Method for quantitatively determining micro-plastic in water environment
A technology for quantitative determination and microplastics, which is applied in the field of environmental analytical chemistry, can solve problems such as easy to block holes and difficult to recycle, and achieve the effect of simple operation and high enrichment factor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
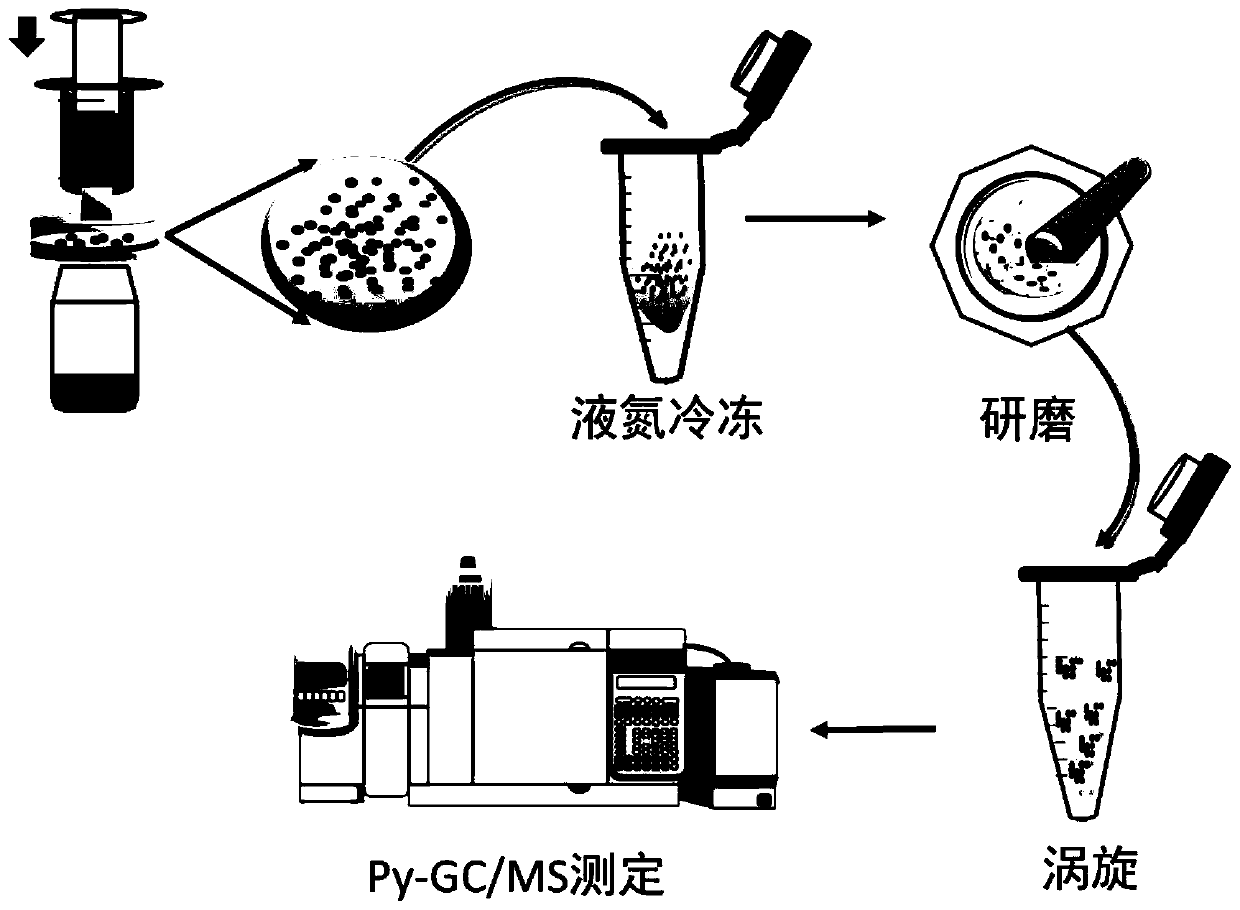
[0046] The method for the quantitative determination of microplastics in the water environment in this embodiment, such asfigure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0047] (1) Filter 100mL of the water sample to be tested with a glass fiber membrane with a pore size of 1 μm, the microplastic particles are trapped and enriched on the glass fiber membrane, and the nanoplastic enters the filtrate;
[0048] (2) The glass fiber membrane enriched with microplastics was frozen with liquid nitrogen, quickly ground and transferred to a 1.5mL centrifuge tube, and deionized water was added to make the volume of the mixed solution 1mL. After thorough mixing, 50μL of the mixed solution (including Glass fiber film and microplastics) are transferred in the sample cup, carry out the mensuration of thermolysis-gas chromatography mass spectrometry (Py-GC / MS) after drying;
[0049] (3) Finally, data analysis was performed, and styrene (m / Z 104) and methyl methacrylate (m / Z 100) were analyz...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Quantitative determination of microplastics in different matrix water bodies.
[0056] First, pass 100mL of different matrix water samples through a glass fiber membrane with a pore size of 1 μm, the microplastic particles are trapped and enriched on the glass fiber membrane, the glass fiber membrane is transferred to a 1.5mL centrifuge tube, frozen in liquid nitrogen for 5min, and then the glass fiber Membrane, quickly ground to no obvious particles, transferred back to the centrifuge tube, added deionized water to ensure that the mixture was 1mL. After fully mixing by vortexing, take 50 μL of the mixed solution in the pyrolysis sample cup, dry it and measure it. Among them, PS microplastics were detected in 6 environmental water samples at a concentration of 1.2-9.2 μg / L, and PMMA microplastics were not detected. As shown in Table 1, it shows that this method can be used for the determination of microplastics at the concentration level of μg / L in environmental water....
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com