Method for degrading rhodamine B by adsorbing vanadium oxide quantum dots through magnetic nanospheres
A technology of magnetic nanospheres and vanadium quantum, applied in chemical instruments and methods, oxidized water/sewage treatment, metal/metal oxide/metal hydroxide catalysts, etc., can solve the problem of large material size, difficult separation, and large specific surface area and other issues, to achieve the effects of environmental friendliness, ingenious ideas, and broad market prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
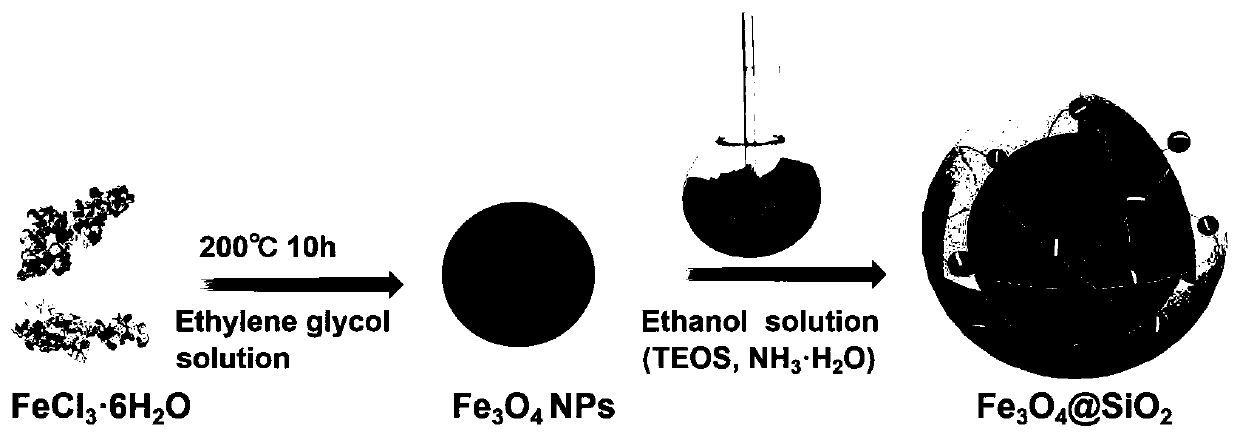
[0039] The preparation of the magnetic ferric oxide involved in the present embodiment and the wrapping of the silicon dioxide layer, the specific synthesis method is carried out according to the steps:
[0040] S1, 1.5g PSSMA was dissolved 1:1 in 80mL ethylene glycol (with FeCl) in a 50°C water bath. 3 ·6H 2 O is the precursor, weigh 1.62g FeCl respectively 3 ·6H 2 O and 4.5g of anhydrous sodium acetate in the above-mentioned alcoholic solution, then transferred to a 100mL polytetrafluoro-lined reaction kettle, heated to 200°C in a blast drying oven, and maintained for ten hours. The precipitate was washed three times with ethanol and deionized water, and then freeze-dried for 24 hours;
[0041] S2. Weigh 50mg ferric oxide nanoparticles and disperse them in 5mL deionized water, then disperse them in a round-bottomed flask equipped with 200mL absolute ethanol and 10mL deionized water to obtain a dispersion, and then ultrasonically treat the above dispersion 15 minutes; the...
Embodiment 2
[0044] The present embodiment verifies the degradation conditions of Rhodamine B, and the specific steps are carried out as follows:
[0045] Weigh 50mg Fe 3 O 4 @SiO 2 Powder, dispersed in 100ml 0.5M NaCl solution, sonicated for 30 minutes, then added 0.75g polydiallyl ammonium chloride (PDDA), mechanically stirred for 1h, washed with water to remove excess PDDA; the same method was used to wrap polyphenylene Sodium ethylene sulfonate (PSS), modified Fe of PDDA 3 O 4 @SiO 2 It is represented by the letters FS (PDDA), and the modified PDDA and PSS are represented by the letters FS (P / S). After the quantum dots are adsorbed respectively, they are represented by the letters VFS (PDDA) and VFS (P / S). Figure 5 (A) As shown in the figure, a-h were controlled as follows, and the UV absorbance was measured after 5 min of reaction, (a) Rh B; (b) RhB+H 2 O 2 ;(c)FS+H 2 O 2 ;(d) VFS+H 2 O 2 ;(e)FS(PDDA)+H 2 O 2 ; (f) VFS(PDDA)+H 2 O 2 ;(g)FS(P / S)+H 2 O 2 ;(h)VFS(P / S) +...
Embodiment 3
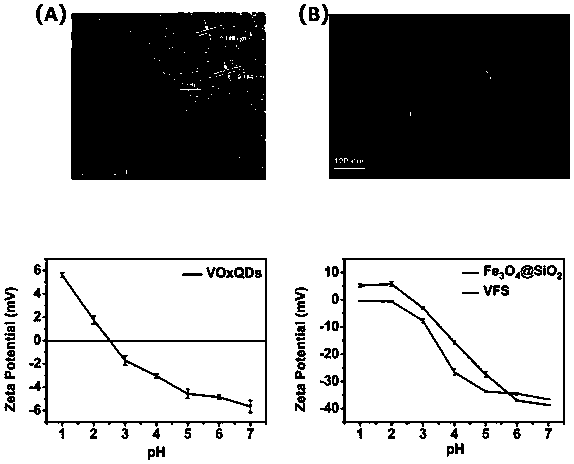
[0048] This example verifies the charge conditions of the silica-coated ferric tetroxide and quantum dots in Example 1 and Example 2. The pure quantum dot alcohol solution has a positive charge at pH=2. The charged state of the dots realizes the adsorption of the quantum dots on the negatively charged surface. The potential difference between the magnetic silicon spheres before and after adsorption is as follows: Figure 4 It shows that the surface potential of the silica-wrapped magnetic silicon sphere is slightly lower than that of the material without adsorption, and the potential value at pH 1-7 is slightly lower, and quantum dots are indeed adsorbed on the surface of the surface silicon sphere.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com