Method for preparing lead oxide by means of scrap lead paste
A technology of lead oxide and waste lead paste is applied in the directions of lead oxide and process efficiency improvement, which can solve the problems of high industrial production cost and large consumption of chemical reagents, and achieves low synthesis cost, high consistency, and synthesis cycle. short effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
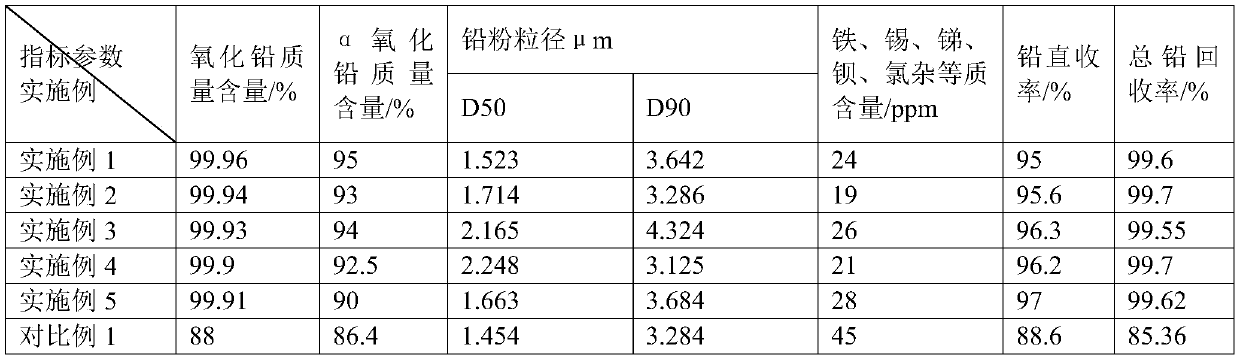
Examples
Embodiment 1
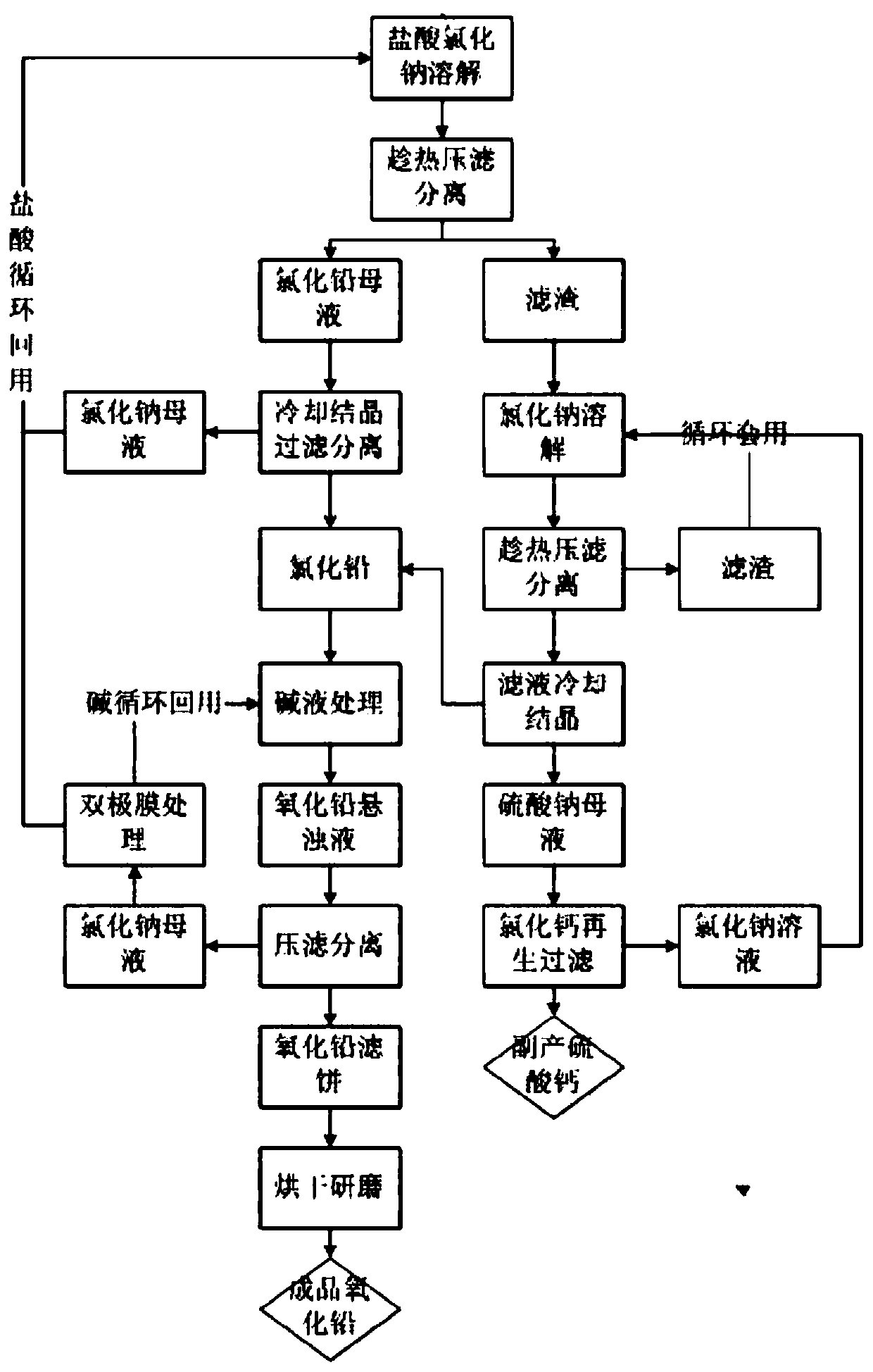
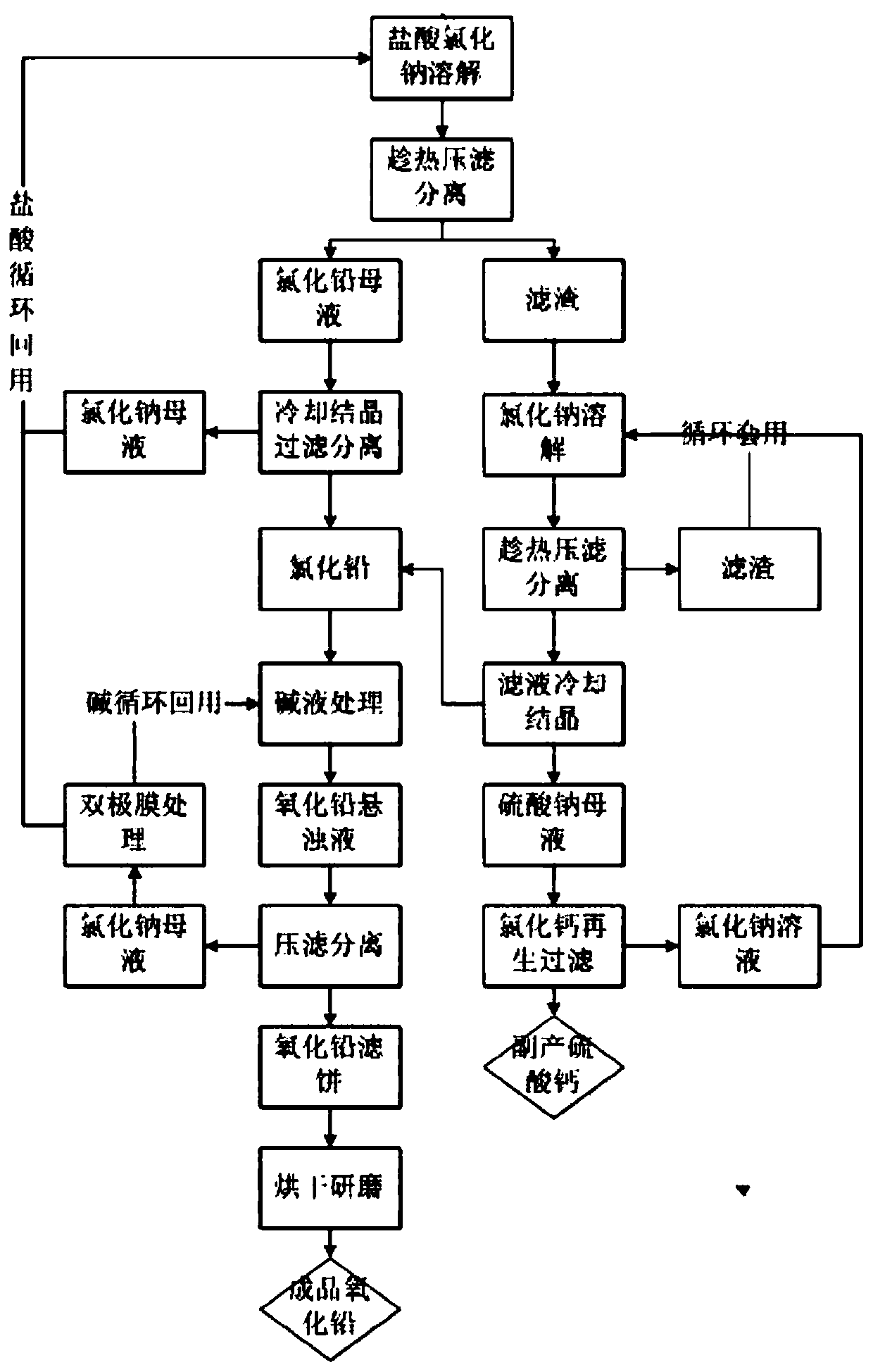
[0034] A method for preparing lead oxide from waste lead plaster, comprising the following preparation steps:
[0035] (1) Dissolving and leaching of lead paste: Put 500g of waste lead paste, 3500g of hydrochloric acid with a mass content of 25% and sodium chloride with a mass content of 5% into an enamel reactor and heat it to 100°C for 2 hours. The dissolution rate of lead ion after the one-step reaction is 61.3%. After the reaction is completed, it is filtered and separated at 70° C., and the filter residue is 243.4 g for later use. The filtrate is cooled and crystallized to separate out pure lead chloride crystals, and the lead chloride is collected by centrifugation, and the filtrate is recycled.
[0036] (2) Dissolution and leaching of the filter residue: the filter residue was sampled to detect that the mass content of lead sulfate was 76.8%, and the water content of the filter residue was 22.6%. Put 243.4g of the filter residue and 1500g of 15% sodium chloride solution ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] The difference with Example 1 is that the following preparation steps are included:
[0043] (1) Dissolving and leaching of lead plaster: Put 500g of waste lead plaster, 2000g of 18% hydrochloric acid by mass content and 3% sodium chloride by mass content into an enamel reactor, heat it to 80°C and keep it warm for 1.5h, then titrate with EDTA Monitor the dissolving rate of the lead ion after the first step reaction to be 62.7%. After the reaction is completed, it is filtered and separated at 68°C. The filter residue is 237.4g for subsequent use.
[0044] (2) Dissolution and leaching of filter residue: filter residue sampling detects that the mass content of lead sulfate is 74.6%, and the water content of filter residue is 24.3%. Put 237.4g of filter residue into the reaction kettle for the last regenerated sodium chloride solution at 100° C. and stir and mix for 2 hours. Filtration and separation, the filter residue 9.4g continued to be dissolved and used mechanically, t...
Embodiment 3
[0050] The difference with Example 1 is that the following preparation steps are included:
[0051] (1) Dissolving and leaching of lead paste: Put 500g of waste lead paste, 4000g of hydrochloric acid with a mass content of 28% and sodium chloride with a mass content of 8% into an enamel reaction kettle and heat it to 115°C for 2.5 hours, then titrate with EDTA The dissolution rate of lead ion after monitoring the first step reaction is 61.8%. After the reaction is completed, it is filtered and separated at 73° C., and the filter residue is 246.7 g for subsequent use.
[0052] (2) Dissolution and leaching of filter residues: filter residues were sampled to detect that the mass content of lead sulfate was 75.3%, and the water content of filter residues was 23.8%. Put 246.7g of filter residues into the reactor with regenerated sodium chloride solution and stir and mix them for 2.3 hours at 115°C. Filtration and separation, the filter residue 16.8g continued to be dissolved and us...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com