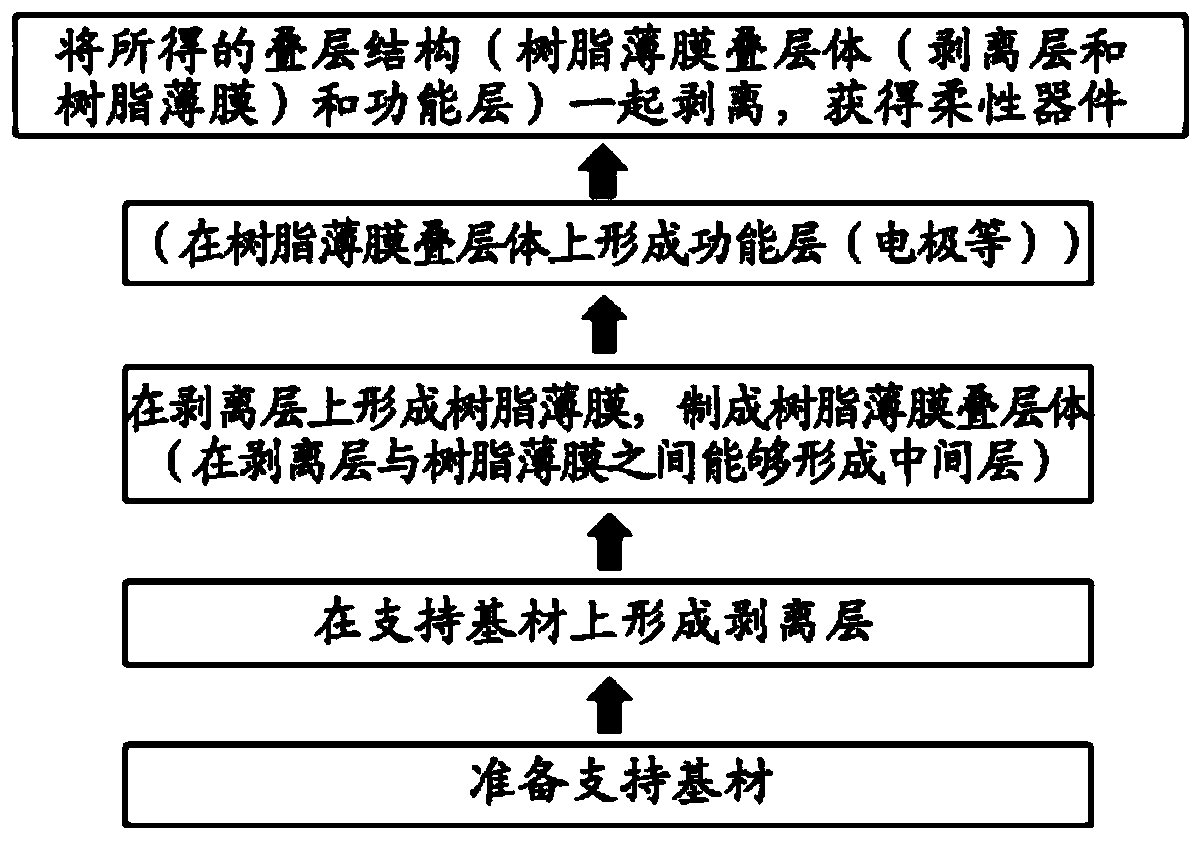
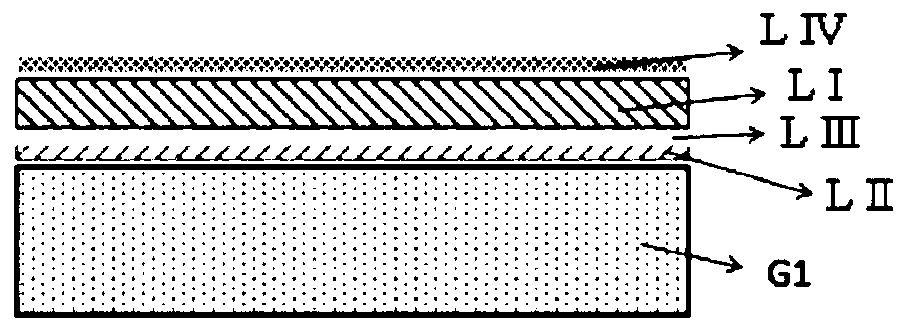
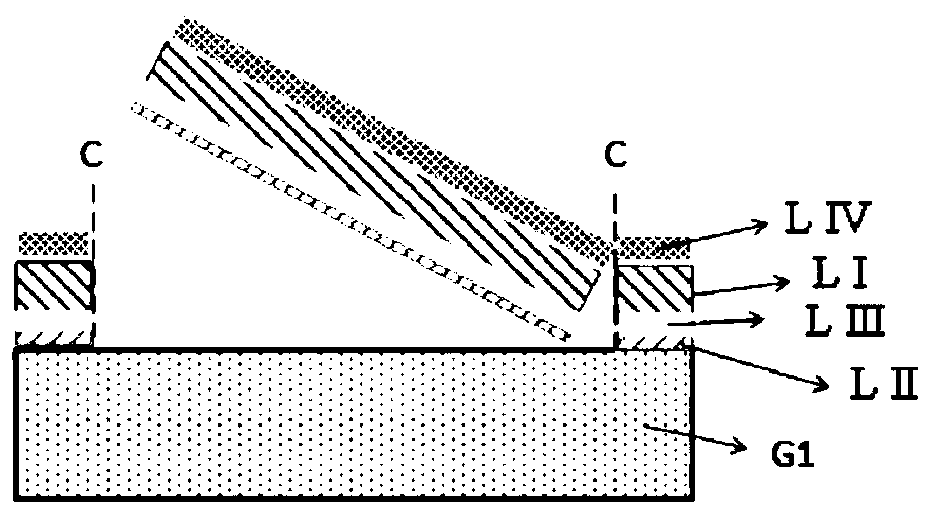
Method for producing substrate for flexible device
A manufacturing method, heat resistance technology, applied in the direction of chemical instruments and methods, final product manufacturing, sustainable manufacturing/processing, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in preventing wrinkles, cracks, difficulty in maintaining positional accuracy and dimensional accuracy, and achieve low-line Expansion coefficient, good reproducibility, low delay effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0230] Hereinafter, although an Example is given and this invention is demonstrated more concretely, this invention is not limited to a following Example.
[0231] The meanings of the abbreviated symbols used in the following examples are as follows.
[0232]
[0233] BODAxx: Bicyclo[2,2,2]octane-2,3,5,6-tetracarboxylic dianhydride
[0234] CBDA: 1,2,3,4-cyclobutane tetracarboxylic dianhydride
[0235]
[0236] TFMB: 2,2’-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzidine
[0237]
[0238] GBL: gamma-butyrolactone
[0239] In addition, in the examples, the apparatus and conditions used for preparation of samples and analysis and evaluation of physical properties are as follows.
[0240] 1) Determination of number average molecular weight and weight average molecular weight
[0241] Number-average molecular weight (hereinafter, abbreviated as Mn) and weight-average molecular weight (hereinafter, abbreviated as Mw) of the polymer in the device: Showdex GPC-101 manufactured by Showa Denko C...
Synthetic example 1
[0268] Synthesis Example 1: Synthesis of Polyimide A (PI-A)
[0269] 25.61 g (0.08 mol) of TFMB was charged in a 250 mL reaction three-necked flask equipped with a nitrogen inlet / outlet, a mechanical stirrer, and a cooler. Then, GBL 173.86g was added, and stirring was started. After the diamine was completely dissolved in the solvent, 10 g (0.04 mol) of BODAxx, 7.84 g (0.04 mol) of CBDA, and 43.4 g of GBL were added immediately after stirring, and heated to 140° C. under nitrogen. Then, 0.348 g of 1-ethylpiperidine was added to the solution, followed by heating at 180° C. for 7 hours under nitrogen. Finally the heating was turned off and the reaction solution was diluted until 10% and kept stirring overnight. After adding the polyimide reaction solution to 2000 g of methanol and stirring for 30 minutes, the polyimide solid was filtered and the polyimide was purified. Furthermore, this polyimide solid was stirred in 2000 g of methanol for 30 minutes, and the polyimide solid ...
example 1
[0271] Example 1: Formation of peeling layer
[0272] At room temperature, 1 g of the polyimide (PI-A) of Synthesis Example 1 was dissolved in the GBL solvent so as to be 8% by mass through a 1 μm filter and gradually filtered under pressure to obtain Composition for forming a release layer. Then, the composition was coated on a glass support substrate, and fired at a temperature of 50° C. for 30 minutes, 140° C. for 30 minutes, and 200° C. for 60 minutes in an air atmosphere. Furthermore, it baked at 300 degreeC for 60 minutes. In this way, a transparent polyimide film was formed as a release layer on the glass support substrate. Table 1 shows its optical and thermal properties.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com