min. After the reaction is finished, the reactant is cooled to room temperature, filtered and washed to obtain a leaching solution containing vanadium, titanium and chromium, ferrous oxalate and leaching residue. Through centrifugal separation, the ferrous oxalate and the leaching residue are fully separated.
[0045] After ICP-AES detection, in the obtained leaching solution, the V leaching rate was 98.2%, the Ti leaching rate was 97.5%, and the Cr leaching rate was 96.3%. The separation rate of ferrous oxalate and leaching residue is 96%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com