Preparation method of lithium ferrous oxalate ion battery negative electrode material with exposed specific oriented crystal faces
A lithium ferrous oxalate and ion battery technology, which is applied in battery electrodes, carboxylate preparation, carboxylate preparation, etc., to achieve low cost and enhance energy storage performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] A method for preparing a negative electrode material for a ferrous oxalate lithium ion battery exposing a specific orientation crystal plane, the specific steps of which are as follows:
[0025] Step 1. Disperse the ferric hydroxide precursor material in a mixed solution composed of 30ml ethanol and 100ml deionized water through an ultrasonic cleaner to obtain a uniformly dispersed mixed turbid solution; wherein, the volume ratio of the precursor material mass to the liquid solution For: 0.5 g: 130 ml;
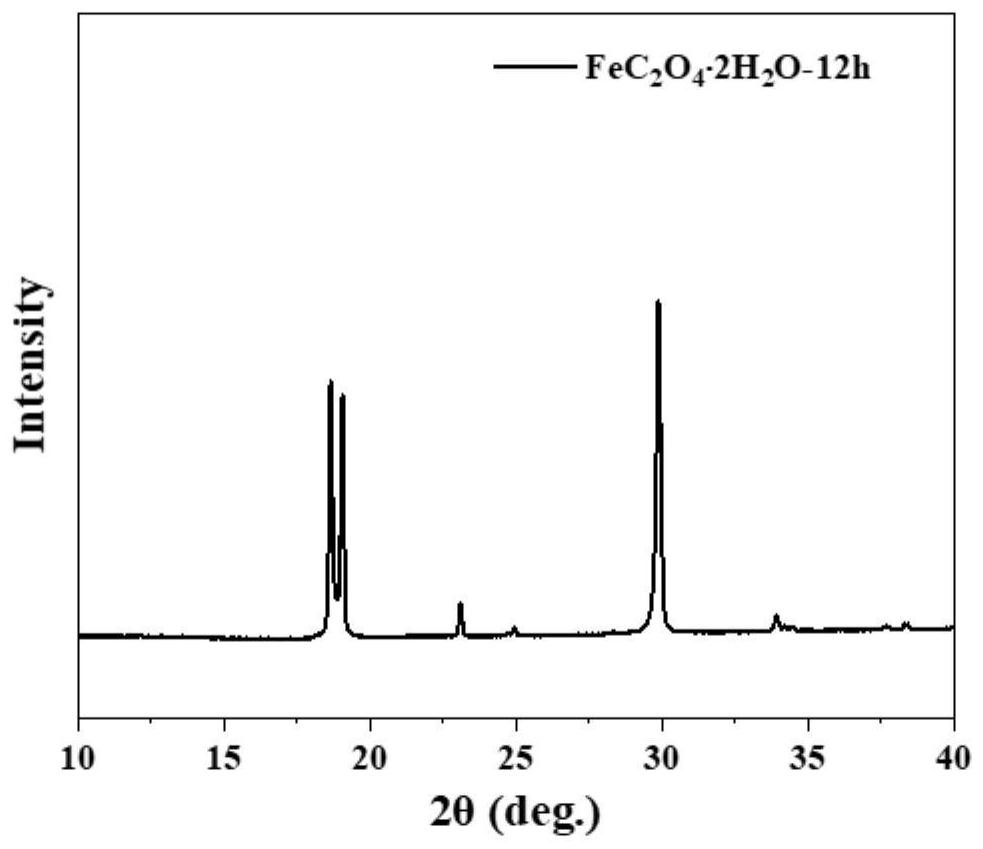
[0026] Step 2. Add 1.3 g of ascorbic acid and 4.0 g of oxalic acid to the uniformly dispersed turbid liquid in step 1, and react at 80° C. for 12 h; after the reaction is completed, filter, wash and dry to obtain a ferrous oxalate material containing crystal water ;
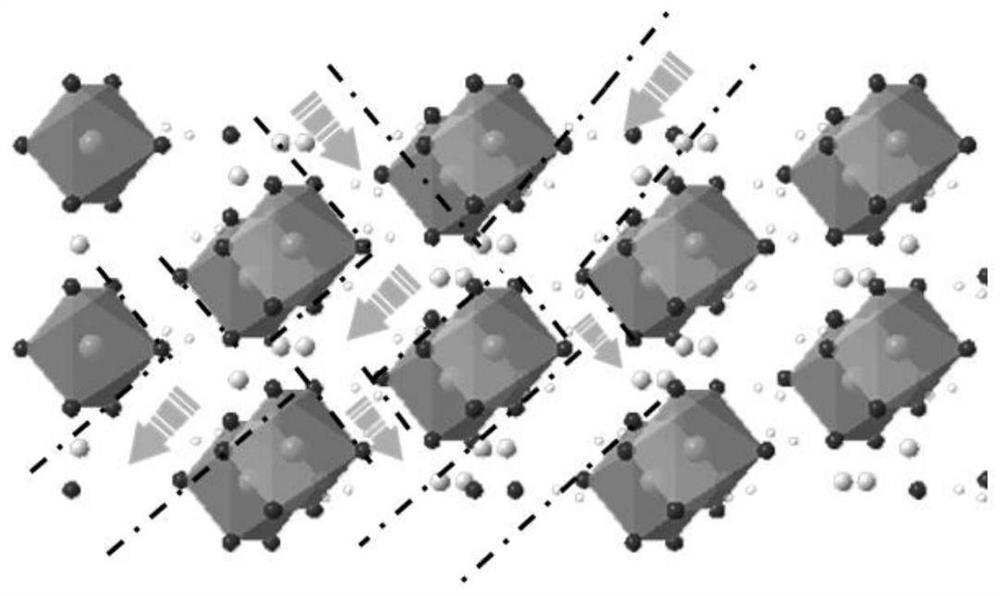
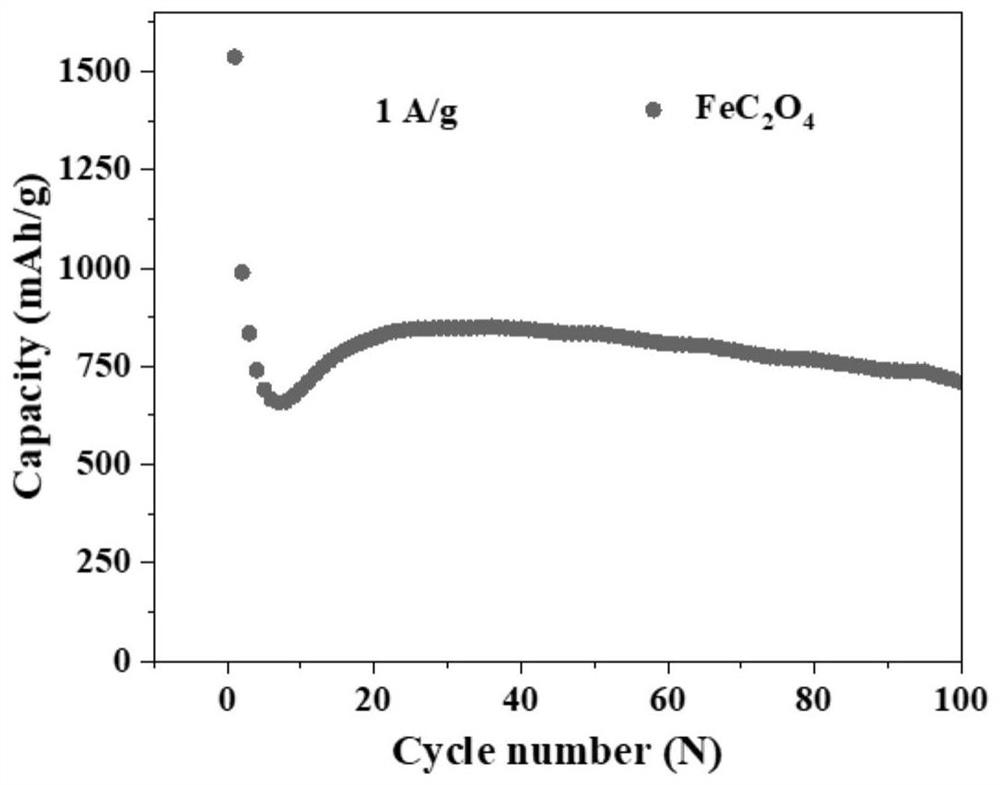
[0027] Step 3. Sintering the crystal water-containing ferrous oxalate material obtained in step 3 at 280° C. for 2 hours under an argon atmosphere to obtain a ferrous oxalate material with exposed (202) c...
Embodiment 2
[0030] A method for preparing a negative electrode material for a ferrous oxalate lithium ion battery exposing a specific orientation crystal plane, the specific steps of which are as follows:
[0031] Step 1. Disperse the ferric hydroxide precursor material in a mixed solution composed of 30ml ethanol and 100ml deionized water through an ultrasonic cleaner to obtain a uniformly dispersed mixed turbid solution; wherein, the volume ratio of the precursor material mass to the liquid solution For: 0.5 g: 130 ml;
[0032] Step 2. Add 1.3g of ascorbic acid and 4.0g of oxalic acid to the uniformly dispersed turbid liquid in step 1, and react at 80°C for 12 h; after the reaction is completed, filter, wash and dry to obtain crystal water exposure (202) Crystalline ferrous oxalate material;
[0033] Step 3. Sintering the crystal water-containing ferrous oxalate material obtained in step 3 at 280° C. for 2 hours under an argon atmosphere to obtain a ferrous oxalate material with expose...
Embodiment 3
[0037] A method for preparing a negative electrode material for a ferrous oxalate lithium ion battery exposing a specific orientation crystal plane, the specific steps of which are as follows:
[0038] Step 1. Disperse the ferric hydroxide precursor material in a mixed solution composed of 30ml ethanol and 100ml deionized water through an ultrasonic cleaner to obtain a uniformly dispersed mixed turbid solution; wherein, the volume ratio of the precursor material mass to the liquid solution For: 0.5 g: 130 ml;
[0039] Step 2. Add 1.3g of ascorbic acid and 4.0g of oxalic acid to the uniformly dispersed cloudy liquid in step 1, and react at 60°C for 24 hours; after the reaction is completed, filter, wash and dry to obtain (202) crystals containing crystal water Surface ferrous oxalate material;
[0040] Step 3. Sintering the crystal water-containing ferrous oxalate material obtained in step 3 at 280° C. for 2 hours under an argon atmosphere to obtain a ferrous oxalate material ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com