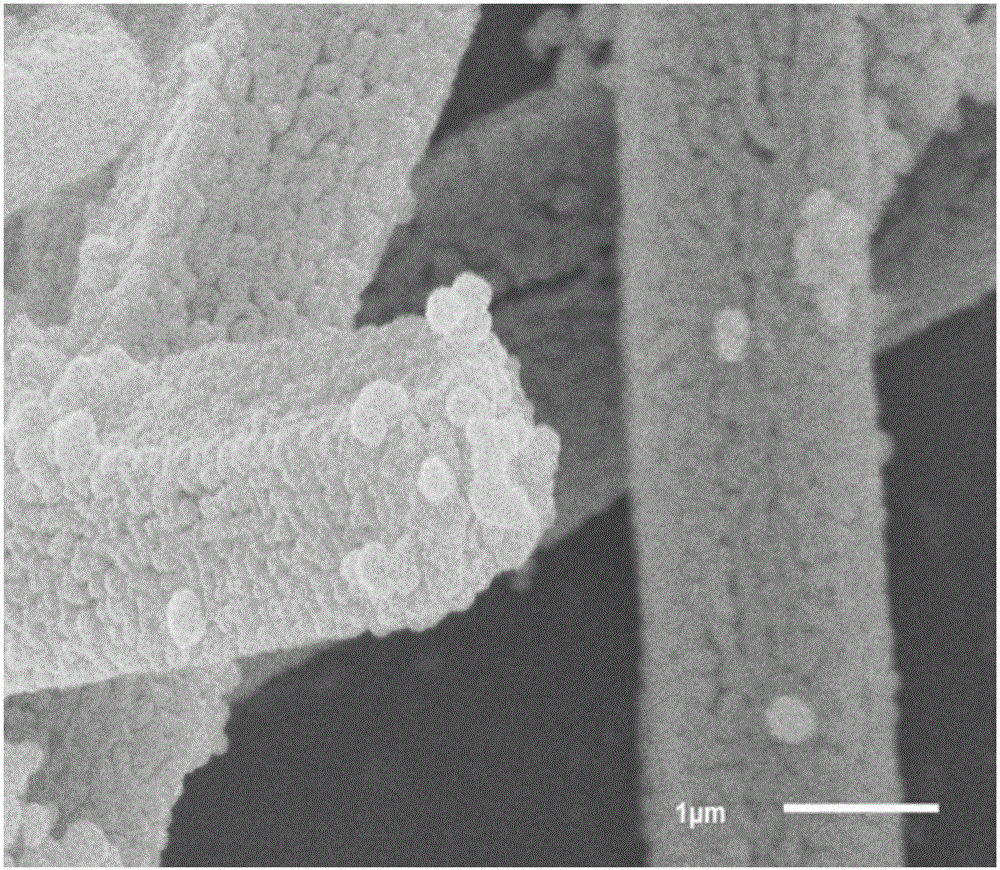
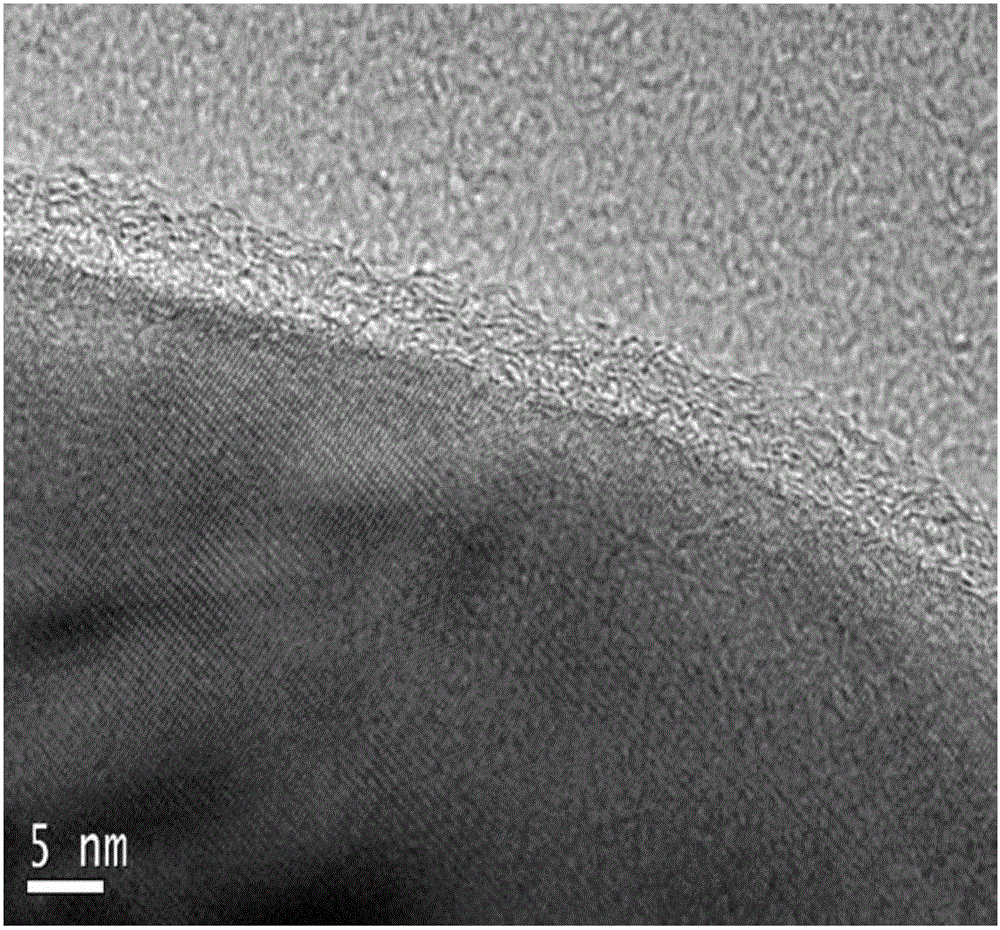
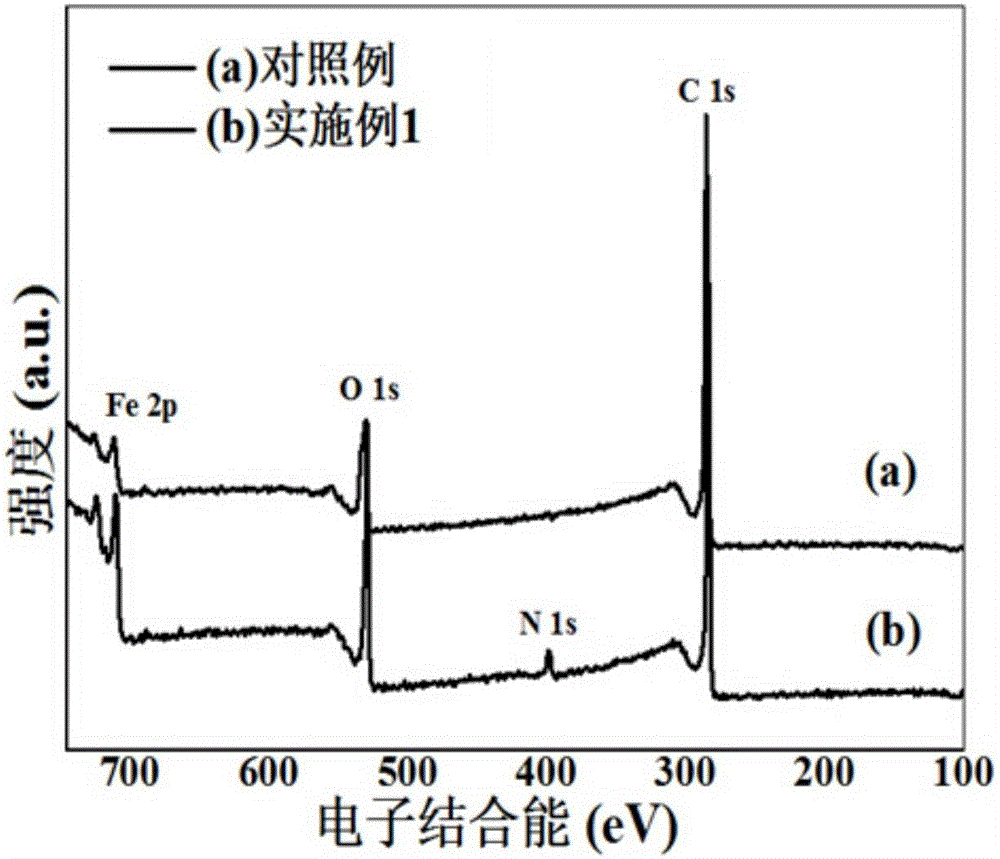
Nitrogen-doped carbon-coated iron oxide negative electrode material for lithium-ion battery and preparation
A technology for lithium ion batteries and negative electrode materials, applied in the field of nitrogen-doped carbon-coated iron oxide negative electrode materials for lithium ion batteries and its preparation field, can solve the problems of poor electrical conductivity of iron oxide negative electrode materials, unsatisfactory cycle efficiency, and poor SEI film Stability and other issues, to achieve the effect of low cost of raw materials, excellent electrochemical performance, and easy availability of raw materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] (1) Add a mixed solution of 60mL deionized water and 60mL absolute ethanol to the beaker, and add 4.05g FeCl to the mixed solution at one time under magnetic stirring 2 4H 2 O, stir for 10min; after the ferrous salt is completely dissolved, slowly add 0.75g Na 2 C 2 o 4 , control the addition for 3 minutes, and continue to stir for 30 minutes to obtain a yellow suspension; transfer the suspension to a 150mL polytetrafluoroethylene-lined reactor, and raise the temperature from room temperature to 180°C at a heating rate of 5°C min -1 , keep warm for 12h; after cooling to room temperature, the reaction product is suction filtered, washed and dried, and the yellow precipitate is collected as the ferrous oxalate precursor; in the air atmosphere, the collected ferrous oxalate solid is heated from room temperature to 600°C , the heating rate was controlled at 5 °C min -1 , keep warm for 5h; after it is naturally cooled to room temperature, a dark red iron oxide material i...
Embodiment 2
[0067] (1) Add a mixed solution of 60mL deionized water and 60mL absolute ethanol to the beaker, and add 4.05g FeCl to the mixed solution at one time under magnetic stirring 2 4H 2 O, stir for 10min; after the ferrous salt is completely dissolved, slowly add 0.75g Na 2 C 2 o 4 , control the addition for 3 minutes, and continue to stir for 30 minutes to obtain a yellow suspension; transfer the suspension to a 150mL polytetrafluoroethylene-lined reactor, and raise the temperature from room temperature to 180°C at a heating rate of 5°C·min -1 , keep warm for 12h; after cooling to room temperature, the reaction product is suction filtered, washed and dried, and the yellow precipitate is collected as the ferrous oxalate precursor; in the air atmosphere, the collected ferrous oxalate solid is heated from room temperature to 600°C , the heating rate was controlled at 5 °C min -1 , keep warm for 5h; after it is naturally cooled to room temperature, a dark red iron oxide material i...
Embodiment 3
[0071] (1) Add a mixed solution of 60mL deionized water and 60mL absolute ethanol to the beaker, and add 4.05g FeCl to the mixed solution at one time under magnetic stirring 2 4H 2 O, stir for 10min; after the ferrous salt is completely dissolved, slowly add 1.2g Na 2 C 2 o 4 , control the addition for 5 minutes, and continue to stir for 30 minutes to obtain a yellow suspension; transfer the suspension to a 150mL polytetrafluoroethylene-lined reactor, and raise the temperature from room temperature to 180°C at a heating rate of 2°C·min -1 , keep warm for 12h; after cooling to room temperature, the reaction product is suction filtered, washed and dried, and the yellow precipitate is collected as the ferrous oxalate precursor; in the air atmosphere, the collected ferrous oxalate solid is heated from room temperature to 600°C , the heating rate was controlled at 2°C min -1 , keep warm for 5h; after it is naturally cooled to room temperature, a dark red iron oxide material is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com