A kind of bio-based epoxy resin curing agent and preparation method thereof
A technology based on epoxy resin and curing agent, applied in the field of bio-based epoxy resin curing agent and its preparation, can solve the problems of environmental pollution, waste of resources, etc., and achieve the reduction of molecular weight, increase of active sites, and increase of active hydroxyl content Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Embodiment 1: Degradation-acidolysis of lignin
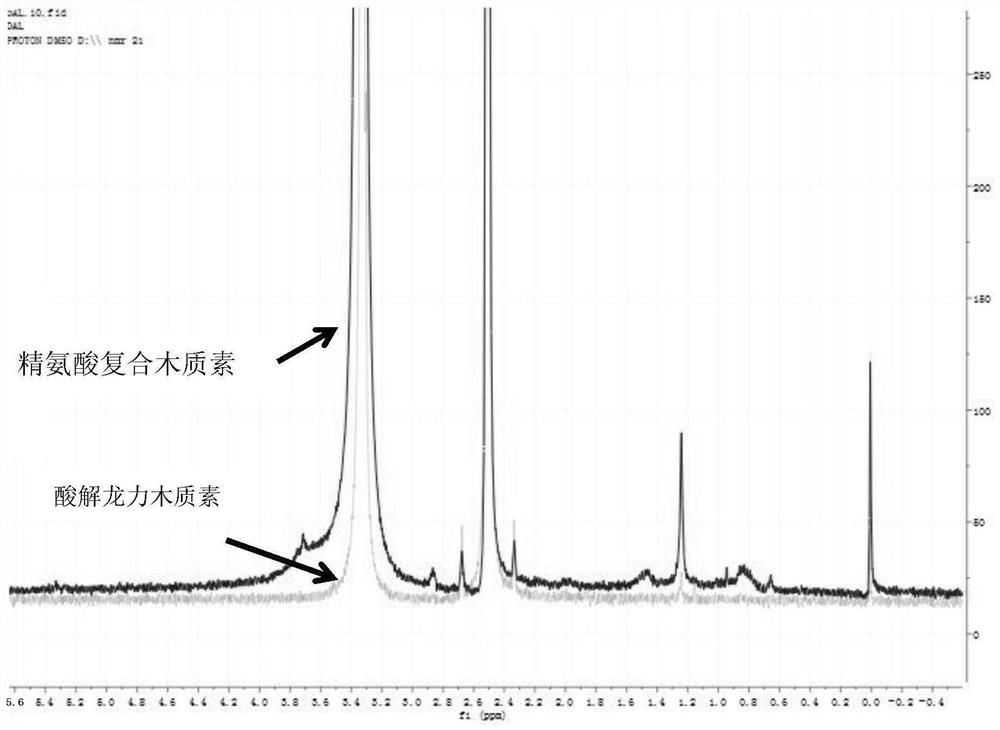
[0030] In a 50 mL reaction flask, 5 g of lignin was added and dissolved in 20 mL of DMF, and 5 g of HBr (mass fraction: 10%) was added, and reacted in a microwave reactor at 90° C. for 30 min. After the reaction, the reactant was cooled to room temperature, added dropwise to 200 mL of 2% hydrochloric acid solution, stirred for 30 min, centrifuged, the precipitate was taken, washed with distilled water, washed until the supernatant was neutral, freeze-dried, By NMR ( figure 2 ) and GPC to detect changes in molecular weight and phenolic hydroxyl before and after acid hydrolysis, the results are shown in Table 1.
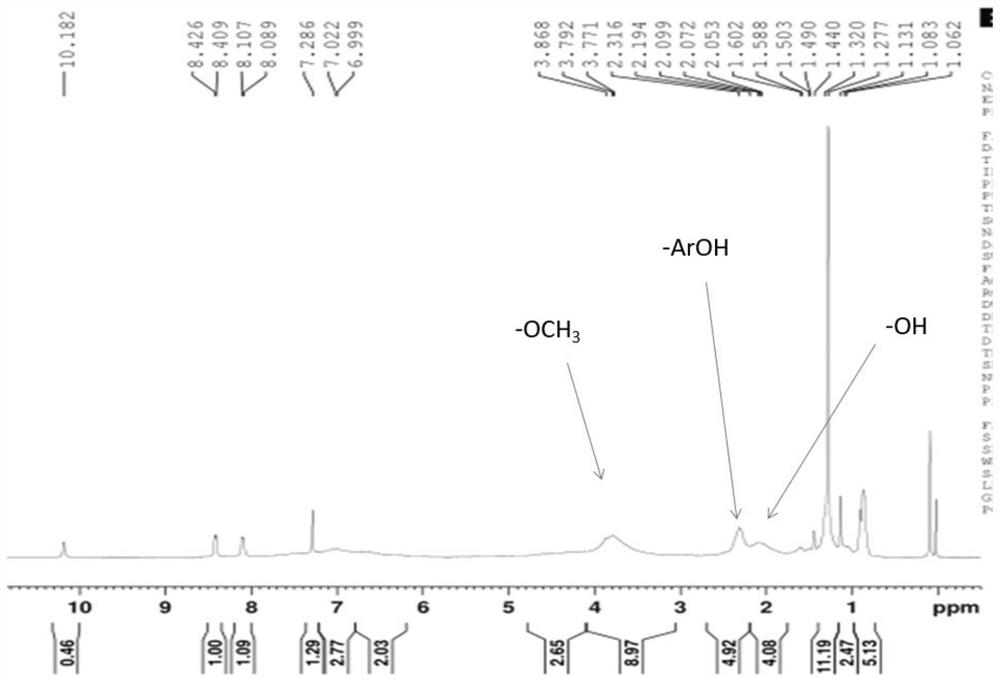
[0031] figure 2 Using p-nitrobenzaldehyde as the internal standard, the -ArOH peak in the figure was integrated, and the phenolic hydroxyl content in the acid-hydrolyzed lignin was calculated to be 4.52%, while the phenolic hydroxyl content in the original lignin was 3.15%. [1] .
Embodiment 2
[0032] Example 2: Pyrolysis of lignin
[0033] 1.5 g of lignin was pyrolyzed at 200° C. for 3 hours to obtain pyrolyzed lignin. By NMR ( figure 1 ) and GPC to detect changes in molecular weight and phenolic hydroxyl content before and after pyrolysis, the results are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0034] Example 3: Hydrogenolysis
[0035] In a 50mL reaction flask, add 1.5g of lignin and dissolve it in 20mL of methanol, then add 0.1g of (Pd) catalyst, feed the mixed solution into a high-pressure reaction kettle with a capacity of 100mL, and pass in 2MPa hydrogen, at 160°C Reaction 6h. After the reaction, the reactant was cooled to room temperature, filtered, and the filtrate was dried by rotary evaporation to obtain a sample. The changes in molecular weight and phenolic hydroxyl content before and after hydrogenolysis were detected by NMR and GPC, and the results are shown in Table 1 below.
[0036] Table 1 Changes in molecular weight and phenolic hydroxyl groups of lignin before and after acidolysis
[0037] sample Phenolic hydroxyl content (wt%) Alcohol hydroxyl content (wt%) Molecular weight (Da) Original lignin 3.15 2.81 3387 Lignin after acid hydrolysis 4.52 3.52 2010 lignin after hydrogenolysis 4.24 3.73 2127 Lignin af...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com