Quick mycorrhiza seedling cultivation method for ectotrophic mycorrhiza fungi
A technology of ectomycorrhizae and cultivation methods, applied in the direction of botany equipment and methods, cultivation, plant cultivation, etc., to achieve the effect of simple operation, high efficiency and short time consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0041]The preparation of above-mentioned mycorrhizal seedling cultivation substrate: excavate the forest topsoil of the ectomycorrhizal fungus of field purpose, soil is crushed the sieve of 1cm aperture, then add perlite or calcined core soil and mix (calcined core soil: forest top soil=2: 1); wherein the calcined core soil is a non-nutrient soil with a pH of 5.5-6.0, which is calcined at a high temperature into particles (1.5-3 mm in diameter).
[0042] Preparation of the mycorrhizal seedling cultivation substrate sterilized by high temperature and high pressure: After adding a small amount of water to the mycorrhizal seedling cultivation substrate and mixing, carry out 121°C, 1.2pa, 3h high temperature and high pressure steam sterilization.
Embodiment 1
[0044] The mycorrhizal seedlings of Russula cyanoxantha were inoculated with aseptic C.
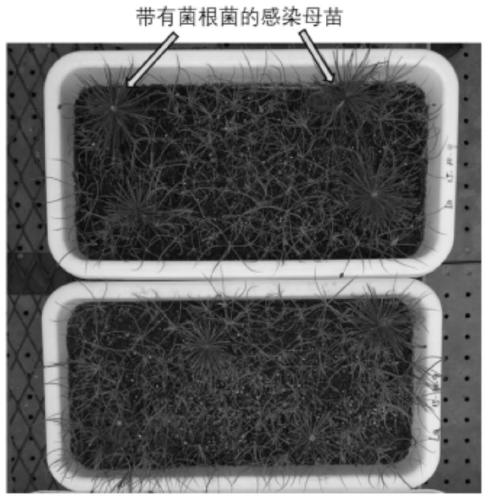
[0045] The Stropharia mycorrhizae used in the experiment were collected from the Tianwu practice forest of the University of Tokyo, Midoricho, West Tokyo City, Tokyo, Japan (such as figure 2 shown), the host is Quercus myrsinifolia, and the host seedlings used in this inoculation experiment are 6-month-old sterile seedlings of the broad-leaved species of Fagaceae Miracle.
[0046] (1) Sterilize the aseptic seedling cultivation soil with steam under high temperature and high pressure at 121° C., 1.2 Pa, for 3 hours to obtain a sterile cultivation substrate, wherein the sterile seedling cultivation soil is selected from vermiculite or mycorrhizal seedling cultivation substrate.
[0047] (2) Disinfection of host seeds: use 30% H 2 o 2 The solution was soaked for 1 hour, then cleaned with tap water, and finally soaked in tap water overnight for later use.
[0048] (3) Cultivation and trea...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Mycorrhizal seedlings formed by inoculating aseptic rice seedlings with Russula mariae mycorrhizae
[0054] The mycorrhizae of Russula japonica used in the experiment were collected from the field training forest of Tokyo University, Midoricho, Nishitokyo City, Tokyo, Japan (such as Figure 4 shown), and its host is Castanopsis militaris. The host seedlings used in this inoculation experiment were 6-month-old sterile seedlings of Castanopsis oryzae.
[0055] (1)-(5) are the same as embodiment 1
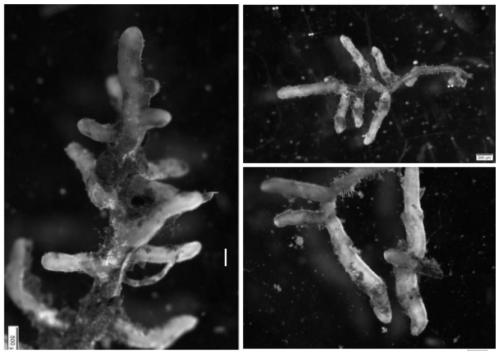
[0056] (6) Formation of mycorrhizae of Russula japonica: the aseptic seedlings inoculated with mycorrhizae formed mycorrhizae during the infection process of 3 months, and successfully infected the roots of aseptic seedlings to form a large number of mycorrhizal seedlings (as shown in the attached Figure 4-5 shown).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com