Method for stripping iron-loaded P2O4 organic phase and removing iron from strip liquor
A stripping liquid and organic phase technology, applied in the field of hydrometallurgy, can solve problems such as inability to get rid of use, poor operating conditions, and large acid-base consumption, and achieve a solution that is dependent on natural weather conditions, strong in practicability, and low in cost Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
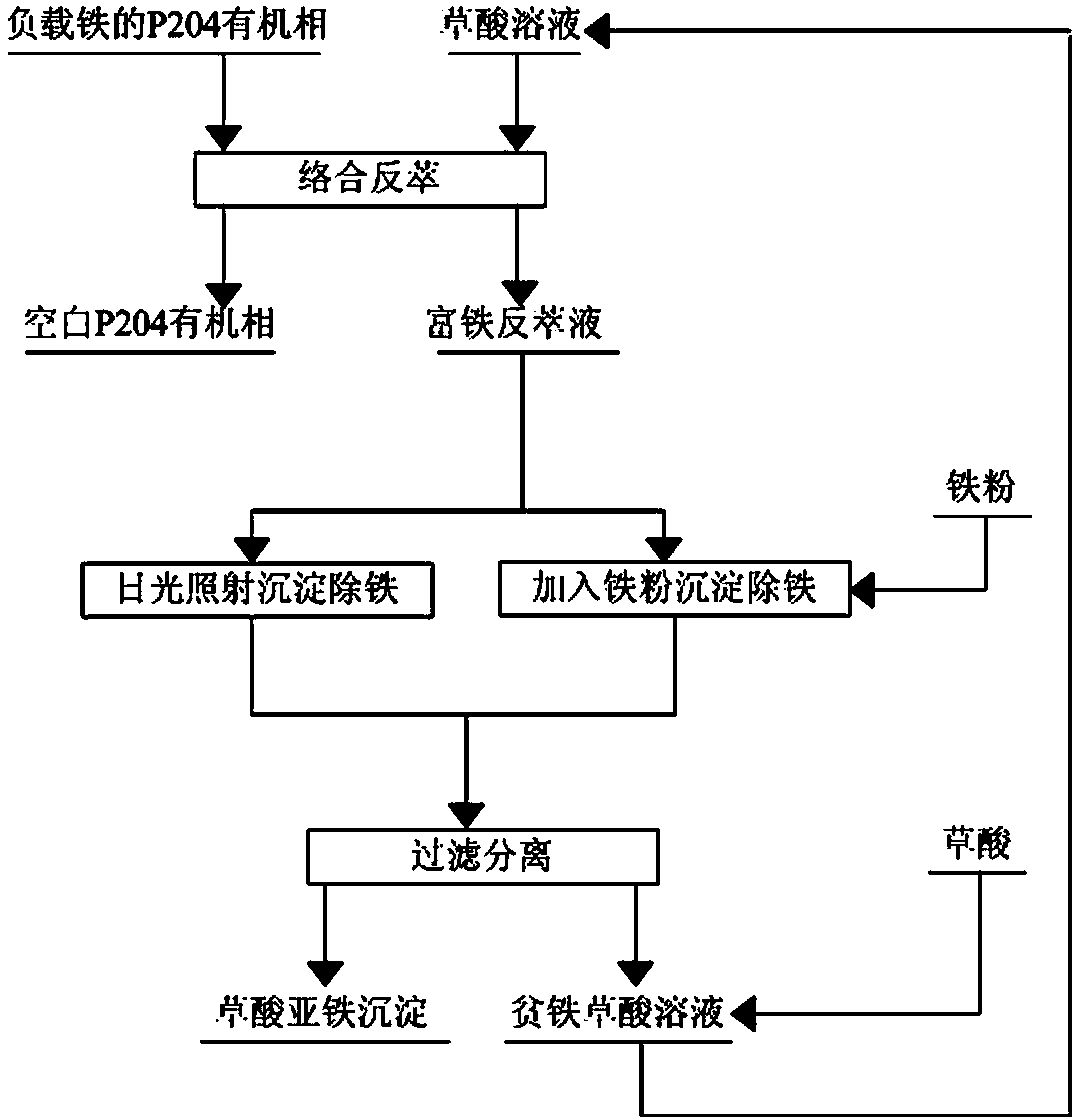
[0031] The volume of extractant P204 accounts for 10% in the P204 organic phase of loaded iron, and the content of Fe(III) is at 0.51g / L;
[0032] with H 2 C 2 o 4 The oxalic acid solution with a mass concentration of 4% was used as the stripping agent, and the iron-loaded P204 organic phase was mixed with the stripping agent at a volume ratio of 1:1 to perform a first-stage stripping. The stripping temperature was 20°C. After the stripping was completed, Obtain iron-rich stripping solution and blank P204 organic phase; the stripping rate of iron in the iron-loaded P204 organic phase is 99.5%;
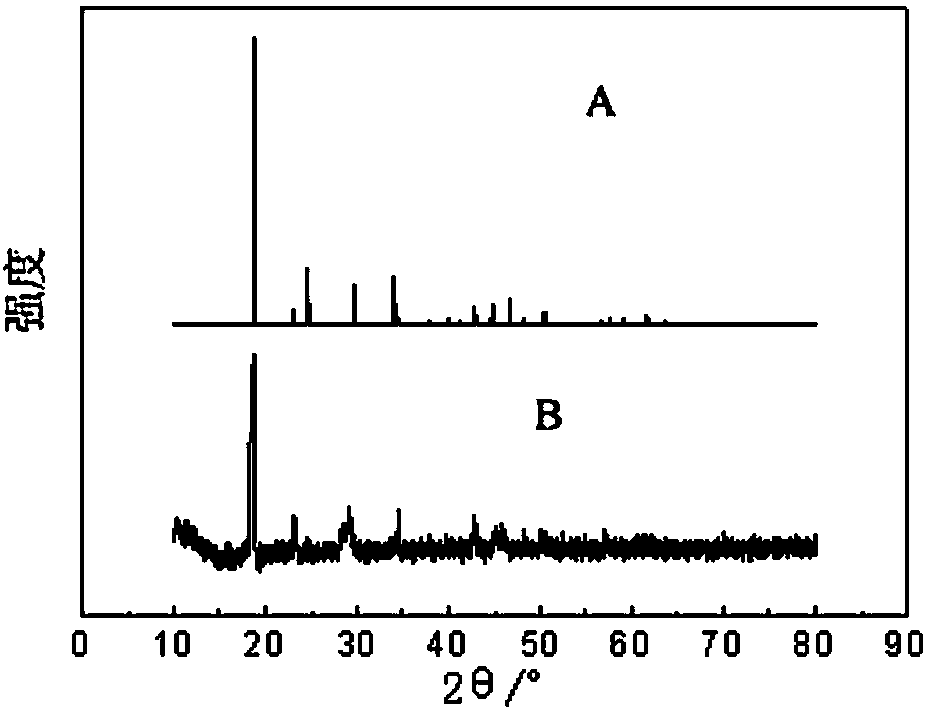
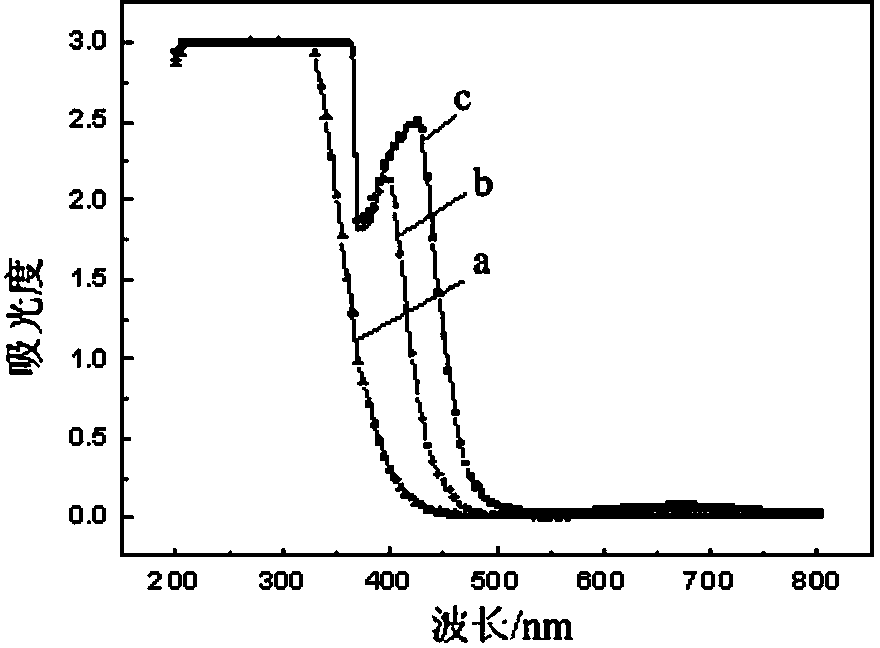
[0033] The iron-rich back-extraction solution is subjected to photodecomposition and precipitation to remove iron by sunlight irradiation, and the sunlight irradiation time is 4 hours;
[0034] Filter the material after precipitation and iron removal to separate the solid phase and liquid phase;
[0035] The separated liquid phase is an iron-poor oxalic acid solution, which is recycl...
Embodiment 2
[0039] The volume of extractant P204 accounts for 40% in the P204 organic phase of loaded iron, and the content of Fe(III) is at 4.89g / L;
[0040] with H 2 C 2 o 4 The oxalic acid solution with a mass concentration of 6% is used as the stripping agent, and the iron-loaded P204 organic phase is mixed with the stripping agent at a volume ratio of 0.5:1 to perform a first-stage stripping. The stripping temperature is 30 ° C. After the stripping is completed Obtain iron-rich stripping solution and blank P204 organic phase; the stripping rate of iron in the iron-loaded P204 organic phase is 99.8%;
[0041] The iron-rich back-extraction solution is subjected to photodecomposition and precipitation to remove iron by sunlight irradiation, and the sunlight irradiation time is 6 hours;
[0042] Filter the material after precipitation and iron removal to separate the solid phase and liquid phase;
[0043] The separated liquid phase is an iron-poor oxalic acid solution, which is recyc...
Embodiment 3
[0047] The volume of extractant P204 in the P204 organic phase of loaded iron accounts for 30%, and the content of Fe(III) is at 2.61g / L;
[0048] with H 2 C 2 o 4 The oxalic acid solution with a mass concentration of 6% is used as the stripping agent, and the P204 organic phase loaded with iron is mixed with the stripping agent at a volume ratio of 3:1 to carry out 3-stage stripping, and the 3-stage stripping is countercurrent stripping, stripping The temperature is 40°C. After the stripping is completed, an iron-rich stripping solution and a blank P204 organic phase are obtained; the stripping rate of iron in the iron-loaded P204 organic phase is 99.6%;
[0049] The iron-rich back-extraction solution is subjected to photodecomposition and precipitation to remove iron by sunlight irradiation, and the sunlight irradiation time is 12 hours;
[0050] Filter the material after precipitation and iron removal to separate the solid phase and liquid phase;
[0051] The separated ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com