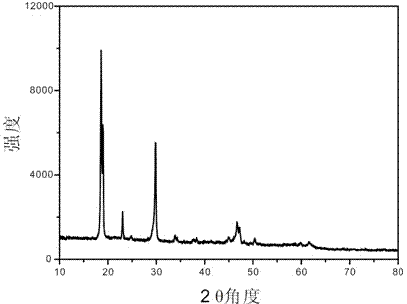
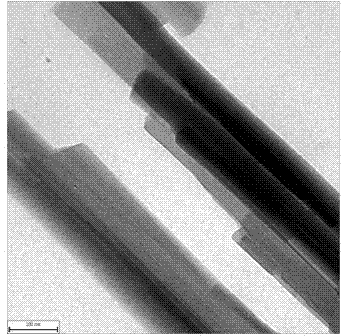
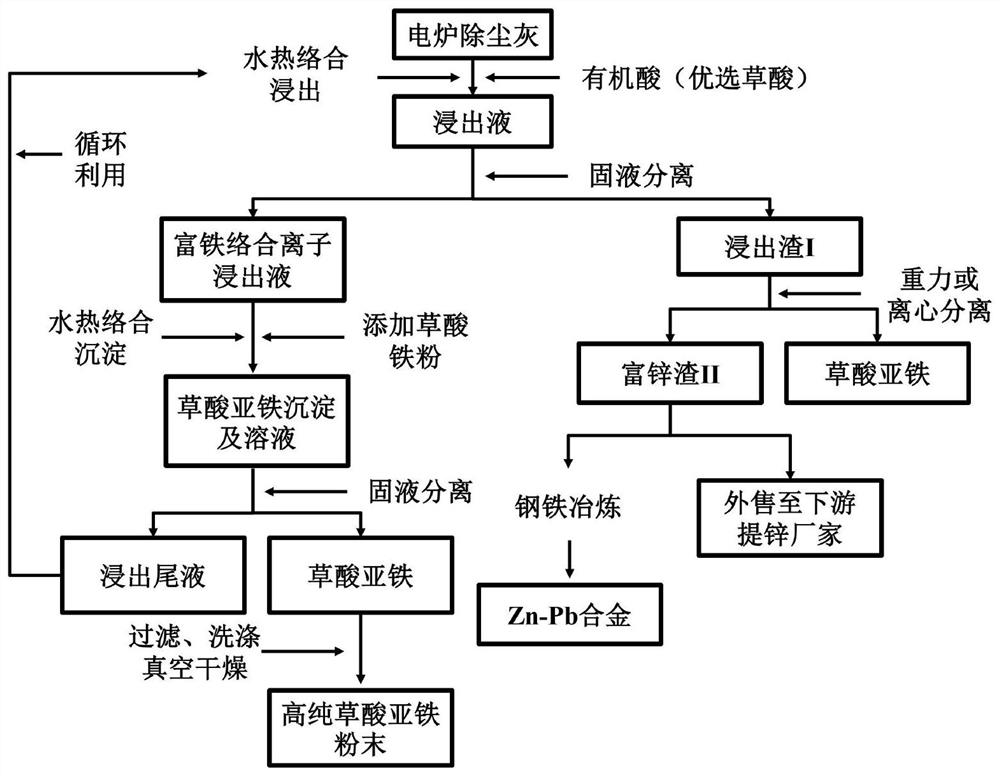
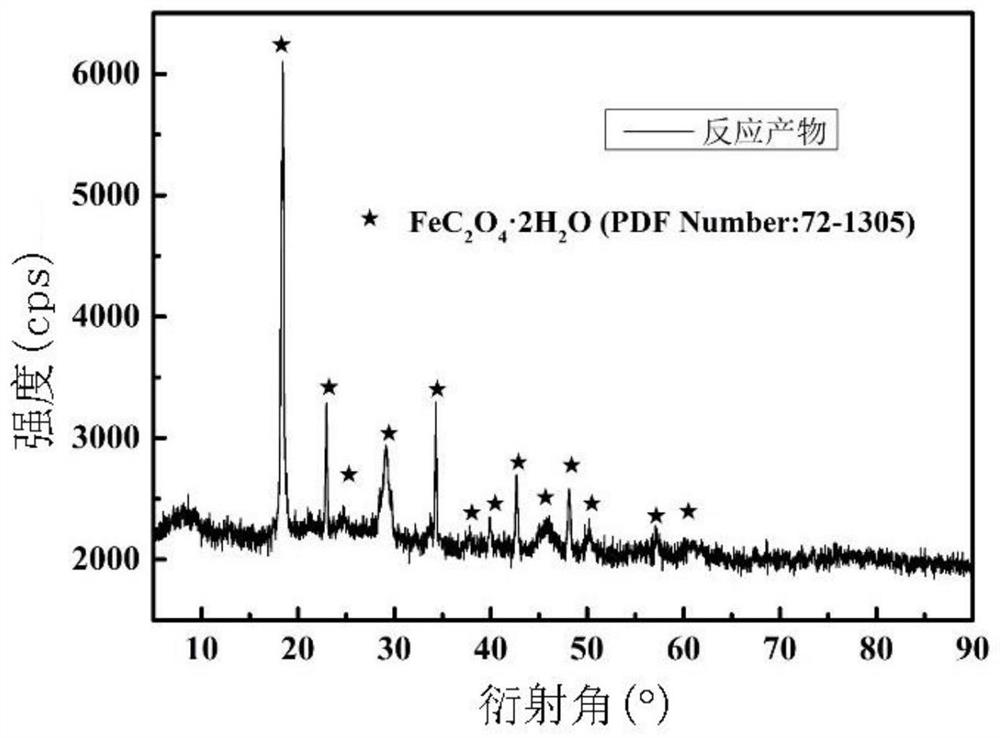
Patents
Literature
44 results about "Iron(II) oxalate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
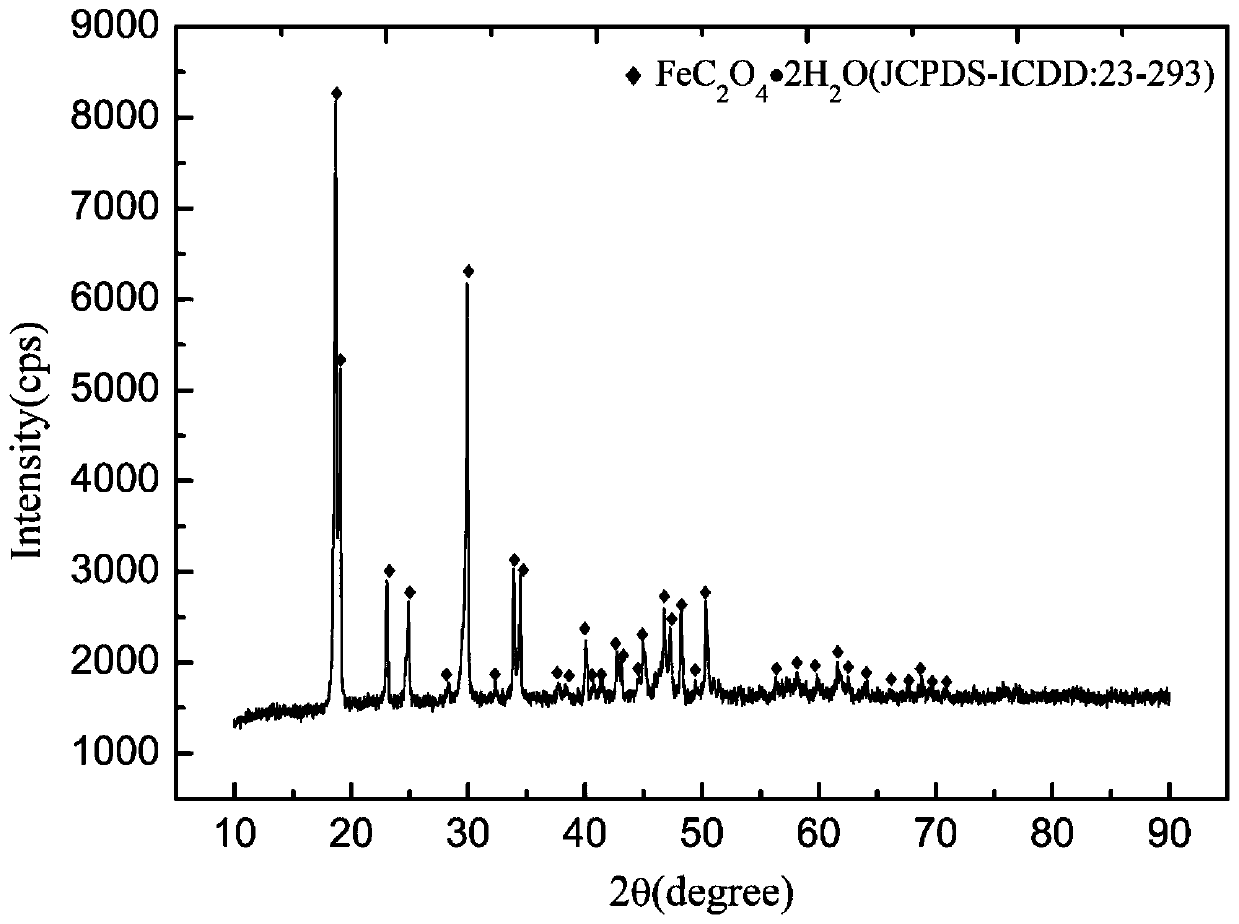
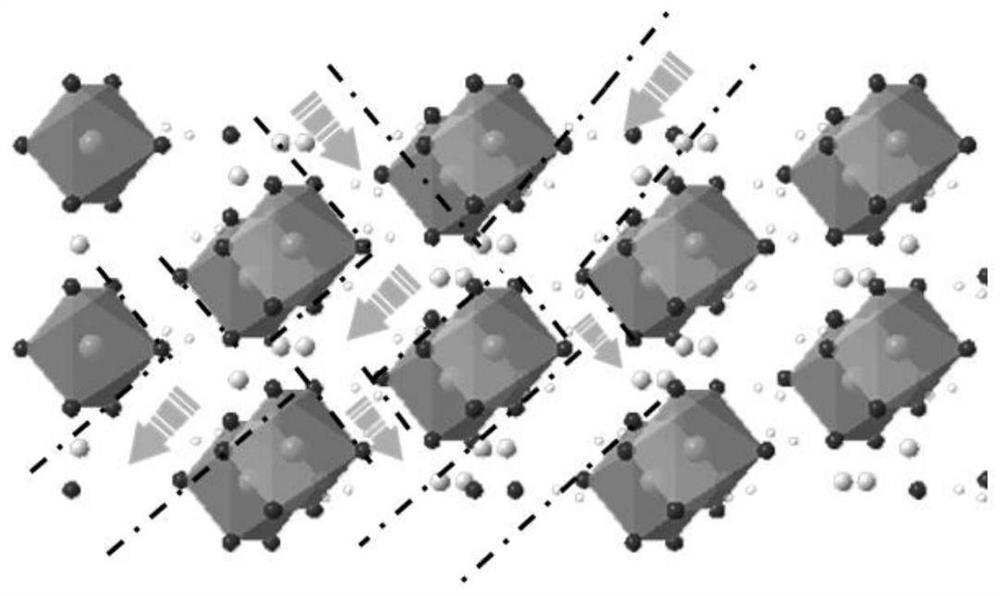
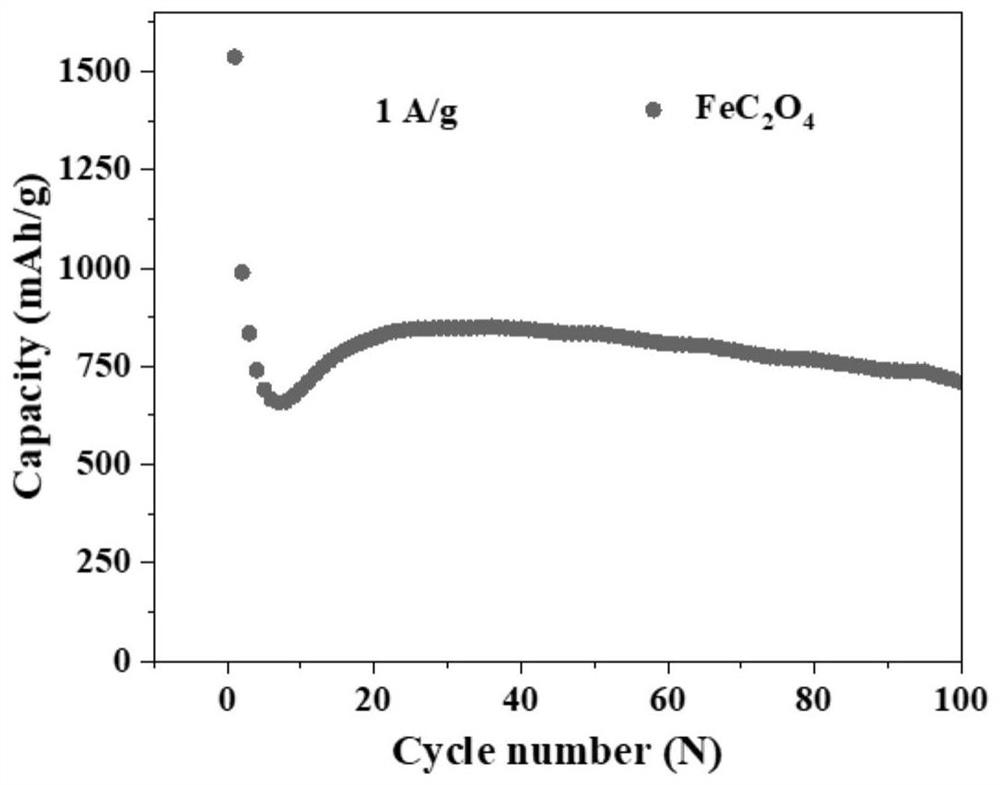
Ferrous oxalate, or iron(II) oxalate, is a inorganic compound with the formula FeC₂O₄ • xH₂O where x is typically 2. These are orange compounds, poorly soluble in water.
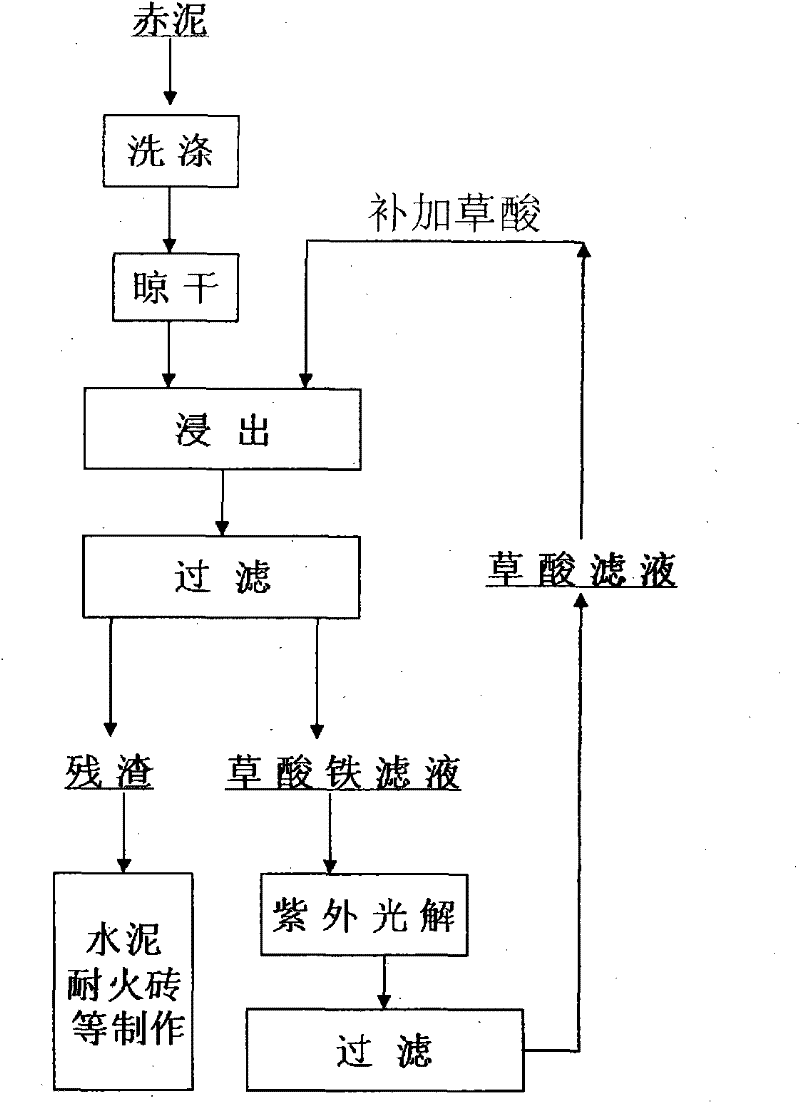
Method for recovering ferric oxide from red mud by leaching-photocatalysis by oxalic acid
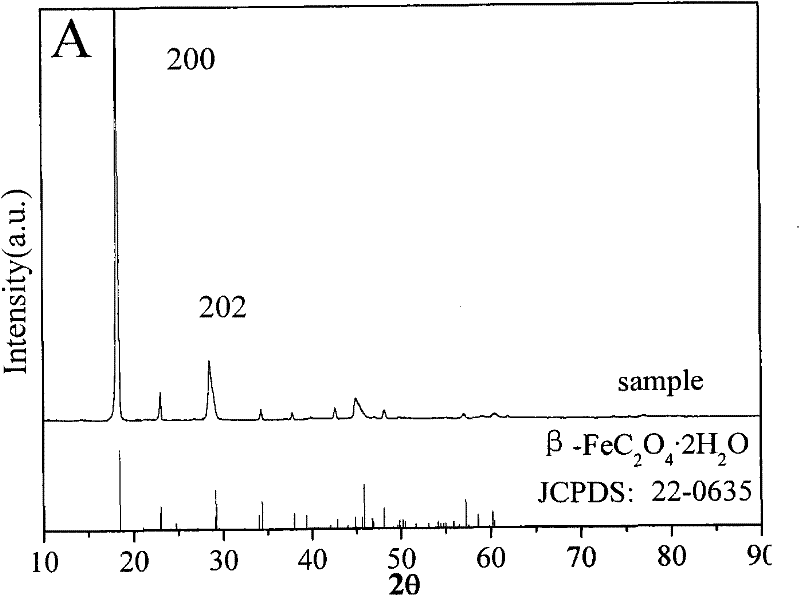
A method for treating red mud by utilizing oxalic acid solution comprises the steps of taking 0.5-1mol / L oxalic acid solution as a leaching agent, mixing air-dried red mud with the oxalic acid solution according to a proportion of 80-120g / L, stirring at 60-90 DEG C for 0.5-4h, and conducting solid-liquid separation to obtain the treated red mud and ferrum-containing oxalic acid solution. The ferric oxide content in the treated red mud is smaller than 1 percent, so that the red mud is applicable to manufacturing of refractory bricks, cement and the like. The ferrum-containing oxalic acid solution is subjected to photochemical reaction under irradiation of ultraviolet light or sunshine, thus being capable of forming ferrous oxalate sedimentation with better crystal. Ferric oxide content of filtrate after being separated from ferrous oxalate sedimentation is smaller than 1g / L, and the filtrate solution is continuously used for treating the red mud as supplement liquid of the leaching agent after being added with proper oxalic acid or being directly used.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
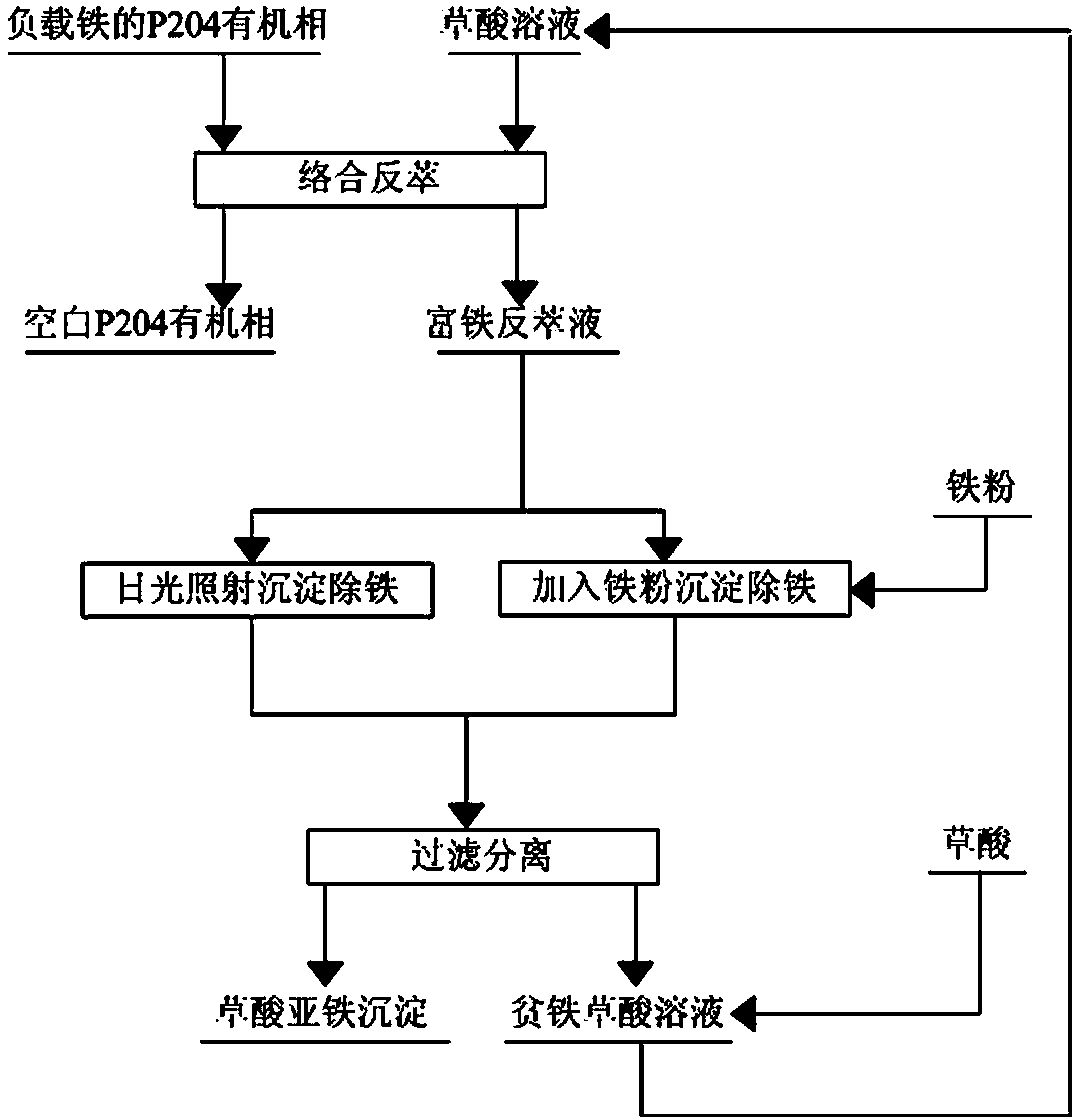
Method for stripping iron-loaded P2O4 organic phase and removing iron from strip liquor
ActiveCN103937980ANo pollution in the processNo dependenciesProcess efficiency improvementOxalateIron powder
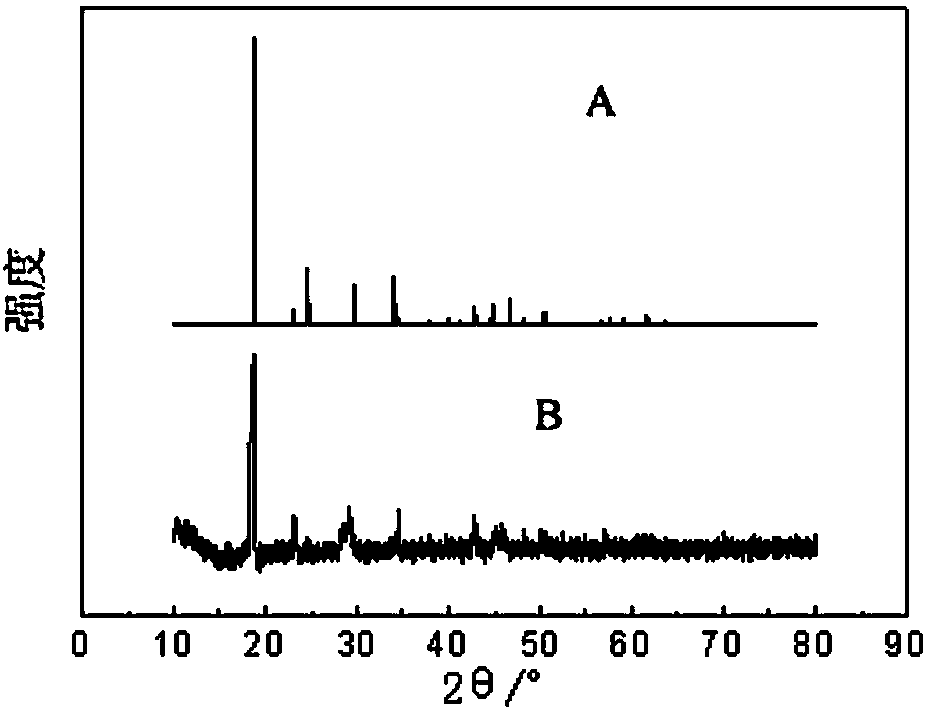
The invention discloses a method for stripping an iron-loaded P2O4 organic phase and removing iron from strip liquor, and belongs to the technical field of hydrometallurgy. The method comprises the following steps: (1) mixing an oxalic acid solution serving as a stripping agent with the iron-loaded P2O4 organic phase, and performing reverse-flow stripping at the temperature of 20-40 DEG C to obtain iron-rich strip liquor and a blank P2O4 organic phase; (2) performing photodecomposition on the iron-rich strip liquor by means of solar radiation to precipitate and remove iron, or adding iron powder into the iron-rich strip liquor under heating and stirring conditions to remove iron by means of reductive precipitation; (3) filtering precipitated and iron-removed materials to separate a solid phase and a liquid phase out; (4) replenishing oxalic acid into the separated liquid phase, namely, an iron-poor oxalic acid solution, returning to the step (1) for recycling, and recycling the solid phase in the form of a ferrous oxalate product. The method is free from acid mist pollution in the operating environment, and has the advantages of simple process, no discharge of waste residues or waste liquor, high efficiency, environmental friendliness and high practicability.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
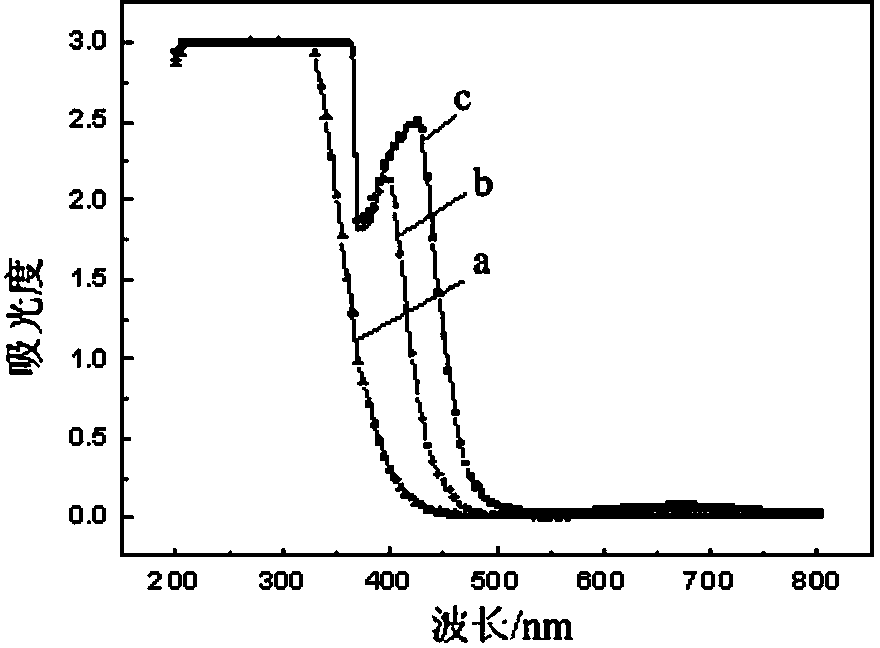
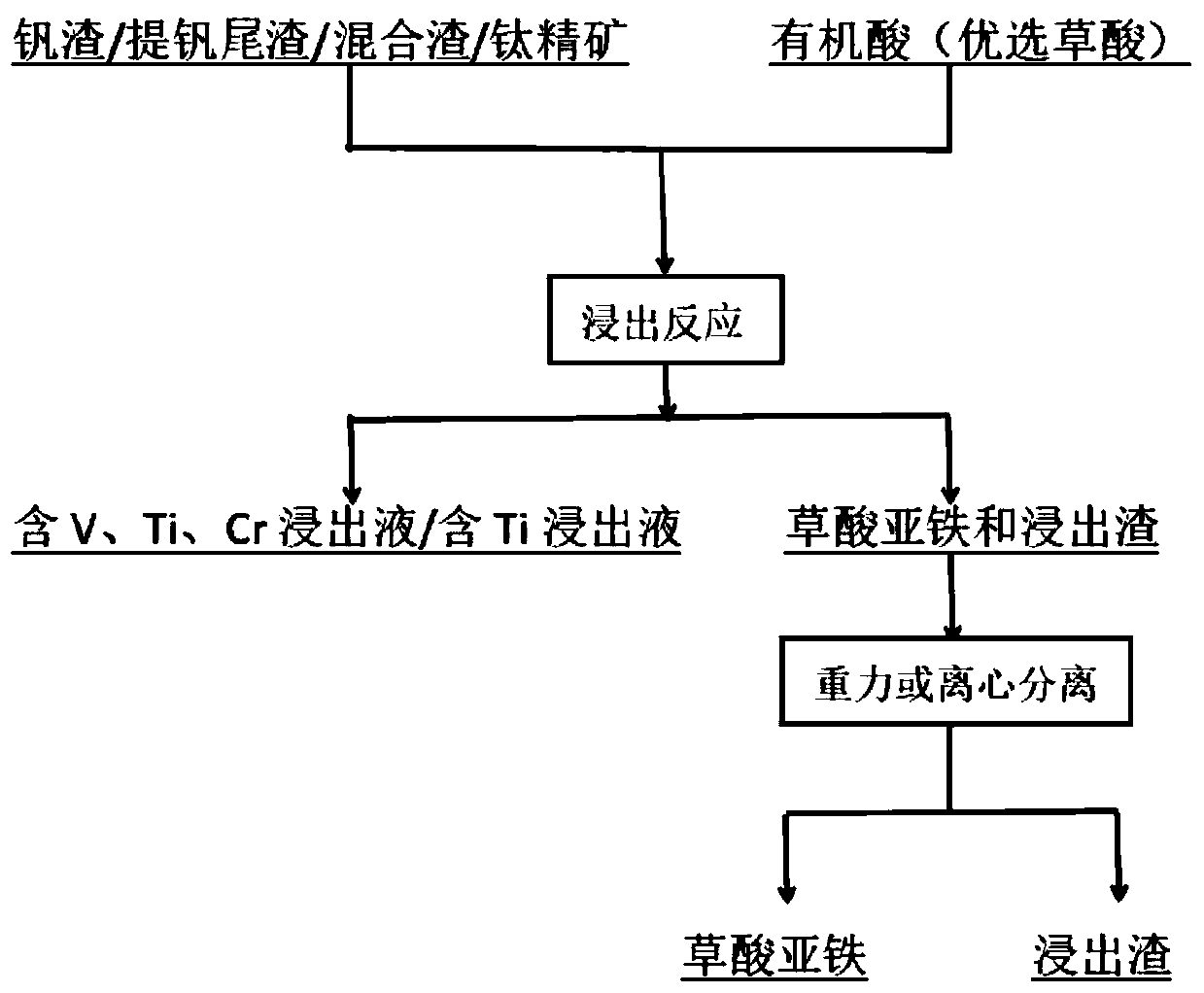
Method for leaching vanadium, titanium and chromium from vanadium, titanium and chromium raw materials by hydrothermal organic acid
ActiveCN111041200AEfficient leachingIncrease added valueProcess efficiency improvementSlagIron(II) oxalate
The invention provides a method for leaching vanadium, titanium and chromium from vanadium, titanium and chromium raw materials by hydrothermal organic acid, and belongs to the technical field of metallurgy. The method comprises the steps that vanadium slag, extracted vanadium tailings, vanadium slag-extracted vanadium tailing mixed slag and titanium concentrate are used as raw materials, and organic acid is used as a leaching agent for hydrothermal reaction in a reactor. The vanadium slag, the extracted vanadium tailings and the vanadium slag-extracted vanadium tailing mixed slag are correspondingly leached by the organic acid to obtain an element solution containing vanadium, titanium and chromium and ferrous oxalate; and the titanium concentrate is leached by the organic acid to obtaina solution contacting titanium and ferrous oxalate. According to the method, the acidity and the high complexing ability of the organic acid are utilized to destroy a phase containing vanadium, titanium and chromium, the complex reaction is generated to form a complex ion solution of [V(C2O4)3]3-, [Ti(C2O4)3]3- and [Cr(C2O4)3]3-, and the efficient leaching of vanadium, titanium and chromium elements is achieved; in addition, the method is simple in process and environment-friendly; the added value of the ferrous oxalate is high; and used equipment is common, the energy consumption is low, anda good application prospect is achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Nitrogen-doped carbon-coated iron oxide negative electrode material for lithium-ion battery and preparation
The invention belongs to the technical field of a negative electrode material for a lithium-ion battery, and discloses a nitrogen-doped carbon-coated iron oxide negative electrode material for the lithium-ion battery and a preparation method of the nitrogen-doped carbon-coated iron oxide negative electrode material. The method comprises the following steps of adding ferrite to a mixed solution of water and ethanol, stirring, dissolving, adding oxalate and stirring to obtain a turbid liquid; heating the turbid liquid to 120-220 DEG C for reaction for 8-15 hours to obtain a ferrous oxalate precursor; heating the ferrous oxalate precursor to 500-600 DEG C and burning the ferrous oxalate precursor for 4-8 hours to obtain an iron oxide; dissolving an emulsifier into water, adding n-butyl methacrylate, acrylonitrile and styrene, heating the solution to 55-65 DEG C, adding an initiator, stirring for 4-10 hours to obtain an emulsion and carrying out demulsification to obtain a polymer; and dispersing the polymer into an organic solvent, adding the iron oxide, stirring for 12-36 hours, separating to obtain a solid, heating the solid to 500-600 DEG C and burning the solid for 2-4 hours to obtain the nitrogen-doped carbon-coated iron oxide negative electrode material with excellent cycle performance and rate capability.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of high purity superfine ferrous oxalate
InactiveCN102344357ALow purityControl granularityCarboxylic acid salt preparationUltrasonic cavitationFiltration
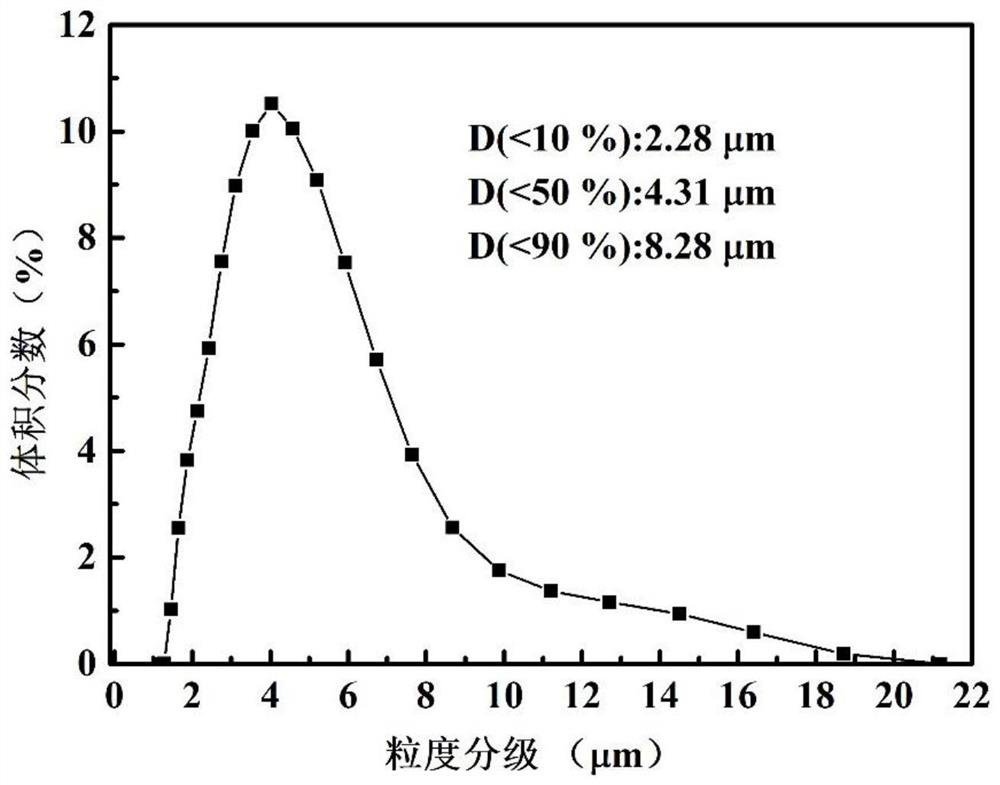
The invention provides a preparation method of high purity superfine ferrous oxalate. Oxalate and ferrous sulfate solids are respectively completely dissolved into deionized water under the action of mechanical agitation, impurities in the obtained solution are removed by adopting a vacuum filtration method; purified ferrous sulfate solution is sprayed into oxalate solution added with dispersant under the action of a high-speed centrifugal sprayer; reaction temperature of the sprayed ferrous sulfate solution and the oxalate solution is controlled to be minus 40 to 20 DEG C, the ferrous sulfate solution and the oxalate solution completely react under the action of ultrasonic cavitation; and generated ferrous oxalate suspension is subjected to separating, washing and drying to obtain ferrous oxalate powder. The purity of synthesized material reaches up to more than 99.5%, average particle size is 0.1-3Mum, and distribution range of the particle size is narrow; meanwhile, process flow is simple, cost is low, and industrialized mass production is easy to realize.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for removing iron ions in trivalent chromium acid solution
ActiveCN106399688AAchieve recyclingRealize high-value utilizationProcess efficiency improvementOxalateIron oxide black
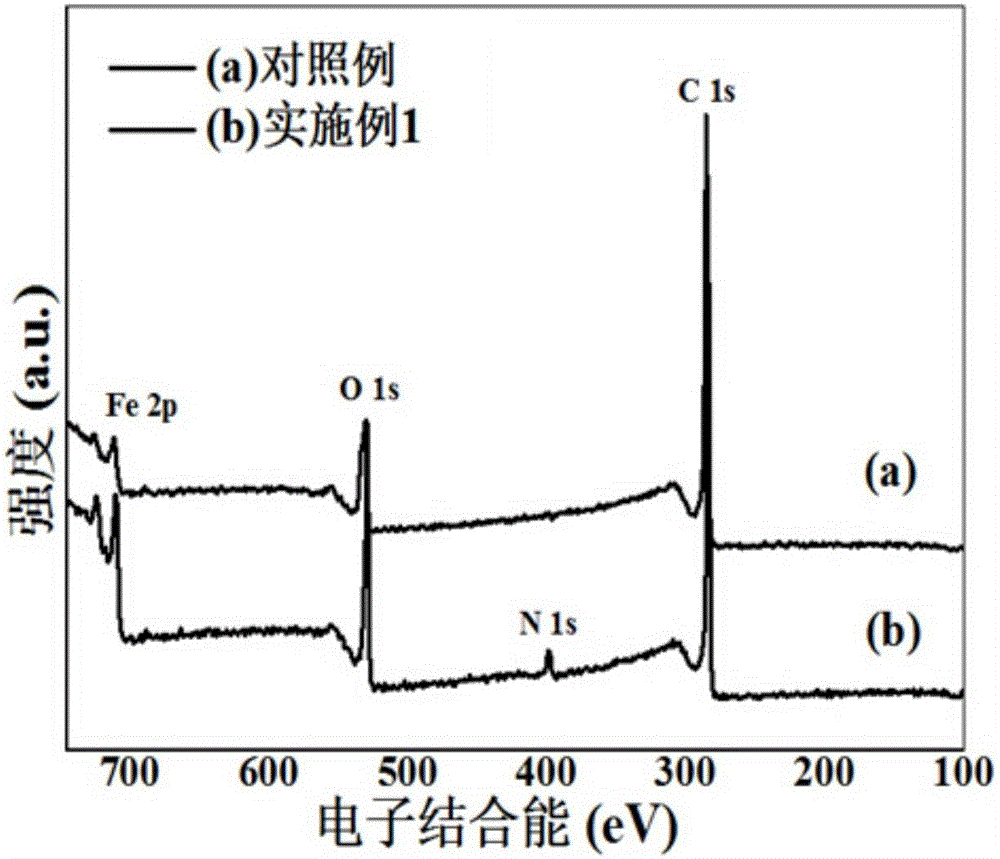
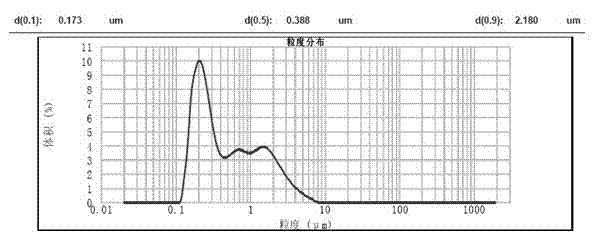
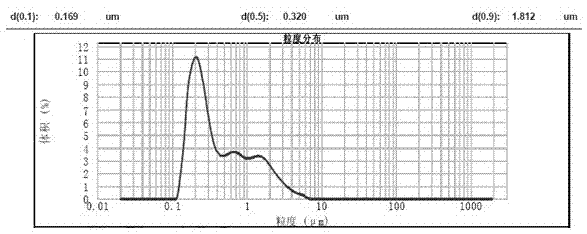
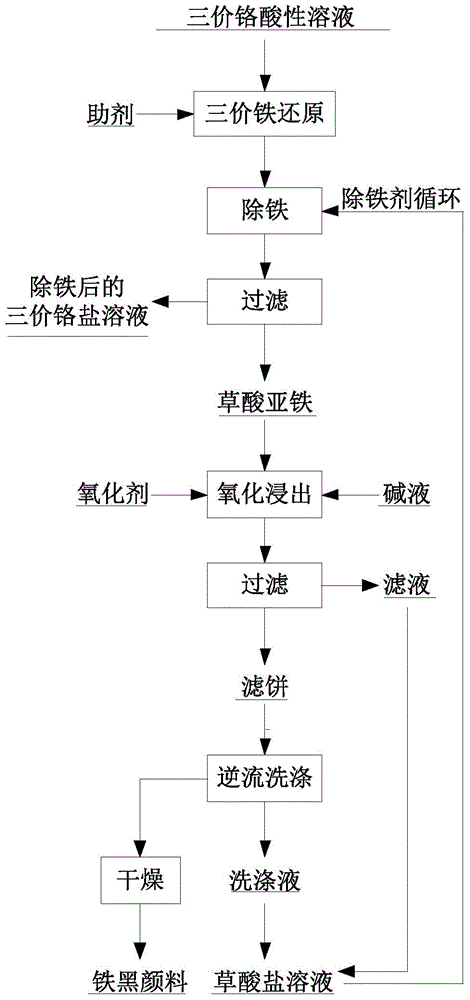
The invention discloses a method for removing iron ions in a trivalent chromium acid solution. The method includes the following steps that an additive is added into the trivalent chromium acid solution to reduce the trivalent ferric ions to bivalent ferric ions, then an oxalate solution is added, leached materials are subjected to liquid-solid separation, and the trivalent chromium acid solution obtained after iron removing is used for producing a chromium slat product; and ferrous oxalate obtained after iron removing is subjected to oxidation leaching in an alkali solution, iron in the ferrous oxalate is converted into ferroferric oxide, oxalate is leached into the solution liquid-solid separation is carried out, an oxalate leaching agent is obtained and used for cyclically removing iron, and the obtained ferroferric oxide becomes a black iron oxide pigment after being dried. According to the method, consumption of an iron removing agent is greatly reduced, iron is removed thoroughly through the trivalent chromium acid solution, the byproduct of black iron oxide can reach the pigment performance of domestic 722 black iron oxide and does not contain high-toxicity hexavalent chromium, and the method can be used in the industries of buildings, coatings and the like.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
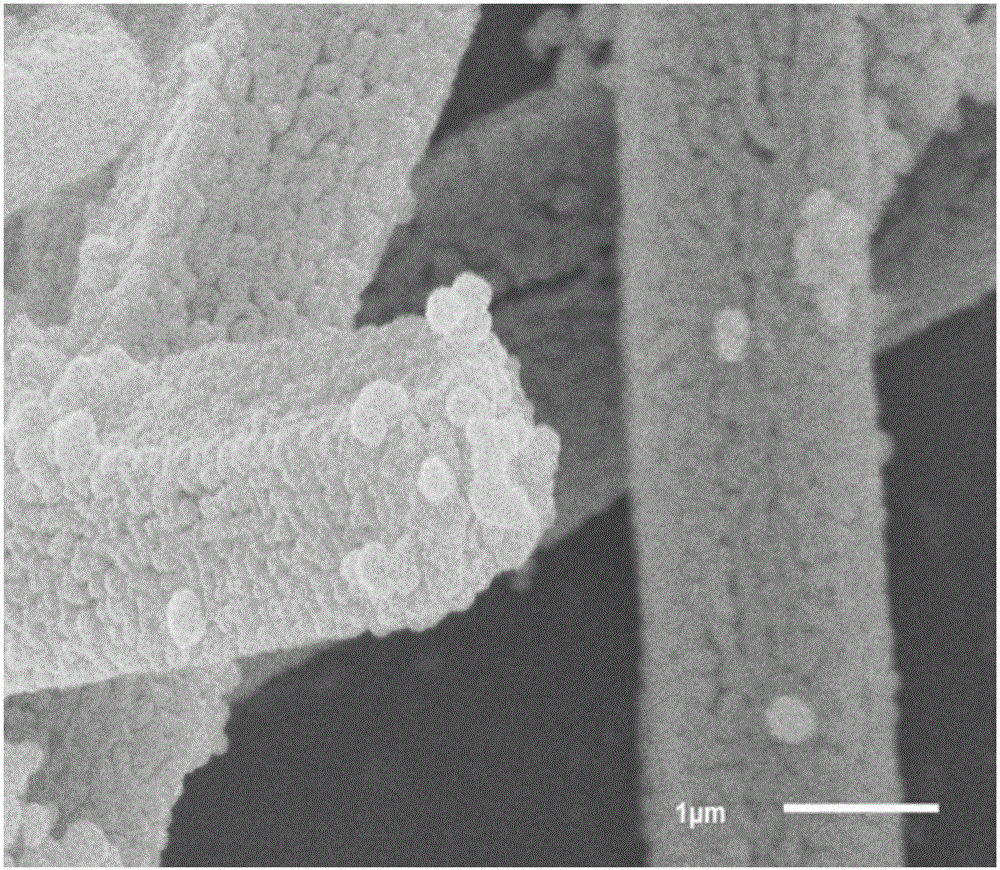
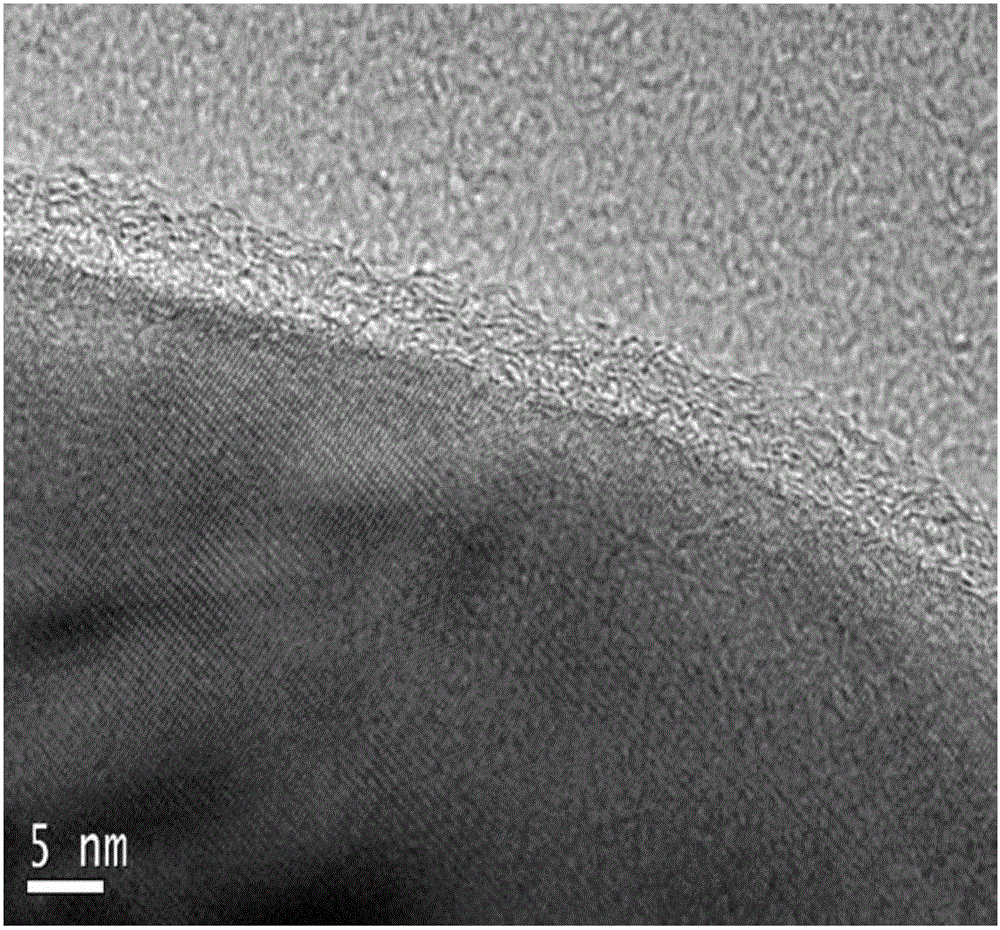
Porous iron oxide structured by nanocrystals and preparation method thereof
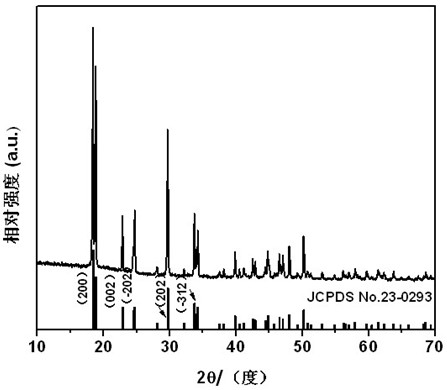
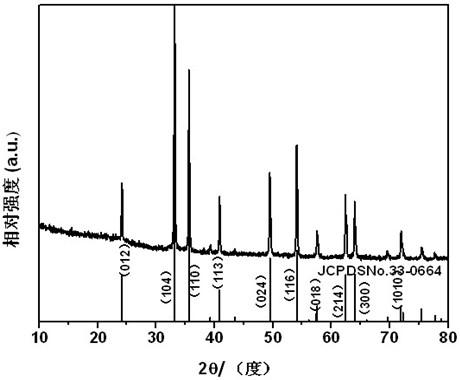
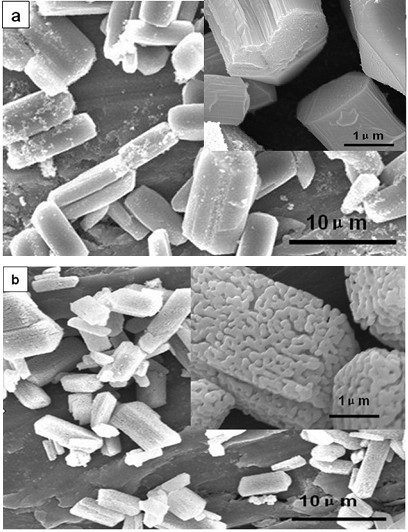
InactiveCN102275997AHigh crystallinityRegular strip-shaped macroscopic morphologyFerric oxidesMicron scaleIron(II) oxalate
The invention discloses a nanocrystalline porous iron oxide and a preparation method thereof. The hydrothermal reaction is carried out with an aqueous solution containing ferrous ions and an aqueous solution containing oxalate, and the precursor ferrous oxalate is first prepared, and the ferrous oxalate is a micron-scale strip shape; then the precursor ferrous oxalate is heat-treated, Porous iron oxide structured by nanocrystals is obtained. The porous iron oxide constructed by nano crystals in the present invention is composed of uniform nanoparticles and has a large specific surface area, which provides excellent conditions for the application of iron oxide. The outstanding advantage of the present invention is that the porous iron oxide obtained by the synthesis method has a regular strip-shaped macroscopic appearance, and the secondary particles that construct the porous structure are nanoparticles, which can meet the requirements of the iron oxide materials in the application fields such as electrode materials and catalytic materials. Specific surface area requirements. Moreover, the method provided by the invention is simple and controllable, and is easy to realize industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Efficient composite Fenton reagent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108191039AEasy to prepareEasy to operateWater treatment compoundsWater contaminantsFenton reagentCerium
The invention discloses an efficient composite Fenton reagent. Ferrous oxalate is used as a main catalyst; other metal salts which are one or several kinds of materials from copper metal salts, cobaltmetal salts, aluminum metal salts, manganese metal salts, nickel metal salts, cadmium metal salts, chromium metal salts, cerium metal salts and palladium metal salts, are added; The reagent has the advantages that the cost during the sewage treatment can be obviously reduced; a complicated device is not needed; the oxidization efficiency is obviously improved; meanwhile, the requirement on the use environment is reduced; good oxidization capability is realized under the acidic and basic conditions; meanwhile, the preparation method of the composite Fenton reagent is simple; the operation is convenient.
Owner:WUHAN TEXTILE UNIV
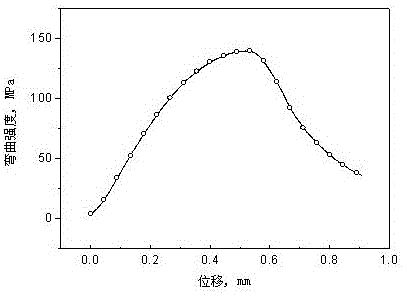
Method for modifying performance of sintered Mn-Cu damping alloy with ferrous oxalate
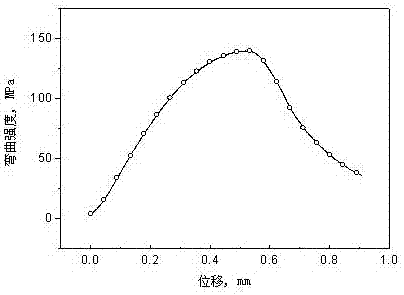
The invention discloses a method for modifying the performance of a sintered Mn-Cu damping alloy with ferrous oxalate. According to the method, sintering is promoted by high-activity iron produced by pyrolysis and hydrogen reduction of the ferrous oxalate, H2O, CO2 and other gases released during pyrolysis and hydrogen reduction of the ferrous oxalate can prevent a compact sealing layer from being formed on the surface of a sintered blank, and pyrolysis, reduction and sintering are performed under the action of hydrogen. Dehydration is performed at 180-240 DEG C with the heat preservation time of 1-4 h; pyrolysis is performed at 400-500 DEG C with the heat preservation time of 1-4 h; reduction is performed at 750-850 DEG C with the heat preservation time of 1-2 h; then a sintering process is finished at 850-950 DEG C with the heat preservation time of 2-4 h; and the heating speed is 5-10 DEG C / min. The sintered Mn-Cu damping alloy prepared according to the method reaches the diameter of 100 mm, the length of 200 mm, the density of 5.10-5.75 g / cm<3>, the hardness of 52-86 HRF and the bending strength of 128-184 MPa and has high uniformity.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Lithium iron phosphate nanorod/graphene composite material as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109904409ASmall particlesUniform particle size distributionMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesOxide compositeSolid state reaction method
The invention discloses a lithium iron phosphate nanorod / graphene composite material as well as a preparation method and an application thereof; the preparation method comprises the following steps offirstly, providing ferrous oxalate / graphene oxide composite material and then carrying out mixing on the ferrous oxalate / graphene oxide composite material and ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and lithium acetate dihydrate according to a certain molar ratio, and carrying out grinding and drying, and next, carrying out high-temperature reaction under the protection of inert gas to obtain the compositematerial. The lithium iron phosphate nanorod / graphene composite material prepared by adopting a two-step solid phase reaction method is small in particle size and uniform in particle size distribution, and has a one-dimensional nanorod-shaped structure, so that the transmission rate of ions can be effectively increased, and the capacity in large-current discharge is not attenuated; graphene is added, so that the surface conductivity of the material is further improved, and meanwhile, the rate performance and the cycling performance of the material are remarkably improved; and in the preparation process of the lithium iron phosphate nanorod / graphene composite material, the reaction conditions are easy to control, the operation is simple, the production cost is low, and industrial production is easy to realize.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of one-dimensional ferrous oxalate nanowire
InactiveCN103922920AHigh crystallinityHigh purityOrganic compound preparationNanotechnologyOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATENanowire
The invention relates to a preparation method of a one-dimensional ferrous oxalate nanowire, belonging to the technical field of nano energy material preparation. The method comprises the steps of hermetically heating a polyhydric alcohol-water solution of ferric iron salt and oxalic acid or a mixed polyhydric alcohol-water solution of ferric iron salt and oxalic acid to 90-180 DEG C, and reacting for 2-24 hours, thus obtaining the one-dimensional ferrous oxalate nanowire with diameter of 150-300 nanometers and length of 20-100 microns. The method is simple in operation process, is low in production cost and is very suitable for industrial production.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Method for producing high purity battery level iron oxalate from pickle liquor
ActiveCN101462942BHigh puritySmall particle sizeCarboxylic acid salt preparationOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATEFerrous salts
The invention relates to a method for producing high-purity battery grade iron oxalate by utilizing pickle liquor, comprising the following steps: the pickle liquor is pre-treated for lowering spent acid content, thus leading the pickle liquor to generate ferrite solution with a certain concentration; then after strict filtering and magnetic separation, the ferrite solution is transported into a reaction kettle, then industry ammonia is added and the solution is stirred for reaction to generate ferrous hydroxide gelatin; the soluble oxalic acid solution is slowly added in and stirred, and then the mixture is stirred by a conversion reaction kettle and heat preservation is carried out, thus obtaining iron oxalate slurry after reaction; iron oxalate mother solution is separated in the iron oxalate slurry, and the separated iron oxalate is washed, dried and crashed for obtaining high-purity superfine iron oxalate products. The method has the beneficial effects that: the pickle liquor in industrial production is fully utilized; a two-step liquid phase method of oxidation and conversion is adopted for leading the reaction to be more fully, so that the reaction rate is greatly improved,the grain diameter of the finished products iron oxalate is fine and uniform, D50 is less than or equal to 5mum, and the content of the iron oxalate is more than or equal to 95.5 percent; furthermore, the pickle liquor is used as raw material, and cyclic utilization and environmental protection of the industrial waste are utilized, thus changing waste into valuable and greatly lowering the production cost.
Owner:HUBEI WANRUN NEW ENERGY TECH DEV
Method for extracting Fe, Zn and Pb from electric furnace fly ash and utilizing Fe, Zn and Pb in high-value mode
InactiveCN113787085AFine granularityHigh recovery rateSolid waste disposalProcess efficiency improvementOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATEReaction temperature
The invention discloses a method for extracting Fe, Zn and Pb from electric furnace fly ash and utilizing Fe, Zn and Pb in a high-value mode. A large amount of dangerous waste electric furnace fly ash is used as a raw material, oxalic acid is used as a leaching agent, and a complex reaction is performed under the reaction conditions of low temperature and normal pressure, so that the purpose of stepwise separating iron and zinc resources is achieved. Under the conditions that the concentration of the oxalic acid is 5-30%, the liquid-solid ratio is 10:1-50:1, the reaction temperature is 30-90 DEG C and the reaction time is 0.5-4 h, the leaching rate of Fe in the electric furnace fly ash can reach 92% or above, the content of Zn (in terms of ZnO) in leaching residues can reach 36% or above, and the purity of finally obtained ferrous oxalate can reach 97% or above. The method is simple in process, low in energy consumption and low in reaction cost; and the obtained ferrous oxalate and zinc-rich residues have higher additional value, meanwhile, the influence on the environment is smaller, and the method has good market application prospects.
Owner:SINOSTEEL MAANSHAN INST OF MINING RES +2
Method for preparing fulvic acid calcium magnesium fertilizers
ActiveCN105175188APromote sustainable developmentIncrease organic matterClimate change adaptationFertilizer mixturesNutrientIron(II) oxalate
The invention discloses a method for preparing fulvic acid calcium magnesium fertilizers. The method includes the steps that 1, raw humic acid powder or sodium humate is added into gulonic acid mother liquor, the mixture is sufficiently stirred for 1 hour and centrifugally filtered, and filter liquor is collected; 2, ferrous sulfate is added into the filter liquor to be stirred, the mixture and oxalic acid generate ferrous oxalate, and filter liquor is collected after filtering is carried out; 3, the pH value of the obtained filter liquor is adjusted through calcium oxide to 2 to 4, the filter liquor is neutralized through magnesium hydrate till the pH value of the filter liquor ranges from 4 to 5, filtering is carried out, and filter liquor is collected; 4, the collected filter liquor is neutralized through potassium hydroxide till the pH value of the collected filter liquor ranges from 6 to 6.5, and fulvic acid calcium magnesium fertilizer intermediate products are obtained; 5, nutrients are added into the intermediate products, the mixture is mixed, dissolved and filtered, and filter liquor is prepared into the fulvic acid calcium magnesium fertilizers. According to the method, fulvic acid which can be conveniently absorbed by plants is generated after scientific harmless treatment is carried out on the gulonic acid mother liquor, the functional fulvic acid calcium magnesium fertilizers are prepared through the chelation performance of the fulvic acid, and the fulvic acid calcium magnesium fertilizers have the effects of resisting drought and diseases, promoting growth of crops and improving soil.
Owner:LIAONING PUTIAN TECH
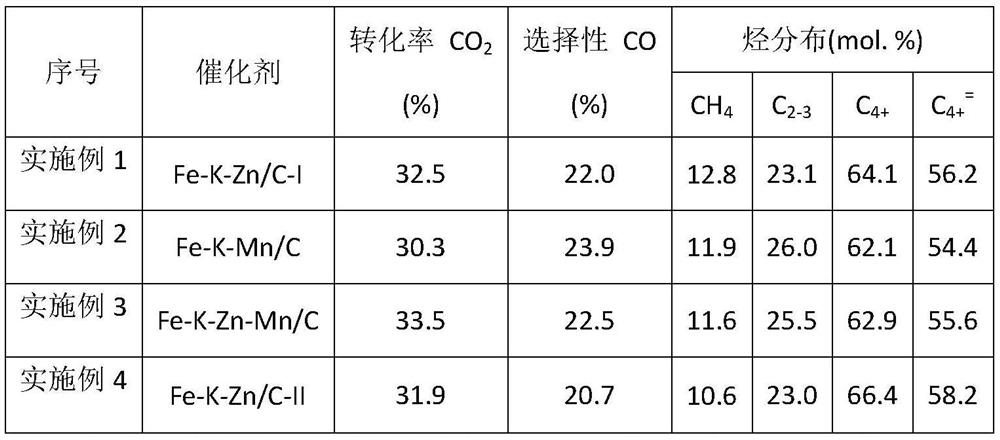
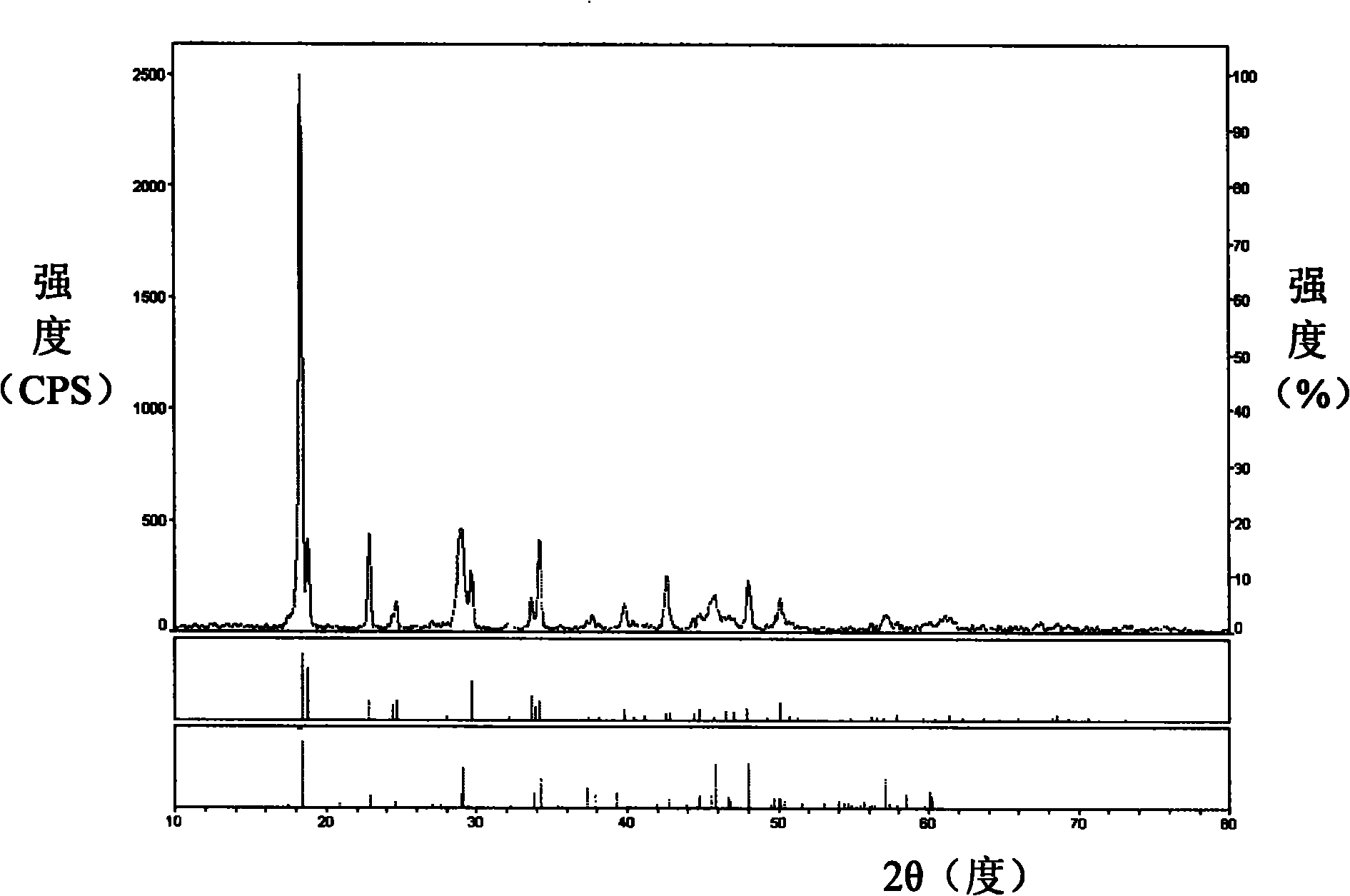
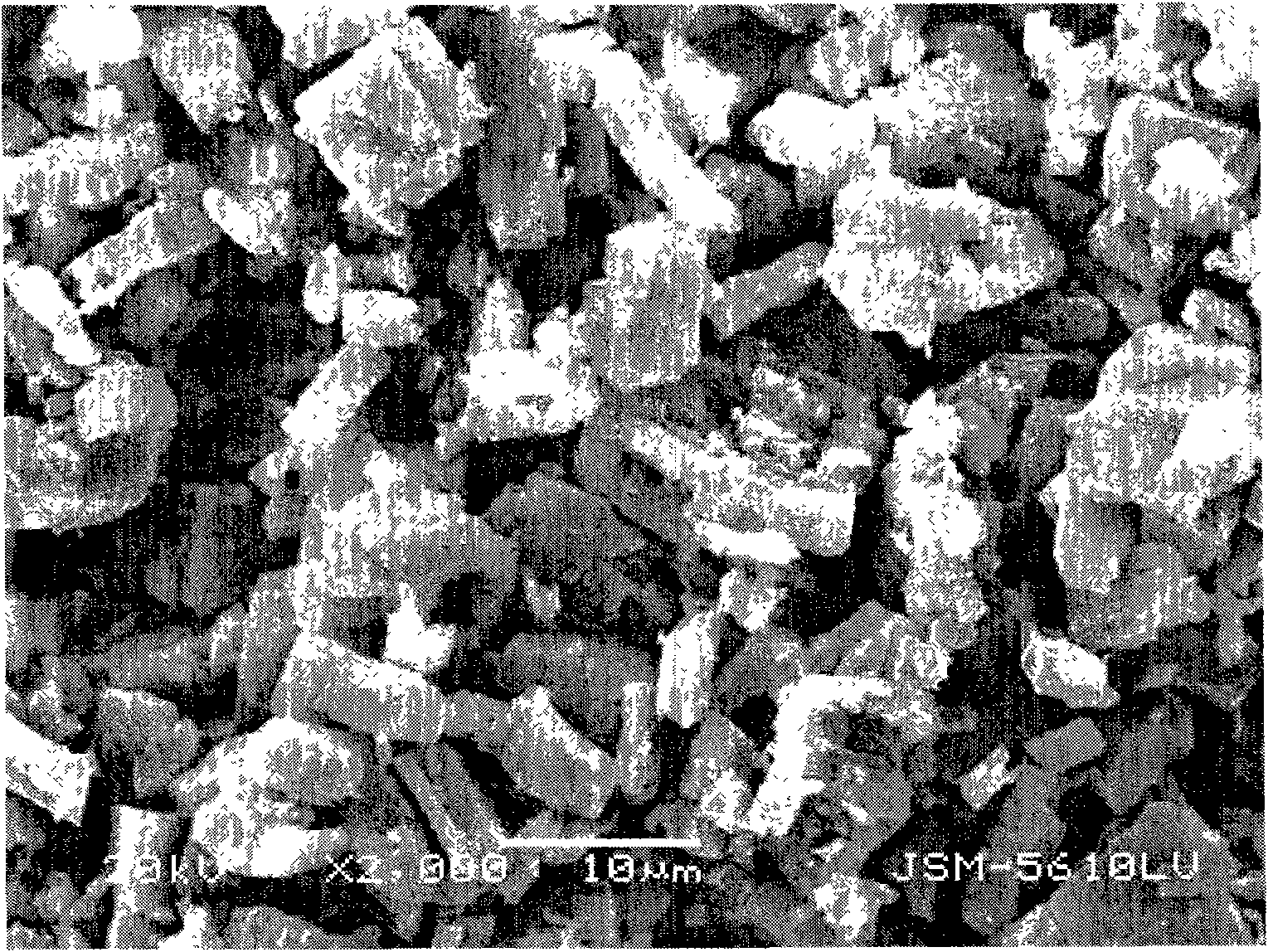
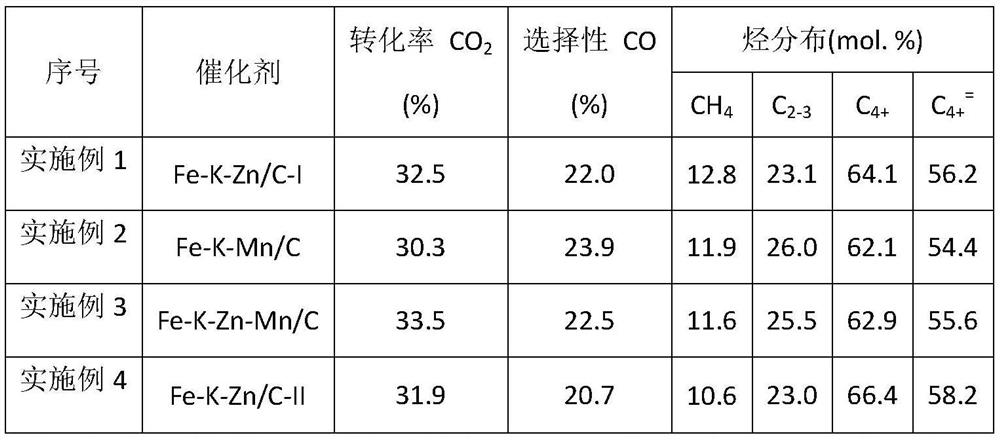
Catalyst for producing high-carbon olefin from mixed gas of carbon dioxide and hydrogen as well as preparation method and application method of catalyst
ActiveCN112973702AReduce the temperatureHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystPhysical chemistry
The invention designs a method for producing high-carbon olefin from mixed gas of carbon dioxide and hydrogen. According to the invention, ferrous oxalate, alkali metal, other metals and carbon are compounded, a ratio of iron to carbon is 0.7: 10 to 6: 10, a molar ratio of iron to other metals is 10: 0.01 to 10: 5, and the mass fraction of the alkali metal in a catalyst is 1-10%; the alkali metal is one or more selected from Na, K and Rb; and the other metal is one or more selected from Mn, Zn, Cu and Co. According to the catalyst, the activity of the catalyst and the selectivity of high-carbon olefin products are greatly improved, a new thought is provided for the conversion process of preparing high-added-value chemicals through selective hydrogenation of carbon dioxide, and the catalyst has good industrial application prospects.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing nano ferroferric oxide
InactiveCN103387267ASimple processEasy to operateMaterial nanotechnologyFerroso-ferric oxidesHigh volume manufacturingPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a method for preparing nano ferroferric oxide. According to the method, ferrous oxalate is subjected to thermal decomposition at 500-520 DEG C in the presence of an inert gas, thus obtaining the nano ferroferric oxide. The method is simple in process and convenient to operate; moreover, a thermal decomposition technology used in the method has low requirement on equipment because of low temperature; in addition, the cost is low due to the adopted ferrous oxalate, so that the method can be used for effectively realizing mass production.
Owner:SUQIAN COLLEGE
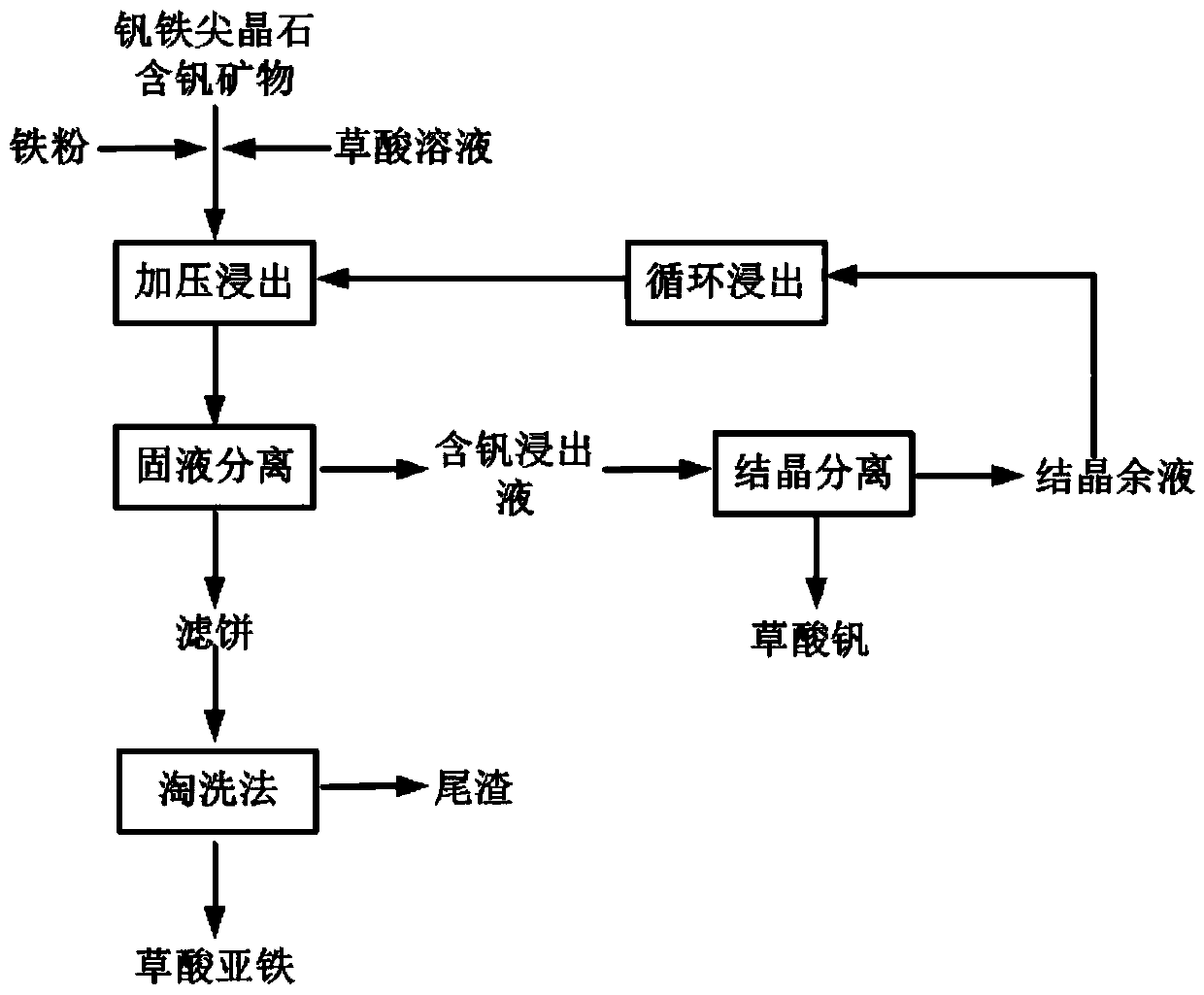
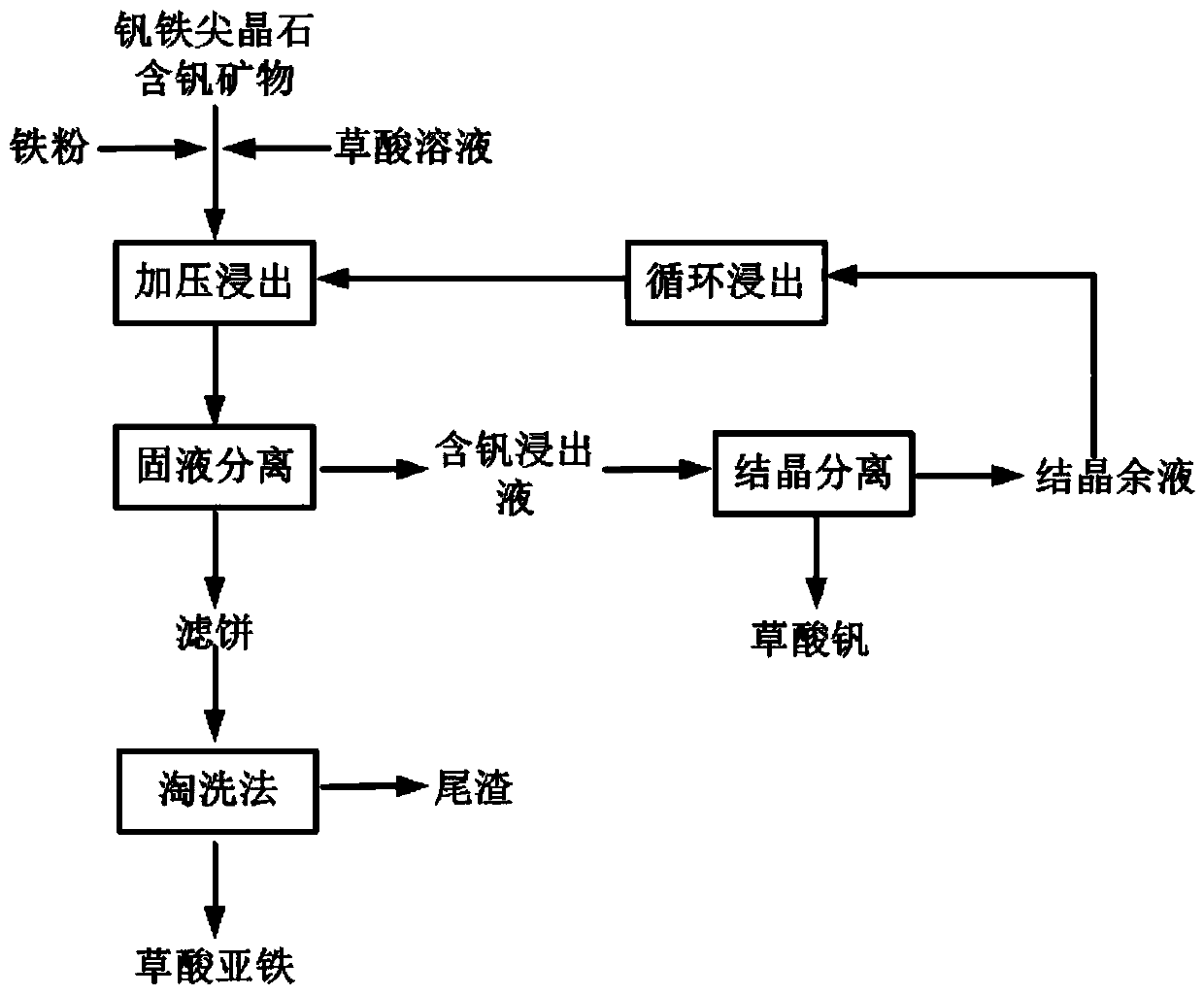
A method for hydrothermal oxalic acid complex leaching of vanadium in vanadium-iron-spinel vanadium-containing minerals
ActiveCN110306044BAchieve separationSimplify the process stepsProcess efficiency improvementOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATEPregnant leach solution
The invention provides a method for leaching vanadium in ferrovanadium spinel vanadium-containing minerals through complexing of hydrothermal oxalic acid, and belongs to the field of leaching of vanadium in ferrovanadium spinel vanadium-containing minerals through a hydrothermal method. According to the method, the ferrovanadium spinel vanadium-containing minerals are used as raw materials, ferrumpowder is used as a reducing agent, an oxalic acid solution is used as a leaching agent, and the ferrovanadium spinel vanadium-containing minerals, the ferrum powder and the oxalic acid are mixed into slurry to react under a hydrothermal condition; and solid-liquid separation is conducted on the slurry obtained after the reaction, so that clean vanadium-containing leachate and a ferrous oxalate by-product are obtained. According to the method, oxalate ions with a the strong complexing effect react with vanadium and ferrum in ferrovanadium spinel to form [V(C2O4)3]<3-> and [Fe(C2O3]<3-> to enter the solution; and the formed [Fe(C2O3]<3-> reacts with the Fe powder to form ferrous oxalate sediment, so that proceeding of the reaction is facilitated, and the leaching reaction rate is increased. By adoption of the method, vanadium in the ferrovanadium spinel vanadium-containing minerals can be effectively extracted, vanadium and ferrum are separated in the leaching process, the process steps are simplified, and the by-product, namely the ferrous oxalate, with high added value is obtained.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
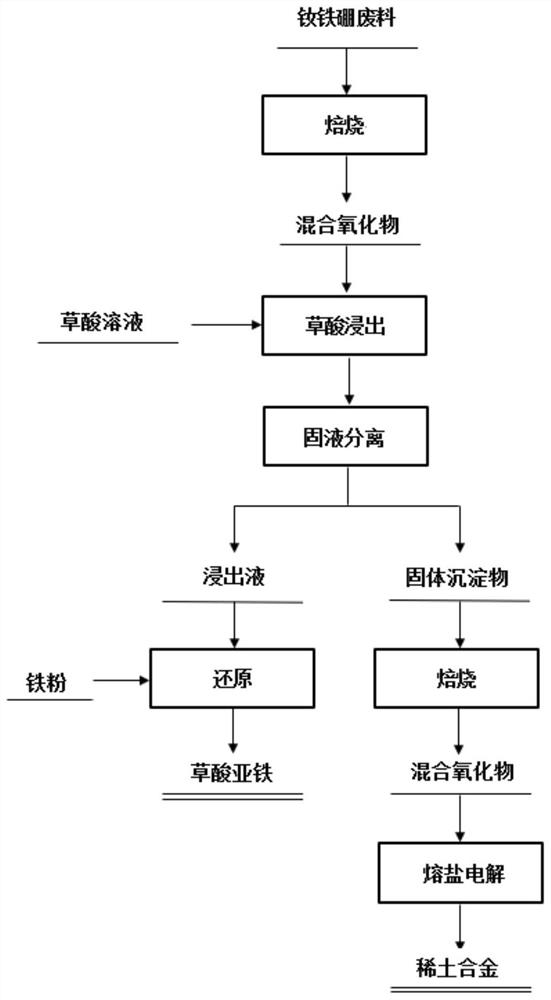
A method for synchronously and efficiently extracting rare earth and iron from high-value recycled NdFeB waste
ActiveCN110607537BEasy to operateEfficient extraction and high process operabilityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid salt preparationOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATEElectrolysis
The invention belongs to the technical field of industrial waste recycling and specifically relates to a method for synchronously and efficiently extracting high-value rare earth and iron from NdFeB waste for reuse. The method of the present invention reacts the oxidation product obtained after oxidizing and roasting the NdFeB waste with the oxalic acid solution to obtain the leach solution containing iron oxalate and the solid precipitate mainly composed of rare earth oxalate, and then only the leach solution and the precipitate Iron reduction and molten salt electrolysis treatment can be carried out respectively to obtain rare earth alloys for the production of NdFeB materials and ferrous oxalate for the production of lithium battery materials. The method only uses oxalic acid solution as a leaching agent and a precipitating agent, and can complete the leaching of iron and the transformation of rare earths in one step, thereby achieving the purpose of simultaneously realizing the efficient extraction and high-value recycling of iron and rare earths. The method of the invention has a short extraction process, is environmentally friendly, can effectively recover and obtain high-value products, and has extremely high process operability.
Owner:赣州稀土友力科技开发有限公司
Method for leaching gold hematite wrapped in second-stage calcine through using oxalic acid
InactiveCN111394577AAchieve reuseImprove leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATEPregnant leach solution
The invention discloses a method for leaching gold hematite wrapped in second-stage calcine through using oxalic acid. The method comprises the steps that firstly, the oxalic acid is added into a leaching tank; the second-stage calcine and water are added into the leaching tank added with the oxalic acid, agitation leaching is carried out, and liquid-solid separation is carried out after the leaching process is ended so as to obtain a leachate and leaching residues; illumination treatment is carried out on the leachate to obtain a faint yellow precipitate and an illuminated solution; and cyaniding leaching is conducted on the leaching residues, liquid-solid separation is conducted after the leaching process is finished, and accordingly gold-containing pregnant solution is obtained. According to the method, the oxalic acid is added, the strong complexing effect of C2O4<2-> on Fe<3+> is utilized, the hematite in the second-stage calcine is leached in the form of an iron oxalate complex,the iron leaching speed is high, the iron leaching rate is high, the energy consumption in the leaching process is low, and industrialization is easy; the leachate is subjected to illumination treatment to obtain ferrous oxalate, part of the oxalic acid is re-used, and recovering of iron, recycling of part of leaching agent oxalic acid and re-using of the system water are achieved; and cyaniding is conducted on iron removal slag for gold extraction, and the leaching rate of gold is effectively increased.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for preparing ferrous oxalate hydrated salt crystal
The invention relates to a preparation method for a hydrous salt crystal of ferrous oxalate. The method comprises a contact reaction between water solution of oxalate and water solution of ferrous salt, which is carried out in the presence of mixed solvent of organic solvent and water; the organic solvent and water are totally soluble. The hydrous salt crystal of ferrous oxalate prepared by the method provided by the invention has small average grain size, as small as 1-5 micron, has good reactivity, and is suitable for being as compound raw material of lithium iron phosphate, an active substrate of anode of lithium-ion secondary batteries.
Owner:海宁市盐官工业投资有限公司
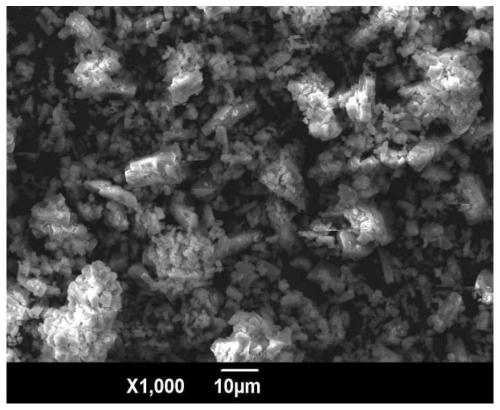
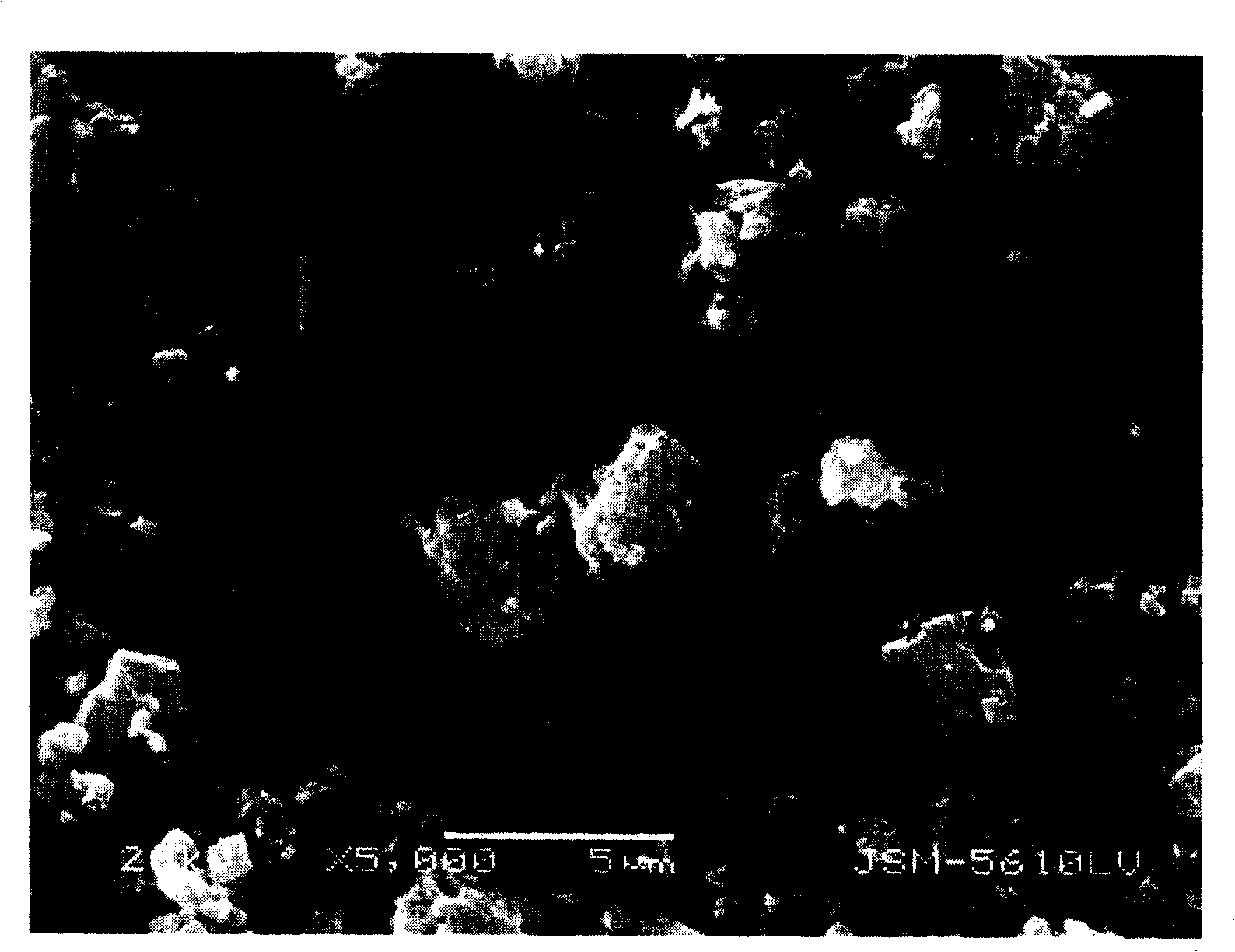
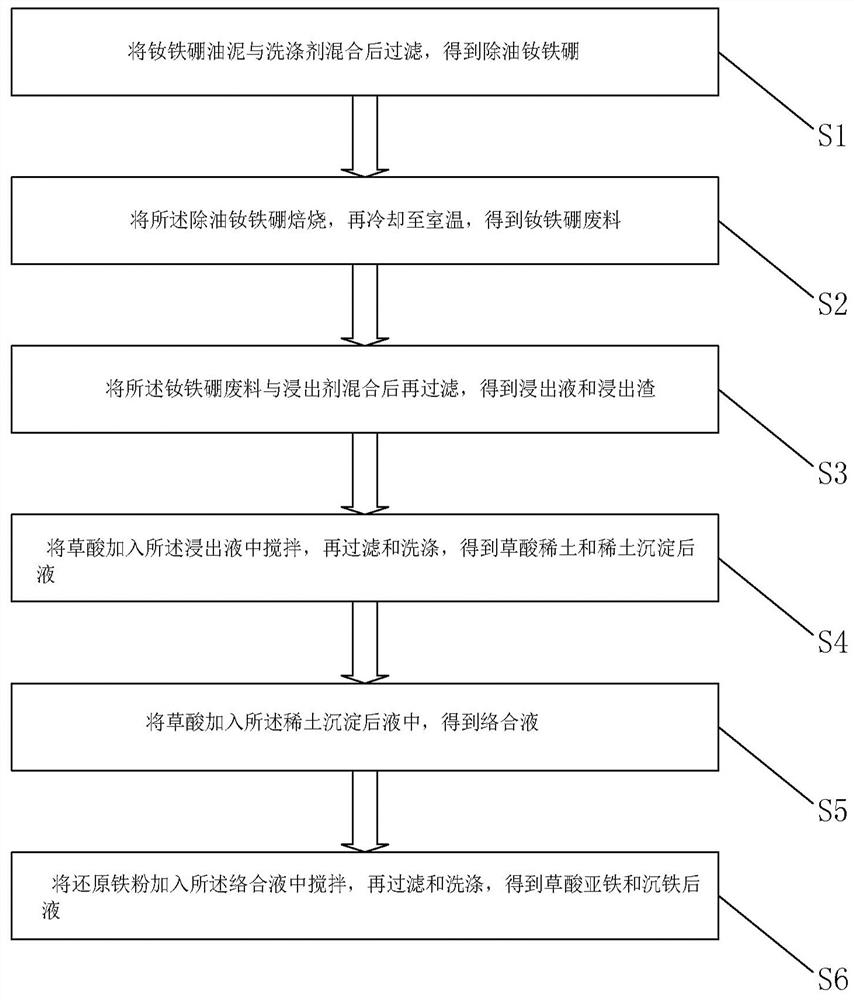
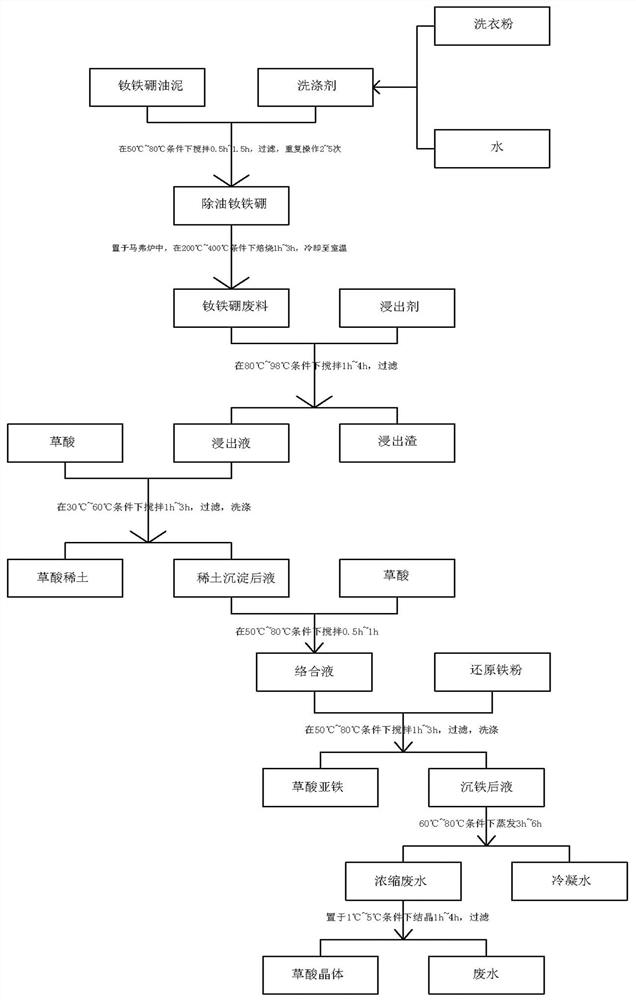
Method for comprehensively recovering rare earth and iron from neodymium iron boron oil sludge
ActiveCN113652550AHigh recovery rateAvoid it happening againRecycling and recovery technologiesProcess efficiency improvementFractional PrecipitationIron(II) oxalate
The invention relates to the technical field of rare earth and iron recovery, in particular to a method for comprehensively recovering rare earth and iron from neodymium iron boron oil sludge. According to the method, oil in the neodymium iron boron oil sludge is removed through a detergent, then oxidizing roasting is conducted, the rare earth and the iron can be converted into corresponding oxides, it is avoided that indissolvable NdFeO3 is generated due to high-temperature roasting, hydrochloric acid is used for leaching the rare earth and the iron obtained after oxidizing roasting at the low temperature, the rare earth and the iron are almost completely dissolved, and through fractional precipitation, the rare earth and the iron are recovered by the aid of rare earth oxalate and ferrous oxalate respectively. The method has the characteristics of easiness in operation, low oxidizing roasting temperature, high rare earth and iron recovery rate and high comprehensive utilization rate of resources.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
The Method of Improving the Properties of Manganese Copper Damping Sintered Alloy Using Ferrous Oxalate
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
A kind of preparation method of fulvic acid calcium magnesium fertilizer
ActiveCN105175188BPromote sustainable developmentIncrease organic matterClimate change adaptationSewage/sludge fertilisersPotassium hydroxideIron(II) oxalate
Owner:LIAONING PUTIAN TECH
A method for separating and extracting iron and nickel from iron and nickel leachate
ActiveCN109881026BSolving the Difficulty of Deep SeparationReduce processing operating costsPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATEIron(II) oxide
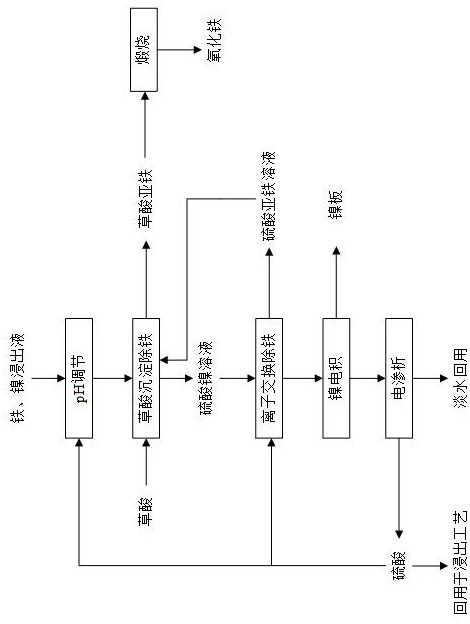
The invention discloses a method for separating and extracting iron and nickel from an iron and nickel leaching solution. In the method, after adjusting the pH of the waste water, oxalic acid precipitation is used to remove iron to obtain ferrous oxalate and nickel sulfate solutions. Ferrous oxalate After calcination, iron oxide is obtained; the nickel sulfate solution is further ion-exchanged to remove iron, and then nickel electrowinning is carried out to obtain a nickel plate. After the solution produced by nickel electrowinning is treated by electrodialysis, fresh water is reused; , The problem of deep separation of nickel leaching solution, the whole process constitutes a closed loop, sulfuric acid and water resources are recycled, the process operation cost is low, iron extraction production can obtain ferrous oxide with a purity >99.5%, and nickel extraction production can obtain nickel plate with a purity greater than 99.995% , high resource utilization rate, good product purity, excellent economic benefits, no waste gas, waste water and waste residue discharge in the whole process, and no secondary pollution.
Owner:BEIJING CYCLE COLUMBUS ENVIRONMENTAL TECH RES INST CO LTD
Preparation method of lithium ferrous oxalate ion battery negative electrode material with exposed specific oriented crystal faces
PendingCN113861015AImprove energy storage performanceLow costOrganic compound preparationCell electrodesFerric hydroxideElectrochemical response
The invention relates to a preparation method of a lithium ferrous oxalate ion battery negative electrode material with exposed specific oriented crystal faces. An iron hydroxide precursor is added into a mixed solution composed of additives such as ascorbic acid and oxalic acid in a specific proportion, and synthesis of a ferrous oxalate nano-material exposing different oriented crystal faces is achieved by controlling the reduction dissolution rate of iron hydroxide in the solution and coordinating the nucleation growth process of the ferrous oxalate material. According to the invention, ascorbic acid is adopted to strengthen reduction dissolution of an acidic oxalic acid solution on ferric hydroxide and regulate and control atomic coordination and an initial crystal stacking rate of ferrous oxalate; meanwhile, the atomic coordination environment and the surface energy of ferrous oxalate crystal particles are interfered by using an organic solvent; therefore, the preparation of the ferrous oxalate material with exposed specific oriented crystal faces is achieved. The ferrous oxalate material with the exposed specific oriented crystal face growth can give full play to the advantages of different types of electrochemical reaction ion diffusion microchannels constructed by arrangement of different crystal face atoms and the characteristic of close arrangement of different oriented crystal face atoms to adjust material stress distribution and energy storage catalytic sites, and the lithium storage performance of the ferrous oxalate material is enhanced.
Owner:云南润久科技有限公司
Method for modification preparation of composite electrode micropowder material by using vanillic acid
InactiveCN107834037ASimple processReduce manufacturing costCell electrodesSecondary cellsVanillic acidComposite electrode
The invention discloses a method for modification preparation of a composite electrode micropowder material by using vanillic acid. The method comprises the steps: according to the atomic ratio of Li1-xYxFePO4, taking a proper amount of lithium acetate, ferrous oxalate, ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and a Pr powder, mixing, then grinding the mixed raw material with an agate mortar, grinding fullyto obtain a precursor powder, then adding a proper amount of vanillic acid, continuing to grind, after being uniform, carrying out heat treatment under the protection of an inert gas atmosphere, naturally cooling to room temperature, and thus obtaining the prepared composite electrode micropowder material modified by vanilla acid.
Owner:张彩缘
Lithium ion composite electrode material doped with citric acid and process thereof
InactiveCN107834039AImprove conductivityImprove charge and discharge performanceCell electrodesSecondary cellsComposite electrodeRoom temperature
The invention relates to a lithium ion composite electrode material doped with citric acid and a process thereof. The process comprises the steps: firstly, taking lithium acetate (CH3COOLi.2H2O, analytically pure), ferrous oxalate (FeC2O4.2H2O, analytically pure), ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (NH4H2PO4, analytically pure), and an Nd powder according to the ratio of Li1-xNdxFePO4 and proportioning, placing in an agate pot, carrying out mixed grinding, grinding to become a pale yellow powder, then adding citric acid, mixing evenly, carrying out heat treatment for a period of time under the protection of an inert gas atmosphere and in the condition of the temperature of 300-400 DEG C firstly, and then carrying out isothermal heat treatment at the temperature of 500-550 DEG C for a period oftime, naturally cooling the obtained product to room temperature under the protection of an inert gas atmosphere, and thus obtaining the lithium ion composite electrode material powder doped with citric acid. The method has the advantages of simple process and low production cost, and the electric conduction and charge and discharge performance of the prepared electrode material powder is good.
Owner:张彩缘
Preparation of iron oxalate hydrous salt crystal
The invention provides a method for preparing ferrous oxalate hydrated salt crystals. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out the contact reaction between a solution A and a solution B. The contact manner and condition of the solution A and the solution B are provided to allow the produced ferrous oxalate hydrated salt to be supersaturated in the reaction mixed solution of the solution A and the solution B. By adopting the method, the prepared ferrous oxalate hydrated salt crystals have smaller average particle size and higher purity.
Owner:海门市创豪工业设计有限公司
Catalyst for producing high-carbon olefins from a mixture of carbon dioxide and hydrogen, and its preparation and application method
ActiveCN112973702BReduce the temperatureHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsCarbon compositesPtru catalyst
The present invention designs a method for producing high-carbon olefins by mixing carbon dioxide and hydrogen. In the present invention, ferrous oxalate, alkali metals, other metals and carbon are compounded, and the ratio of iron to carbon is 0.7:10 to 6:10. The molar ratio of iron and other metals is 10:0.01-10:5, wherein the mass fraction of alkali metals in the catalyst is 1%-10%; alkali metals are one or more of Na, K and Rb, and other metals One or more of Mn, Zn, Cu and Co. The catalyst of the present invention greatly improves the activity of the catalyst and the selectivity of high-carbon olefin products, provides a new idea for the conversion process of carbon dioxide selective hydrogenation to produce high value-added chemicals, and has good industrial application prospects.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Corrosion-resistance magnetic material and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN107731440AImprove corrosion resistanceIncrease magnetic inductionInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsEpoxyBenzaldehyde
The invention discloses a preparing method of a corrosion-resistance magnetic material. The preparing method comprises the following steps of adding 3,4-dimethoxy benzaldehyde, 2-hydroxybenzylamine, 4-tertiary butyl phenol and 3-benzyloxypropionitrile into distilled water, and stirring for 5-10 min; then adding acetylsalicylic acid and tribromoethanol, raising the temperature to 50-60 DEG C, and stirring to conduct a reaction for 30-50 min; adding ferrous oxalate dehydrate and nickel methyl sulfonate into the solution, raising the temperature to 100-120 DEG C, and continuously conducting a reaction for 5-8 h; drying at the temperature of 150-180 DEG C, and roasting at the temperature of 200-250 DEG C to obtain mixed powder A; adding novolac epoxy and the mixed powder A into a ball grindingmill to be mixed to obtain the corrosion-resistance magnetic material.
Owner:SUZHOU KEMAO ELECTRONICS MATERIALS TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com