Preparation method of fusiform iron oxide single crystal nano material
A technology of single-crystal nanometer and iron oxide, which is applied in the direction of nanotechnology, nanotechnology, nanotechnology for materials and surface science, etc., can solve the problems of cumbersome preparation methods, slow electron transfer speed, poor electrical conductivity, etc., and achieve large capacity And cycle performance, reduce the dissipation of electrons, reduce the effect of production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] (1) 50mL 0.2mol / L FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O and 10mL of 0.01mol / L NaH 2 PO 4 well mixed;
[0029] (2) hydrothermally reacting the mixed solution obtained in step (1) at 80° C. for 72 hours;
[0030] (3) Filtering the reacted sample in step (2), putting the obtained precipitate into a vacuum drying chamber at 80° C. to dry to obtain a fusiform iron oxide single crystal nanomaterial;
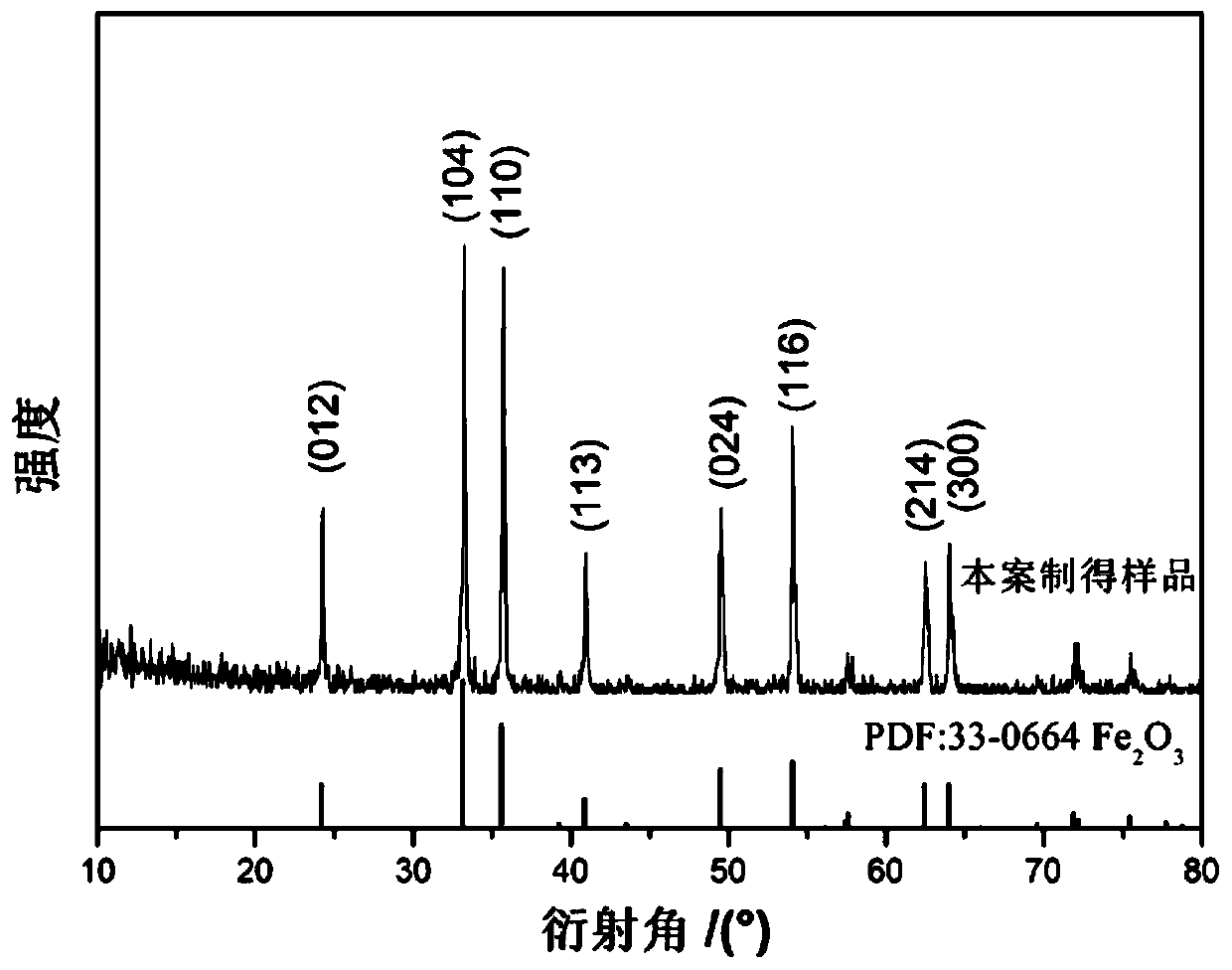
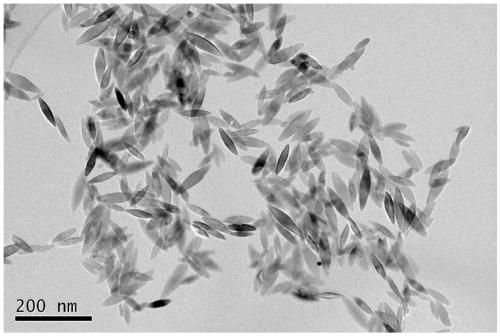
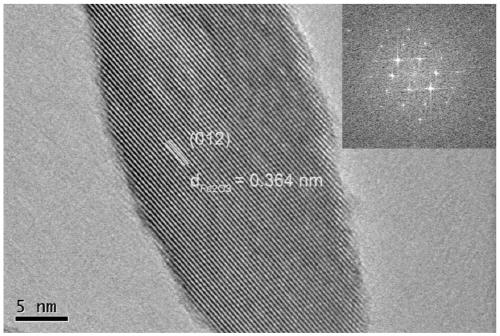
[0031] Carry out X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscope to the ferric oxide material obtained in the embodiment, by figure 1 As can be seen, the material that the present invention obtains is ferric oxide material; By figure 2 It can be seen that the ferric oxide material is a shuttle-shaped nanometer material, and the ferric oxide material prepared by this method has high purity and no other impurities; image 3 It shows that the ferric oxide material obtained in this example has a single crystal structure.
[0032] Assembling and performance testing of lithium-ion batteries: mix ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] (1) 100mL 0.5mol / L FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O and 2mL of 0.05mol / L NaH 2 PO 4 well mixed;
[0035] (2) hydrothermally reacting the mixed solution obtained in step (1) at 120° C. for 24 hours;
[0036] (3) Filtering the reacted sample in step (2), putting the obtained precipitate into a vacuum drying chamber at 80° C. to dry to obtain a fusiform iron oxide single crystal nanomaterial;
[0037] The assembly and performance test of the lithium-ion battery are the same as in Example 1, and the stable discharge capacity is shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0039] (1) 60mL 0.4mol / L FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O and 5mL of 0.04mol / L NaH 2 PO 4 well mixed;
[0040] (2) hydrothermally reacting the mixed solution obtained in step (1) at 120° C. for 24 hours;
[0041] (3) Filtering the reacted sample in step (2), putting the obtained precipitate into a vacuum drying chamber at 80° C. to dry to obtain a fusiform iron oxide single crystal nanomaterial;
[0042] The assembly and performance test of the lithium-ion battery are the same as in Example 1, and the stable discharge capacity is shown in Table 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com